Professional Documents
Culture Documents
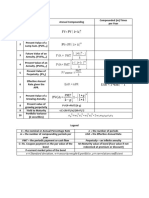
) K + 1 PV ( FV: PVGP PMT/ (K-G) (C+ (M-P) /N) / (M+P) /2 + + 2
Uploaded by
Shubham AggarwalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
) K + 1 PV ( FV: PVGP PMT/ (K-G) (C+ (M-P) /N) / (M+P) /2 + + 2
Uploaded by
Shubham AggarwalCopyright:
Available Formats
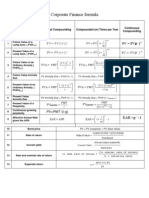
Compounded (m) Times
Formula For: Annual Compounding
per Year
Future Value of a
1
Lump Sum. (FVIFk,n)
FV = PV( 1 + k )n
Present Value of a
2
Lump Sum. (PVIFk,n)
PV = FV( 1 + k )-n
Future Value of an ( 1 + k )n - 1
3 FVA = PMT
Annuity. (FVIFAk,n)
k
Present Value of an 1 - ( 1 + k )
-n
4 PVA = PMT
Annuity. (PVIFAk,n)
k
Present Value of PMT
5 PVperpetuity =
Perpetuity. (PVp) k
Effective Annual
6 Rate given the EAR = APR EAR = (1 + k/m) m - 1
APR.
PMT 1 + g
n
Present Value of a
PVGA = 1−
(k − g ) 1 + k
7
Growing Annuity.
Present value of
8 PVGP=PMT/(k-g)
growing perpetuity
9 Yield to Maturity =(C+(M-P)/n)/(M+P)/2
Portfolio Variance
10 𝜎𝑝 2 = 𝑤1 2 𝜎1 2 + 𝑤2 2 𝜎2 2 + 2𝑤1 𝑤2 𝜌12 𝜎1 𝜎2
(2 securities)
Legend
k = the nominal or Annual Percentage Rate n = the number of periods
m = the number of compounding periods per EAR = the Effective Annual Rate
year
PMT = the periodic payment or cash flow Perpetuity = an infinite annuity
C= Rs. Coupon payment on the par value of the M=Maturity value of bond (Face value if not
bond redeemed at premium or discount)
P=current market price of the bond
𝛔 = 𝐒𝐭𝐚𝐧𝐝𝐚𝐫𝐝 𝐝𝐞𝐯𝐢𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧, 𝐰 = 𝐬𝐞𝐜𝐮𝐫𝐢𝐭𝐲 𝐰𝐞𝐢𝐠𝐡𝐭 𝐢𝐧 𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐭𝐟𝐨𝐥𝐢𝐨, 𝛒 = 𝐜𝐨𝐫𝐫𝐞𝐥𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐜𝐨𝐞𝐟𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐢𝐞𝐧𝐭
You might also like
- FV PV (1+ K) : Fva PMT (1+k) - 1 1 - (1+ K)Document1 pageFV PV (1+ K) : Fva PMT (1+k) - 1 1 - (1+ K)tanyaNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money Formula SheetDocument2 pagesTime Value of Money Formula SheetMD Abrar FaiyazNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money FormulasDocument2 pagesTime Value of Money FormulasZubayer HussainNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Cover Formulas COMM 308 JMSBDocument4 pagesFinal Exam Cover Formulas COMM 308 JMSBmeilleurlNo ratings yet
- Distance Test PDFDocument10 pagesDistance Test PDFSoneni HandaNo ratings yet
- TVM formulae cheat sheetDocument4 pagesTVM formulae cheat sheetShawron weevNo ratings yet
- FV PV: LN LN (1)Document2 pagesFV PV: LN LN (1)Danneek BillingsNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance FormulasDocument3 pagesCorporate Finance FormulasMustafa Yavuzcan83% (12)
- Equation List - COMM 308 - Booth Et Al Text, 4 Edition: FV FV PV KDocument3 pagesEquation List - COMM 308 - Booth Et Al Text, 4 Edition: FV FV PV Kadcyechicon123No ratings yet
- Economics of solar PV power plant cost analysisDocument4 pagesEconomics of solar PV power plant cost analysisHisham BasherNo ratings yet
- Ba4827 FormulaSheet1Document2 pagesBa4827 FormulaSheet1kesgencNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance FormulasDocument2 pagesCorporate Finance FormulasFira SyawaliaNo ratings yet
- Equation Formula: 1 1 FV PMT 1Document3 pagesEquation Formula: 1 1 FV PMT 1JMSB09No ratings yet
- Valuation and Rates of Return ChapterDocument16 pagesValuation and Rates of Return ChapterLourdios EdullantesNo ratings yet
- Financial Management - Paper 1: Chapter: - Indian Financial SystemDocument23 pagesFinancial Management - Paper 1: Chapter: - Indian Financial SystemToyaj JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Cong ThucDocument12 pagesCong ThucGiang Thái HươngNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance Equations NotesDocument4 pagesCorporate Finance Equations NotesSotiris HarisNo ratings yet
- Time value of money cheat sheetDocument3 pagesTime value of money cheat sheetTechbotix AppsNo ratings yet
- Formulas Bonds: Cpn Income+ price change APY(Approximate Yield to MaturityDocument1 pageFormulas Bonds: Cpn Income+ price change APY(Approximate Yield to MaturityGhitaNo ratings yet
- BA 2802 - Principles of Finance Formula Sheet For The Second Interim ExamDocument1 pageBA 2802 - Principles of Finance Formula Sheet For The Second Interim ExamEda Nur EvginNo ratings yet
- Finance 430 Executive SummaryDocument31 pagesFinance 430 Executive SummaryEin LuckyNo ratings yet
- Profit Margin Total Assets Turnover Equity Multiplier: Formula AFDocument4 pagesProfit Margin Total Assets Turnover Equity Multiplier: Formula AFDiva Tertia AlmiraNo ratings yet
- FIN222 Equations NotesDocument49 pagesFIN222 Equations NotesSotiris HarisNo ratings yet
- I. Financial Management: 1. Time Value of MoneyDocument21 pagesI. Financial Management: 1. Time Value of MoneyAritra ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Measuring Productivity and Forecasting TechniquesDocument5 pagesMeasuring Productivity and Forecasting TechniquesShawron weevNo ratings yet
- Adms3530f18 Final Exam Formula Sheet PDFDocument6 pagesAdms3530f18 Final Exam Formula Sheet PDFSandy SandNo ratings yet
- Depreciation, Capital Recovery and Break Even AnalysisDocument6 pagesDepreciation, Capital Recovery and Break Even AnalysisMa. Angeline GlifoneaNo ratings yet
- TVM - Formula SheetDocument1 pageTVM - Formula Sheetwarriorsoul1029No ratings yet
- Interest Rates That Vary With Time: I A I CWDocument3 pagesInterest Rates That Vary With Time: I A I CWTepe HolmNo ratings yet
- Physics 12 Formula SheetDocument3 pagesPhysics 12 Formula SheetJacob TamashiroNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Foundations of FinanceDocument5 pagesFormula Sheet Foundations of Financeyukti100% (1)
- Terzaghi's Consolidation Equation - Closed Form SolutionDocument5 pagesTerzaghi's Consolidation Equation - Closed Form SolutionhasnizalNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money Formulas SheetDocument1 pageTime Value of Money Formulas SheetBilal HussainNo ratings yet
- Test 2 Formula SheetDocument1 pageTest 2 Formula Sheetgabriella portelliNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheets-GDBA505 – must be returned after exam < 40Document3 pagesFormula Sheets-GDBA505 – must be returned after exam < 40FLOREAROMEONo ratings yet
- Hedging Interest Rate RiskDocument14 pagesHedging Interest Rate RiskVictor ManuelNo ratings yet
- Nataliemoore Time Value of MoneyDocument4 pagesNataliemoore Time Value of MoneyMaurice AgbayaniNo ratings yet
- A Level Physics Data Formulae RelationshipsDocument8 pagesA Level Physics Data Formulae RelationshipsArnav yogeshwar PurmessurNo ratings yet
- Cournot Competition Model Equilibrium PricesDocument5 pagesCournot Competition Model Equilibrium PricesRaulNo ratings yet
- Profitability, Alternative Investments and ReplacementsDocument32 pagesProfitability, Alternative Investments and ReplacementsNaser SalehNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Finance 1Document12 pagesMathematical Finance 1Brijesh MishraNo ratings yet
- 5865489Document46 pages5865489Amit JhaNo ratings yet
- BussFin. Formula SheetDocument2 pagesBussFin. Formula SheetkikennojinseiNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Corporate FinanceDocument19 pagesFormula Sheet Corporate FinancePatricia TekgültekinNo ratings yet
- MAF101 Formula Sheet-2010TR1Document2 pagesMAF101 Formula Sheet-2010TR1Ann VuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Non-Linear Equations: Nguyen Thi Minh TamDocument26 pagesChapter 2: Non-Linear Equations: Nguyen Thi Minh TamPhương Anh Nguyễn0% (1)
- Formula Sheet - Study Version. - Portfolio Management PDFDocument2 pagesFormula Sheet - Study Version. - Portfolio Management PDFAnhthu DangNo ratings yet
- PMBOK Formulas GuideDocument4 pagesPMBOK Formulas GuideWilliam Rojas MoralesNo ratings yet
- Selection of Useful FormulasDocument3 pagesSelection of Useful FormulasМаша СкрипченкоNo ratings yet
- 351 F 22 Exam EquationsDocument1 page351 F 22 Exam EquationsEdaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandMathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Corporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandCorporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Delhivery Revenue SourcesDocument5 pagesDelhivery Revenue SourcesShubham AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Infrastructure Sector in India: Government Initiative and InvestmentDocument13 pagesInfrastructure Sector in India: Government Initiative and InvestmentShubham AggarwalNo ratings yet
- DRW Technology Situational AnalysisDocument2 pagesDRW Technology Situational AnalysisMighty SinghNo ratings yet
- Revenue Breakup of DelhiveryDocument5 pagesRevenue Breakup of DelhiveryShubham AggarwalNo ratings yet
- V Information and Regulatory EconomicsDocument3 pagesV Information and Regulatory EconomicsShubham AggarwalNo ratings yet
- TQM CapstoneDocument1 pageTQM CapstoneShubham AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Finance SheetDocument3 pagesFinance SheetShubham AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Study - Id65431 - Domestic Tourism in IndiaDocument58 pagesStudy - Id65431 - Domestic Tourism in IndiaShubham AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Q1. How Structurally Attractive Is The Russian Ice Cream Market? Discuss How Its Industry Structure Can Be Made More Attractive? (663 Words)Document5 pagesQ1. How Structurally Attractive Is The Russian Ice Cream Market? Discuss How Its Industry Structure Can Be Made More Attractive? (663 Words)Hongbo HaNo ratings yet
- Ice Fili Analysis: Presented by Group11-Anuraj Antil Ishan Malik Kanishka Singh Sunny Malik Surya DeswalDocument13 pagesIce Fili Analysis: Presented by Group11-Anuraj Antil Ishan Malik Kanishka Singh Sunny Malik Surya DeswalKanishka SinghNo ratings yet
- Question 1: Read The Following Case and Attempt The Questions BelowDocument4 pagesQuestion 1: Read The Following Case and Attempt The Questions BelowShubham Aggarwal0% (1)
- Ice-Fili Market Share Loss AnalysisDocument4 pagesIce-Fili Market Share Loss AnalysisAlejandro MontoyaNo ratings yet
- DRW Technology Situational AnalysisDocument2 pagesDRW Technology Situational AnalysisMighty SinghNo ratings yet
- DRWDocument2 pagesDRWShubham AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Solutions PDFDocument5 pagesChapter 7 Solutions PDFShubham AggarwalNo ratings yet
- India's thriving travel and tourism industryDocument60 pagesIndia's thriving travel and tourism industryShubham AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Stock Valuation Problems SolvedDocument6 pagesStock Valuation Problems SolvedShubham Aggarwal100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Solutions PDFDocument5 pagesChapter 7 Solutions PDFShubham AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Bond Valuation SolutionsDocument7 pagesBond Valuation SolutionsShubham AggarwalNo ratings yet
- TVM Solution-Q5Document2 pagesTVM Solution-Q5Shubham AggarwalNo ratings yet
- R R R R R R: Solutions To Chapter 9 ProblemsDocument2 pagesR R R R R R: Solutions To Chapter 9 ProblemsAshutosh BiswalNo ratings yet
- Risk&return SolutionsDocument1 pageRisk&return Solutionslakshay chawlaNo ratings yet
- Problems - Time Value of Money PDFDocument1 pageProblems - Time Value of Money PDFShubham AggarwalNo ratings yet
- India's thriving travel and tourism industryDocument60 pagesIndia's thriving travel and tourism industryShubham AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Problems - Cost of Capital PDFDocument1 pageProblems - Cost of Capital PDFShubham AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Study - Id65431 - Domestic Tourism in IndiaDocument58 pagesStudy - Id65431 - Domestic Tourism in IndiaShubham AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Problems - Valuation of Bonds and StocksDocument1 pageProblems - Valuation of Bonds and StocksShubham AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Economic CalculationDocument7 pagesEconomic CalculationsingsaranNo ratings yet
- Automobiles August 2020Document27 pagesAutomobiles August 2020Muskan ValbaniNo ratings yet