Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Design of Microstrip Patch Antenna For 5g Applications: T.Kiran, N.Mounisha, CH - Mythily, D.Akhil, T.V.B.Phani Kumar
Uploaded by
Karima MazenOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Design of Microstrip Patch Antenna For 5g Applications: T.Kiran, N.Mounisha, CH - Mythily, D.Akhil, T.V.B.Phani Kumar
Uploaded by
Karima MazenCopyright:
Available Formats
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE)
e-ISSN: 2278-2834,p- ISSN: 2278-8735.Volume 13, Issue 1, Ver. I (Jan.- Feb. 2018), PP 14-17
www.iosrjournals.org
Design of Microstrip Patch Antenna for 5g Applications
T.Kiran1, N.Mounisha2, Ch.Mythily2, D.Akhil2, T.V.B.Phani Kumar3
(B.Tech , ECE Department, KoneruLakshmaiah Education Foundation , Vaddeswaram(522502),India)1,2
(Associate Professor,ECE Department ,KoneruLakshmaiah Education Foundation
,Vaddeswaram(522502),India)3
Corresponding Author: T.Kiran
Abstract: This paper is embedded with microstrip patch antenna that is constructed for future 5G wireless
communications. The antenna has a compressed structure of 11mm x 8 mm x 0.5mm, including the ground
plane. This antenna is designed using Rogers RT/duroid 5880 substrate used as dielectric material with a
miniaturized size of 4.4mm x 3.3mm. Its dielectric constant is 2.2 and has thickness of 0.5 mm. This microstrip
patch antenna resonates at frequencies of 28 GHz and 50 GHz. The antenna is simulated by using high
frequency structure simulator. The antenna provides a gain of 2.6dB. The structure of antenna and various
specifications such as return loss, vswr, gain plot and radiation pattern are discussed.
Keywords:Feed, HFSS, Microstrip Patch, Slot, 5G.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Date of Submission: 11-01-2018 Date of acceptance: 25-01-2018
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
I. Introduction
Present wireless communication technology is expanding rapidly due to the increase in the numbers of
users in terms of internet usage. We have come across 1G, 2G, 3G and recently 4G LTE technologies. One of
the provoking factors that affect the today’s wireless communication is lack of feasible frequency resources. So
to solve this problem, research has been started in 5G wireless communication at millimeter frequency band,
which ranges between 20 GHz to 300 GHz. Mostly the frequency range used for 5G research are in range of 24
GHz to 60 GHz [1]. Numerous fields have adopted the 5G technology with Internet of things (IOT). One of the
goals of 5G technology is to connect millions of devices together. This future 5G technology can be used in
smart cities, smart transportation and robotics.
The agile decrease in size of mobile devices prone to develop miniature antennas that could fit in those
devices without affecting the function [2]. This caused to the raise of microstrip patch antennas in 20 th century.
Microstrip patch antenna consists of a thin metal foil mounted on a substrate, beneath the substrate there is a
presence of ground[3]. This microstrip patch antenna can be integrated very easily on the surface of PCB, which
can be used in mobile devices as well. Mostly these antennas are used in microwave and millimeter frequency
bands.
II. Design Equations For Patch Antennas
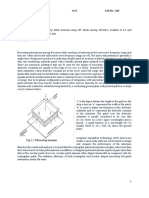
The blue print of microstrip patch antenna that is developed at 28 GHz and 50 GHz shown in figure 1.
This uses an inset line feeding technique. The measurements of patch are 4.4 mm x 3.3 mm. The thickness of
substrate is 0.5 mm with a rectangular slot cut on it. Distinct parameters are considered for developing the
antenna such as dielectric constant, thickness of substrate (ts = 0.5 mm) and resonant frequency (r f = 28.3 GHz).
The complete dimensions are shown in table below. The impedance of feed is 50 ohms. In HFSS the lumped
port is used to excitethe antenna. Since the antenna is of very small size to match the impedance of patch and
feed line, inset type feeding is chosen for maximum transfer of power.
The analysis of microstrip antenna is done using cavity and transmission line model[4]. The design
methodology and equations are portrayed under:
𝐶
𝑚= ...(1)
(𝑒 𝑟 +1)
2𝑟 𝑓
2
Where M is the width of patch, C is speed of light that is 3 x 10 8, rfis the resonant frequency that is 28 GHz for
future 5G applications and er is dielectric constant that is 2.2
−1
(𝑒 +1) (𝑒 −1) 𝑘 2
𝑒𝑒𝑓𝑓 = 𝑟 + 𝑟 1 + 12 …(2)
2 2 𝑚
Here k is height of substrate that is 0.5 mm.
𝐶
𝑛𝑒𝑓𝑓 = … (3)
2𝑟 𝑓 𝑒 𝑒𝑓𝑓
DOI: 10.9790/2834-1301011417 www.iosrjournals.org 14 | Page
Design Of Microstrip Patch Antenna For 5g Applications
Where n is the length of patch
𝑚
(𝑒 𝑒𝑓𝑓 +0.3)( +0.264 )
𝛥𝑛 = 0.412𝑘 𝑘
𝑚 … (4)
(𝑒 𝑒𝑓𝑓 −0.258 )( +0.8)
𝑘
𝑛 = 𝑛𝑒𝑓𝑓 − 2𝛥𝑛 … (5)
Fig-1. Designed Microstrip Patch Antenna
The size of Substrate is 11 mm x8 mm which is made up of Rogers RT 5880 with a thickness of 0.5
mm. The length and width of patch are 4.4 mm, 3.3 mm respectively. The depth of inset feed is 0.94 mm and
width is 0.445 mm. The length and width of slot are 0.385 mm, 4.24 mm respectively. The width of microstrip
line is 0.77 mm.
The entire blue print is built using HFSS [5], the substrate is made like a box as per dimensions and
perfect E1 boundary is assigned. Now Patch is made on the surface of substrate as per dimensions. An inset slot
is made on the both sides of feed to maintain impedance matching. The patch and feed are united and boundary
perfect E2 is assigned. Now ground plane is carved at bottom of substrate that is assigned with perfect E3
boundary. Now lumped feed is given to microstrip line with impedance of 50 ohm. The radiation box is drawn
with the antenna inside the radiation box which is made of vacuum.
III. Figures And Tables
The parameters used in designing the microstrip patch antenna are shown in the table-1
TABLE-1. Rectangular Patch Antenna
S.No Parameter Dimension (mm)
1 ns 11
2 ms 8
3 np 4.4
4 mp 3.3
5 nf 3.3
6 mf 0.77
7 mg 11
8 ng 8
9 ngs 4.24
10 mgs 0.385
11 nis 0.94
12 mis 0.445
13 K 0.5
Table-2.Output Parameters
Parameter Patch Antenna
Resonant Frequency 28.3 GHz
VSWR 1.58
Gain 2.6 dB
DOI: 10.9790/2834-1301011417 www.iosrjournals.org 15 | Page
Design Of Microstrip Patch Antenna For 5g Applications
IV. Simulation Results
Return Loss Plot
The S11 parameters are considered as antenna return loss parameters. Considering -10 dB to be the base value,
the return loss obtained at 28 GHz is 21 dB and return loss obtained at 50 GHz is 31 dB respectively. Fig shows
the plot of return loss.
Fig-2. S-Parameters
VSWR Plot
The Voltage Standing Wave Ration (VSWR) is shown In Fig . The ideal value of VSWR is 1 dB and practically
it should not be more than 2.5 dB. This antenna has VSWR of 1.58 dB at 1.58 GHz.
Fig-3. VSWR
Gain Plot
The 3D plot shows the gain of antenna. The antenna has a gain of 2.6 dB. Fig shows the gain of patch.
DOI: 10.9790/2834-1301011417 www.iosrjournals.org 16 | Page
Design Of Microstrip Patch Antenna For 5g Applications
Fig-4.Gain
Radiation Pattern
Fig-5. Radiation Pattern
V. Conclusion
In this paper the microstrip patch antenna is designed for future 5G communications. The antenna
resonates at frequencies of 28.3 GHz and 50.3 GHz with a return loss of 21 dB and 31 dB respectively. The
antenna is best suitable for devices that have a space constraint and can be easily integrated. The Structure of
antenna is compressed to 11 mm x 8 mm x 0.5 mm.
References
[1]. Straightpath Communication Inc. “A straight Path Towards 5G(white paper)” September 16, 2015.
[2]. S. Chen and J. Zhao, "The requirements, challenges, and technologies for 5G of terrestrial mobile
telecommunication," in IEEE Communications Magazine, vol. 52, no. 5, pp. 36-43, May 2014.
[3]. Lel, Kai Forg,LukKwai-Mann: Microstrip patch Antenna, (World scientific, ISBN-184816453X,PP- 8-12)
[4]. C.A.Balanis,Antenna Theory: Analysis and Design,(3rd edition Wiley, New York ,2005).
[5]. Ansoft HFSS. Ver 12 Ansys Corporation. Available At WWW.ansoft.com.
T.Kiran "Design of Micro strip Patch Antenna for 5g Applications." IOSR Journal of
Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) 13.1 (2018): 14-17.
DOI: 10.9790/2834-1301011417 www.iosrjournals.org 17 | Page
You might also like
- Radio Frequency Identification and Sensors: From RFID to Chipless RFIDFrom EverandRadio Frequency Identification and Sensors: From RFID to Chipless RFIDNo ratings yet
- Experiment No:4 Aim - : Date: 4/1/19 Ycce Roll No: 260Document6 pagesExperiment No:4 Aim - : Date: 4/1/19 Ycce Roll No: 260Sandeep MehtreNo ratings yet
- 83 Design and OptimizationDocument8 pages83 Design and OptimizationKenza KnouzNo ratings yet
- Design Note Dn023: 868 MHZ, 915 MHZ and 955 MHZ Inverted F AntennaDocument14 pagesDesign Note Dn023: 868 MHZ, 915 MHZ and 955 MHZ Inverted F Antennacayo_sincheNo ratings yet
- Design of Slotted Waveguide Antenna for Radar at X-BandDocument3 pagesDesign of Slotted Waveguide Antenna for Radar at X-BandSyed Nazim shahNo ratings yet
- Meta Material Based MIMO Antenna With Frequency Selective Surface For Gain EnhancementDocument9 pagesMeta Material Based MIMO Antenna With Frequency Selective Surface For Gain EnhancementSoufian LakritNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Rectangular Microstrip Patch AntennaDocument6 pagesSimulation of Rectangular Microstrip Patch AntennaNeeraj K PushkaranNo ratings yet
- Design of Inset Feed Microstrip Patch Antenna For Bluetooth ApplicationDocument3 pagesDesign of Inset Feed Microstrip Patch Antenna For Bluetooth ApplicationAnonymous kw8Yrp0R5rNo ratings yet
- Ijert: Designing Superdirective Patch Antenna Array Using MetamaterialDocument4 pagesIjert: Designing Superdirective Patch Antenna Array Using MetamaterialMuhtar IzuNo ratings yet
- Ijece - Design and Performance Analysis of Various Parameters of Single and Multi Layer of MspasDocument6 pagesIjece - Design and Performance Analysis of Various Parameters of Single and Multi Layer of Mspasiaset123No ratings yet
- Swra 227 ADocument17 pagesSwra 227 AbaruaeeeNo ratings yet
- a045104-1095Document6 pagesa045104-1095Par VeenNo ratings yet
- Design of Transparent Antenna For 5G WirDocument7 pagesDesign of Transparent Antenna For 5G WirThiripurasundari DNo ratings yet
- Designing A Tri-Band Microstrip Antenna For Targetting 5g Broadband CommunicationsDocument5 pagesDesigning A Tri-Band Microstrip Antenna For Targetting 5g Broadband CommunicationsKarima MazenNo ratings yet
- IJRPR15531Document5 pagesIJRPR15531ELECTRO MECHNo ratings yet
- Baviskar2016 PDFDocument2 pagesBaviskar2016 PDFkhyatichavdaNo ratings yet
- LAB 2 Parametric Optimization of Microstrip Patch Antenna DesignDocument34 pagesLAB 2 Parametric Optimization of Microstrip Patch Antenna DesignAzimah Zainal OfficiqlNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Ms Patch Antenna Aea04bbaDocument3 pagesPerformance Analysis of Ms Patch Antenna Aea04bbaisse mohamoudNo ratings yet
- Write Up1Document10 pagesWrite Up1Ishita AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Truncated Microstrip Square Patch Array Antenna 2 X 2 Elements With Circular Polarization For S-Band Microwave FrequencyDocument6 pagesTruncated Microstrip Square Patch Array Antenna 2 X 2 Elements With Circular Polarization For S-Band Microwave FrequencyAshim ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Improvement of Efficiency Parameter of A Microstrip Patch Antenna Operating at 2.4 GHZ For WlanDocument6 pagesImprovement of Efficiency Parameter of A Microstrip Patch Antenna Operating at 2.4 GHZ For Wlanavneet sandhuuuNo ratings yet
- Dual Antenna For WLAN Based On An Array Coupled by MicrostripsDocument3 pagesDual Antenna For WLAN Based On An Array Coupled by MicrostripsCristian Calle GarciaNo ratings yet
- Peningkatan Unjuk Kerja Antena Yagi Mikrostrip Dengan Teknik Defected Ground Structure (DGS) Dumbbell Untuk Aplikasi Indoor Wireless Lan 2,4 GHZDocument5 pagesPeningkatan Unjuk Kerja Antena Yagi Mikrostrip Dengan Teknik Defected Ground Structure (DGS) Dumbbell Untuk Aplikasi Indoor Wireless Lan 2,4 GHZJasmine WinataNo ratings yet
- Jjap Harun 2004Document5 pagesJjap Harun 2004ABM Harun-ur RashidNo ratings yet
- Design and Simulation of Multi Band Microstrip Antenna Array For Satellite ApplicationsDocument4 pagesDesign and Simulation of Multi Band Microstrip Antenna Array For Satellite ApplicationsAnmar SamiNo ratings yet
- Corporatefed SpringerDocument8 pagesCorporatefed Springer109Sangeeta SinghNo ratings yet
- Design of Microstrip Antenna For C-Band FrequencyDocument9 pagesDesign of Microstrip Antenna For C-Band FrequencyCampaigns Of HistoryNo ratings yet
- Antenna Design and Implementation Patch Diamond ArDocument7 pagesAntenna Design and Implementation Patch Diamond ArSid Ahmed MadjidNo ratings yet
- Mircostrip Patch Antenna With E Shaped Structure For S-Band ApplicationsDocument5 pagesMircostrip Patch Antenna With E Shaped Structure For S-Band ApplicationsijsretNo ratings yet
- 5G Tecnica BOMDocument5 pages5G Tecnica BOMAml LimaNo ratings yet
- Design of Microstrip Patch Antenna With Specific Structure IDocument13 pagesDesign of Microstrip Patch Antenna With Specific Structure Ihim4alllNo ratings yet
- Good ShapeDocument5 pagesGood Shapehusam hamidNo ratings yet
- So So Is: E GHZ GHZDocument2 pagesSo So Is: E GHZ GHZThiripurasundari DNo ratings yet
- ) Rectangular Patch Antenna Array For Radar Application - JournalDocument6 pages) Rectangular Patch Antenna Array For Radar Application - Journalpradeep BNo ratings yet
- Size Reduction of Rectangular Microstrip Antenna Using SlotsDocument4 pagesSize Reduction of Rectangular Microstrip Antenna Using SlotsanshulNo ratings yet
- 4db4 PDFDocument4 pages4db4 PDFNaimul HasanNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Microstrip Patch Antenna at 2.4 GHZ For WLAN Application Using HFSSDocument7 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Microstrip Patch Antenna at 2.4 GHZ For WLAN Application Using HFSSmaleeha khanNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation On The Design and Optimization of A W-Lan Band Rectangular Micro Strip Patch Antenna With Transmision Line FeedingDocument4 pagesExperimental Investigation On The Design and Optimization of A W-Lan Band Rectangular Micro Strip Patch Antenna With Transmision Line Feedingmagy1989No ratings yet
- V5i3 Ijertv5is030037Document5 pagesV5i3 Ijertv5is030037Ramya RNo ratings yet
- Effects of Superstrate On Electromagnetically and PDFDocument11 pagesEffects of Superstrate On Electromagnetically and PDFAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Microstrip Patch Antenna Array at 3.8 GHZ For WiMax and UAV ApplicationssDocument4 pagesMicrostrip Patch Antenna Array at 3.8 GHZ For WiMax and UAV ApplicationssHassan SajjadNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Electronics and Communications (AEÜ)Document9 pagesInternational Journal of Electronics and Communications (AEÜ)Karima MazenNo ratings yet
- Design Engineering: Design A Rectangular Patch Antenna Using PythonDocument10 pagesDesign Engineering: Design A Rectangular Patch Antenna Using Pythongest100% (1)
- High Speed Layout Design GuidelinesDocument26 pagesHigh Speed Layout Design Guidelineschetanswamy4649100% (1)
- Optimization of Micro Strip Patch Antenna With Zig-Zag Slot in Broadband CommunicationDocument4 pagesOptimization of Micro Strip Patch Antenna With Zig-Zag Slot in Broadband Communications nandiNo ratings yet
- Design of A Corner Truncated Patch Antenna Array With Four Elements For Wireless ApplicationsDocument4 pagesDesign of A Corner Truncated Patch Antenna Array With Four Elements For Wireless ApplicationsimaculateNo ratings yet
- Simulation Study MIMO Beamforming MISO SIMODocument7 pagesSimulation Study MIMO Beamforming MISO SIMOgroupe1 stNo ratings yet
- Design, Simulation and Fabrication of Patch Array Antenna For Indian Regional Navigation Satellite SystemDocument9 pagesDesign, Simulation and Fabrication of Patch Array Antenna For Indian Regional Navigation Satellite SystemYossef ARNo ratings yet
- Design of 2.4Ghz Patch Antennae For Wlan ApplicationsDocument13 pagesDesign of 2.4Ghz Patch Antennae For Wlan ApplicationsAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Microstrip Patch Antenna at 2.4 GHZ For WLAN Application Using HFSSDocument7 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Microstrip Patch Antenna at 2.4 GHZ For WLAN Application Using HFSSMati ur rahman khanNo ratings yet
- Swra 227 DDocument16 pagesSwra 227 DBhaskara Naik SNo ratings yet
- A Design Rule For Inset-Fed Rectangular Microstrip Patch Antenna PDFDocument10 pagesA Design Rule For Inset-Fed Rectangular Microstrip Patch Antenna PDFVijaya ShreeNo ratings yet
- Miniature Helical PCB Antenna For 868 MHZ or 915-920 MHZDocument25 pagesMiniature Helical PCB Antenna For 868 MHZ or 915-920 MHZA.G. MonteroNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Microstrip Patch Array Antenna at 28 GHZDocument6 pagesCharacterization of Microstrip Patch Array Antenna at 28 GHZPhương Linh TrầnNo ratings yet
- Aperture Coupled Fed Micro-Strip Patch AntennaDocument5 pagesAperture Coupled Fed Micro-Strip Patch AntennaemremiranNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Low Pass Filter Using Microstrip LineDocument4 pagesDesign and Implementation of Low Pass Filter Using Microstrip LineEmad AlsurrajNo ratings yet
- Frequency Reconfigurable Triple Band-Notched Ultra-Wideband Antenna With Compact SizeDocument11 pagesFrequency Reconfigurable Triple Band-Notched Ultra-Wideband Antenna With Compact SizenikitaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Microstrip Patch Antenna and Observe Effect of Changing Parameter at 5.4GhzDocument6 pagesComparative Analysis of Microstrip Patch Antenna and Observe Effect of Changing Parameter at 5.4GhzLuqman HakimiNo ratings yet
- CantennaDocument14 pagesCantennaMalkuth_TachtonNo ratings yet
- Design and Performance Analysis of Microstrip Patch Antenna For C Band ApplicationsDocument5 pagesDesign and Performance Analysis of Microstrip Patch Antenna For C Band ApplicationsKarima MazenNo ratings yet
- Assembly Language Overview and ExampleDocument22 pagesAssembly Language Overview and Exampletesfu zewduNo ratings yet
- Lumped Equivalent Models of Narrowband Antennas and Isolation Enhancement in A Three Antennas SystemDocument8 pagesLumped Equivalent Models of Narrowband Antennas and Isolation Enhancement in A Three Antennas SystemPr eeTNo ratings yet
- Designing A Tri-Band Microstrip Antenna For Targetting 5g Broadband CommunicationsDocument5 pagesDesigning A Tri-Band Microstrip Antenna For Targetting 5g Broadband CommunicationsKarima MazenNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Microstrip Patch Antenna For 5G ApplicationsDocument4 pagesDesign and Implementation of Microstrip Patch Antenna For 5G ApplicationsKarima MazenNo ratings yet
- S-Parameter Simulation and OptimizationDocument40 pagesS-Parameter Simulation and OptimizationQuang-Trung LuuNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Electronics and Communications (AEÜ)Document9 pagesInternational Journal of Electronics and Communications (AEÜ)Karima MazenNo ratings yet
- Design of Slotted Microstrip Patch Antenna For 5G ApplicationDocument6 pagesDesign of Slotted Microstrip Patch Antenna For 5G ApplicationKarima MazenNo ratings yet
- Ali-Akram2020 Article Decision-MakingMethodBasedOnFu PDFDocument20 pagesAli-Akram2020 Article Decision-MakingMethodBasedOnFu PDFKarima MazenNo ratings yet
- Ali-Akram2020 Article Decision-MakingMethodBasedOnFu PDFDocument20 pagesAli-Akram2020 Article Decision-MakingMethodBasedOnFu PDFKarima MazenNo ratings yet
- Ali-Akram2020 Article Decision-MakingMethodBasedOnFu PDFDocument20 pagesAli-Akram2020 Article Decision-MakingMethodBasedOnFu PDFKarima MazenNo ratings yet
- SCCM PrerequisitesDocument6 pagesSCCM PrerequisitesPonalo GabathuseNo ratings yet
- Practical File Xii ItDocument4 pagesPractical File Xii ItDiya Biswas100% (1)
- Gateway CaseDocument10 pagesGateway CaseSomesh KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Research Topic/Title A. Description of The Project: 1. RationaleDocument5 pagesResearch Topic/Title A. Description of The Project: 1. Rationalemark belloNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Challenges - How To Deal With ItDocument54 pagesCyber Security Challenges - How To Deal With ItLawrence LauNo ratings yet
- Ukhra 50 Tr. Oil Leakage Work - 36Document1 pageUkhra 50 Tr. Oil Leakage Work - 36gaurav vermaNo ratings yet
- Fire Security ProductsDocument3 pagesFire Security ProductsvvvvmvaNo ratings yet
- Role of Computers in TransportDocument36 pagesRole of Computers in TransportPrateek Singla100% (2)
- Customizing HCM HeadersDocument7 pagesCustomizing HCM Headersvemulapalli1100% (1)
- Desktop Engineering 2010-03Document82 pagesDesktop Engineering 2010-03PerryShopsNo ratings yet
- Remote Monitoring & Control of RACON BeaconDocument2 pagesRemote Monitoring & Control of RACON Beacon송현호No ratings yet
- A Convergence of Key Trends: Kept Large Amounts of Information Information On TapeDocument14 pagesA Convergence of Key Trends: Kept Large Amounts of Information Information On TapePratiksha DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- JohndeereDocument53 pagesJohndeereapi-34687573513% (8)
- Origin ManualDocument20 pagesOrigin ManualANDRES GOMEZNo ratings yet
- Oracle - Prepaway.1z0 068.v2019!03!20.by - Max.96q 2Document65 pagesOracle - Prepaway.1z0 068.v2019!03!20.by - Max.96q 2sherif hassan younisNo ratings yet
- Over ModulationDocument5 pagesOver ModulationAbenk's BembenkNo ratings yet
- Top 5 Best Earbuds 2020Document10 pagesTop 5 Best Earbuds 2020farooq pervezNo ratings yet
- 5800 Instructions Pour Le Remplacement de L'element Chauffant Du Réservoir D'alimentationDocument12 pages5800 Instructions Pour Le Remplacement de L'element Chauffant Du Réservoir D'alimentationKirelbysNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineer Ibrahim El-DehiDocument5 pagesCivil Engineer Ibrahim El-DehiIbrahim EldiehyNo ratings yet
- Fruit-Classification ReportDocument17 pagesFruit-Classification ReportAditya B NNo ratings yet
- Trace GC Ultra Preventive Maintenance Schedule May 2010Document98 pagesTrace GC Ultra Preventive Maintenance Schedule May 2010DanielNo ratings yet
- IMAGEnet I-Base en New CIDocument6 pagesIMAGEnet I-Base en New CISamuel DJOSSOUNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5: IPC - Semaphore and Shared Memory: Message QueuesDocument6 pagesLecture 5: IPC - Semaphore and Shared Memory: Message Queuessamir2013No ratings yet
- TLE-ICT-CSS 10-Q1 - ICCS Week 1Document17 pagesTLE-ICT-CSS 10-Q1 - ICCS Week 1jayson santosNo ratings yet
- Ingram Transit Center routes and scheduleDocument2 pagesIngram Transit Center routes and schedulemattNo ratings yet
- PDVSA N-263 Rev.0, Oct.01 Data Sheet For Electrical Requirements For Packaged EquipmentDocument1 pagePDVSA N-263 Rev.0, Oct.01 Data Sheet For Electrical Requirements For Packaged EquipmentJose Antonio Salazar HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Allegro Current Sensor Ltspice ModelsDocument11 pagesAllegro Current Sensor Ltspice ModelshajaNo ratings yet
- UTECH Maple Hospitalar CatalogoDocument24 pagesUTECH Maple Hospitalar CatalogoDavid Ferreira BarretoNo ratings yet
- Get Power Gp12-200 12v 200ahDocument2 pagesGet Power Gp12-200 12v 200ahDouglas SantanaNo ratings yet
- 19-0431 Rev 2 8/01Document12 pages19-0431 Rev 2 8/01mubs73No ratings yet
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeFrom EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsFrom EverandMicrosoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsNo ratings yet
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamFrom EverandAWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Study Guide: CLF-C01 ExamRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Computer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityFrom EverandComputer Systems and Networking Guide: A Complete Guide to the Basic Concepts in Computer Systems, Networking, IP Subnetting and Network SecurityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (543)
- ITIL 4: Digital and IT strategy: Reference and study guideFrom EverandITIL 4: Digital and IT strategy: Reference and study guideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Hacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsFrom EverandHacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Hacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.From EverandHacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- 2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersFrom Everand2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesFrom EverandThe Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Set Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNFrom EverandSet Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- PHP BLUEPRINT: An Essential Beginners Guide to Learn the Realms of PHP From A-ZFrom EverandPHP BLUEPRINT: An Essential Beginners Guide to Learn the Realms of PHP From A-ZNo ratings yet
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionFrom EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Designing and Building Security Operations CenterFrom EverandDesigning and Building Security Operations CenterRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)
- Practical Electronics for Inventors, Fourth EditionFrom EverandPractical Electronics for Inventors, Fourth EditionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)