Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Passive Damping Technique for 2-DOF Vibration System
Uploaded by
فرح تامر0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views12 pagesvibration absorber PowerPoint
Original Title
vibration absorber
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentvibration absorber PowerPoint
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views12 pagesPassive Damping Technique for 2-DOF Vibration System
Uploaded by
فرح تامرvibration absorber PowerPoint
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
Vibration Absorber
The first passive damping
technique we will learn!
Vibration Absorber #WikiCourses
http://WikiCourses.WikiSpaces.com
Mohammad Tawfik
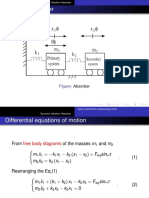
For a 2-DOF System
• For the shown 2-DOF
system, the equations
of motion may be
written as:
Mx Kx f
f1
• Where: f
f2
Vibration Absorber #WikiCourses
http://WikiCourses.WikiSpaces.com
Mohammad Tawfik
For Harmonic Excitation
• We may write the f1Cos1t
equation for each of Mx Kx
0
the excitation
frequency in the form 0
Mx Kx
f 2Cos 2t
of:
• Then we may add
both solutions!
Vibration Absorber #WikiCourses
http://WikiCourses.WikiSpaces.com
Mohammad Tawfik
Consider the first force
• We may write the 1
equation in the form: Mx Kx f1Cost
0
• And the solution in x1
x Cos t
the form: x2
• Which will give: x1
x Cos t 2 x
2
x2
Vibration Absorber #WikiCourses
http://WikiCourses.WikiSpaces.com
Mohammad Tawfik
The equation of motion becomes
2 m1 0 k1 k 2 k 2 x1 f1
m2 k 2
2
k 2 x2 0
0
• Get x1() and find out when does it equal
to zero!
Vibration Absorber #WikiCourses
http://WikiCourses.WikiSpaces.com
Mohammad Tawfik
Using the Dynamic Stiffness
Matrix
• Writing down the dynamic stiffness matrix:
2 m1 K1 K 2 K2 x1 f1
K2 m2 K 2 x2 0
2
Getting the inverse:
2 m2 K 2 K2
x1 K2 m1 K1 K 2
2
f1
x
2 m1 K1 K 2 m2 K 2 K 2
2 2 2
0
Vibration Absorber #WikiCourses
http://WikiCourses.WikiSpaces.com
Mohammad Tawfik
Obtaining the Solution
• Multiply the inverse by the right-hand-side
x1 1 2
m2 K 2 f1
x m m 4 m K K m K 2 K K
2 1 2 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 K 2 f1
• For the first degree of freedom:
x1
m
K 2 f1
2
2 0
m1m2 m2 K1 K 2 m1 K 2 K1 K 2
4 2
Vibration Absorber #WikiCourses
http://WikiCourses.WikiSpaces.com
Mohammad Tawfik
Vibration Absorber
• For the first degree of freedom to be
stationary, i.e. x1=0
• The excitation frequency have to satisfy:
K2
m2
• Note that this frequency is equal to the
natural frequency of the auxiliary spring-
mass system alone
Vibration Absorber #WikiCourses
http://WikiCourses.WikiSpaces.com
Mohammad Tawfik
Vibration absorber
Vibration Absorber #WikiCourses
http://WikiCourses.WikiSpaces.com
Mohammad Tawfik
Vibration absorber
Vibration Absorber #WikiCourses
http://WikiCourses.WikiSpaces.com
Mohammad Tawfik
Homework #2
• Repeat the example of this lecture using
f2=f3=0 and f1=1 AND f1=f2=0 and f3=1
• Plot the response of each mass for each
of the excitation functions
• Comment on the results in the lights of
your understanding of the concept of
vibration absorber
Vibration Absorber #WikiCourses
http://WikiCourses.WikiSpaces.com
Mohammad Tawfik
Homework #2 (cont’d)
• Use modal decomposition
(diagonalization) to obtain the same
results.
Vibration Absorber #WikiCourses
http://WikiCourses.WikiSpaces.com
Mohammad Tawfik
You might also like
- Cowell - The Wizards of Once PDFDocument315 pagesCowell - The Wizards of Once PDFtatoes n lases100% (1)
- Inventory Valiuation Raw QueryDocument4 pagesInventory Valiuation Raw Querysatyanarayana NVSNo ratings yet
- Beginning Vibration Analysis FundamentalsDocument96 pagesBeginning Vibration Analysis FundamentalsBarcsa RudolfNo ratings yet
- 41-How To Calculate Air Temp in Unconditioned SpacesDocument3 pages41-How To Calculate Air Temp in Unconditioned Spacesalmig200No ratings yet
- JSMSC - TDv3 6 20Document251 pagesJSMSC - TDv3 6 20Jason20170% (1)
- Aimt ProspectusDocument40 pagesAimt ProspectusdustydiamondNo ratings yet
- CS6002 1 MS Coursework Year 2012/13Document4 pagesCS6002 1 MS Coursework Year 2012/13duck19000No ratings yet
- Iso 2954 2012 en PDFDocument8 pagesIso 2954 2012 en PDFJulio CastilloNo ratings yet
- Poster - Vibration Energy Harvesting From Dynamic Absorber Using Piezoelectric TransducerDocument1 pagePoster - Vibration Energy Harvesting From Dynamic Absorber Using Piezoelectric TransducerLuqmaan Hakiem Sulaiman100% (1)
- Practical Use of Dynamic Vibration AbsorbersDocument4 pagesPractical Use of Dynamic Vibration AbsorbersDan-jones TudziNo ratings yet
- Optimal Design of A Damped Dynamic Vibration AbsorberDocument21 pagesOptimal Design of A Damped Dynamic Vibration AbsorberShrikant DholeNo ratings yet
- Sleeve Bearing Problems: Oil Whip and Whirl ExplainedDocument2 pagesSleeve Bearing Problems: Oil Whip and Whirl ExplainedmtttusharNo ratings yet
- Extracto ISO 10816Document10 pagesExtracto ISO 10816clroyo9475No ratings yet
- Enhancing System Reliability BookDocument4 pagesEnhancing System Reliability BookMuadz EswanNo ratings yet
- DIS 20806 Balancing PDFDocument30 pagesDIS 20806 Balancing PDFzaidbismaNo ratings yet
- Figure 1 - Typical FFT Showing Gear MisalignmentDocument4 pagesFigure 1 - Typical FFT Showing Gear MisalignmentDario SesarNo ratings yet
- BHJDynamics Damper InfoDocument10 pagesBHJDynamics Damper Infosuhas110No ratings yet
- GV240 Series: Advanced Switching SolutionsDocument7 pagesGV240 Series: Advanced Switching SolutionsBiagio PadulaNo ratings yet
- Vibration ManualDocument32 pagesVibration Manualsayed1234No ratings yet
- NuggetsDocument202 pagesNuggetsfazzlieNo ratings yet
- Ch3 Balancing of Rigid - Flexible - Linked PDFDocument119 pagesCh3 Balancing of Rigid - Flexible - Linked PDFAlexis CordovaNo ratings yet
- CEP VFD ManualDocument234 pagesCEP VFD ManualUsama ZubairNo ratings yet
- Rolling Element Bearings Vibration AnalysisDocument10 pagesRolling Element Bearings Vibration AnalysisSiva Kulanji100% (1)
- EM 81 - Pump Vibrations Part IIDocument2 pagesEM 81 - Pump Vibrations Part IIΡαφαηλ Καμ.100% (1)
- 237258Document14 pages237258Alberto Remolar100% (1)
- AN011 Basics of Structural Testing Analysis PDFDocument16 pagesAN011 Basics of Structural Testing Analysis PDFdejavu_45No ratings yet
- Effective Use of Statistical Models To Establish and Update Vibration AlarmDocument11 pagesEffective Use of Statistical Models To Establish and Update Vibration AlarmMohammadreza GalebanNo ratings yet
- Iso 13373 9 2017Document12 pagesIso 13373 9 2017ThejaswiniNo ratings yet
- Training, Class I, Testing, IIb, 1-10Document12 pagesTraining, Class I, Testing, IIb, 1-10luis_hernandez_qNo ratings yet
- Balance VibrationDocument4 pagesBalance VibrationZaidiNo ratings yet
- Compresor Reciprocante Protección Y Gestión - GEDocument16 pagesCompresor Reciprocante Protección Y Gestión - GEOdlanier José MendozaNo ratings yet
- Power Station Engine Generator Vibration Analysis ReportDocument5 pagesPower Station Engine Generator Vibration Analysis ReportDerrick AramNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Vibration AbsorberDocument67 pagesDynamic Vibration AbsorberNajeeb ShakirNo ratings yet
- Critical Speed PDFDocument10 pagesCritical Speed PDFParamasivam VeerappanNo ratings yet
- Istec Bookazine Vibration WebDocument77 pagesIstec Bookazine Vibration WebJarot PrakosoNo ratings yet
- Asme B73-1 PDFDocument52 pagesAsme B73-1 PDFJoan Camilo PovedaNo ratings yet
- Vibration SwitchesDocument12 pagesVibration SwitchesAnonymous 1dVLJSVhtrNo ratings yet
- 5000 KW Gearbox High Pinion Bearing Temperatures 1644227029Document7 pages5000 KW Gearbox High Pinion Bearing Temperatures 1644227029MC ANo ratings yet
- TOMAS UsersManualDocument94 pagesTOMAS UsersManualrodruren01No ratings yet
- Article Overall Vibration Values For Reliable Wind Turbines PDFDocument4 pagesArticle Overall Vibration Values For Reliable Wind Turbines PDFrrNo ratings yet
- Oil Whirl and WhipDocument8 pagesOil Whirl and WhipAsim GillaniNo ratings yet
- Online TextbookDocument6 pagesOnline TextbookYanuar KrisnahadiNo ratings yet
- Vibxpert 2 Manual English 112010Document170 pagesVibxpert 2 Manual English 112010santiago6767% (3)
- Vibration ChartDocument1 pageVibration ChartdilkisunoNo ratings yet
- Vibration Monitoring: Envelope Signal ProcessingDocument14 pagesVibration Monitoring: Envelope Signal ProcessingDkdkkd100% (1)
- API Standards For Mechanical Rotating Machinery: September 2020Document4 pagesAPI Standards For Mechanical Rotating Machinery: September 2020khabiranNo ratings yet
- 2P-Balancing Using SKF Microlog PDFDocument6 pages2P-Balancing Using SKF Microlog PDFAbhishek DasNo ratings yet
- Successful Solution: To The Challenge ofDocument2 pagesSuccessful Solution: To The Challenge ofKenny RuizNo ratings yet
- Bently Nevada Proximity Probe System Reliability Benefits-EnDocument8 pagesBently Nevada Proximity Probe System Reliability Benefits-EnTodorosss JjNo ratings yet
- Monitoring and Analysis of Machine VibrationDocument6 pagesMonitoring and Analysis of Machine VibrationAvinashNo ratings yet
- Dm200 CatalogDocument6 pagesDm200 CatalogAS_865025438No ratings yet
- Technical Specifications: CAB 920 - The Perfect Combination of Simplicity and PerformanceDocument6 pagesTechnical Specifications: CAB 920 - The Perfect Combination of Simplicity and PerformanceMitulNo ratings yet
- Motors:: The Past Is PresentDocument6 pagesMotors:: The Past Is Presenteko bagus sunaryoNo ratings yet
- 4 6048713583825524153Document18 pages4 6048713583825524153Dan PardoNo ratings yet
- Preview - ISO+20816 5 2018Document6 pagesPreview - ISO+20816 5 2018hemza boukemmaNo ratings yet
- 303mills PDFDocument32 pages303mills PDFfaisalNo ratings yet
- Condition Monitoring of Centrifugal Blower Using Vibration Analysis PDFDocument10 pagesCondition Monitoring of Centrifugal Blower Using Vibration Analysis PDFJose PradoNo ratings yet
- Roots BlowerDocument2 pagesRoots Blowereko bagus sunaryoNo ratings yet
- A Beginners TutorialDocument56 pagesA Beginners Tutorialvijayabaskaran PalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Vibration Analysis of Reciprocating CompressorsDocument3 pagesVibration Analysis of Reciprocating Compressorskokoro48karaNo ratings yet
- ISO 10816 - Severidad en Vibracion PDFDocument2 pagesISO 10816 - Severidad en Vibracion PDFJuan Carlos Bonifacio BricenoNo ratings yet
- Proceedings of the Metallurgical Society of the Canadian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Fracture Mechanics, Winnipeg, Canada, August 23-26, 1987From EverandProceedings of the Metallurgical Society of the Canadian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Fracture Mechanics, Winnipeg, Canada, August 23-26, 1987W. R. TysonNo ratings yet
- Structural Health MonitoringFrom EverandStructural Health MonitoringDaniel BalageasNo ratings yet
- 02vibrationabsorber 150601135301 Lva1 App6892 PDFDocument12 pages02vibrationabsorber 150601135301 Lva1 App6892 PDFفرح تامرNo ratings yet
- Supervisor: Dr. K.K. WijesundaraDocument23 pagesSupervisor: Dr. K.K. Wijesundarakhawaldeh jamalNo ratings yet
- Wk11 Lectrure11 12dec2017 FinalDocument15 pagesWk11 Lectrure11 12dec2017 Finalهاني احمدNo ratings yet
- Statistical Modelling For Exposure Measurement Er-Wageningen University and Research 365647Document168 pagesStatistical Modelling For Exposure Measurement Er-Wageningen University and Research 365647فرح تامرNo ratings yet
- Rspa 1966 0095Document16 pagesRspa 1966 0095فرح تامرNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy Lecture NotesDocument103 pagesMetallurgy Lecture Notesفرح تامرNo ratings yet
- Measurement: Block FlatnessDocument16 pagesMeasurement: Block Flatnessفرح تامرNo ratings yet
- Abbe Error/Offset: SynonymsDocument4 pagesAbbe Error/Offset: Synonymsفرح تامرNo ratings yet
- 10.1007 - 978 1 84996 311 4Document346 pages10.1007 - 978 1 84996 311 4فرح تامرNo ratings yet
- Maintenancestrategy 180118134028Document20 pagesMaintenancestrategy 180118134028فرح تامرNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Common Vibration Problems: Prof. Dr. Fawkia RamadanDocument13 pagesDiagnosis of Common Vibration Problems: Prof. Dr. Fawkia Ramadanفرح تامر100% (1)
- Types of Maintenance: Prepared by Rathod Abhik (13MMF0001)Document20 pagesTypes of Maintenance: Prepared by Rathod Abhik (13MMF0001)RadivojJovanovNo ratings yet
- INDUSTRIAL TRAINING AT RELIANCE INDUSTRIES LIMITEDDocument92 pagesINDUSTRIAL TRAINING AT RELIANCE INDUSTRIES LIMITEDفرح تامرNo ratings yet
- 02vibrationabsorber 150601135301 Lva1 App6892 PDFDocument12 pages02vibrationabsorber 150601135301 Lva1 App6892 PDFفرح تامرNo ratings yet
- Manual Ed1080adig enDocument69 pagesManual Ed1080adig enStefan IstratescuNo ratings yet
- Vibration Isolators FinalDocument54 pagesVibration Isolators Finalفرح تامرNo ratings yet
- Absorber 150509193218 Lva1 App6891 PDFDocument18 pagesAbsorber 150509193218 Lva1 App6891 PDFفرح تامرNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Vibration AbsorberDocument36 pagesDynamic Vibration Absorberفرح تامرNo ratings yet
- Programmer Competency Matrix - Sijin JosephDocument8 pagesProgrammer Competency Matrix - Sijin JosephkikiNo ratings yet
- Configuration Management and ISO 9001Document7 pagesConfiguration Management and ISO 9001Simone MeschinoNo ratings yet
- Far Eastern University Institute of Tourism and Hotel Management Tourism Management Program 1 Semester A.Y. 2019 - 2020Document46 pagesFar Eastern University Institute of Tourism and Hotel Management Tourism Management Program 1 Semester A.Y. 2019 - 2020Mico BolorNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Concrete Strength Using Flyash and Rice Husk AshDocument10 pagesAssessment of Concrete Strength Using Flyash and Rice Husk AshNafisul AbrarNo ratings yet
- To Quantitative Analysis: To Accompany by Render, Stair, Hanna and Hale Power Point Slides Created by Jeff HeylDocument94 pagesTo Quantitative Analysis: To Accompany by Render, Stair, Hanna and Hale Power Point Slides Created by Jeff HeylNino NatradzeNo ratings yet
- PVC and CPVC Pipes - Schedule 40 & 80Document8 pagesPVC and CPVC Pipes - Schedule 40 & 80yarzar17No ratings yet
- Insert - Elecsys Anti-HBs II - Ms - 05894816190.V2.EnDocument4 pagesInsert - Elecsys Anti-HBs II - Ms - 05894816190.V2.EnyantuNo ratings yet
- Aruksha ResumeDocument2 pagesAruksha Resumeapi-304262732No ratings yet
- Main Application of Fans and BlowerDocument5 pagesMain Application of Fans and Blowermissy forlajeNo ratings yet
- Organic Vapour List PDFDocument1 pageOrganic Vapour List PDFDrGurkirpal Singh MarwahNo ratings yet
- Vertical Transportation SystemDocument15 pagesVertical Transportation SystemAnupama MorankarNo ratings yet
- 00001Document20 pages00001Maggie ZhuNo ratings yet
- An Improvement in Endodontic Therapy You Will AppreciateDocument2 pagesAn Improvement in Endodontic Therapy You Will AppreciateIs MNo ratings yet
- Service Manual for Daewoo Mini Component Sound SystemsDocument46 pagesService Manual for Daewoo Mini Component Sound SystemsDaifred GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- CS Sample Paper 1Document10 pagesCS Sample Paper 1SpreadSheetsNo ratings yet
- Explicit Instruction: A Teaching Strategy in Reading, Writing, and Mathematics For Students With Learning DisabilitiesDocument3 pagesExplicit Instruction: A Teaching Strategy in Reading, Writing, and Mathematics For Students With Learning DisabilitiesKatherineNo ratings yet
- Boost productivity and networking with a co-working café in Iligan CityDocument4 pagesBoost productivity and networking with a co-working café in Iligan CityJewel Cabigon0% (1)
- Astm D 4417Document4 pagesAstm D 4417Javier Celada0% (1)
- Solutions for QAT1001912Document3 pagesSolutions for QAT1001912NaveenNo ratings yet
- GRL+Prosp - EDocument2 pagesGRL+Prosp - Ethoma111sNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 22es14aDocument77 pagesUnit-3 22es14atejvimathNo ratings yet
- Toyota's Marketing StrategyDocument14 pagesToyota's Marketing StrategyLavin Gurnani0% (1)
- Kaseya Performance and Best Practices Guide: Authors: Jacques Eagle Date: Thursday, April 29, 2010Document34 pagesKaseya Performance and Best Practices Guide: Authors: Jacques Eagle Date: Thursday, April 29, 2010markdavidboydNo ratings yet
- Gen - Biology 2 Module 2Document12 pagesGen - Biology 2 Module 2Camille Castrence CaranayNo ratings yet