Professional Documents
Culture Documents
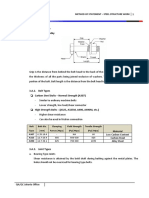
A) Under Nut Fitting B) Under Bolt Head Fitting Key Key: BS EN 14399-9:2009
Uploaded by
JafarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A) Under Nut Fitting B) Under Bolt Head Fitting Key Key: BS EN 14399-9:2009
Uploaded by
JafarCopyright:
Available Formats
BS EN 14399-9:2009
EN 14399-9:2009 (E)
a) under nut fitting b) under bolt head fitting
Key Key
--`,,,,`,,``,,`,`,`,```,`,,,,``,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---
1 Direct tension indicator 1 Direct tension indicator
2 Nut face washer 2 Bolt face washer
3 Gap 3 Gap
4 Washer according to EN 14399-6 4 Washer according to EN 14399-5 or -6 (not
required for property class 8.8)
Figure 8 —Tightening of the assembly by rotation of the bolt head
5.2 Functional characteristics of direct tension indicators in the assembly
A specified feeler gauge, see Table 9, shall be used to determine that the required bolt preload has been
achieved by the assembly.
Table 9 — Thickness of the feeler gauge
Dimensions in millimetres
Direct tension indicator positions Designation H8 and H10
Thickness of feeler gauge
Under bolt head, when nut is rotated
(Figure 7a)
0,40
Under nut, when bolt is rotated
(Figure 8a)
Under nut, when nut is rotated
(Figure 7b)
0,25
Under bolt head, when bolt is rotated
(Figure 8b)
NOTE Tests have shown the need for a smaller gap when the direct tension indicator is used under the rotated
component. Direct tension indicators fitted as specified will result in the same loads being attained when the bolts are
tightened to the specified gaps.
The average specified indicator gap shall be determined using the following measurement procedure; the
feeler gauge shall be used as a "no go" inspection tool. The feeler gauge shall be pointed at the centre of the
bolt (see Figure 9) and shall refuse to enter the number of refusal spaces specified in Table 10.
Copyright British Standards Institution
19
Provided by IHS under license with BSI - Uncontrolled Copy Licensee=Istanbul Teknik Universtesi/5956919001
No reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS Not for Resale, 12/10/2010 01:28:26 MST
BS EN 14399-9:2009
EN 14399-9:2009 (E)
Table 10 — Feeler gauge requirements
Number of indicator Minimum number of feeler
protrusions gauge refusals
4 3
5 3
6 4
7 4
8 5
9 5
Figure 9 — Checking the indicator gap (example with six protrusions)
--`,,,,`,,``,,`,`,`,```,`,,,,``,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---
5.3 Functional characteristics of the bolt/nut/washer(s)/direct tension indicator assembly
5.3.1 General
The functional characteristics of the bolt/nut/washer(s)/direct tension indicator assembly shall be achieved
when tested in accordance with the following.
The principle of the test is to tighten the bolt/nut/washer(s)/direct tension indicator assembly and to measure,
during tightening, the following parameters:
the relative rotation between the nut and the bolt,
the bolt force.
This test procedure is based on the requirements according to EN 14399-2 and incorporates requirements
applicable to assemblies which include direct tension indicators; where necessary special testing conditions
and procedures according to Annex A may be applied.
5.3.2 Test procedure
5.3.2.1 Suitability test for preloading with direct tension indicator in an assembly
Direct tension indicators conforming to EN 14339-9 are suitable according to EN 14399-2 provided they are
used in an assembly that includes fasteners in accordance with EN 14399-3, -4, -7 or -8 that have been tested
in accordance with EN 14399-2 to determine the relative rotation between the bolt and nut. The k-class values
shall not be determined for K1 or K2 and shall be declared K0.
Initial type tests shall be carried out separately for the direct tension indicator under the bolt head and under
the nut. The initial type test shall be used to demonstrate that ∆θ2 measured with assemblies incorporating a
direct tension indicator exceeds ∆θ2, min, by at least 10 %.
20
Copyright British Standards Institution
Provided by IHS under license with BSI - Uncontrolled Copy Licensee=Istanbul Teknik Universtesi/5956919001
No reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS Not for Resale, 12/10/2010 01:28:26 MST
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Voe219920201 SD110 V1.4Document175 pagesVoe219920201 SD110 V1.4Dhru Ti100% (5)
- 129 1968 Chevrolet Camaro Factory Assembly Manual PDFDocument455 pages129 1968 Chevrolet Camaro Factory Assembly Manual PDFNatalia GarridoNo ratings yet
- Welding Symbol Guide (ISO 2553Document32 pagesWelding Symbol Guide (ISO 2553Marcelo CunhaNo ratings yet
- AR4 Robot ManulDocument289 pagesAR4 Robot ManulMohammad NasutionNo ratings yet
- AstmDocument6 pagesAstmLuis SuazoNo ratings yet
- Metric Bolt Torque Table from Oread Verbindungstechnik GmbHDocument1 pageMetric Bolt Torque Table from Oread Verbindungstechnik GmbHJafarNo ratings yet
- Oread 8.8 - 10.9 Metric Bolt Torque Table 2016-SignedDocument1 pageOread 8.8 - 10.9 Metric Bolt Torque Table 2016-SignedJafarNo ratings yet
- N 1 - Use The Information Provided in 8.1.3 To Obtain The Approximate Coating Thickness From The Coating Weight (Mass)Document1 pageN 1 - Use The Information Provided in 8.1.3 To Obtain The Approximate Coating Thickness From The Coating Weight (Mass)JafarNo ratings yet
- A) Under Nut Fitting B) Under Bolt Head Fitting Key Key: BS EN 14399-9:2009Document1 pageA) Under Nut Fitting B) Under Bolt Head Fitting Key Key: BS EN 14399-9:2009JafarNo ratings yet
- EN 14399-9 - Feeler Gauge RequirementsDocument1 pageEN 14399-9 - Feeler Gauge RequirementsJafarNo ratings yet
- TechnicalDocument2 pagesTechnicalJafarNo ratings yet
- Consumable MTCDocument1 pageConsumable MTCJafarNo ratings yet
- Pyrolite 15 PDS PDFDocument5 pagesPyrolite 15 PDS PDFbhavesh solankiNo ratings yet
- CH3 1 Welding Joint SymbolsDocument32 pagesCH3 1 Welding Joint SymbolsJafarNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel Sub-Grades JR J0 J2 OverviewDocument1 pageStructural Steel Sub-Grades JR J0 J2 OverviewJafarNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel Sub-Grades JR, J0 and J2 Does It Matter PDFDocument1 pageStructural Steel Sub-Grades JR, J0 and J2 Does It Matter PDFJafarNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel Sub-Grades JR, J0 and J2 PDFDocument1 pageStructural Steel Sub-Grades JR, J0 and J2 PDFJafarNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel Sub-Grades JR, J0 and J2 Does It MatterDocument1 pageStructural Steel Sub-Grades JR, J0 and J2 Does It MatterJafarNo ratings yet
- Superfix Fastener Catalogue 2008 PDFDocument147 pagesSuperfix Fastener Catalogue 2008 PDFEdmond ChowNo ratings yet
- Perfil de Aluminio FastenDocument139 pagesPerfil de Aluminio FastenIng GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Daihatsu DK 28 201810081042Document228 pagesDaihatsu DK 28 201810081042mazlum doğan DemirkolNo ratings yet
- Cable ladder tray material summaryDocument1 pageCable ladder tray material summaryaung aungNo ratings yet
- Tightening Torques Lubricants Tools: AB 0100 EN Servicing SAMSON ProductsDocument174 pagesTightening Torques Lubricants Tools: AB 0100 EN Servicing SAMSON ProductsGordinhorsNo ratings yet
- DIN Hex Bolts and Plugs ChartDocument1 pageDIN Hex Bolts and Plugs ChartTuff qualityNo ratings yet
- Sym Euro MX 125 Service ManualDocument193 pagesSym Euro MX 125 Service ManualJavier GallegoNo ratings yet
- SIP-ignition-performance Manual 240122 210229Document12 pagesSIP-ignition-performance Manual 240122 210229ahmad.abdolahi1402No ratings yet
- Brick Veneer Masonry: Rev # Description of Change Author WP# DateDocument8 pagesBrick Veneer Masonry: Rev # Description of Change Author WP# DateMatthew Ho Choon LimNo ratings yet
- ASM2011LO Captured Screw CatalogDocument294 pagesASM2011LO Captured Screw CatalogArjun PanditNo ratings yet
- MOS SS-HTB Tightening PartDocument9 pagesMOS SS-HTB Tightening PartjimdabrondNo ratings yet
- Electra Voy 88911 ManualDocument14 pagesElectra Voy 88911 Manualpockyrevolution100% (1)
- 212 Si 04Document30 pages212 Si 04Hector BoliboNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet AgitatorDocument10 pagesData Sheet AgitatorEdi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Pins and BushingsDocument12 pagesPins and BushingsIsaque Elias CorreiaNo ratings yet
- STC-EOS Samurai Transfer Case Cradle InstallationsDocument25 pagesSTC-EOS Samurai Transfer Case Cradle Installationsfm.gruianuNo ratings yet
- The Donkey Engine Model Has Strong Steam Power AppealDocument4 pagesThe Donkey Engine Model Has Strong Steam Power AppealimgopalNo ratings yet
- UTC Distributor Request ASQR-01 Form 9: Boards, Semiconductors)Document5 pagesUTC Distributor Request ASQR-01 Form 9: Boards, Semiconductors)FilipNo ratings yet
- Table 8 - Clamping forces and prevailing torques for hexagon nuts and hexagon nuts with flange with coarse threadDocument4 pagesTable 8 - Clamping forces and prevailing torques for hexagon nuts and hexagon nuts with flange with coarse threadpalani.djp100% (1)
- OEM Gardner Denver PZ-7Document8 pagesOEM Gardner Denver PZ-7Juan Diego Vargas100% (1)
- CYLINDER HEAD AND ENGINE ASSEMBLY PARTSDocument15 pagesCYLINDER HEAD AND ENGINE ASSEMBLY PARTSchuck lancer AlquisolaNo ratings yet
- What Every Sailor Needs To Know About Seacocks: The Four Main Types of Seacock: Pros and ConsDocument2 pagesWhat Every Sailor Needs To Know About Seacocks: The Four Main Types of Seacock: Pros and ConsRicky WrightNo ratings yet
- C4000 PM en 31 PDFDocument195 pagesC4000 PM en 31 PDFDmitryNo ratings yet
- Empower CT & CTA Installation & Site Survey ManualDocument20 pagesEmpower CT & CTA Installation & Site Survey Manualbody2030No ratings yet
- PV Elite Saddle AnalysisDocument4 pagesPV Elite Saddle AnalysismrosNo ratings yet
- 2lfl MastDocument23 pages2lfl MastMelwyn FernandesNo ratings yet
- Boq 608553Document15 pagesBoq 608553sahil kotwalNo ratings yet