0% found this document useful (0 votes)
424 views9 pagesChapter One: (I, 2i, Etc)
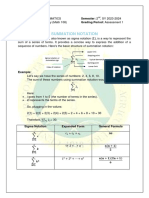
1) Numbers are abstract concepts that are used as tools in science and technology to solve problems and make predictions. They are applied in fields like medicine, engineering, and modeling natural phenomena.
2) Beyond applications, numbers also hold intrinsic beauty for mathematicians in theorems, patterns, and properties. The Fibonacci sequence and Pascal's triangle are examples that appeal for their aesthetic qualities.
3) Numbers form hierarchies from natural numbers to integers to rational and irrational numbers to real and complex numbers. Very large numbers are expressed scientifically using exponents and zeroes to track multiples of ten.
Uploaded by
Ciara LadromaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
424 views9 pagesChapter One: (I, 2i, Etc)
1) Numbers are abstract concepts that are used as tools in science and technology to solve problems and make predictions. They are applied in fields like medicine, engineering, and modeling natural phenomena.
2) Beyond applications, numbers also hold intrinsic beauty for mathematicians in theorems, patterns, and properties. The Fibonacci sequence and Pascal's triangle are examples that appeal for their aesthetic qualities.
3) Numbers form hierarchies from natural numbers to integers to rational and irrational numbers to real and complex numbers. Very large numbers are expressed scientifically using exponents and zeroes to track multiples of ten.
Uploaded by
Ciara LadromaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd