Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hungary: Structure and Development of Tax Revenues
Uploaded by
Swastik GroverOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hungary: Structure and Development of Tax Revenues
Uploaded by
Swastik GroverCopyright:
Available Formats
1 Hungary
Hungary
Structure and development of tax revenues
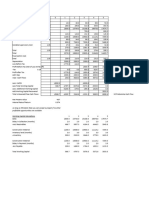
Table HU.1: Revenue (% of GDP)
2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013
I. Indirect taxes 16.2 15.6 15.1 16.0 15.8 16.6 17.7 17.5 18.8 18.7
VAT 8.8 8.3 7.5 7.9 7.7 8.4 8.6 8.5 9.2 9.0
II. Direct taxes 8.9 8.9 9.3 10.2 10.5 9.8 7.9 6.3 6.8 6.7
Personal income 6.5 6.5 6.7 7.1 7.5 7.2 6.4 4.9 5.3 5.0
Corporate income : : : : : : : : : :
III. Social Contributions ( compulsory actual contributions) 12.1 12.4 12.4 13.5 13.5 13.0 11.9 13.0 13.0 13.0
Employers’ 9.3 9.6 9.4 9.6 9.6 9.1 7.7 7.8 7.6 7.5
Households’ 2.8 2.8 3.0 3.9 3.9 3.9 4.2 5.2 5.4 5.5
IV. Less: amounts assessed but unlikely to be collected : : : : : : : : : :
V. Total (I + II + III – IV) 37.2 36.9 36.8 39.7 39.7 39.3 37.6 36.9 38.6 38.4
VI. Social contributions (imputed + voluntary
0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.0 0.2 0.1 0.1 0.1
contributions)
VII. Total (incl. Imputed + voluntary contributions (V+VI) 37.3 37.0 36.9 39.8 39.8 39.4 37.7 37.0 38.7 38.5
Source: Eurostat (online data code: gov_10a_taxag)
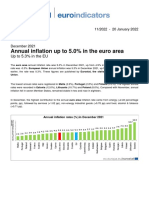
Figure HU.1: Total receipts from taxes and compulsory social contributions, 2013 (% of GDP)
50
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
0
Denmark
France
Belgium
Finland
Italy
Sweden
Austria
EA-19
Luxembourg
EU-28
Hungary
Germany
Netherlands
Slovenia
Croatia
Czech Republic
Greece
Portugal
United Kingdom
Malta
Spain
Estonia
Poland
Cyprus
Slovakia
Ireland
Bulgaria
Latvia
Romania
Lithuania
Iceland
Source: Eurostat (online data code: gov_10a_taxag) Norway
Figure HU.2: Tax revenues by main taxes, compared to EU-28, 2013 (% of GDP)
Value added type
taxes (VAT)
Social 12
contributions
Compulsory 9
Other (mainly
households actual 6 indirect) taxes
Indirect taxes social contributions
3
0
Compulsory Taxes on individual or
employers actual household income
social contributions incl. holding gains
Taxes on the income
Direct taxes or profits of
corporations
EU-28 HU
Source: Eurostat (online data code: gov_10a_taxag)
60 Taxation trends in the European Union
Hungary 1
Latest tax reforms
Table HU.2: Latest tax reforms
Description of measure Change Date
Personal income tax
Tax relief for families with 2 children, increase from 2016 to 2019 by HUF 2 500/month In force from:
Base decrease
(from HUF 10 000 to HUF 20 000). 1.1.2016
Tax relief for newly-weds: HUF 5 000/month for two years or up to entitlement to In force from:
Base decrease
family benefit after child. 1.1.2015
In force from:
PIT rate is reduced from 16 % to 15 %. Rate decrease
1.1.2016
Corporate income tax
In force from:
Loss generated from 2015 may only be carried forward until 2020. N/A
1.1.2015
In force from:
Modification of the tax credit scheme linked to supporting sport. Base decrease
1.1.2015
Reduction of CIT obligations for banks in 2015 (or in the case of a remaining negative
In force from:
difference, also in following years) in view of recalculated interest income in years Base decrease
1.11.2014
2008–14.
Value-added tax
Start-up companies will be subject to monthly filing of VAT returns, no yearly filing in In force from:
N/A
excess of a certain turnover. 1.1.2015
Detailed VAT reporting applies to invoice indicating at least HUF 1 million (reduced In force from:
N/A
from HUF 2 million). 1.1.2015
VAT rate is reduced from 27 % to 5 % on sale of cattle, sheep and goat and the sale of In force from:
Rate decrease
their meat as intermediary products. 1.1.2015
Introduction of exemption for the supply of goods and services intended specifically In force from:
Rate decrease
for military. 1.1.2015
In force from:
No exemption on portfolio management services for private clients. Rate increase
1.1.2015
In force from:
VAT rate is reduced from 27 % to 5 % on pork carcass meat. Rate decrease
1.1.2016
Alcohol excises
Re-introduction of a 50 % reduced rate on production of fruit distillates by licenced In force from:
Introduction (increase)
distilleries (up to 50 litres/year intended for personal consumption in the household). 1.1.2015
In force from:
Single standard rate (HUF 333 385) is re-instated instead of a dual standard rate. Rate decrease
1.1.2015
Introduction of flat rate tax of HUF 1 000/year on production of fruit distillates
In force from:
by a fruit grower (up to 50 litres/year intended for personal consumption in the Rate increase
1.1.2015
household).
Complying with minimum excise duty rates set in the EU Energy Tax Directive, due
In force from:
to changes in the HUF/EUR exchange rate, the refund on commercial diesel was Rate increase
1.1.2015
decreased by HUF 6 per litre.
Energy excises
In force from:
Raise in the excise duty rate on oils used for heating and gas used as motor fuel (about + 5 %). Rate increase
1.1.2015
Energy tax is raised: electricity HUF 310.5/MWh (up from HUF 295), natural gas: HUF 93.5/GJ In force from:
Rate increase
(up from HUF 88.5), coal: HUF 2 516/1 000 kg (up from HUF 2 390). 1.1.2015
Introduction of tax refund for uses energy products in mineralogical processes (brick, In force from:
Rate decrease
cement, ceramics). 1.1.2015
Tobacco excises
Raise in the excise duty rate of cigarettes: cigarettes HUF 15 700/1 000 pieces + 25 % of
In force from:
retail price (from 31 %), but at least HUF 28 000/1 000 pieces (+ 12 %); fine cut and other Rate N/A
4.1.2015
tobacco: HUF 14 000/kg (+ 12 %) and abolition of retail price (52 %).
Taxation trends in the European Union 61
1 Hungary
Table HU.2: Latest tax reforms (continued)
Description of measure Change Date
Other, non-harmonised excises
Increase of security deposit for authorised wholesalers: mineral oils: HUF 600 million, In force from:
N/A
tobacco: HUF 22 million, other HUF 20 million. 3.11.2015
Other types of tax
Public health tax on alcoholic beverages: indirect tax based on alcoholic content (HUF
20/l for 1.2–5 %, HUF 100/l for 5–15 %, HUF 300/l for 15–25 %, HUF 500/l for 25–35 %, In force from:
Introduction (increase)
HUF 700/l for 35–45 %, HUF 900/l for over 45 %). Fruit distillates and herbal bitters are 1.1.2015
exempt.
Tax on tobacco companies: progressive tax on the turnover of companies in the
In force from:
tobacco sector, tax base: 0.2 % up to HUF 30 billion, 2,5 % from HUF 30 billion to Introduction (increase)
1.2.2015
HUF 60 billion, 4.5 % in excess of HUF 60 billion.
Food inspection fee: progressive levy on the turnover of companies in the FMCG
sector. Tax base: 0.1 % from HUF 500 million to HUF 50 billion, 1 % from HUF 50 billion
In force from:
to HUF 100 billion, 2 % from HUF 150 billion to HUF 200 billion, 3 % from Rate increase
1.1.2015
HUF 200 billion to HUF 250 billion, 4 % from HUF 250 billion to HUF 300 billion, 6 % in
excess of HUF 300 billion.
Sectoral tax on financial institutions is extended to investment funds (tax is 0.05 %), In force from:
Introduction (increase)
and it is abolished for investment management. 1.1.2015
Introduction of an annual flat rate on bank card (HUF 800/year and HUF 500/year for In force from:
Rate neutral
card with contactless payment function) instead of the volume-based method. 1.1.2015
The environmental product charge is extended to paper and certain chemicals and In force from:
Introduction (increase)
plastics. 1.1.2015
Local taxes: authorisation granted to local municipalities to levy local tax on natural In force from:
Introduction (increase)
persons on any taxable event (save those that are taxed ot national level). 1.1.2015
Modification of treasury taxation in financial transaction levy (exemption for certain In force from:
Base decrease
transactions). 1.1.2015
A temporary tax credit linked to Ukranian crisis introduced within sectoral tax on In force from:
Base decrease
financial institutions tax. 1.1.2015
In force from:
Local taxes: buyer-seller cooperatives are exempt from local business tax. Base decrease
1.1.2015
The rate of financial organisations tax on banks is reduced from 0.53 % to 0.31 % from In force from:
Rate decrease
2016 and to 0.21 % from 2017. 1.1.2016
Employers’ social contributions
In force from:
Phase-out of Job protection Act in public sector. Base neutral
1.1.2015
In force from:
Modification of the Job protection Act for mothers (returning from child care leave). Base decrease
1.1.2015
Administrative, compliance related measures
Introduction of a system monitoring the movement of goods for the purpose of risk In force from:
N/A
analysis (EKAER). 1.1.2015
Source: DG Taxation and Customs Union. Further information on national tax reforms, including announcements of forthcoming measures, can be found in the tax
reforms database.
62 Taxation trends in the European Union
Hungary 1
Main features of the tax system
Table HU.3: Individual taxation (PIT)
General
resident: worldwide income (subject to double-tax relief)
Base and jurisdiction
non-resident: domestic income
Tax unit/ taxation of couples and families separate taxation
there are 4 categories of income with specific taxation rules:
System and Applicable rates income from employment and pensions, income from business
activities, capital income and capital gains income
Global / Labour income scheme
–
children: The basis of income tax can be reduced by HUF
750 000 per year/each dependent for families having one or two
children), or HUF 2 475 000 per year/each dependent for families
having at least three children) (child allowances can also offset SSC
Basic allowance
liabilities).
first marriage: The tax base can be reduced by HUF 375 000 per
year per marriage, provided at least one of the couple is getting
married for the first time. The allowance can be used for maximum
2 years.
flat rate
Rate schedule
16 %
Surtaxes –
Regional and local surcharges –
Top statutory PIT rate (including surcharges) 16 %
Owner-occupied dwelling included
Capital income included
Income from renting movable property 16 %
Income from renting immovable property 16 %
Capital gains (immovable property) 16 %
Capital gains (movable property) 16 %
Dividends 16 % creditable withholding
Interests on deposits and special savings accounts 16 % final withholding; interests from LT accounts: 0 %, 10 %, 16 %
Interests on corporate and government bonds 16 % final withholding
Other specific features and alternative regimes
benefits in kind & other non-monetary income (games) 16 % on 1.19 times the value
pension income exempted
small-scale agricultural producers exempted if revenues < HUF 600 000
Other tax provisions
Main tax credits & deductions
10 % of income OR based on real expenses (only for
Professional expenses
self-employed)
Pension savings yes (20 %, capped, tax refunds)
Health savings yes (20 %, capped, tax refund)
Disabled persons yes (capped, tax credit)
Small-scale agricultural producers yes (capped, tax credit)
Mortgage no
Others (not exhaustive) union membership fees
Treatment of losses (business/self-employed income) (limited) 5-year carry forward, (limited) 2-year carry backward
Source: DG Taxation and Customs Union, on the basis of information provided by the national Ministries of Finance. For more detail, the TEDB database contains an
extensive inventory of the main taxes in force in the EU Member States, including their legal basis, assessment base, main exemptions, applicable rate(s), economic
and statistical classification.
Taxation trends in the European Union 63
1 Hungary
Table HU.4: VAT
Tax rates
Standard 27 %
Reduced rate(s) 5 % and 18 %
Table HU.5: Corporate taxation (CIT)
Tax rates
19 % (over HUF 500 million of the positive tax base)/10 % (below
Nominal corporate income tax rate
HUF 500 million of the positive tax base)
Central government surcharge
Regional government surcharge
Local government surcharge
Top CIT statutory rate (incl. surcharges) (¹) 20.6 %
small business tax 16 % (special conditions e.g. 25 employees or
Special tax rate for SMEs (all-in rate)
less and revenue and balance sheet below HUF 500 million) (²)
Tax base worldwide income
Anti-avoidance
Limits to interest deductions yes (thin cap rule of 3:1 debt to equity)
Transfer pricing rules yes, arm's length principle
Controlled foreign company (CFC) yes
Controlled foreign company (CFC) for passive income only no
Allowance for Corporate Equity no
(¹) Including the local business tax of maximum 2 % that applies on the gross operating profit.
(²) Taxpayers taxed under the small business tax scheme shall be exempted from the declaration and payment of: corporate tax, social contribution tax and vocational training
contribution.
Table HU.6: Social contributions
employment income, income from business and self-employed
Base activities, income from sports/entertainment, income from
occasional activities
Employers’ contributions
Total rate 27 % (¹)
of which:
Capped contributions no
Employees’ contributions
Total rate 18.5 %
of which: pensions 10 %, healthcare 7 %, unemployment 1.5 %
Capped contributions no
(¹) There is an additional + 1.5 % vocational training contribution, not paid by all employers.
Table HU.7: Wealth and transaction taxes
Inheritance and gift tax yes
Real estate taxation
Recurrent real estate tax yes
Regional differentiation yes
Tax discount for primary dwelling no (¹)
Real estate transfer tax yes
Net wealth tax no
(¹) Exemption is available for handicapped and retired people.
Source: DG Taxation and Customs Union, on the basis of information provided by the national Ministries of Finance. For more detail, the TEDB database contains an
extensive inventory of the main taxes in force in the EU Member States, including their legal basis, assessment base, main exemptions, applicable rate(s), economic
and statistical classification.
64 Taxation trends in the European Union
You might also like
- Taxation and Tax Policies in the Middle East: Butterworths Studies in International Political EconomyFrom EverandTaxation and Tax Policies in the Middle East: Butterworths Studies in International Political EconomyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- PT PDFDocument5 pagesPT PDFSwastik GroverNo ratings yet
- Taxation Trends in The European Union - 2012 173Document1 pageTaxation Trends in The European Union - 2012 173d05registerNo ratings yet
- Sanitärtechnik Eisenberg GMBH - FinancialsDocument2 pagesSanitärtechnik Eisenberg GMBH - Financialsin_daHouseNo ratings yet
- 2 19072023 Ap enDocument4 pages2 19072023 Ap enfaceitszapkaNo ratings yet
- Euro Area and EU28 Job Vacancy Rates at 2.3%: Fourth Quarter of 2018Document4 pagesEuro Area and EU28 Job Vacancy Rates at 2.3%: Fourth Quarter of 2018Valter SilveiraNo ratings yet
- (Ii) Longer Vehicle Lives Delay The EV RevolutionDocument6 pages(Ii) Longer Vehicle Lives Delay The EV RevolutionBob FisherNo ratings yet
- Summary Tables CountryDocument4 pagesSummary Tables CountryDanyel TanasaNo ratings yet
- Taxation Trends in The European Union - 2012 165Document1 pageTaxation Trends in The European Union - 2012 165d05registerNo ratings yet
- Taxation Trends in The European Union - 2012 167Document1 pageTaxation Trends in The European Union - 2012 167d05registerNo ratings yet
- 1250 220111 PPT BP 2021 Abi Version Final-Rev4 InglesDocument37 pages1250 220111 PPT BP 2021 Abi Version Final-Rev4 InglesRaul FretesNo ratings yet
- Annual Inflation Down To 1.2% in The Euro AreaDocument4 pagesAnnual Inflation Down To 1.2% in The Euro AreaDan BNo ratings yet
- B2C E-Commerce StatisticsDocument20 pagesB2C E-Commerce StatisticsMaihong NguyenNo ratings yet
- Fiscal PolicyDocument15 pagesFiscal Policyngupta690No ratings yet
- Figure 1: Distribution of Population by Dwelling Type, 2018: Living Conditions in Europe Housing StatisticsDocument42 pagesFigure 1: Distribution of Population by Dwelling Type, 2018: Living Conditions in Europe Housing StatisticsjackNo ratings yet
- Annual Inflation Up To 5.0% in The Euro AreaDocument4 pagesAnnual Inflation Up To 5.0% in The Euro AreaĐăng Khoa VũNo ratings yet
- Inversion de Los HogaresDocument11 pagesInversion de Los HogaresgabrielaNo ratings yet
- Euro Area Unemployment at 8.1%: September 2018Document6 pagesEuro Area Unemployment at 8.1%: September 2018Alexandra BeudeanNo ratings yet
- Tugas ALK Chapter 7Document8 pagesTugas ALK Chapter 7Alief AmbyaNo ratings yet
- Bright Line Sol.Document3 pagesBright Line Sol.Sudesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- 915 529 Supplement Landmark XLS ENGDocument32 pages915 529 Supplement Landmark XLS ENGPaco ColínNo ratings yet
- Annual Trading Report: Strictly ConfidentialDocument3 pagesAnnual Trading Report: Strictly ConfidentialMunazza FawadNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument5 pagesProject ReportHarshit ChiraniaNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument5 pagesProjectHarshit ChiraniaNo ratings yet
- Group ProjectDocument6 pagesGroup ProjectTAHA MOULVINo ratings yet
- Dr. Sen's FFDocument16 pagesDr. Sen's FFnikhilluniaNo ratings yet
- Mediaset (MS - MI) : 3Q03 Results On TuesdayDocument8 pagesMediaset (MS - MI) : 3Q03 Results On Tuesdaypoutsos1984No ratings yet
- Sample Assignment Name: Matrix No: CompanyDocument20 pagesSample Assignment Name: Matrix No: CompanynurainNo ratings yet
- Private Sector Debt, Non-Consolidated (TIPSPD10) : Open Product Page Open in Data BrowserDocument10 pagesPrivate Sector Debt, Non-Consolidated (TIPSPD10) : Open Product Page Open in Data BrowserRazvan DumitruNo ratings yet
- Financial PlanDocument8 pagesFinancial PlanwajeehaNo ratings yet
- M DAS CmaDocument16 pagesM DAS CmageeksacctupNo ratings yet
- Industry - Trends - Food - Beverages - January - 2022Document18 pagesIndustry - Trends - Food - Beverages - January - 2022TheaNo ratings yet
- Touchpoints Budget2020Document38 pagesTouchpoints Budget2020Elaine YeapNo ratings yet
- Annual Inflation Up To 1.9% in The Euro AreaDocument4 pagesAnnual Inflation Up To 1.9% in The Euro AreaClaudiuNo ratings yet
- Year Fed Min Wage Min Wage Relative To 1970 CPI Wage/CPIDocument5 pagesYear Fed Min Wage Min Wage Relative To 1970 CPI Wage/CPIJohnny AppleseedNo ratings yet
- FINM7044 Assignment 1 Group Company ModelDocument42 pagesFINM7044 Assignment 1 Group Company ModelMesh MohNo ratings yet
- Hourly Labour Costs 2016Document14 pagesHourly Labour Costs 2016Anonymous VRspXsmNo ratings yet
- CGII 2019-2020 Solution - FreqExame - StudentsDocument10 pagesCGII 2019-2020 Solution - FreqExame - StudentsBeatriz RodriguesNo ratings yet
- This Spreadsheet Supports STUDENT Analysis of The Case "Bob's Baloney" (UVA-F-1942)Document4 pagesThis Spreadsheet Supports STUDENT Analysis of The Case "Bob's Baloney" (UVA-F-1942)LAWZ1017No ratings yet
- Unprecedented Fall in OECD GDP by 9.8% in Q2 2020Document2 pagesUnprecedented Fall in OECD GDP by 9.8% in Q2 2020Βασίλης ΒήτταςNo ratings yet
- Landmark CaseDocument22 pagesLandmark CaseLauren KlaassenNo ratings yet
- Part A.1 Tariffs and Imports: Summary and Duty Ranges: Viet NamDocument1 pagePart A.1 Tariffs and Imports: Summary and Duty Ranges: Viet NamPrabhuNo ratings yet
- Excel Bodyshop EFDocument18 pagesExcel Bodyshop EFgestion integralNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis:: Internship ReportDocument5 pagesRatio Analysis:: Internship ReportsahhhhhhhNo ratings yet
- BudgetBrief 2015 PDFDocument85 pagesBudgetBrief 2015 PDFFarukh MalikNo ratings yet
- Reinventing Construction ICTC FINALDocument32 pagesReinventing Construction ICTC FINALParidz AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Cash Received by Gavi 2000 2019 As of 31 December 2019Document1 pageCash Received by Gavi 2000 2019 As of 31 December 2019MickelleCostantinoSheaNo ratings yet
- Vie Key Indicators 2021Document4 pagesVie Key Indicators 2021Nguyên NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Taxation Challenges For Bangladesh: Sams Uddin AhmedDocument9 pagesTaxation Challenges For Bangladesh: Sams Uddin AhmedNusrat ShatyNo ratings yet
- Atherine S OnfectioneryDocument3 pagesAtherine S OnfectioneryVanshika SinghNo ratings yet
- Income Statement Template: Strictly ConfidentialDocument9 pagesIncome Statement Template: Strictly ConfidentialAnthony BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Additional Information: Ratio AnalysisDocument7 pagesAdditional Information: Ratio Analysisashokdb2kNo ratings yet
- Revenue Statistics Asia and Pacific IndonesiaDocument2 pagesRevenue Statistics Asia and Pacific Indonesiakimseongyun123No ratings yet
- Revenue Statistics Asia and Pacific VietnamDocument2 pagesRevenue Statistics Asia and Pacific VietnamThanh HuyềnNo ratings yet
- Exerciese of Chapter ThreeDocument6 pagesExerciese of Chapter ThreeMohammad Al AkoumNo ratings yet
- Adnan TestDocument10 pagesAdnan TestAisar UddinNo ratings yet
- Budget Brief 2017Document70 pagesBudget Brief 2017shahzad32552372No ratings yet
- Operating Statement Borrower's Name: XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXDocument13 pagesOperating Statement Borrower's Name: XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXAbhishek GoenkaNo ratings yet
- Offshore Wind in Europe: Subtittle If Needed. If Not MONTH 2018Document40 pagesOffshore Wind in Europe: Subtittle If Needed. If Not MONTH 2018albert wangNo ratings yet
- CV Case 3Document40 pagesCV Case 3neelakanta srikarNo ratings yet
- Indonesia's New Tax Reform: Potential and Direction: Mohamad Ikhsan, Ledi Trialdi, Syarif SyahrialDocument3 pagesIndonesia's New Tax Reform: Potential and Direction: Mohamad Ikhsan, Ledi Trialdi, Syarif SyahrialSwastik GroverNo ratings yet
- Invitation Brochure 9th RMLNLU SCC Online® International Media Law Moot Court Competition 2021Document24 pagesInvitation Brochure 9th RMLNLU SCC Online® International Media Law Moot Court Competition 2021Swastik GroverNo ratings yet
- Indonesia Third Indonesia Fiscal Reform Development Policy Loan ProjectDocument81 pagesIndonesia Third Indonesia Fiscal Reform Development Policy Loan ProjectSwastik GroverNo ratings yet
- Tax Administration Reform and The Society in Indonesia Prasetyo PDFDocument32 pagesTax Administration Reform and The Society in Indonesia Prasetyo PDFSwastik GroverNo ratings yet
- Can Indonesia Reform Its Tax System? Problems and Options: Tulane Economics Working Paper SeriesDocument46 pagesCan Indonesia Reform Its Tax System? Problems and Options: Tulane Economics Working Paper SeriesSwastik GroverNo ratings yet
- 114 Penn St. L. Rev. 1003Document44 pages114 Penn St. L. Rev. 1003Swastik GroverNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Tax Reform On The Hospitality Sector: Some Evidence of The Republic of CroatiaDocument4 pagesThe Impact of Tax Reform On The Hospitality Sector: Some Evidence of The Republic of CroatiaSwastik GroverNo ratings yet
- Atlantic City: Building A Foundation For A Shared ProsperityDocument64 pagesAtlantic City: Building A Foundation For A Shared ProsperitySwastik GroverNo ratings yet
- Lessons From Indonesian Tax Administration Reform Phase 1 (2001-2008) : Does Good Governance Matter?Document49 pagesLessons From Indonesian Tax Administration Reform Phase 1 (2001-2008) : Does Good Governance Matter?Swastik GroverNo ratings yet
- The Reinvention of Atlantic City New Jersey Institutional Investors Conference April 9, 2015Document17 pagesThe Reinvention of Atlantic City New Jersey Institutional Investors Conference April 9, 2015Swastik GroverNo ratings yet
- PRN 2011-028 (43 NJR 278 (A) )Document3 pagesPRN 2011-028 (43 NJR 278 (A) )Swastik GroverNo ratings yet
- Formation of A Sale of Goods ContractDocument2 pagesFormation of A Sale of Goods ContractSwastik GroverNo ratings yet
- Assignment SynopsisDocument6 pagesAssignment SynopsisSwastik GroverNo ratings yet
- Perspectives of Tax Reforms in Croatia: Expert Opinion SurveyDocument35 pagesPerspectives of Tax Reforms in Croatia: Expert Opinion SurveySwastik GroverNo ratings yet
- Working Papers: The Wiiw Balkan ObservatoryDocument46 pagesWorking Papers: The Wiiw Balkan ObservatorySwastik GroverNo ratings yet
- Tax Administration Reform in Transition: The Case of CroatiaDocument40 pagesTax Administration Reform in Transition: The Case of CroatiaSwastik GroverNo ratings yet
- Foreign Exchange Refers To Foreign Currency and Where The Exchange of These Foreign CurrenciesDocument8 pagesForeign Exchange Refers To Foreign Currency and Where The Exchange of These Foreign CurrenciesSwastik GroverNo ratings yet
- Assignment Synopsis ForexDocument6 pagesAssignment Synopsis ForexSwastik GroverNo ratings yet
- Croatia World Bank WPS8203Document54 pagesCroatia World Bank WPS8203Swastik GroverNo ratings yet
- Topic: Gentle Justice in Contemporary Indaian SocietyDocument6 pagesTopic: Gentle Justice in Contemporary Indaian SocietySwastik GroverNo ratings yet
- Constitution Seminar 2020 by RMLNLUDocument1 pageConstitution Seminar 2020 by RMLNLUSwastik GroverNo ratings yet
- A Synopsis On: Submitted By-ABHILASH MISHRA (B.A LL. B Semester - 1) Submitted To - Mr. HARISH CHAND SINGHDocument5 pagesA Synopsis On: Submitted By-ABHILASH MISHRA (B.A LL. B Semester - 1) Submitted To - Mr. HARISH CHAND SINGHSwastik GroverNo ratings yet
- Legislative Drafting P M BakshiDocument9 pagesLegislative Drafting P M BakshiSwastik GroverNo ratings yet
- Legislative DraftingDocument14 pagesLegislative DraftingSwastik GroverNo ratings yet
- Topic: Gentle Justice in Contemporary Indaian SocietyDocument6 pagesTopic: Gentle Justice in Contemporary Indaian SocietySwastik GroverNo ratings yet
- Aftermath of Artificial Intelligence On TeslaDocument5 pagesAftermath of Artificial Intelligence On TeslaSwastik GroverNo ratings yet
- Structural Changes in The Dairy Industry and TheirDocument9 pagesStructural Changes in The Dairy Industry and TheirTamar MakhviladzeNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman Halaman 84-91 CBA AkmanDocument5 pagesRangkuman Halaman 84-91 CBA AkmanHaryo BagaskaraNo ratings yet
- JD Edwards Enterpriseone 9.X: Release Highlights (Applications)Document13 pagesJD Edwards Enterpriseone 9.X: Release Highlights (Applications)alcajaNo ratings yet
- Gavekal PresentationDocument35 pagesGavekal PresentationFernando KlingNo ratings yet
- TATA MOTORS Profit and Loss SheetDocument1 pageTATA MOTORS Profit and Loss SheetKaushal RautNo ratings yet
- Onoja Adotse - History of Agila Economy 1700 - 1900Document59 pagesOnoja Adotse - History of Agila Economy 1700 - 1900Onoja Adotse100% (1)
- NASSCOM Annual Report 2011-2012Document41 pagesNASSCOM Annual Report 2011-2012Devarsh YagnikNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire On Health InsuranceDocument15 pagesQuestionnaire On Health InsurancePRACHI DAS100% (7)
- When Should The Government Intervene in The Economy?: 1. Market FailureDocument4 pagesWhen Should The Government Intervene in The Economy?: 1. Market FailurenishmaNo ratings yet
- Revision 3 National Income Economics IBDocument4 pagesRevision 3 National Income Economics IBSean CalvinNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 (Page 71-73) Task 1Document11 pagesUnit 8 (Page 71-73) Task 1Ml MastersNo ratings yet
- TTM 10 Time Value of Money - LanjutanDocument58 pagesTTM 10 Time Value of Money - LanjutanDede KurniatiNo ratings yet
- Date Target Company Name Parent Deal Type Buyer (S) Seller (S) Deal Value ($ MN) % Sought Sector Sub IndustryDocument1 pageDate Target Company Name Parent Deal Type Buyer (S) Seller (S) Deal Value ($ MN) % Sought Sector Sub Industrysaahil kinkhabwalaNo ratings yet
- Solved Claire Consumes Three Goods Out of Her Income Food FDocument1 pageSolved Claire Consumes Three Goods Out of Her Income Food FM Bilal SaleemNo ratings yet
- Audit Report Elesterio 1Document5 pagesAudit Report Elesterio 1Jeffrey DuranNo ratings yet
- Hr. ScorecardDocument11 pagesHr. ScorecardMoustafa Mahmoud100% (4)
- Plastic MoenyDocument59 pagesPlastic MoenyAppasaheb ManeNo ratings yet
- Industries Development and Regulation ActDocument12 pagesIndustries Development and Regulation Actnavneetsingh86No ratings yet
- 20.2 Letter of Intent To Purchase A BusinessDocument5 pages20.2 Letter of Intent To Purchase A BusinessPeeve Kaye BalbuenaNo ratings yet
- Specialized BanksDocument29 pagesSpecialized BankskhusbuNo ratings yet
- Technical - Tutorial - de 232323Document33 pagesTechnical - Tutorial - de 232323ANDRES GUILLERMO CUBILLOS OCAMPONo ratings yet
- Strategy Execution Steps PDFDocument4 pagesStrategy Execution Steps PDFOjonimi AdegbeNo ratings yet
- Compilation of LettersDocument17 pagesCompilation of LettersJonathan Adones B. EstrellerNo ratings yet
- BCLE 2000C PG 04 Jan2019Document21 pagesBCLE 2000C PG 04 Jan2019myturtle gameNo ratings yet
- PT Komatsu Marketing and Support Indonesia: ImageDocument1 pagePT Komatsu Marketing and Support Indonesia: Imageandi fikriadiNo ratings yet
- GST Returns Reconciliation - MALLESHAM GAMPADocument27 pagesGST Returns Reconciliation - MALLESHAM GAMPArakianand007No ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Canadian 5th Edition Williamson Test BankDocument35 pagesMacroeconomics Canadian 5th Edition Williamson Test Banksinapateprear4k100% (11)
- Global Economic Crisis - ProjectDocument9 pagesGlobal Economic Crisis - ProjectaasthasinghtomarNo ratings yet
- 9 Riccardo BellofioreDocument21 pages9 Riccardo BellofioreMike LeonNo ratings yet
- Operations Management Lecture - 2Document6 pagesOperations Management Lecture - 2tusharNo ratings yet