0% found this document useful (0 votes)
101 views2 pagesTurmeric Quality Standards and Testing
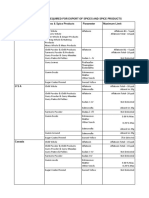
This document provides information on turmeric including its common name, botanical name, and minimum requirements. Turmeric must be clean, whole rhizomes with the characteristic aroma and flavor, and free of contaminants. Test parameters and reference ranges are provided for traits like moisture content, foreign matter, defective rhizomes, and curcuminoid content. Explanations of terms and the sampling plan and procedure are also described.
Uploaded by
BASIC LIFECopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
101 views2 pagesTurmeric Quality Standards and Testing
This document provides information on turmeric including its common name, botanical name, and minimum requirements. Turmeric must be clean, whole rhizomes with the characteristic aroma and flavor, and free of contaminants. Test parameters and reference ranges are provided for traits like moisture content, foreign matter, defective rhizomes, and curcuminoid content. Explanations of terms and the sampling plan and procedure are also described.
Uploaded by
BASIC LIFECopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd