Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Don Honorio Ventura State University: College of Hospitality and Tourism Management
Uploaded by
Princess Aquilla KimOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Don Honorio Ventura State University: College of Hospitality and Tourism Management
Uploaded by
Princess Aquilla KimCopyright:
Available Formats
DON HONORIO VENTURA STATE UNIVERSITY
Cabambangan, Villa de Bacolor 2001, Pampanga, Philippines
Tel. No. (6345) 458 0021; Fax (6345) 458 0021 Local 211
COLLEGE OF HOSPITALITY AND TOURISM MANAGEMENT
CHAPTER 1 4. Franchised
HOTELS – PAST and PRESENT They are independently owned hotels that
affiliate themselves with a chain.
LODGING MANAGEMENT ASSOCIATION
Franchisee – pays a franchise fee to the
Overview chain & Franchiser – in exchange for the
The present state of the hotel industry is as broad as rights to use the name
it ever was in the past. They also benefits from national marketing
Variations of design, structure & operation are campaigns.
immense. The chain provides SOP & other
It is important to understand its basic hotel’s administration guidelines so that a
ownership & how that structure is related to hotel’s consistent level of quality & service is
ownership arrangement. maintained
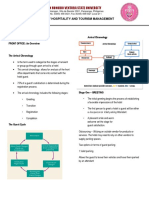
Lodging Management Associations Centralized Reservation System (CRS)
The relationship between ownership and management • provides the consumer with an avenue to locate a
Owner-operated hotel of choice in a certain location.
Owner-managed • They provide toll free telephone numbers to
encourage travelers to
Independent use their facility.
Franchised • It can generate significant
demand for a hotel through
Management contract brand loyalty.
5. Management Contract
1. Owner-operated Agreement between investors or owners of
a project, and a management
A hotel run by an owner and the owners family.
company hired for coordinating and
2. Owner-managed overseeing a contract.
Hotels are those where the owner has hired The chain maintains a high level of control
additional (nonfamily) personnel to help run as the chain operates the hotel on the
the property. Owners behalf.
The overall management remains with the Revenue Source
owner, but day-to-day operations can be in
Is the result of a product or service a hotel makes
the other hands.
available to guest for a price. The size and scope of
Not Chain Affiliated these sources can differ greatly from hotel to hotel.
3. Independent
Are not chain affiliated
They are responsible to the owner for the
hotel’s performance. (Group of Managers)
they are responsible to the owner for the
hotel’s performance
The owner has no role in management or
day to day operation.
It eliminates any potential conflict of interest
DON HONORIO VENTURA STATE UNIVERSITY
Cabambangan, Villa de Bacolor 2001, Pampanga, Philippines
Tel. No. (6345) 458 0021; Fax (6345) 458 0021 Local 211
COLLEGE OF HOSPITALITY AND TOURISM MANAGEMENT
Three Main Revenue Source PROFIT MARGIN
1. Sleeping Rooms Profit Margin
2. Meeting / Function Space Is determined by comparing the sales revenue
versus the cost incurred in providing a service or
3. Outlets / Ancillary revenue sources product.
A. Sleeping Rooms Room Cost
Is traditionally the main product of any hotel. A Analysis, one must look at what it cost the hotel to
hotel’s primary purpose is to provide keep a room up and running in relation to what that
accommodation. room is sold for to the average guest.
Room rate- the price of each room. Food Cost
Occupancy – is the measurement of how many Is defined as the cost of a particular food item in
rooms are sold each night versus how many rooms relation to the price for which it is sold. The cost is
the hotel has available to sell. often measured as a percentage.
B. Meeting / Function Space Captive Audience
Group Function Is defined as guest who are staying at the hotel and
Can be a meeting meal, dance, exposition will, for convenience and lack of other options, utilize
or any gathering of more than one person. the outlets in the hotel.
REVENUE SOURCES Opportunity Cost
Revenue sources Sleeping rooms at a hotel are considered a
perishable commodity.
a. Selling the space for a specified period.
The proceeds from the renting of these Each night, when a room goes unsold, the hotel
rooms is called room rental. loses that opportunity to ever sell it again. A hotel
cannot regain that opportunity
b. Providing the food and beverage service in
these rooms. This revenue is called Group Catering Contribution
banquet or catering service Is defined as the catering business acquired by a
C. Outlet / Ancillary Revenue Sources hotel that has all, or a major portion of, the attendees
staying at the hotel itself.
Outlet
Prepared by:
Is defined as a food and beverage point of
sale. Ex. Restaurant, bars, lounges and Ms. Charlene P. Morillo
Instructor
other outlets.
Ancillary
Revenue sources outside of sleeping rooms
or food/beverage.
Ex. Hotel’s business center, golf course,
tennis center, audio/visual services or gift
shop. Others sources include
products/services available inside the guest
room.
You might also like
- Fo - History of HotelsDocument3 pagesFo - History of Hotelsakiza.cavanNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Hospitality IndustryDocument47 pagesIntroduction to Hospitality IndustryKhatelyn lañojanNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document15 pagesModule 1Jen BoNo ratings yet
- Sha611 Hotel Real Estate ParticipantsDocument2 pagesSha611 Hotel Real Estate Participantsnhật minh phạm trầnNo ratings yet
- Opsman ReviewerDocument3 pagesOpsman ReviewerKris Tel YbañezNo ratings yet
- Housekeeping Training MaterialsDocument67 pagesHousekeeping Training MaterialsAgung Prasetyo Wibowo100% (3)
- Analisis Foda AirbnbDocument4 pagesAnalisis Foda AirbnbEliana MorilloNo ratings yet
- Hotel Ownership Models and Affiliation TypesDocument3 pagesHotel Ownership Models and Affiliation TypesAlie GurreaNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document10 pagesCH 2api-421468107No ratings yet
- Module 3.2Document9 pagesModule 3.2Jessica RoseNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document15 pagesModule 1goyalnandaniNo ratings yet
- Aoam (Prelim)Document8 pagesAoam (Prelim)Elizabeth YaoNo ratings yet
- Operational Issues and Organizational Structure in HotelsDocument23 pagesOperational Issues and Organizational Structure in HotelsJessie Jr. GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Hayes HOM 03e IM RevDocument390 pagesHayes HOM 03e IM RevNgọc Anh Kate100% (2)
- Function Space Revenue PDFDocument16 pagesFunction Space Revenue PDFFelipe Andres Araneda GallardoNo ratings yet
- Forms of Ownership in A Hotel IndustryDocument7 pagesForms of Ownership in A Hotel IndustryAnnie VargheseNo ratings yet
- Front Office Operations: Module - 6BDocument16 pagesFront Office Operations: Module - 6BSuneel SharmaNo ratings yet
- Hotel FM Report LatestDocument27 pagesHotel FM Report LatestTickson TanNo ratings yet
- Facilities Management: Topic 1Document22 pagesFacilities Management: Topic 1sim hamimNo ratings yet
- 01 Areas in Room Division PresentationDocument30 pages01 Areas in Room Division PresentationRishina CabilloNo ratings yet
- Case 2 AirbnbDocument6 pagesCase 2 AirbnbNikitaNo ratings yet
- TQM and Customer Service Models in Hospitality IndustryDocument3 pagesTQM and Customer Service Models in Hospitality IndustryFlorian M. GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing Five ForcesDocument3 pagesFactors Influencing Five ForcesVIJAYA MNo ratings yet
- Where Would You Like To Stay?: o Think of The Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Type o Which Would You Choose? Why?Document7 pagesWhere Would You Like To Stay?: o Think of The Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Type o Which Would You Choose? Why?Alie GurreaNo ratings yet
- The Role and Importance of Hospitality & GuestDocument10 pagesThe Role and Importance of Hospitality & GuestHossein SalaarNo ratings yet
- Case Study Safety at Downtown HotelDocument10 pagesCase Study Safety at Downtown HotelJana Andrea LoriegaNo ratings yet
- Jeraldine Romero Bshm4a RMH Activity 3Document20 pagesJeraldine Romero Bshm4a RMH Activity 3Jeraldine RomeroNo ratings yet
- General Introduction: 1.1. How Airbnb OperatesDocument3 pagesGeneral Introduction: 1.1. How Airbnb OperatesTrà Kiều ThuNo ratings yet
- Ntroduction To Ospitality AND Ourism: Room Division OperationsDocument64 pagesNtroduction To Ospitality AND Ourism: Room Division OperationsΒασιλεία ΕυαγγέλουNo ratings yet
- Tmpe ReviewerDocument6 pagesTmpe ReviewerDafney Jane C. ProcesoNo ratings yet
- Written Document: Background of The ScenarioDocument6 pagesWritten Document: Background of The ScenarioPrasan Xangxa RaiNo ratings yet
- Pipez Final DeliverableDocument45 pagesPipez Final Deliverableapi-661174679No ratings yet
- Hfo Prelim ReviewerDocument12 pagesHfo Prelim ReviewerStephanie DuranNo ratings yet
- Universidad Tecnológica de La Riviera Maya Name: Citlali Guadalupe Solís VelascoDocument3 pagesUniversidad Tecnológica de La Riviera Maya Name: Citlali Guadalupe Solís VelascoCtlali SolisNo ratings yet
- Business Case Study - Entertainment ParkDocument8 pagesBusiness Case Study - Entertainment ParkShivaniNo ratings yet
- ROOM-RATES-AND-INTERDEPARTMENTAL-COMMUNICATIONDocument17 pagesROOM-RATES-AND-INTERDEPARTMENTAL-COMMUNICATIONRochell Serranillo BanicoNo ratings yet
- Question 1 Case AirbnbDocument2 pagesQuestion 1 Case AirbnbQuynh Phuong PhamNo ratings yet
- JD - Relationship ManagerDocument1 pageJD - Relationship ManagerAbhishek TiwariNo ratings yet
- MONTANO - Emerging Tech TrendsDocument3 pagesMONTANO - Emerging Tech TrendsEstela Marie MontanoNo ratings yet
- Four Stages of The Guest CycleDocument3 pagesFour Stages of The Guest Cyclemaniza manillaNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Reservation Management System Case Study: Grand Ville HotelsDocument8 pagesDesign and Implementation of Reservation Management System Case Study: Grand Ville HotelsShablamoNo ratings yet
- Action Plan-Front Office Department Analysis Action To Be Taken Objectives Personnel Involved/ In-Charge Time Fram eDocument7 pagesAction Plan-Front Office Department Analysis Action To Be Taken Objectives Personnel Involved/ In-Charge Time Fram eMaricar Llamado Puño50% (2)
- Internal Control: OrganisationsDocument18 pagesInternal Control: OrganisationsINFO STATIONERSNo ratings yet
- First City Providential College: Rate DesignationsDocument25 pagesFirst City Providential College: Rate DesignationsAngel BambaNo ratings yet
- Room Tariff StructureDocument9 pagesRoom Tariff StructurenevilleatnibrNo ratings yet
- Written Document Background of The Scenario: 1.introduction of Hospitality IndustryDocument6 pagesWritten Document Background of The Scenario: 1.introduction of Hospitality IndustryPrasan Xangxa RaiNo ratings yet
- Best Practices in Hotel OperationsDocument14 pagesBest Practices in Hotel OperationsImee S. YuNo ratings yet
- Competitive Analysis of Sleeping PodsDocument51 pagesCompetitive Analysis of Sleeping PodsRALPH JOSEPH SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Front Office ServicesDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Front Office Serviceskpop stanNo ratings yet
- 21M133 Sourabh Kumar Service MarketingDocument3 pages21M133 Sourabh Kumar Service Marketingsourabh kumarNo ratings yet
- Role of Housekeeping in Hospitality IndustryDocument181 pagesRole of Housekeeping in Hospitality IndustrySriviraja Rani100% (1)
- HOSPA RM Ebook (V2) - Guia PráticoDocument95 pagesHOSPA RM Ebook (V2) - Guia PráticomarianapedropintoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Quality ServiceDocument8 pagesReviewer in Quality ServiceLittle GiantNo ratings yet
- Business Model Canvas - Air BNB ExampleDocument2 pagesBusiness Model Canvas - Air BNB ExampleSemon AungNo ratings yet
- Hotel FranchiseDocument10 pagesHotel FranchiseTariku HailuNo ratings yet
- Operations Management ReviewerDocument2 pagesOperations Management ReviewerMary Ianne Therese GumabongNo ratings yet
- Airbnb: National Economics University Adfanced Finance ProgramDocument12 pagesAirbnb: National Economics University Adfanced Finance ProgramKaddy JennerNo ratings yet
- Services Marketing Airbnb Audit 1 PDFDocument22 pagesServices Marketing Airbnb Audit 1 PDFhrishikeshNo ratings yet
- Outline L2 Tourism Hospitality MarketingDocument3 pagesOutline L2 Tourism Hospitality MarketingPaul Christian DayandayanNo ratings yet
- Don Honorio Ventura State University: College of Hospitality and Tourism ManagementDocument2 pagesDon Honorio Ventura State University: College of Hospitality and Tourism ManagementPrincess Aquilla KimNo ratings yet
- Don Honorio Ventura State University: College of Hospitality and Tourism ManagementDocument5 pagesDon Honorio Ventura State University: College of Hospitality and Tourism ManagementPrincess Aquilla KimNo ratings yet
- Don Honorio Ventura State University: College of Hospitality and Tourism ManagementDocument2 pagesDon Honorio Ventura State University: College of Hospitality and Tourism ManagementPrincess Aquilla KimNo ratings yet
- Don Honorio Ventura State University: College of Hospitality and Tourism ManagementDocument5 pagesDon Honorio Ventura State University: College of Hospitality and Tourism ManagementPrincess Aquilla KimNo ratings yet
- Don Honorio Ventura State University: College of Hospitality and Tourism ManagementDocument2 pagesDon Honorio Ventura State University: College of Hospitality and Tourism ManagementPrincess Aquilla KimNo ratings yet
- 6025 Business Studies Form 5 ProjectDocument7 pages6025 Business Studies Form 5 ProjectsimbamundawararaNo ratings yet
- Analisis Biaya Standar Sebagai Alat Pengendali Biaya Produksi (Studi Pada Perusahaan Meubel "WIJAYANTI", Ngadiboyo, Rejoso, Nganjuk Tahun 2013)Document9 pagesAnalisis Biaya Standar Sebagai Alat Pengendali Biaya Produksi (Studi Pada Perusahaan Meubel "WIJAYANTI", Ngadiboyo, Rejoso, Nganjuk Tahun 2013)Jihan NurulNo ratings yet
- 13 - Findings and Suggestion PDFDocument9 pages13 - Findings and Suggestion PDFKhushboo GuptaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Financial Management: SubjectDocument7 pagesStrategic Financial Management: SubjectVijay SinghNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis of APLDocument15 pagesRatio Analysis of APLTusarkant BeheraNo ratings yet
- Econophysics - The Physics of Money and MarketDocument4 pagesEconophysics - The Physics of Money and MarketAbhijit Kar Gupta100% (3)
- Managing Financial ServicesDocument5 pagesManaging Financial ServicesUmang GoelNo ratings yet
- Big Data AnalyticsDocument8 pagesBig Data AnalyticsNoamanNo ratings yet
- Cadbury Dairy Milk Marketing ProjectDocument14 pagesCadbury Dairy Milk Marketing ProjectAnand singhNo ratings yet
- Ojaswi GoyalDocument7 pagesOjaswi GoyalojukhouNo ratings yet
- Need and Importance of Business EthicsDocument3 pagesNeed and Importance of Business Ethicspriya0301100% (1)
- Tuscan Lifestyles Case, Customer Lifetime ValueDocument4 pagesTuscan Lifestyles Case, Customer Lifetime ValueJeff Lien100% (4)
- Qualification Institute Board/University Year % / CgpaDocument1 pageQualification Institute Board/University Year % / CgpaBharatSubramonyNo ratings yet
- Name of Faculty: Gauri Shankar Sharma Subject: RPS Semester: V Session: 2021-22 (Odd Sem) Branch: EE Batch: A Unit: V Date of Submission: 11/11/21Document30 pagesName of Faculty: Gauri Shankar Sharma Subject: RPS Semester: V Session: 2021-22 (Odd Sem) Branch: EE Batch: A Unit: V Date of Submission: 11/11/21PRABHAT KUMARNo ratings yet
- Demo - Nism 5 A - Mutual Fund ModuleDocument7 pagesDemo - Nism 5 A - Mutual Fund ModuleDiwakarNo ratings yet
- Bill Ackman Pershing Square Long StarbucksDocument43 pagesBill Ackman Pershing Square Long Starbucksmarketfolly.com100% (5)
- Brand Visibility of Dollar Industries LtdDocument79 pagesBrand Visibility of Dollar Industries LtdKHUSHAL MITTAL 1650424No ratings yet
- Price Levied Is Inclusive For All Items As Listed Terms & Conditions Apply OOS - Out of ScopeDocument1 pagePrice Levied Is Inclusive For All Items As Listed Terms & Conditions Apply OOS - Out of ScopeSaid AlbadaaiNo ratings yet
- ITC Supply Chain AnalysisDocument2 pagesITC Supply Chain AnalysisR AnandaNo ratings yet
- SWIFT Sugarcane Juice LaunchDocument12 pagesSWIFT Sugarcane Juice LaunchParvezMridhaNo ratings yet
- Answers To Chapter 15 QuestionsDocument12 pagesAnswers To Chapter 15 Questionssharan678950% (4)
- Capital Asset Pricing Model: Econ 487Document45 pagesCapital Asset Pricing Model: Econ 487yassine0077No ratings yet
- "Mutual Fund: Lump Sum Investment VS SIP": Presented By, SaritaDocument23 pages"Mutual Fund: Lump Sum Investment VS SIP": Presented By, SaritaSarita GurnuleNo ratings yet
- Day2 1Document111 pagesDay2 1Antariksh ShahwalNo ratings yet
- What Is The Role of Managerial Economics in Different Functional Areas of BusinessDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Role of Managerial Economics in Different Functional Areas of BusinessFahad ButtNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Practice Problem Set #1: Time Value of MoneyDocument18 pagesSolutions To Practice Problem Set #1: Time Value of MoneyraymondNo ratings yet
- B.E Analysis: Dr. Raza Ali KhanDocument11 pagesB.E Analysis: Dr. Raza Ali KhanFarjad ArifNo ratings yet
- Kasus Chapter 2-AnswerDocument3 pagesKasus Chapter 2-Answermadesugandhi100% (1)
- IBM Assignment 3Document2 pagesIBM Assignment 3Le PhucNo ratings yet
- Fin440 Chapter 17Document21 pagesFin440 Chapter 17Md. Shaikat Alam Joy 1421759030No ratings yet
- Dealers of Lightning: Xerox PARC and the Dawn of the Computer AgeFrom EverandDealers of Lightning: Xerox PARC and the Dawn of the Computer AgeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (88)
- Waiter Rant: Thanks for the Tip—Confessions of a Cynical WaiterFrom EverandWaiter Rant: Thanks for the Tip—Confessions of a Cynical WaiterRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (487)
- The War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesFrom EverandThe War Below: Lithium, Copper, and the Global Battle to Power Our LivesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- The Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumFrom EverandThe Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (12)
- The United States of Beer: A Freewheeling History of the All-American DrinkFrom EverandThe United States of Beer: A Freewheeling History of the All-American DrinkRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (7)
- The Kingdom of Prep: The Inside Story of the Rise and (Near) Fall of J.CrewFrom EverandThe Kingdom of Prep: The Inside Story of the Rise and (Near) Fall of J.CrewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (25)
- The Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyFrom EverandThe Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyNo ratings yet
- Summary: Unreasonable Hospitality: The Remarkable Power of Giving People More than They Expect by Will Guidara: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: Unreasonable Hospitality: The Remarkable Power of Giving People More than They Expect by Will Guidara: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (5)
- Dot Complicated: Untangling Our Wired LivesFrom EverandDot Complicated: Untangling Our Wired LivesRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Vulture Capitalism: Corporate Crimes, Backdoor Bailouts, and the Death of FreedomFrom EverandVulture Capitalism: Corporate Crimes, Backdoor Bailouts, and the Death of FreedomNo ratings yet
- Pick Three: You Can Have It All (Just Not Every Day)From EverandPick Three: You Can Have It All (Just Not Every Day)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Freight Dispatcher Training: How to Build and Run a Successful Truck Dispatching Business Without Owning a Single TruckFrom EverandFreight Dispatcher Training: How to Build and Run a Successful Truck Dispatching Business Without Owning a Single TruckRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- AI Superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the New World OrderFrom EverandAI Superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the New World OrderRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (398)
- So You Want to Start a Podcast: Finding Your Voice, Telling Your Story, and Building a Community that Will ListenFrom EverandSo You Want to Start a Podcast: Finding Your Voice, Telling Your Story, and Building a Community that Will ListenRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (35)
- Women's Work: The First 20,000 Years: Women, Cloth, and Society in Early TimesFrom EverandWomen's Work: The First 20,000 Years: Women, Cloth, and Society in Early TimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (190)
- Blood, Sweat, and Pixels: The Triumphant, Turbulent Stories Behind How Video Games Are MadeFrom EverandBlood, Sweat, and Pixels: The Triumphant, Turbulent Stories Behind How Video Games Are MadeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (335)
- Build: An Unorthodox Guide to Making Things Worth MakingFrom EverandBuild: An Unorthodox Guide to Making Things Worth MakingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (121)
- Data-ism: The Revolution Transforming Decision Making, Consumer Behavior, and Almost Everything ElseFrom EverandData-ism: The Revolution Transforming Decision Making, Consumer Behavior, and Almost Everything ElseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (12)
- Becoming Trader Joe: How I Did Business My Way and Still Beat the Big GuysFrom EverandBecoming Trader Joe: How I Did Business My Way and Still Beat the Big GuysRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Copywriting Secrets: How Everyone Can Use the Power of Words to Get More Clicks, Sales, and Profits...No Matter What You Sell or Who You Sell It To!From EverandCopywriting Secrets: How Everyone Can Use the Power of Words to Get More Clicks, Sales, and Profits...No Matter What You Sell or Who You Sell It To!Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- The Toyota Way (Second Edition): 14 Management Principles from the World's Greatest ManufacturerFrom EverandThe Toyota Way (Second Edition): 14 Management Principles from the World's Greatest ManufacturerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (121)
- The Machine That Changed the World: The Story of Lean Production-- Toyota's Secret Weapon in the Global Car Wars That Is Now Revolutionizing World IndustryFrom EverandThe Machine That Changed the World: The Story of Lean Production-- Toyota's Secret Weapon in the Global Car Wars That Is Now Revolutionizing World IndustryRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- Rainmaker: Superagent Hughes Norton and the Money Grab Explosion of Golf from Tiger to LIV and BeyondFrom EverandRainmaker: Superagent Hughes Norton and the Money Grab Explosion of Golf from Tiger to LIV and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)