Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antibiotics - Fosfomycin
Uploaded by
Ss0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Antibiotics - Fosfomycin.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesAntibiotics - Fosfomycin
Uploaded by
SsCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
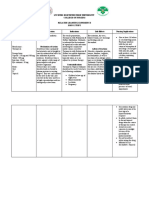
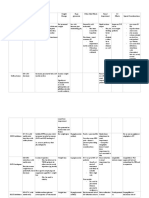
Fosfomycin
Mode of Action Bactericidal Inhibits first step of bacterial cell
wall synthesis
Indications Acute uncomplicated Enterobacteriaceae Second line (oral)
cystitis in females o Inc E coli
E faecalis
Bacterial infections Complicated UTI When other agents are either
due to susceptible Osteomyelitis unsuitable or ineffective (IV)
organisms
Contraindications Sachet contains 2.2g Avoid in
sucrose Hereditary fructose
intolerance
Glucose-galactose
malabsorption
Sucrose-isomaltase
insufficiency
Renal Is predominantly renally cleared Manufacturer states C/I in
CrCl<10mL/min
Pregnancy Single dose doesn’t increase risk Only use when other drugs are
of congenital malformations unsuitable
Breastfeeding Small amounts pass into breast No human data available
milk Single dose likely safe
May cause loose
bowels in baby
Adverse effects Common (>1%) Diarrhoea
Nausea
Infrequent (0.1-1%) Parasthesias Usually circum-oral
Rare ((<0.1%) Hypersensitivity
reactions
o Anaphylaxis
o Angioedema
o Rash
Taste disturbance
Dosage Oral 3g single dose Females >12yrs age
Counselling Mix sachet contents in water and drink immediately
Works best if taken before bed after emptying bladder
Is less effective for Avoid taking these on same day or within 2 days after taking
UTIs if taken at same fosfomycin
time as
Sodium bicarb
Ural
Citralite
Citravescent
Effective urinary concentrations achieved regardless of timing around food
NOTES Injection not available May be able to access through SAS
in Australia
Is not suitable for Oral administration is unlikely to achieve necessary systemic
pyelonephritis concentration
https://amhonline.amh.net.au.acs.hcn.com.au/chapters/anti-infectives/antibacterials/other-antibacterials/fosfomycin?
menu=home
You might also like
- Fosfomycin: Mode of Action IndicationsDocument2 pagesFosfomycin: Mode of Action IndicationsSsNo ratings yet
- Santiago, Gwyneth Julia B.-Bsn2-D-Drug StudyDocument2 pagesSantiago, Gwyneth Julia B.-Bsn2-D-Drug StudyGwyneth SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Terramycin - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTerramycin - Drug StudyBolasoc, HazelNo ratings yet
- Cancer Cell-Specific AgentsDocument5 pagesCancer Cell-Specific AgentsRomwella May AlgoNo ratings yet
- Bumetanide MIMSDocument2 pagesBumetanide MIMSIndri WahyuniNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyArianna Jasmine MabungaNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin (Amoxycillin) : PresentationDocument4 pagesAmoxicillin (Amoxycillin) : PresentationRavikiran SuryanarayanamurthyNo ratings yet
- Name: Sophia Angela Famor BSN12EDocument4 pagesName: Sophia Angela Famor BSN12EZumi IskakNo ratings yet
- Banned and Dangerous Substances Commonly Given To Horses Sent To SlaughterDocument29 pagesBanned and Dangerous Substances Commonly Given To Horses Sent To SlaughterDark DragonNo ratings yet
- Mebendazole Drug Study for Worm InfestationsDocument6 pagesMebendazole Drug Study for Worm InfestationsJeah Bearl AbellarNo ratings yet
- Ivermectin Tablet 12mg Ivermectin GKL2120943310A1 2021Document2 pagesIvermectin Tablet 12mg Ivermectin GKL2120943310A1 2021dwiky rama100% (1)
- Actions of Drugs during BreastfeedingDocument2 pagesActions of Drugs during BreastfeedingVenusNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyJessa BorreNo ratings yet
- AnticholinergicsDocument5 pagesAnticholinergicsWan TokNo ratings yet
- Community Pharmacy Counselling Checklist V3Document5 pagesCommunity Pharmacy Counselling Checklist V3apNo ratings yet
- Urinary Germicides PharmaDocument11 pagesUrinary Germicides PharmaMaria Pina Barbado PonceNo ratings yet
- ) Pharmacology Drug StudyDocument8 pages) Pharmacology Drug StudyFatima KateNo ratings yet
- Acne MedicationsDocument7 pagesAcne MedicationsSudesna Roy ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Drug Card Grid: Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion)Document2 pagesDrug Card Grid: Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion)Khaleel BalogunNo ratings yet
- Oral Antiprotozoal DrugsDocument6 pagesOral Antiprotozoal DrugsQusai BassamNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug Studycruz_johnraymond100% (1)
- DTR PediaDocument3 pagesDTR PediaMajojay AmadorNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapeutic RecordDocument3 pagesDrug Therapeutic RecordMajojay AmadorNo ratings yet
- Drug Record for Lasix and MetoprololDocument3 pagesDrug Record for Lasix and MetoprololMajojay AmadorNo ratings yet
- Short Product InfosDocument9 pagesShort Product Infosjulia_jayronwaldoNo ratings yet
- Vermox Tablet& Suspension Patient Information LeafletDocument1 pageVermox Tablet& Suspension Patient Information Leafletpharmacia1.comNo ratings yet
- Drug Use in Pregnancy and Breast FeedingDocument28 pagesDrug Use in Pregnancy and Breast FeedingStanley Tatenda MukonoNo ratings yet
- Atropine NaloxoneDocument3 pagesAtropine NaloxoneAaron ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mode of Action Indications/Contraindicati Ons Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations BeforeDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mode of Action Indications/Contraindicati Ons Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations BeforeMikko McDonie VeloriaNo ratings yet
- Transfer of Drugs Across The Placenta and Breast. Influence of Pregnancy On Drug Dose Adverse Effects of Drugs in PregnancyDocument23 pagesTransfer of Drugs Across The Placenta and Breast. Influence of Pregnancy On Drug Dose Adverse Effects of Drugs in PregnancyJes CmtNo ratings yet
- Enicillin-Like Antibiotics. Diarrhea, Nausea, Vomiting, HeadacheDocument5 pagesEnicillin-Like Antibiotics. Diarrhea, Nausea, Vomiting, HeadachePauline AñesNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for treating pediatric infectious diarrheaDocument10 pagesGuidelines for treating pediatric infectious diarrheaOasis LimitedNo ratings yet
- Drug CiproDocument1 pageDrug CiproSrkocherNo ratings yet
- DoxycyclineDocument1 pageDoxycyclineRimsha AzeemNo ratings yet
- H. Influenza: 75-100 Mg/kg/day PO Divided q8hr For 10 Days Not To Exceed 4,000 Mg/dayDocument4 pagesH. Influenza: 75-100 Mg/kg/day PO Divided q8hr For 10 Days Not To Exceed 4,000 Mg/dayAlcala, Mariaden A.No ratings yet
- Ds Ob 3Document4 pagesDs Ob 3katrinakylagNo ratings yet
- Sample - Drug Index DatabaseDocument12 pagesSample - Drug Index DatabaseEubert John VenturinaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Diethystilbestrol)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY (Diethystilbestrol)Avianna CalliopeNo ratings yet
- Antifungal AgentsDocument42 pagesAntifungal AgentsOluwatobi AyomideNo ratings yet
- Antiprotozoal AgentsDocument4 pagesAntiprotozoal AgentsReem NurNo ratings yet
- CefuroximeDocument2 pagesCefuroximeJon Corpuz AggasidNo ratings yet
- AmoxicillinDocument2 pagesAmoxicillindheng05No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyKhalil Jane VillarinoNo ratings yet
- Genitourinary SystemDocument7 pagesGenitourinary SystemJulianna Rheaven JoreNo ratings yet
- FluconazoleDocument3 pagesFluconazoleMary Kate ClarosNo ratings yet
- Snakebite Drug StudyDocument7 pagesSnakebite Drug StudyDevon RevillaNo ratings yet
- Gemina Files RleDocument9 pagesGemina Files RleJenelyn GeminaNo ratings yet
- Anthelmintics AgentsDocument3 pagesAnthelmintics AgentsSimran SidhuNo ratings yet
- Medications for PICU PatientsDocument2 pagesMedications for PICU PatientsSweety KurnNo ratings yet
- ncmh drug studyDocument5 pagesncmh drug studyHeartlee NapuranNo ratings yet
- Worm Infestation in ChildrenDocument4 pagesWorm Infestation in ChildrenOleOhhNo ratings yet
- College Nursing Alternative Learning Experience Oxytocin Methotrexate Side EffectsDocument4 pagesCollege Nursing Alternative Learning Experience Oxytocin Methotrexate Side EffectsKimberly Almacen RoblesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MisoprostolDocument2 pagesDrug Study Misoprostolrica sebabillones100% (1)
- Drug Study MisoprostolDocument2 pagesDrug Study Misoprostolrica sebabillonesNo ratings yet
- Adverse Drug Reactions: Dr. V. Jagadeesan, Former Deputy Director (Sr. Grade), National Institute of Nutrition, HyderabadDocument32 pagesAdverse Drug Reactions: Dr. V. Jagadeesan, Former Deputy Director (Sr. Grade), National Institute of Nutrition, Hyderabadapurupa1No ratings yet
- Cushing ReviewerDocument3 pagesCushing ReviewerLuiciaNo ratings yet
- PXprofile History Drugstudy PUDDocument8 pagesPXprofile History Drugstudy PUDPaola CruzNo ratings yet
- (Udah) AntiamubaDocument20 pages(Udah) AntiamubaMohammad Rizki PratamaNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument6 pagesPharmacologyZubair KhanNo ratings yet
- The Perfect Egg Allergy Diet Cookbook:The Complete Nutrition Guide For Treating And Managing Symptoms Of Egg Allergy With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesFrom EverandThe Perfect Egg Allergy Diet Cookbook:The Complete Nutrition Guide For Treating And Managing Symptoms Of Egg Allergy With Delectable And Nourishing RecipesNo ratings yet
- Resp - Part A - AnswersDocument1 pageResp - Part A - AnswersSsNo ratings yet
- Cytochrome P450 2D6 Known Drug Interaction Chart: Drugs Metabolized by CYP2D6 Enzyme Drug Inhibitors of CYP2D6 EnzymeDocument1 pageCytochrome P450 2D6 Known Drug Interaction Chart: Drugs Metabolized by CYP2D6 Enzyme Drug Inhibitors of CYP2D6 EnzymeSsNo ratings yet
- 100 Clinical Cases in Medicine - PasTest - Cardiac OnlyDocument30 pages100 Clinical Cases in Medicine - PasTest - Cardiac OnlySsNo ratings yet
- Resp - Part A - AnswersDocument1 pageResp - Part A - AnswersSsNo ratings yet
- Paeds - Part A - AnswersDocument3 pagesPaeds - Part A - AnswersSsNo ratings yet
- Resp - Part A - StemDocument1 pageResp - Part A - StemSsNo ratings yet
- Resp - Part A - StemDocument1 pageResp - Part A - StemSsNo ratings yet
- Paeds - Part A - StemDocument2 pagesPaeds - Part A - StemSsNo ratings yet
- Paeds MCQs Part 1Document34 pagesPaeds MCQs Part 1SsNo ratings yet
- Table Diabetic Drugs - TemplateDocument5 pagesTable Diabetic Drugs - TemplateSsNo ratings yet
- Bonus Paeds MCQs With ExplanationsDocument17 pagesBonus Paeds MCQs With ExplanationsSsNo ratings yet
- Case 1Document2 pagesCase 1SsNo ratings yet
- Type I (Polymicrobial - Anaerobes and Aerobes) Usually Older Adults And/orDocument6 pagesType I (Polymicrobial - Anaerobes and Aerobes) Usually Older Adults And/orSsNo ratings yet
- Type I (Polymicrobial - Anaerobes and Aerobes) Usually Older Adults And/orDocument6 pagesType I (Polymicrobial - Anaerobes and Aerobes) Usually Older Adults And/orSsNo ratings yet
- KARNATAKA MANUFACTURING UNITSDocument3 pagesKARNATAKA MANUFACTURING UNITSUsman DarNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyRuby Mae AguavivaNo ratings yet
- Medicamente Toxice Comercializate in RomaniaDocument18 pagesMedicamente Toxice Comercializate in Romaniamaryanne_bb895No ratings yet
- Modul-2 Pengobatan TBDocument180 pagesModul-2 Pengobatan TBJane BiringanNo ratings yet
- USFDA OTC Monograph - M019-Antiperspirant Drug Products For OTC Human Use 11.23.2021Document4 pagesUSFDA OTC Monograph - M019-Antiperspirant Drug Products For OTC Human Use 11.23.2021CY LINNo ratings yet
- Esketamine Nasal Sray 84 MGDocument7 pagesEsketamine Nasal Sray 84 MGMd. Abdur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Formulation, Development and Optimization of Propranolol FDDS Sustained Release As An Anti-HypertensiveDocument9 pagesFormulation, Development and Optimization of Propranolol FDDS Sustained Release As An Anti-HypertensiveZainab JavedNo ratings yet
- Herbal Medicine: Gentle Yet Powerful RemediesDocument12 pagesHerbal Medicine: Gentle Yet Powerful RemediesLarissa MarinaNo ratings yet
- SESSION 6 - QuinolonesDocument15 pagesSESSION 6 - QuinolonesBruno NjawikeNo ratings yet
- #Ftssolid 3 Bab Iv Contoh TabletDocument30 pages#Ftssolid 3 Bab Iv Contoh TabletdickyNo ratings yet
- Pricelist 15-03-2009Document85 pagesPricelist 15-03-2009Maria BourceanuNo ratings yet
- Re-Purposing Drugs To Combat COVID-19: Niel Karrow, Department of Animal Biosciences, University of GuelphDocument12 pagesRe-Purposing Drugs To Combat COVID-19: Niel Karrow, Department of Animal Biosciences, University of GuelphKraft DinnerNo ratings yet
- ParkinsonDocument30 pagesParkinsonRebecca HarsNo ratings yet
- ROFLUMILASTDocument13 pagesROFLUMILASTSanjay TalrejaNo ratings yet
- Project Dawn Brochure0515Document2 pagesProject Dawn Brochure0515api-265745737No ratings yet
- PT. Bina Mitra Jaya BersamaDocument25 pagesPT. Bina Mitra Jaya BersamaHADI PRAYITNONo ratings yet
- 1 AntihistamineDocument15 pages1 Antihistaminepranay shettigarNo ratings yet
- Opioids Medicinal ChemistryDocument38 pagesOpioids Medicinal ChemistryDaniel WangNo ratings yet
- OndansetronDocument11 pagesOndansetronIlyes FerenczNo ratings yet
- CYP450 Chart 5.2016Document8 pagesCYP450 Chart 5.2016bl9nkverseNo ratings yet
- How To Improve Clinical Pharmacy Practice Using Key Performance IndicatorsDocument5 pagesHow To Improve Clinical Pharmacy Practice Using Key Performance IndicatorsTaufik Qur RaufNo ratings yet
- Drug InteractionsDocument10 pagesDrug Interactionscamelle sisonNo ratings yet
- epidyolex-SmPC Product-Information - enDocument38 pagesepidyolex-SmPC Product-Information - enpharmashri5399No ratings yet
- KIMED - HSA ANALGESIKvDocument21 pagesKIMED - HSA ANALGESIKvKuni RofiatyNo ratings yet
- Anfrah 31oktDocument81 pagesAnfrah 31oktFarmasi RSI AminahNo ratings yet
- Infrastructure Requirement For B.Pharma & D. PharmaDocument2 pagesInfrastructure Requirement For B.Pharma & D. Pharmaanon_968573480No ratings yet
- Drug-Receptor Interactions and PharmacodynamicsDocument4 pagesDrug-Receptor Interactions and Pharmacodynamicshussam mazinNo ratings yet
- EBM Tear Off - EB C4Document2 pagesEBM Tear Off - EB C4faith2rescoberNo ratings yet
- Bioequivalence of Two Pregabalin 300 MG Capsules (Neurexal and Lyrica) in Healthy Human VolunteersDocument5 pagesBioequivalence of Two Pregabalin 300 MG Capsules (Neurexal and Lyrica) in Healthy Human VolunteerscaturNo ratings yet
- MicrodosingDocument9 pagesMicrodosingblondaylibra100% (2)