Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Characteristics of Work Sampling Study
Uploaded by
SagarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Characteristics of Work Sampling Study
Uploaded by
SagarCopyright:
Available Formats
Work sampling
Work sampling is the statistical technique for determining the proportion of time spent by workers in
various defined categories of activity (e.g. setting up a machine, assembling two parts, idle…etc.).[1] It
is as important as all other statistical techniques because it permits quick analysis, recognition, and
enhancement of job responsibilities, tasks, performance competencies, and organizational work
flows. Other names used for it are 'activity sampling', 'occurrence sampling', and 'ratio delay study'.[2]
In a work sampling study, a large number of observations are made of the workers over an extended
period of time. For statistical accuracy, the observations must be taken at random times during the
period of study, and the period must be representative of the types of activities performed by the
subjects.
One important usage of the work sampling technique is the determination of the standard time for a
manual manufacturing task. Similar techniques for calculating the standard time are time study,
standard data, and predetermined motion time systems.
Characteristics of work sampling study
The study of work sampling has some general characteristics related to the work condition:
One of them is the sufficient time available to perform the study. A work sampling study usually requires a
substantial period of time to complete. There must be enough time available (several weeks or more) to conduct the study.
Another characteristic is multiple workers. Work sampling is commonly used to study the activities of multiple
workers rather than one worker.
The third characteristic is long cycle time. The job covered in the study has relatively a long cycle time.
The last condition is the non-repetitive work cycles. The work is not highly repetitive. The jobs consist of various
tasks rather than a single repetitive task. However, it must be possible to classify the work activities into a distinct number
of categories.
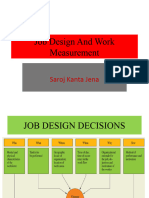
Steps in conducting a work sampling study
There are several recommended steps when starting to prepare a work sampling study:[1]
1. Define the manufacturing tasks for which the standard time is to be determined.
2. Define the task elements. These are the defined broken-down steps of the task that will be observed during the
study. Since a worker is going to be observed, additional categories will likely be included as well, such as "idle",
"waiting for work", and "absent".
3. Design the study. This includes designing the forms that will be used to record the observations, determining how
many observations will be required, deciding on the number of days or shifts to be included in the study, scheduling the
observations, and finally determining the number of observers needed.
4. Identify the observers who will do the sampling.
5. Start the study. All those who are affected by the study should be informed about it.
6. Make random visits to the plant and collect the observations.
7. After completing the study, analyze and present the results. This is done by preparing a report that summarizes
and analyzes all data and making recommendations when required.
You might also like
- Ch11 The Balance of PaymentsDocument11 pagesCh11 The Balance of PaymentsSagar100% (1)
- Bowl of SakiDocument2 pagesBowl of SakiSagarNo ratings yet
- Ch11 The Balance of PaymentsDocument11 pagesCh11 The Balance of PaymentsSagar100% (1)
- Chapter 14 Simulation Modeling: Quantitative Analysis For Management, 11e (Render)Document20 pagesChapter 14 Simulation Modeling: Quantitative Analysis For Management, 11e (Render)Jay BrockNo ratings yet
- Work SamplingDocument3 pagesWork SamplingAmit SahuNo ratings yet
- Revision NotesDocument5 pagesRevision NotesIvyNo ratings yet
- Module Iv - Operations Management: Dr.A.Abirami / OmDocument20 pagesModule Iv - Operations Management: Dr.A.Abirami / OmBalujagadishNo ratings yet
- Wage AdministrationDocument8 pagesWage AdministrationRahul KalathilNo ratings yet
- Seatwork No.2Document2 pagesSeatwork No.2Raljon SilverioNo ratings yet
- AAP Duduuu Duddu DudduDocument13 pagesAAP Duduuu Duddu Duddusantoshmishra5510No ratings yet
- Work MeasurementDocument7 pagesWork MeasurementsamgeorgemaxNo ratings yet
- Job DesignDocument30 pagesJob DesignNassar KhokharNo ratings yet
- Work Measurement - TIME STUDYDocument10 pagesWork Measurement - TIME STUDYMarcel PretzelNo ratings yet
- Work MeasurementDocument4 pagesWork MeasurementMiguel HernandezNo ratings yet
- Design of Work SystemsDocument19 pagesDesign of Work SystemsmanopavanNo ratings yet
- Work MeasurementDocument10 pagesWork Measurementimrannila910No ratings yet
- Ba 506 Operations Management Narrative Report Job Design and Work Measurement (Part 2)Document4 pagesBa 506 Operations Management Narrative Report Job Design and Work Measurement (Part 2)Ruth Ann DimalaluanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document36 pagesUnit 2realguy556789No ratings yet
- 1.) Define Time Study? What Are The Objectives of It? Explain The Step by Step Procedure of It?Document7 pages1.) Define Time Study? What Are The Objectives of It? Explain The Step by Step Procedure of It?Rajat YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter Seven Work Design and MeasurementDocument7 pagesChapter Seven Work Design and MeasurementJohn Carlo TarlitNo ratings yet
- Work MeasurementDocument6 pagesWork MeasurementRohan SehgalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Motion StudyDocument44 pagesChapter 5: Motion StudyBaleje JeremyNo ratings yet
- Work Study, Motion Study, Time StudyDocument8 pagesWork Study, Motion Study, Time StudyParvathy Suresh0% (1)
- Workstudy Workmeasurement 150216233634 Conversion Gate01Document17 pagesWorkstudy Workmeasurement 150216233634 Conversion Gate01Dotecho Jzo EyNo ratings yet
- Work StudyDocument27 pagesWork Studyismael opondoNo ratings yet
- Work StudyDocument5 pagesWork StudyLovepreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document10 pagesModule 4pittviper313No ratings yet
- Course Outcomes: Topic Iv: Time StudyDocument11 pagesCourse Outcomes: Topic Iv: Time StudyAngelo RoqueNo ratings yet
- Work MeasurementDocument23 pagesWork MeasurementruchikaNo ratings yet
- Work SamplingDocument36 pagesWork SamplingAakashMehtaNo ratings yet
- Time and Motion StudyDocument12 pagesTime and Motion StudyKshipra Garg0% (1)
- Om Ay2022 Ras 7Document22 pagesOm Ay2022 Ras 7justineinobacan58No ratings yet
- Time StudyDocument12 pagesTime StudyBrandon ParraNo ratings yet
- Work MeasurementDocument33 pagesWork MeasurementAkshay DhekaneNo ratings yet
- Work Measurements: CompanyDocument32 pagesWork Measurements: CompanyVibhaSharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit-III Time Study (Work Measurement) Time Study: DefinitionsDocument15 pagesUnit-III Time Study (Work Measurement) Time Study: DefinitionsAbhishek AruaNo ratings yet
- Time MotionDocument12 pagesTime MotionMarriiam AliNo ratings yet
- VIII SEM I.E.Lab Exp 1Document7 pagesVIII SEM I.E.Lab Exp 1Raghvendra Singh ShaktawatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Design of Work SystemsDocument6 pagesChapter 7 - Design of Work Systemshello_khay100% (1)
- Iv UnitDocument3 pagesIv Unitpavan kumarNo ratings yet
- Work Study: Dr. Sanchayan MukherjeeDocument16 pagesWork Study: Dr. Sanchayan MukherjeeSirsendu GhoshalNo ratings yet
- PR 3Document8 pagesPR 3mech bhabhaNo ratings yet
- SCRIPT TQM Developing Work Methods SDocument3 pagesSCRIPT TQM Developing Work Methods SNarvasa, Jazper Hart O.No ratings yet
- Work SamplingDocument5 pagesWork SamplingRoshan SinghNo ratings yet
- WORK STUDY METHOD STUDY TIME STUDY OoooDocument33 pagesWORK STUDY METHOD STUDY TIME STUDY OoooRahul DodiyaNo ratings yet
- Work Study Including Method Study and Time StudyDocument21 pagesWork Study Including Method Study and Time StudyPrudhvi Sairam ChundruNo ratings yet
- Work Measurement Note For AssignmentDocument3 pagesWork Measurement Note For Assignmentsamuel debebeNo ratings yet
- Techniques of Work Measurement in Production ManagementDocument2 pagesTechniques of Work Measurement in Production ManagementSameer KhanNo ratings yet
- Time and Motion StudyDocument2 pagesTime and Motion StudyYogendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Maie Work MeasurementDocument6 pagesMaie Work MeasurementLa GraciahNo ratings yet
- Prof. V.B.Shah Insitute of Management, Amroli, Surat: Course: S.Y.Bba (Sem - Iv)Document24 pagesProf. V.B.Shah Insitute of Management, Amroli, Surat: Course: S.Y.Bba (Sem - Iv)Vasu PatelNo ratings yet
- Work StudyDocument21 pagesWork StudysivainamduguNo ratings yet
- Work Oriented MethodsDocument2 pagesWork Oriented MethodsHadia ZafarNo ratings yet
- WORKSTUDYDocument88 pagesWORKSTUDYRamees KpNo ratings yet
- Topic 12&13 - Work Study & Costs-SDocument30 pagesTopic 12&13 - Work Study & Costs-SsteyvohmannaNo ratings yet
- (POM) Unit 4 Short NoteDocument9 pages(POM) Unit 4 Short NoteSourabh GuhaNo ratings yet
- Techniques of Work MeasurementDocument2 pagesTechniques of Work MeasurementabdulghaforNo ratings yet
- Method StudyDocument50 pagesMethod Studywintoday01100% (2)
- M.M Fathima Naseela EU/IS/08/MS/40Document12 pagesM.M Fathima Naseela EU/IS/08/MS/40Fathima NaseelaNo ratings yet
- HW1Document4 pagesHW1J KeplerNo ratings yet
- Job Design and Work MeasurementsDocument14 pagesJob Design and Work MeasurementsRuth Ann DimalaluanNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide To Work Study [Revised Edition]From EverandPractical Guide To Work Study [Revised Edition]Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Top 10 Best Beaches To Visit in The WorldDocument8 pagesTop 10 Best Beaches To Visit in The WorldSagarNo ratings yet
- Types of Knee InjuriesDocument6 pagesTypes of Knee InjuriesSagarNo ratings yet
- 5 Trends Which Will Trasform The Automotive IndustryDocument2 pages5 Trends Which Will Trasform The Automotive IndustrySagarNo ratings yet
- Abstract Wallpaper-1Document16 pagesAbstract Wallpaper-1SagarNo ratings yet
- Xtreme Shred Keto BHB ReviewsDocument5 pagesXtreme Shred Keto BHB ReviewsSagarNo ratings yet
- What Is Monsplasty?Document8 pagesWhat Is Monsplasty?SagarNo ratings yet
- Things To Know Before Visiting HawaiiDocument4 pagesThings To Know Before Visiting HawaiiSagarNo ratings yet
- Structure of ArticleDocument1 pageStructure of ArticleSagarNo ratings yet
- Can I Grow Marijuana in AlaskaDocument3 pagesCan I Grow Marijuana in AlaskaSagarNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Managing Ethics in The WorkplaceDocument4 pagesBenefits of Managing Ethics in The WorkplaceSagarNo ratings yet
- Right From Mosque To Mountains - Places To Visit in Pakistan - EditedDocument2 pagesRight From Mosque To Mountains - Places To Visit in Pakistan - EditedSagarNo ratings yet
- Kylea Ultimate Keto ReviewDocument7 pagesKylea Ultimate Keto ReviewSagarNo ratings yet
- Understanding Ethics and Morality in BusinessDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Ethics and Morality in BusinessSagarNo ratings yet
- BBA 2018-21 External Viva Voce Presentation ScheduleDocument12 pagesBBA 2018-21 External Viva Voce Presentation ScheduleSagarNo ratings yet
- CourierDocument1 pageCourierSagarNo ratings yet
- Pandit Rajmani Tigunait - Sakti - The Power in TantraDocument233 pagesPandit Rajmani Tigunait - Sakti - The Power in Tantrarprarpra100% (3)
- Internship Report Topic "Sales & Marketing Strategies of Business Solutions Limited"Document37 pagesInternship Report Topic "Sales & Marketing Strategies of Business Solutions Limited"His IdeaNo ratings yet
- ExportsDocument1 pageExportsSagarNo ratings yet
- Format - Ijhss - A Study On The Comparative Analysis of State Bank of India and Industrial CreditDocument7 pagesFormat - Ijhss - A Study On The Comparative Analysis of State Bank of India and Industrial Creditiaset123No ratings yet
- Gita Commentary by Abhinava Gupta PDFDocument375 pagesGita Commentary by Abhinava Gupta PDFNataliaTodeasaNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship ProjectDocument37 pagesSummer Internship ProjectSagarNo ratings yet
- Create Following Charts As Suggested in The Questions.: Sales and Produce DepartmentDocument2 pagesCreate Following Charts As Suggested in The Questions.: Sales and Produce DepartmentKumar SwetanshNo ratings yet
- Living With A Siddha PDFDocument4 pagesLiving With A Siddha PDFSagarNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Module 1: What Should You Upload As SolutionDocument1 pageAssignment For Module 1: What Should You Upload As SolutionSanchit MathurNo ratings yet
- The Historicity of Vikramaditya and Salivahana1 by K M RaoDocument10 pagesThe Historicity of Vikramaditya and Salivahana1 by K M RaoSagarNo ratings yet
- Siddhas of South PDFDocument180 pagesSiddhas of South PDFSagarNo ratings yet
- Master of Magical Power The Nath Siddhas in The Light of Esoteric Notions by Gorden DjurdjevicDocument334 pagesMaster of Magical Power The Nath Siddhas in The Light of Esoteric Notions by Gorden DjurdjevicИгорь Кислов100% (2)
- Online Generation of Association Rules: Support CondenceDocument10 pagesOnline Generation of Association Rules: Support CondenceaddminNo ratings yet
- Intrusion Detection in Software Defined Network Using Machine LearningDocument11 pagesIntrusion Detection in Software Defined Network Using Machine LearningdataprodcsNo ratings yet
- DP 2Document19 pagesDP 2ADVAITANo ratings yet
- ANUP (Original) PDFDocument12 pagesANUP (Original) PDFAnup ŠářkarNo ratings yet
- A 15 02Document5 pagesA 15 02fathieldrassiNo ratings yet
- American Journal of Physics Volume 39 Issue 6 1971 (Doi 10.1119 - 1.1986246) Ferrell, Thomas L. - Hamilton-Jacobi Perturbation TheoryDocument7 pagesAmerican Journal of Physics Volume 39 Issue 6 1971 (Doi 10.1119 - 1.1986246) Ferrell, Thomas L. - Hamilton-Jacobi Perturbation TheoryCarlosChapoNo ratings yet
- Byte-Oriented Efficient Implementation of The NIST Statistical Test SuiteDocument6 pagesByte-Oriented Efficient Implementation of The NIST Statistical Test SuiteJaroslav HnipirdoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Management Science: Monday 21 November 2022Document17 pagesIntroduction To Management Science: Monday 21 November 2022Saad SalmanNo ratings yet
- Machine LearningDocument40 pagesMachine LearningKailash Kumar Kailly100% (1)
- Unit 2 - StackDocument31 pagesUnit 2 - StackJesica D'cruzNo ratings yet
- Algorithm Flow ChatDocument4 pagesAlgorithm Flow ChatSunny MauryaNo ratings yet
- CQF June 2021 M3L1 ExercisesDocument2 pagesCQF June 2021 M3L1 ExercisesStacey LiuNo ratings yet
- Applied Soft Computing Journal: Omer Berat Sezer Mehmet Ugur Gudelek Ahmet Murat OzbayogluDocument32 pagesApplied Soft Computing Journal: Omer Berat Sezer Mehmet Ugur Gudelek Ahmet Murat OzbayogluViviana GeraldinNo ratings yet
- DAA - Unit V - Dynamic ProgrammingDocument37 pagesDAA - Unit V - Dynamic ProgrammingnishkarshNo ratings yet
- EBE Ch2Document10 pagesEBE Ch2Syed Muhammad Haris HayatNo ratings yet
- Math of Deep Learning Neural NetworksDocument9 pagesMath of Deep Learning Neural NetworksagalassiNo ratings yet
- A Mathematical Essay On Logistic Regression: Awik DharDocument4 pagesA Mathematical Essay On Logistic Regression: Awik DharAwik DharNo ratings yet
- Automatic Control: Radouan Ait Mouha ID:12190210101Document19 pagesAutomatic Control: Radouan Ait Mouha ID:12190210101Redouan Ait MouhaNo ratings yet
- Ch-3 Ardens TheoremDocument16 pagesCh-3 Ardens Theoremcoderanonymous5No ratings yet
- Sanusi 2021 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1752 012004Document12 pagesSanusi 2021 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1752 012004Rohan sharmaNo ratings yet
- Random VariablesDocument57 pagesRandom VariablesJaff LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 Advanced Data ModelingDocument24 pagesChapter 05 Advanced Data ModelingChong Fong KimNo ratings yet
- Genetic Algorithm Solution of The TSP Avoiding Special Crossover and MutationDocument6 pagesGenetic Algorithm Solution of The TSP Avoiding Special Crossover and MutationMuhammad FadzreenNo ratings yet
- Prak Fiskom - 1187030011 - Fitri Indah Anggreani - 12 - Metode RegresiDocument17 pagesPrak Fiskom - 1187030011 - Fitri Indah Anggreani - 12 - Metode RegresiFitri Indah AnggreaniNo ratings yet
- Floyd-Warshall Algorithm Questions and Answers - Sanfoundry PDFDocument13 pagesFloyd-Warshall Algorithm Questions and Answers - Sanfoundry PDFHuma AshrafNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument27 pagesLiterature ReviewMohit choubeyNo ratings yet
- FoC HW1 2024Document2 pagesFoC HW1 2024T MNo ratings yet
- The Simplex Algorithm: Putting Linear Programs Into Standard Form Introduction To Simplex AlgorithmDocument25 pagesThe Simplex Algorithm: Putting Linear Programs Into Standard Form Introduction To Simplex AlgorithmmritroyNo ratings yet





























































![Practical Guide To Work Study [Revised Edition]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/245836753/149x198/e8597dfaef/1709916910?v=1)






















































