Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kuliah 02 - Solubility of Minerals and EDL Theory
Kuliah 02 - Solubility of Minerals and EDL Theory
Uploaded by
sri rahayu0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views52 pagesThe document discusses how mineral particles interact with water, noting that some minerals will completely dissolve while others will only partially dissolve or be insoluble. It then lists solubility rules for common salts and minerals based on their anionic components. The surface of mineral particles can become electrostatically charged when placed in water due to interactions between the mineral and water molecules.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses how mineral particles interact with water, noting that some minerals will completely dissolve while others will only partially dissolve or be insoluble. It then lists solubility rules for common salts and minerals based on their anionic components. The surface of mineral particles can become electrostatically charged when placed in water due to interactions between the mineral and water molecules.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views52 pagesKuliah 02 - Solubility of Minerals and EDL Theory
Kuliah 02 - Solubility of Minerals and EDL Theory
Uploaded by
sri rahayuThe document discusses how mineral particles interact with water, noting that some minerals will completely dissolve while others will only partially dissolve or be insoluble. It then lists solubility rules for common salts and minerals based on their anionic components. The surface of mineral particles can become electrostatically charged when placed in water due to interactions between the mineral and water molecules.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 52
FLOTASI
Lecture 02:
Properties of Mineral Surface
Agus Prasetya, PhD.
S2 Minat Mineral Processing
DTK FT UGM
What happens with mineral particles when they are
placed in water?
mineral particles dissolved in water
a. Completely dissolved in water (larut sempurna)
Example: NaCl, KCl
b. Sparingly dissolved in water (larut sebagian/sulit larut)
Example: (Ca)3(PO4)2, CaCO3
mineral particles dissolved in water
Solubility Rules
1. All common salts of the Group 1A elements *) (such as Na+, K+ and
Li+) and ammonium (NH4+) are soluble
2. All common salts containing acetate (CH3COO-) or nitrate (NO3-) are
soluble, except those of silver (Ag) and lead (Pb)
3. All compounds containing sulfate (SO42-) are soluble, EXCEPT those
of barium (Ba), strontium (Sr), lead (Pb), calcium (Ca), silver (Ag) and
mercury (Hg)
4. Except for those compounds following Rule 1, compounds containing
carbonate (CO32-), hydroxide (OH-), oxide (O2-) and phosphates (PO43-
) are INsoluble
*) refered to Periodic Table
SOLUBILITY PRODUCTS OF SELECTED MINERALS
SOLUBILITY PRODUCTS OF VARIOUS Pb MINERALS
mineral particles react with water
mineral particles electrostatically charged in water
Surface Charge: How does it come from?
You might also like
- Chemistry on Modified Oxide and Phosphate Surfaces: Fundamentals and ApplicationsFrom EverandChemistry on Modified Oxide and Phosphate Surfaces: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- S-Block Elements: Solubility TrendsDocument2 pagesS-Block Elements: Solubility TrendsHansel GoyalNo ratings yet
- Activity 9 - Properties of MetalDocument30 pagesActivity 9 - Properties of MetalAbbey Frosty'Knight Dawn MortaleNo ratings yet
- Salt AnalysisDocument4 pagesSalt AnalysisMarietta ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document6 pagesModule 3Daneilla BanksNo ratings yet
- S BlockDocument39 pagesS BlockKithminiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4Document4 pagesExperiment 4Jc Goh100% (2)
- Solubility Rules: Except: Ag HG, PBDocument1 pageSolubility Rules: Except: Ag HG, PBrickyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 428 Reactionsin Aqueous Equilibria 29Document99 pagesChapter 428 Reactionsin Aqueous Equilibria 29Kent NguyenNo ratings yet
- Study QuestionsDocument1 pageStudy QuestionsDilla RositaNo ratings yet
- 2.6 NotesDocument6 pages2.6 NotesLisa DentonNo ratings yet
- C13 Properties of Metals PC SlidesDocument39 pagesC13 Properties of Metals PC SlidesBasil ChinNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Chemical Reactions - Skeleton NotesDocument80 pagesUnit 4 - Chemical Reactions - Skeleton Notesyejawir236No ratings yet
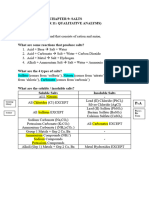
- Must Know For Chapter 9 - Salts (And C11 Qualitative Analysis)Document4 pagesMust Know For Chapter 9 - Salts (And C11 Qualitative Analysis)Chaw Wei HengNo ratings yet
- 10 Group2 NotesDocument10 pages10 Group2 NotesBrendon MuriraNo ratings yet
- SCH1201 - Inorganic Chemistry Ii - Group Elements & Their CompoundsDocument268 pagesSCH1201 - Inorganic Chemistry Ii - Group Elements & Their CompoundssanelisofuturemoyoNo ratings yet
- Net Ionic EquationsDocument15 pagesNet Ionic EquationsAikaterine SmithNo ratings yet
- Solubility Rules2 PDFDocument1 pageSolubility Rules2 PDFFernandaIbarraVázquezNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2023 S-Block Elements Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadDocument12 pagesJEE Main 2023 S-Block Elements Revision Notes - Free PDF DownloadRuhaan Bansal, 11B2, 51No ratings yet
- Activity 6 - Writing Ionic EquationsDocument6 pagesActivity 6 - Writing Ionic Equationsjoseph cyron solidumNo ratings yet
- 2 The Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals PDFDocument9 pages2 The Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals PDFAdnan DeparNo ratings yet
- Regolith Geochemistry & Mineralogy: Mehrooz F AspandiarDocument53 pagesRegolith Geochemistry & Mineralogy: Mehrooz F AspandiarChinox LokooNo ratings yet
- Unit Test 01 S BlockDocument5 pagesUnit Test 01 S BlockDevin GamageNo ratings yet
- Water Solubility ChartDocument3 pagesWater Solubility ChartLuzarro BNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Qualitative Analysis of CationsDocument8 pagesExperiment 4 Qualitative Analysis of CationsUzo Paul NwabuisiNo ratings yet
- Aqueous Reactions and SolutionsDocument12 pagesAqueous Reactions and SolutionsDavid Jonathan Polo100% (1)
- Note REACTIVITY SERIES OF METALSDocument3 pagesNote REACTIVITY SERIES OF METALSSamuel AjanaNo ratings yet
- Solubility Rules Practice WorksheetDocument2 pagesSolubility Rules Practice WorksheetSarah Yetti0% (1)
- Notes - Ch9.1Document5 pagesNotes - Ch9.1Triet NguyenNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Part 1 EdexcelDocument3 pagesGroup 2 Part 1 EdexcelKevin The Chemistry TutorNo ratings yet
- Types of Decomposition ReactionDocument19 pagesTypes of Decomposition ReactionSrynnENo ratings yet
- Group 2Document15 pagesGroup 2Behzod ShoraimovNo ratings yet
- Chem 125 07.10.2019Document9 pagesChem 125 07.10.2019nilofar jawadiNo ratings yet
- 11 S - Block Element Study NotesDocument12 pages11 S - Block Element Study NotesGaurav ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 1C Fundamentals of Chemistry 2019Document13 pagesLecture Notes 1C Fundamentals of Chemistry 2019Tango Jhecee Meir, D.No ratings yet
- S-Block ElementDocument31 pagesS-Block ElementSiva ChamlingNo ratings yet
- The S-Block ElementsDocument55 pagesThe S-Block Elementswealthy58771% (7)
- ChemistryDocument23 pagesChemistryAbhishek PawarNo ratings yet
- Untitled Document 3Document5 pagesUntitled Document 3Isha WaniNo ratings yet
- Properties of Alkali Earth MetalsDocument2 pagesProperties of Alkali Earth MetalsAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Mehrooz F AspandiarDocument53 pagesMehrooz F AspandiarmohammedalmasriNo ratings yet
- Copper Cycle Report SP16Document12 pagesCopper Cycle Report SP16BirobaNo ratings yet
- 10 Nature of Oxides2Document28 pages10 Nature of Oxides2James WongNo ratings yet
- PCBR - Volume 3 - Issue 3 - Pages 202-220Document19 pagesPCBR - Volume 3 - Issue 3 - Pages 202-220Syarifah NabilaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument2 pagesChemistryDimitri BlackwoodNo ratings yet
- I - A Group Elements: Alkali MetalsDocument13 pagesI - A Group Elements: Alkali MetalsTrần Nhật Khánh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Manganese 22028Document55 pagesManganese 22028Rodrigo CastroNo ratings yet
- Expt 1 Qualitative Analysis Procedure SP 2017Document18 pagesExpt 1 Qualitative Analysis Procedure SP 2017Jonathan ZhangNo ratings yet
- Chemical Tests of Some Ions in SaltDocument5 pagesChemical Tests of Some Ions in Saltmohammed hassen mohammedNo ratings yet
- 2 Group Two Elements: Beryllium Be Magnesium MG Calcium Ca Strontium SR Barium BaDocument6 pages2 Group Two Elements: Beryllium Be Magnesium MG Calcium Ca Strontium SR Barium BaTheodora HamletNo ratings yet
- 2.7 Chemical Nomenclature: Check Your LearningDocument8 pages2.7 Chemical Nomenclature: Check Your Learningclancy jembiaNo ratings yet
- All InorganicDocument125 pagesAll InorganicMarco WongNo ratings yet
- Cation SeparationDocument22 pagesCation SeparationDiane Angeles50% (2)
- 11.3 Powerpoint - Net Ionic Equations CE 2Document25 pages11.3 Powerpoint - Net Ionic Equations CE 2Lauren BoersmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document23 pagesChapter 4V KumarNo ratings yet
- Regolith GeochemistryDocument53 pagesRegolith GeochemistrydaveanthonyNo ratings yet
- Ioc C3 DPP L4Document3 pagesIoc C3 DPP L4iamadityakmrNo ratings yet
- ...Document20 pages...Laisa VittoNo ratings yet
- Lab GTM SaltsDocument4 pagesLab GTM Saltspeter edwardNo ratings yet