Professional Documents
Culture Documents
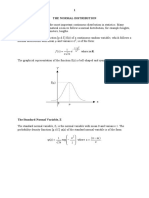
f (x) = e ∞ 0. E (X) =μ∧V (X) =σ μ, σ: Normal Distribution
Uploaded by
Chandler Manlongat0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pageThis document discusses the normal distribution, which describes a random variable with a probability density function that is symmetric around the mean and bell-shaped. A normal random variable is denoted by N(μ, σ^2) where μ is the mean and σ^2 is the variance. Key properties are that the mode occurs at the mean, the distribution is symmetric about the mean, and it is concave downward between μ-σ and μ+σ and concave upward otherwise.
Original Description:
Original Title
dasd.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the normal distribution, which describes a random variable with a probability density function that is symmetric around the mean and bell-shaped. A normal random variable is denoted by N(μ, σ^2) where μ is the mean and σ^2 is the variance. Key properties are that the mode occurs at the mean, the distribution is symmetric about the mean, and it is concave downward between μ-σ and μ+σ and concave upward otherwise.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views1 pagef (x) = e ∞ 0. E (X) =μ∧V (X) =σ μ, σ: Normal Distribution
Uploaded by
Chandler ManlongatThis document discusses the normal distribution, which describes a random variable with a probability density function that is symmetric around the mean and bell-shaped. A normal random variable is denoted by N(μ, σ^2) where μ is the mean and σ^2 is the variance. Key properties are that the mode occurs at the mean, the distribution is symmetric about the mean, and it is concave downward between μ-σ and μ+σ and concave upward otherwise.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
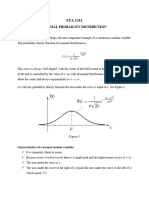
Normal Distribution
Compute the probability distributions of a
random variable for both discrete and
continuous data.
A random variable X with probability density
function
2
−(x− μ)
1 2σ
2
f ( x )= e −∞< x <∞
√ 2 πσ
Is a normal random variable with parameters μ
where −∞< x <∞ and σ > 0. Also,
E ( X ) =μ∧V ( X ) =σ 2
And the notation N( μ , σ 2 ) is used to denote the
distribution.
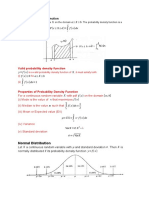
Properties of Normal Distribution
1. The mode which is the point on the
horizontal axis where the curve is a
maximum, occurs at x=μ.
2. The curve is symmetric about a vertical
axis through the mean μ.
3. The curve has its point of inflection at
x=μ ± σ and it is concave downward if
μ−σ < X < μ+ ¿ σ and it is concave
upward otherwise.
You might also like
- Normal Distribution: X N X FDocument5 pagesNormal Distribution: X N X FK.Prasanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Business Stat & Emetrics101Document38 pagesBusiness Stat & Emetrics101kasimNo ratings yet
- Probability: Continuous Random Variable-IDocument3 pagesProbability: Continuous Random Variable-IBala BalajiNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics: I. Learning QuestionsDocument7 pagesProbability and Statistics: I. Learning QuestionsQuỳnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chebysev Inequality: Suppose and VarianceDocument13 pagesChebysev Inequality: Suppose and VarianceMuthusivaramapandian MuthurajNo ratings yet
- SSP4SE AppaDocument10 pagesSSP4SE AppaÖzkan KaleNo ratings yet
- The Multivariate Normal Distribution: Exactly Central LimitDocument59 pagesThe Multivariate Normal Distribution: Exactly Central LimitVictor ChenNo ratings yet
- Most Important Theoratical Questions of QTDocument26 pagesMost Important Theoratical Questions of QTIsmith PokhrelNo ratings yet
- 1 The Normal Distribution: Where X RDocument2 pages1 The Normal Distribution: Where X RAkshay BundhooNo ratings yet
- Week+4 RV RevisedDocument15 pagesWeek+4 RV RevisedAfiQah AzizNo ratings yet
- Multivariate DistributionsDocument8 pagesMultivariate DistributionsArima AckermanNo ratings yet
- Lecture11 (Week 12) UpdatedDocument34 pagesLecture11 (Week 12) UpdatedBrian LiNo ratings yet
- Exactly Central Limit: Multivariate Statistical MethodsDocument18 pagesExactly Central Limit: Multivariate Statistical MethodsTolesa F BegnaNo ratings yet
- Chap6 BivariateNormalDocument28 pagesChap6 BivariateNormalMariem KsontiniNo ratings yet
- Engineering Probability and Statistics Statistics: Mathematical ExpectationDocument18 pagesEngineering Probability and Statistics Statistics: Mathematical ExpectationDinah Jane MartinezNo ratings yet
- Variance and Standard Deviation Math 217 Probability and StatisticsDocument3 pagesVariance and Standard Deviation Math 217 Probability and StatisticsThầy Trung Cấp TốcNo ratings yet
- Multi Varia Da 1Document59 pagesMulti Varia Da 1pereiraomarNo ratings yet
- Math403 - 4.0 Continuous Probability DistributionDocument42 pagesMath403 - 4.0 Continuous Probability DistributionMae FalcunitinNo ratings yet
- Stat NotesDocument14 pagesStat NotesTreanungkur MalNo ratings yet
- Random Variable Modified PDFDocument19 pagesRandom Variable Modified PDFIMdad HaqueNo ratings yet
- Review of Random VariablesDocument8 pagesReview of Random Variableselifeet123No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Inequalities and Asymptotic EstimatesDocument9 pagesLecture 4 Inequalities and Asymptotic Estimateskientrungle2001No ratings yet
- Kalman Notes 001Document11 pagesKalman Notes 001sadiksnmNo ratings yet
- STSnewDocument96 pagesSTSnewPatryk MartyniakNo ratings yet
- Random Vectors and Multivariate Normal DistributionDocument6 pagesRandom Vectors and Multivariate Normal DistributionJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Business Decision Making II Continuous Probability DistributionsDocument11 pagesBusiness Decision Making II Continuous Probability DistributionsUyen ThuNo ratings yet
- Common Probability Distributions: 1.1 Bernoulli DistributionDocument6 pagesCommon Probability Distributions: 1.1 Bernoulli DistributionMathew Carl WaniwanNo ratings yet
- Prof Stanley Dukin Lectures Statistical MechanicsDocument43 pagesProf Stanley Dukin Lectures Statistical MechanicsEdney GranhenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 DistributionDocument101 pagesLecture 3 DistributionSabbir Hasan MonirNo ratings yet
- Random Signals and NoiseDocument83 pagesRandom Signals and NoisespellbindguyNo ratings yet
- 1 Continuous Probability Distributions: ObjectivesDocument20 pages1 Continuous Probability Distributions: ObjectivesManibalanNo ratings yet
- Section06 SolutionsDocument15 pagesSection06 SolutionsMuhammad asafNo ratings yet
- Solution To Exercise 1.14: Econometric Theory and MethodsDocument1 pageSolution To Exercise 1.14: Econometric Theory and MethodsLeonard Gonzalo Saavedra AstopilcoNo ratings yet
- Section06 SolutionsDocument11 pagesSection06 SolutionsKarimaNo ratings yet
- c3 DistDocument21 pagesc3 Disttarek mahmoudNo ratings yet
- Continuous Random VariableDocument44 pagesContinuous Random Variableranjitbiswal547No ratings yet
- Types of Random VariablesDocument4 pagesTypes of Random VariablesHazell DNo ratings yet
- Parameter EstimationDocument34 pagesParameter EstimationJose Leonardo Simancas GarciaNo ratings yet
- c3 DistDocument21 pagesc3 DistRiajiminNo ratings yet
- Probability Formula SheetDocument11 pagesProbability Formula SheetJake RoosenbloomNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - NotesDocument3 pagesWeek 3 - NotesnaghulNo ratings yet
- Continuous Distributions: Section 2Document27 pagesContinuous Distributions: Section 2eng ineera100% (1)
- Probability: Background Material: 1 Basic DefinitionsDocument4 pagesProbability: Background Material: 1 Basic DefinitionsXZxzASNo ratings yet
- Limits Theorem: Markov's InequalityDocument4 pagesLimits Theorem: Markov's InequalityDare DevilNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution Normal Probability Distribution: Mean Continuous Random Variable (X)Document5 pagesNormal Distribution Normal Probability Distribution: Mean Continuous Random Variable (X)Marvin ArceNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 FormulasDocument3 pagesExam 2 Formulasvrinda dwivediNo ratings yet
- Probability Bounds: Simple Bounds On ExpectationDocument3 pagesProbability Bounds: Simple Bounds On ExpectationMohammad AslamNo ratings yet
- (Maths) - Normal DistributionDocument4 pages(Maths) - Normal Distributionanonymous accountNo ratings yet
- Normal Probaility DistributionDocument13 pagesNormal Probaility DistributionAbdul TukurNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 HHJJDocument6 pagesLecture 11 HHJJHarshita ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Distributions 2Document3 pagesTheoretical Distributions 2bnanduriNo ratings yet
- Chap4 ElsyDocument60 pagesChap4 ElsyKamil IbraNo ratings yet
- Distribuciones de ProbabilidadesDocument10 pagesDistribuciones de ProbabilidadesPatricio Antonio VegaNo ratings yet
- Probability DistributionDocument21 pagesProbability Distributiontaysirbest0% (1)
- Probability and Statistics: PopulationDocument14 pagesProbability and Statistics: PopulationAjaya Kumar Patel100% (1)
- MachineLearningInFinance 2023 Topic2Document73 pagesMachineLearningInFinance 2023 Topic2Terry JonesNo ratings yet
- DistributionsDocument1 pageDistributionsApoorva ReddyNo ratings yet
- Multivariate AnalysisDocument25 pagesMultivariate AnalysisPaul EthamNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- 2nd TheoryDocument1 page2nd TheoryChandler ManlongatNo ratings yet
- 1st TheoriesDocument1 page1st TheoriesChandler ManlongatNo ratings yet
- Charisse M. Manlongat: Determination. ConfidenceDocument1 pageCharisse M. Manlongat: Determination. ConfidenceChandler ManlongatNo ratings yet
- English For Academic and Professional PurposesDocument2 pagesEnglish For Academic and Professional PurposesChandler ManlongatNo ratings yet
- 1st TheoryDocument2 pages1st TheoryChandler ManlongatNo ratings yet
- 1st TheoriesDocument1 page1st TheoriesChandler ManlongatNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry (Reviewer) : Charisse Manlongat STEM301 SY. 2021-2022Document5 pagesGeneral Chemistry (Reviewer) : Charisse Manlongat STEM301 SY. 2021-2022Chandler ManlongatNo ratings yet
- 1st TheoryDocument2 pages1st TheoryChandler ManlongatNo ratings yet
- 2nd TheoryDocument1 page2nd TheoryChandler ManlongatNo ratings yet
- Scope: State and Path Functions RevisitedDocument4 pagesScope: State and Path Functions RevisitedChandler ManlongatNo ratings yet
- Continuous Random Variables and Probability DistributionsDocument45 pagesContinuous Random Variables and Probability DistributionsChandler ManlongatNo ratings yet
- FFF PDFDocument19 pagesFFF PDFshin ismaelNo ratings yet
- Uts TwinsDocument5 pagesUts TwinsChandler ManlongatNo ratings yet