Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cont Chapter 1
Uploaded by
Teh Chu Leong0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesOriginal Title
CONT CHAPTER 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views2 pagesCont Chapter 1
Uploaded by
Teh Chu LeongCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Sensitivity
of the skin towards stimuli depends on
a. the number of receptors
b. the thickness of the skin epidermis
Combination of the sense of taste and the sense of smell
- A person suffers from cold have no appetite to eat because their sense of smell is weak
- The nasal cavity is filled with mucus and prevents chemical substances in food to be
detected by the smell receptors
Limitations of sight
- Optical illusions
- Blind spot
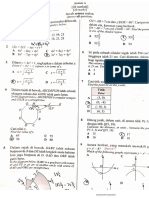
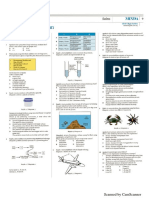
Defects of sight
Short-sightedness (myopia) Long-sightedness (Hypermetropia)
See near objects clearly but distant objects See distant objects clearly but near objects
are blurry are blurry
- Eye lens are too thick - Eye lens are too thin
- Eyeball are too long - Eyeball are too short
[Drawing] [Drawing]
Image formed in front of the retina Image formed behind the retina
[Drawing] [Drawing]
Concave lenses to diverge light Convex lenses to converge light
Astigmatism
See part of an object clearer than the rest of the object
[Drawing]
Caused by the uneven curvature of the cornea or eye lens
Can be corrected using cylindrical lenses
Defects of hearing – using hearing aid
Innovation and technology to improve the ability of sensory organs
- Magnifying glass
- Telescope
- Stethoscope
- Microscope
- Loudspeaker
Stimuli and responses in plants
a. Tropism
i. Phototropism – the response of plants towards light
a. Positive phototropism – shoots of plants
b. Negative phototropism – roots of plants
ii. Hydrotropism – the response of plants towards water
a. Positive hydrotropism – roots of plants
b. Negative hydrotropism – shoots of plants
iii. Geotropism – the response of plants towards gravity
a. Positive geotropism – roots of plants
b. Negative geotropism – shoots of plants
iv. Thigmotropism – the response of plants towards touch
a. Cucumber plants – tendrils
b. Morning glory plants – twining stems
(Positive tropism – part of plant grows towards stimulus)
(Negative tropism – part of plant grows away from stimulus)
b. Nastic movement
- The response of plants towards touch but does not depend on the direction of the
stimulus
- Occurs more rapidly than tropism
- Serves as a defense against its enemies and strong wind
- Mimosa sp. – by folding its leaves inwards when touched
Stereoscopic vision Monocular vision
[DRAWING] [DRAWING]
Both eyes at the front of the head Both eyes at the sides of the head
A narrow field of vision A wide field of vision
To estimate distance accurately To detect the enemies coming from any
direction
Three dimensional images formed in the Two dimensional images formed in the non-
overlapping fields of vision overlapping fields of vision
Most predators Most preys
Stereophonic hearing
- Hearing using both ears
- To determine the direction of the sound accurately
You might also like
- CamScanner 09-07-2021 23.11Document14 pagesCamScanner 09-07-2021 23.11Teh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- Scanned DocumentsDocument23 pagesScanned DocumentsTeh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- Scanned DocumentsDocument6 pagesScanned DocumentsTeh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- Scanned DocumentsDocument17 pagesScanned DocumentsTeh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- Characteristics 特征 请列出reptile的2个特征Document2 pagesCharacteristics 特征 请列出reptile的2个特征Teh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 09-09-2021 22.20Document14 pagesCamScanner 09-09-2021 22.20Teh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- Geografi Ting. 2 Praktis 2 Peta TopografiDocument7 pagesGeografi Ting. 2 Praktis 2 Peta TopografiTeh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- Science F1C3Document8 pagesScience F1C3Teh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- Scanned DocumentsDocument19 pagesScanned DocumentsTeh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 09-01-2021 21.45Document14 pagesCamScanner 09-01-2021 21.45Teh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Chapter 4 ReproductionDocument7 pagesForm 1 Chapter 4 ReproductionTeh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 09-06-2021 22.29Document14 pagesCamScanner 09-06-2021 22.29Teh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- Employment Income - Derivation, Exemptions, Types and DeductionsDocument57 pagesEmployment Income - Derivation, Exemptions, Types and DeductionsTeh Chu Leong100% (1)
- Form 3 Chapter 5 ThermochemistryDocument1 pageForm 3 Chapter 5 ThermochemistryTeh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- Cont. Chapter 2Document1 pageCont. Chapter 2Teh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- Capitalallowances 1Document29 pagesCapitalallowances 1Teh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- Pages From Dr. Shamsuddin L. Taya, Prof Madya Dr. Ariffin S.M. Omar & Prof Madya Dr. Veit Jan Nicol Stark 02Document2 pagesPages From Dr. Shamsuddin L. Taya, Prof Madya Dr. Ariffin S.M. Omar & Prof Madya Dr. Veit Jan Nicol Stark 02Teh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- F3 Chapter 9 & 10Document2 pagesF3 Chapter 9 & 10Teh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Resident Status For IndividualDocument23 pagesTopic 2 Resident Status For IndividualTeh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary 词汇 Kosa KataDocument1 pageVocabulary 词汇 Kosa KataTeh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- Calculate Capital Allowances for Hire Purchase and Special CircumstancesDocument13 pagesCalculate Capital Allowances for Hire Purchase and Special CircumstancesTeh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- Hidden Firestation Pix PDFDocument2 pagesHidden Firestation Pix PDFWhy ZuuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PolygonDocument1 pageChapter 4 PolygonTeh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- Section A/ Bahagian A (20 Marks/Markah) : TingkatanDocument18 pagesSection A/ Bahagian A (20 Marks/Markah) : TingkatanSong Sing LikNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management and Business Policy 15e, Global EditionDocument37 pagesStrategic Management and Business Policy 15e, Global EditionTeh Chu Leong0% (1)
- 34 PERCUBAAN SAINS PT3 + S JWP (MINDA BH) PDFDocument8 pages34 PERCUBAAN SAINS PT3 + S JWP (MINDA BH) PDFTeh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Algebraic FormulaeDocument1 pageChapter 3 Algebraic FormulaeTeh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- Answer Scheme Question 1 (30 Marks) A.: Bkam3023 Management Accounting IiDocument14 pagesAnswer Scheme Question 1 (30 Marks) A.: Bkam3023 Management Accounting IiTeh Chu LeongNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management ProcessDocument18 pagesStrategic Management ProcessNo Mi ViNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- How To Start Calisthenics Workout - The Beginners Ultimate Calisthenics Workout Plan and Body Building Routine For A Healthy Lifestyle. - D, Fryer (2021)Document33 pagesHow To Start Calisthenics Workout - The Beginners Ultimate Calisthenics Workout Plan and Body Building Routine For A Healthy Lifestyle. - D, Fryer (2021)Gustavo Gonzalez ServaNo ratings yet
- Perlos HistoryDocument21 pagesPerlos HistoryRiyali TardyNo ratings yet
- Jesus Uplifts The PoorDocument10 pagesJesus Uplifts The Poor명연우No ratings yet
- E Ipcrf Ebacuado, Joynalyn F.Document9 pagesE Ipcrf Ebacuado, Joynalyn F.Joynalyn Ebacuado- AdvientoNo ratings yet
- Neisseria and HaemophilusDocument15 pagesNeisseria and HaemophilusEdwin CvNo ratings yet
- Banking Question PapersDocument12 pagesBanking Question Papersmohak khinNo ratings yet
- Chap4 Q Consumer Behavior and Marketing StrategiesDocument14 pagesChap4 Q Consumer Behavior and Marketing StrategiesAdib WasiNo ratings yet
- Standard QAPDocument9 pagesStandard QAPsivaNo ratings yet
- Laurie BakerDocument12 pagesLaurie BakerchaplinNo ratings yet
- Text CDocument1,100 pagesText CAli NofalNo ratings yet
- Under The Oak Tree Part 2Document94 pagesUnder The Oak Tree Part 2suakasenaNo ratings yet
- MBR-STP Design Features PDFDocument7 pagesMBR-STP Design Features PDFManjunath HrmNo ratings yet
- 570-ULSP status index instrument cablesDocument184 pages570-ULSP status index instrument cableskumarnpccNo ratings yet
- Moderate and Extreme HypofractionationDocument32 pagesModerate and Extreme HypofractionationsamuelfsjNo ratings yet
- Pedest Tbox Toolbox - 4 Sidewalks and Walkways PDFDocument44 pagesPedest Tbox Toolbox - 4 Sidewalks and Walkways PDFbagibagifileNo ratings yet
- Labor Law in United KingdomDocument108 pagesLabor Law in United KingdomPanagiotis OptionalNo ratings yet
- Standards.: General Fastener Standards BS OrderDocument33 pagesStandards.: General Fastener Standards BS OrderamdarvishvandNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Accounting Cycle 1 - Recording Business Transactions and Accounting For Service Entities - Part BDocument29 pagesModule 6 - Accounting Cycle 1 - Recording Business Transactions and Accounting For Service Entities - Part BAbelNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry I BCM211: Zatilfarihiah RasdiDocument24 pagesBiochemistry I BCM211: Zatilfarihiah Rasdiستي نوراسيقينNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Sensor Simulator - JumperDocument7 pagesOxygen Sensor Simulator - JumperBrianssrt4100% (2)
- MetallizationDocument51 pagesMetallizationjust4u2cjoshy67% (3)
- Wire Rope Slings Si 2 - 2 EmmDocument2 pagesWire Rope Slings Si 2 - 2 EmmheppyfaebanffNo ratings yet
- Sage Yb October2015Document460 pagesSage Yb October2015olopNo ratings yet
- Acidified Foods Guidance 2010-08-02 (Clean)Document39 pagesAcidified Foods Guidance 2010-08-02 (Clean)Victor SchneiderNo ratings yet
- Concept Map (Cells: Sci Bio)Document1 pageConcept Map (Cells: Sci Bio)lu.justina100% (8)
- De Thi Thu Vao 10 Mon Tieng Anh Quan Dong Da Ha NoiDocument5 pagesDe Thi Thu Vao 10 Mon Tieng Anh Quan Dong Da Ha NoiTrang VuongNo ratings yet
- Formula Costo SandblastingDocument20 pagesFormula Costo SandblastingSerch VillaNo ratings yet
- Argumentative Essay-Nursing HomesDocument1 pageArgumentative Essay-Nursing HomesHM TanNo ratings yet
- Steps in Balancing Redox ReactionsDocument28 pagesSteps in Balancing Redox ReactionsRUZCHEMISTRYNo ratings yet
- English Task "Analytical Exposition": Smoking BansDocument7 pagesEnglish Task "Analytical Exposition": Smoking BansFirda RazaqNo ratings yet