Professional Documents
Culture Documents
It Produces The Electrical Impulses That Cause Your Heart To Beat
Uploaded by
Badrakh AdiyasurenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
It Produces The Electrical Impulses That Cause Your Heart To Beat
Uploaded by
Badrakh AdiyasurenCopyright:
Available Formats
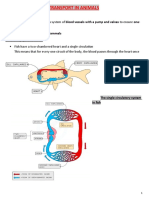
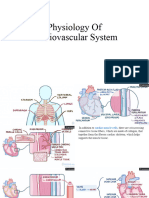
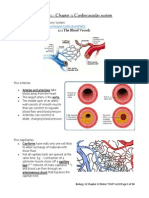
9.1 a system of blood vessels with a pump and valves to ensure one-way flow of blood.
9.2 blood containing a lot of oxygen
9.3 in the lungs
9.4 left
9.5 In a double circulatory system, blood flows from the heart to the lungs, and then back to the heart
again before travelling to the rest of the body. In a single circulatory system, blood flows directly from
the lungs or gills to the rest of the body.
9.6 It means oxygenated blood is transported body cells faster, at higher pressure.
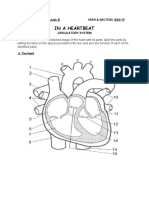
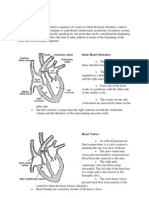
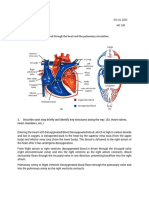
9.7 a) left atrium
b) right atrium
9.8 between the atria and the ventricles
9.9 septum
9.10 a right ventricle left ventricle
9.11 they contain more cardiac muscle, which can give a greater force when they contract. This is used
to pump blood through the body
9.12 it has more cardiac muscle, used to insert more force to pump blood all around the body rather
than the lungs
9.13 with an ECG, by measuring pulse rate, listening to the sound of valves closing
9.14 the pulse is the widening of the arteries, caused by blood travelling through it each time the heart
beats.
9.15 a) three
b) roughly 0.7 seconds
9.16 to bring blood to the muscles faster, to give the oxygen necessary for the release of energy
9.17 It's a small mass of specialized cells in the top of the right atrium, It produces the electrical
impulses that cause your heart to beat
9.18 the extra CO2 dissolves in blood plasma, which reduces the Ph. This is sensed by the brain, which
increases the frequency of the nerve impulses sent to the pacemaker
9.19 the valves are pushed closed by the high pressure of the blood in the ventricles. This prevents
blood flowing back into the atria.
You might also like
- Worksheet - Heart & Circulation KeyDocument3 pagesWorksheet - Heart & Circulation KeyJenn YumulNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideFrom EverandCirculatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Cardio Vascular SystemDocument8 pagesCardio Vascular SystemguptaasitNo ratings yet
- (Lecture 7) The Cardiovascular, Respiratory and Lymphatic SystemDocument32 pages(Lecture 7) The Cardiovascular, Respiratory and Lymphatic SystemKasraSrNo ratings yet
- LECT 11. Anatomy of CVSDocument61 pagesLECT 11. Anatomy of CVSDr. SaniaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Review Worksheet KEYDocument7 pagesCirculatory System Review Worksheet KEYJerilee SoCute WattsNo ratings yet
- Transport in AnimalsDocument19 pagesTransport in Animalsmohamed komiNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument25 pagesThe Circulatory SystemRahil BhavanNo ratings yet
- Preparation Tasks - Week 6Document7 pagesPreparation Tasks - Week 6Άγγελος ΧαβέλαςNo ratings yet
- 8 Transport in AnimalsDocument24 pages8 Transport in AnimalsMariam ShehabNo ratings yet
- Animal Transport Systems ExplainedDocument34 pagesAnimal Transport Systems ExplainedSatire GojoNo ratings yet
- BMAT Biology Revision NotesDocument9 pagesBMAT Biology Revision Notesmissymar123100% (5)
- PHYSIOLOGY by Kanze Ul EmanDocument11 pagesPHYSIOLOGY by Kanze Ul EmanMuhammad Farhan100% (1)
- Anaphy Cardio XIIDocument15 pagesAnaphy Cardio XIIRue Cheng MaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System ActivityDocument5 pagesCirculatory System ActivityKeen Jude CaminosNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular-System NURSING BNS321 STUDY DIAGRAM AND NOTESDocument9 pagesCardiovascular-System NURSING BNS321 STUDY DIAGRAM AND NOTESKingpinNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Cardiovascular SystemDocument19 pagesPhysiology of Cardiovascular SystemDavid JishkarianiNo ratings yet
- 224392278 BMAT Biology Revision Notesรรร PDFDocument9 pages224392278 BMAT Biology Revision Notesรรร PDFB. ChillNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System SummaryDocument9 pagesCardiovascular System SummaryTaskeen BaberNo ratings yet
- CardiovascularDocument92 pagesCardiovascularRolinette DaneNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System: Arteries VeinsDocument27 pagesThe Cardiovascular System: Arteries VeinsMark Anthony DiegoNo ratings yet
- BIO241 Heart Structure and Function LabDocument3 pagesBIO241 Heart Structure and Function LabJames Jung100% (1)
- The Heart, Part 1 - Under Pressure: Crash Course A&P # 25Document5 pagesThe Heart, Part 1 - Under Pressure: Crash Course A&P # 25Jordan TorresNo ratings yet
- Transport in Animals-Topic 9Document14 pagesTransport in Animals-Topic 9sukiiNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Presented by DR Aparna Ramachandran Mds 1 Dept of Public Health DentistryDocument73 pagesCardiovascular System: Presented by DR Aparna Ramachandran Mds 1 Dept of Public Health DentistryAparna RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Cardiac CycleDocument3 pagesCardiac CycleKhadijah HabeebahNo ratings yet
- Minggu 13 Peredaran DarahDocument11 pagesMinggu 13 Peredaran Darahcuksam27No ratings yet
- PMLS 2 6-13 (Lec)Document26 pagesPMLS 2 6-13 (Lec)Ricci Gwennmorei TaghapNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Vessels: Ba-Etilayoo AtingaDocument89 pagesCardiovascular System: Vessels: Ba-Etilayoo AtingaKofi Fofie-AsieduNo ratings yet
- BSBA - NATSCI 1: Cardiovascular SystemDocument6 pagesBSBA - NATSCI 1: Cardiovascular Systemshela ambasNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Transport in HumansDocument11 pages5.2 Transport in Humans박찬우No ratings yet
- The Equine Cardiovascular SystemDocument7 pagesThe Equine Cardiovascular SystemSavannah Simone PetrachenkoNo ratings yet
- Iii. Anatomy and Physiology The Cardiovascular System: Arteries VeinsDocument7 pagesIii. Anatomy and Physiology The Cardiovascular System: Arteries Veinskian5No ratings yet
- Cardio 1Document4 pagesCardio 1Liam Jacque LapuzNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: K. Hariharan Iv Eee - 'B'Document33 pagesCardiovascular System: K. Hariharan Iv Eee - 'B'Hari Haran100% (1)
- Cardiac Cycle.: Basic Heart StructureDocument9 pagesCardiac Cycle.: Basic Heart StructureMohammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- CAPEc 06Document30 pagesCAPEc 06Isheba Warren83% (6)
- Chapter 13: Cardiovascular SystemDocument69 pagesChapter 13: Cardiovascular SystemFidaNo ratings yet
- 81: Mammalian Heart and Its RegulationDocument75 pages81: Mammalian Heart and Its RegulationIt's Ika100% (1)
- CardiovascularDocument7 pagesCardiovascularapi-294104473No ratings yet
- Circulatory System and Heart Biology Summarisation.Document5 pagesCirculatory System and Heart Biology Summarisation.Jumana ElkhateebNo ratings yet
- 0654 IGCSE - Transportation in Plants and Animals PDFDocument12 pages0654 IGCSE - Transportation in Plants and Animals PDFDavid ReeseNo ratings yet
- 3 The Human HeartDocument27 pages3 The Human HeartOlivia MorenteNo ratings yet
- CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY NOTESDocument20 pagesCARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY NOTESVivek ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Ciculatory SystemDocument21 pagesCiculatory SystemSabrina LavegaNo ratings yet
- CVS 2Document153 pagesCVS 2khalidtalal8000No ratings yet
- CVS FullDocument32 pagesCVS FullLianne PalinsadNo ratings yet
- Transport in ManDocument40 pagesTransport in ManßéršerK4040 KyùNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument7 pagesCirculatory SystemWisdom DzombeNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesCirculatory SystemJpaw Kidman100% (1)
- Types of Circulatory SystemsDocument8 pagesTypes of Circulatory SystemsJanis Micaela EsmasNo ratings yet
- Bio 12 Ch12 Cardiovascular Sys Notes PackageDocument16 pagesBio 12 Ch12 Cardiovascular Sys Notes Packagekw2533No ratings yet
- Research Questions-: How The Blood FlowsDocument5 pagesResearch Questions-: How The Blood FlowsAasritha SenagapallyNo ratings yet
- 213 CardiacDocument2 pages213 Cardiacapi-308815018No ratings yet
- Magna YeDocument2 pagesMagna YekceesevillaNo ratings yet
- CirculationDocument3 pagesCirculationAIKA BAYANo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Cardiovascular SystemDocument23 pagesAnatomy of Cardiovascular SystemElvira Wisakhadewi100% (1)
- 23 2Document1 page23 2Badrakh AdiyasurenNo ratings yet
- Every Country Has Poor People and Every Country Has Different Ways of Dealing With The PoorDocument1 pageEvery Country Has Poor People and Every Country Has Different Ways of Dealing With The PoorBadrakh AdiyasurenNo ratings yet
- 23 4Document1 page23 4Badrakh AdiyasurenNo ratings yet
- 23 3Document1 page23 3Badrakh AdiyasurenNo ratings yet
- Kami Export Badrakh Preparing - Salt - Docx 1 1 PDFDocument19 pagesKami Export Badrakh Preparing - Salt - Docx 1 1 PDFBadrakh AdiyasurenNo ratings yet
- Every Country Has Poor People and Every Country Has Different Ways of Dealing With The PoorDocument1 pageEvery Country Has Poor People and Every Country Has Different Ways of Dealing With The PoorBadrakh AdiyasurenNo ratings yet
- 23 3Document1 page23 3Badrakh AdiyasurenNo ratings yet
- 23 4Document1 page23 4Badrakh AdiyasurenNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (14)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (327)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- Daniel Kahneman's "Thinking Fast and Slow": A Macat AnalysisFrom EverandDaniel Kahneman's "Thinking Fast and Slow": A Macat AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (130)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)