Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Scalars and Vectors: Scalar: Vector
Uploaded by
abrahamrv44Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Scalars and Vectors: Scalar: Vector
Uploaded by
abrahamrv44Copyright:
Available Formats
Scalars and Vectors
Mehrdad Negahban (1999)
Scalar: A quantity like mass or temperature which only has a magnitude
Vector: A quantity like heat flux or force which has both a magnitude and a direction
(denoted by a bold faced character, an underlined character, or a character with a arrow
on it)
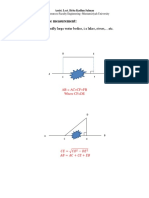
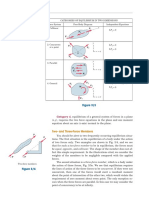
Vector Addition: Vector Addition follows the parallelogram law described be the figure
Resolution of a Vector: A vector can be resolved along different directions using the
parallelogram rule. The figure shows how one resolves vector c into
components a and b which are along the given directions
The math you need:
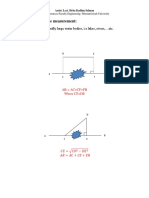
o For a right triangle:
a2+ b2 = c2
Source URL: http://emweb.unl.edu/negahban/em223/note2/note2.htm
Saylor URL: http://www.saylor.org/courses/ME102
© Mehrdad Negahban Saylor.org
Used by permission. Page 1 of 3
tan() = b/a
sin() = b/c
cos() = a/c
o For a general triangle:
Sine law:
Cosine law:
Source URL: http://emweb.unl.edu/negahban/em223/note2/note2.htm
Saylor URL: http://www.saylor.org/courses/ME102
© Mehrdad Negahban Saylor.org
Used by permission. Page 2 of 3
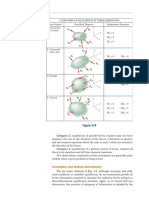
o A line intersecting parallel lines:
Source URL: http://emweb.unl.edu/negahban/em223/note2/note2.htm
Saylor URL: http://www.saylor.org/courses/ME102
© Mehrdad Negahban Saylor.org
Used by permission. Page 3 of 3
You might also like
- Kato, Kurokawa, Saito - Number Theory I. Fermat's Dream SDocument157 pagesKato, Kurokawa, Saito - Number Theory I. Fermat's Dream SJohnny80% (5)
- Area Moment of Inertia, Denoted by IDocument9 pagesArea Moment of Inertia, Denoted by IДрагослав БјелицаNo ratings yet
- Maths IGCSE Quick Revision RecoveredDocument6 pagesMaths IGCSE Quick Revision RecoveredShifa RizwanNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual: Prepared byDocument10 pagesSolutions Manual: Prepared bychiragNo ratings yet
- Enset Bambili Baccalaureat Mathematics 2013Document4 pagesEnset Bambili Baccalaureat Mathematics 2013Arcel MoubeNo ratings yet
- Vectors - Notebook November 23, 2017Document3 pagesVectors - Notebook November 23, 2017The LegendaryCarrotMasterNo ratings yet
- PhysicsSE 10 Ch03 PowerPointsDocument42 pagesPhysicsSE 10 Ch03 PowerPointsmkdatosNo ratings yet
- Nsejs Reshuffling-Test: 1. PhysicsDocument8 pagesNsejs Reshuffling-Test: 1. PhysicsSarthak ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1Document5 pagesMidterm 1estifanos.sefiw.17No ratings yet
- MCQ DTSDocument3 pagesMCQ DTSraja93satNo ratings yet
- 0606 Y13 SP 1 PDFDocument16 pages0606 Y13 SP 1 PDFGloria TaylorNo ratings yet
- Mathematics/Eng Eco/Basic Eng Trivia Examination Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument6 pagesMathematics/Eng Eco/Basic Eng Trivia Examination Multiple Choice QuestionsMarc Danielle G Josue IINo ratings yet
- DELHIDocument7 pagesDELHIPriyanka DubeyNo ratings yet
- DPP2Document4 pagesDPP2Sneha MalikNo ratings yet
- ch03 HW KeyDocument7 pagesch03 HW KeyNasser SANo ratings yet
- Trigo Cheatsheet Less AppDocument3 pagesTrigo Cheatsheet Less ApptowgayNo ratings yet
- Mcqs PhysicsDocument55 pagesMcqs PhysicsZeeshan100% (1)
- For Practice Trigonometric FormulasDocument2 pagesFor Practice Trigonometric FormulasDin FerizovićNo ratings yet
- Altitude Equation DerivationDocument4 pagesAltitude Equation DerivationdanilorodrNo ratings yet
- CH 22Document63 pagesCH 22mariamNo ratings yet
- CH 03Document10 pagesCH 03Qassem MohaidatNo ratings yet
- Outline 3 Supersonic WedgeDocument10 pagesOutline 3 Supersonic WedgetktdNo ratings yet
- Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics: SciencedirectDocument10 pagesTheoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics: SciencedirectDevan1984No ratings yet
- Gs2022 QP PhyDocument21 pagesGs2022 QP PhyAkNo ratings yet
- Physics 2122 Week 1 10 by Kuya CharlesDocument15 pagesPhysics 2122 Week 1 10 by Kuya CharlesChoe Yoek SoekNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21: Types of Interfaces: Coherent, Semi-Coherent, and IncoherentDocument7 pagesLecture 21: Types of Interfaces: Coherent, Semi-Coherent, and IncoherentSudeepta MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Obstacles During The Measurement:: The Obstacles Are Genearally Large Water Bodies, I.E Lakes, Rivers, EtcDocument6 pagesObstacles During The Measurement:: The Obstacles Are Genearally Large Water Bodies, I.E Lakes, Rivers, EtcbalsamNo ratings yet
- Obstacles During The Measurement:: The Obstacles Are Genearally Large Water Bodies, I.E Lakes, Rivers, EtcDocument6 pagesObstacles During The Measurement:: The Obstacles Are Genearally Large Water Bodies, I.E Lakes, Rivers, EtcroseNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Mec420 Jan 2018 - s1 - AnswerDocument14 pagesFinal Exam Mec420 Jan 2018 - s1 - AnswerIrfan SyafiqNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument9 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentSai Rahul KakiNo ratings yet
- Phys 202 Midterm 3 EquationsDocument1 pagePhys 202 Midterm 3 EquationsNoah GrafNo ratings yet
- TRIGONOMETRYDocument4 pagesTRIGONOMETRYPENDON, JORELLENo ratings yet
- Bgcse Maths Pp3 2022Document12 pagesBgcse Maths Pp3 2022Tshegofatso Legadiko100% (1)
- Competishun: PhysicsDocument18 pagesCompetishun: Physicsgojosatoru101001No ratings yet
- Week7Quiz AnswersDocument4 pagesWeek7Quiz AnswersChin AliciaNo ratings yet
- Lecture-6 - Power Systems 3rd YearDocument4 pagesLecture-6 - Power Systems 3rd YearIraqi for infoNo ratings yet
- Vector Class Notes and QuestionDocument2 pagesVector Class Notes and QuestionConstantine ByzantineNo ratings yet
- EE2 Mathematics: Vector Calculus: J. D. GibbonDocument31 pagesEE2 Mathematics: Vector Calculus: J. D. GibbonJasmy PaulNo ratings yet
- Solutions of Triangle: Nurture CourseDocument28 pagesSolutions of Triangle: Nurture CourseGrag Me100% (1)
- PHYS 212 AnswersDocument19 pagesPHYS 212 AnswersJiaqi TangNo ratings yet
- Ch3 Numerical Methods Lecture Notes Part OneDocument4 pagesCh3 Numerical Methods Lecture Notes Part OneAbdiqani Mohamed AdanNo ratings yet
- MSE101 Final Examination 2018 AnswerDocument14 pagesMSE101 Final Examination 2018 Answerعبدالملك جمالNo ratings yet
- Math 9Document5 pagesMath 9Absy BunsayNo ratings yet
- Second Test of EMT PDFDocument3 pagesSecond Test of EMT PDFkamran100% (1)
- MT - Phys2 - Summer 23 - Version A - With AnswersDocument6 pagesMT - Phys2 - Summer 23 - Version A - With AnswersaamerbolookiNo ratings yet
- What Is The Formula For Taking Load From Two Way Slab For Beam DesignDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Formula For Taking Load From Two Way Slab For Beam DesignDeep Debnath100% (1)
- HW#4 TrigonometryDocument94 pagesHW#4 Trigonometrymr.bagssy loopNo ratings yet
- Emf HW 1Document1 pageEmf HW 1Krunal PatelNo ratings yet
- 2013 MywbutDocument7 pages2013 MywbutagniNo ratings yet
- MIT2 25F13 Vector ProblemDocument12 pagesMIT2 25F13 Vector ProblemIhab Omar0% (1)
- Genetics FinalDocument11 pagesGenetics Finalmrx2312.rxNo ratings yet
- Problem29 61Document1 pageProblem29 61IENCSNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Vibration - DampingDocument13 pagesMechanical Vibration - Dampingcsdharankar2No ratings yet
- 3.1 Conceptual Questions: Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two or Three Dimensions VectorsDocument18 pages3.1 Conceptual Questions: Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two or Three Dimensions VectorsnourNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Electricchargesfield Tp04Document6 pages12 Physics Electricchargesfield Tp04AVNEESH CHAUBEYNo ratings yet
- Physics - Ch5 VectorsDocument25 pagesPhysics - Ch5 VectorsNur IffatinNo ratings yet
- CH 24Document71 pagesCH 24mariamNo ratings yet
- Static Force Analysis ExampleDocument2 pagesStatic Force Analysis Exampleabrahamrv44No ratings yet
- Exportar Páginas Meriam Kraige Engineering Mechanics Statics 7th txtbk1Document1 pageExportar Páginas Meriam Kraige Engineering Mechanics Statics 7th txtbk1abrahamrv44No ratings yet
- 1.2 Beams With Uniform Load and End Moments: CHAPTER 1: Analysis of BeamsDocument8 pages1.2 Beams With Uniform Load and End Moments: CHAPTER 1: Analysis of Beamsabrahamrv44No ratings yet
- Exportar Páginas Meriam Kraige Engineering Mechanics Statics 7th Txtbk4Document1 pageExportar Páginas Meriam Kraige Engineering Mechanics Statics 7th Txtbk4abrahamrv44No ratings yet
- Beam Calculator Online (Calculate The Reactions - Draws Bending Moment - Shear Force - Axial Force) - 8Document2 pagesBeam Calculator Online (Calculate The Reactions - Draws Bending Moment - Shear Force - Axial Force) - 8abrahamrv44No ratings yet
- Diagrama Del Cuerpo Libre - EstáticaDocument13 pagesDiagrama Del Cuerpo Libre - Estáticaabrahamrv44No ratings yet
- Introducing PolyCAD 9Document11 pagesIntroducing PolyCAD 9Ramon Velasco StollNo ratings yet
- Fold in Origami and Unfold MathDocument8 pagesFold in Origami and Unfold Mathapi-21940065No ratings yet
- Maths: National InteractiveDocument5 pagesMaths: National InteractiveBIKAS KUMARNo ratings yet
- Prefi Calculus DraftDocument2 pagesPrefi Calculus Draftralph crucilloNo ratings yet
- MIT18 100CF12 Prob Set 4Document5 pagesMIT18 100CF12 Prob Set 4Muhammad TaufanNo ratings yet
- Physics Lquiz (Tov1) 04 by - @askvilengDocument4 pagesPhysics Lquiz (Tov1) 04 by - @askvilengPranav GaurNo ratings yet
- Solid Mechanics FormulasDocument26 pagesSolid Mechanics FormulasLindi NewmanNo ratings yet
- Notes On Anger Issues 07Document12 pagesNotes On Anger Issues 07aishathleen abdullaNo ratings yet
- Abbott Intro To Real Analysis CH 3 NotesDocument2 pagesAbbott Intro To Real Analysis CH 3 NotesYTANo ratings yet
- Practice Worksheet Paper 2Document9 pagesPractice Worksheet Paper 2Ertuğrul Eren DurakNo ratings yet
- Lecture7, Linear TransformationDocument36 pagesLecture7, Linear TransformationHisham MostafaNo ratings yet
- CN Chap05 - Equilibrium of A Rigid BodyDocument13 pagesCN Chap05 - Equilibrium of A Rigid BodyJohn Mark Manalo RosalesNo ratings yet
- 5.6 RSGDocument3 pages5.6 RSGHuan HuanNo ratings yet
- Statistical Shape Analysis in ArchaeologyDocument5 pagesStatistical Shape Analysis in ArchaeologyYosueNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3-Circle Area and PerimeterDocument14 pagesMODULE 3-Circle Area and PerimetersyarelNo ratings yet
- Class-X Mathematics H.O.T.S. Summative Assessment-II 2016-17Document2 pagesClass-X Mathematics H.O.T.S. Summative Assessment-II 2016-17Apex Institute50% (2)
- Conditionally Exponential Convex FunctionsDocument6 pagesConditionally Exponential Convex FunctionsManar MaherNo ratings yet
- STPM Trials 2009 Math T Paper 1 (Terengganu)Document3 pagesSTPM Trials 2009 Math T Paper 1 (Terengganu)Jessica JonesNo ratings yet
- Surveying NotesDocument10 pagesSurveying NotesCarl NellasNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes (Chapter 2.2 (B) Double Integrals As Surface Area)Document4 pagesLecture Notes (Chapter 2.2 (B) Double Integrals As Surface Area)shinee_jayasila2080No ratings yet
- Pdms Piping Modeling CommandsDocument25 pagesPdms Piping Modeling Commandsvijayakumar2015No ratings yet
- Dinamica - Presentacion 2Document24 pagesDinamica - Presentacion 2Jhonny CarbonóNo ratings yet
- Chambered AirfoilDocument8 pagesChambered AirfoilrevandifitroNo ratings yet
- Amath 4Document14 pagesAmath 4ericdravenll6427No ratings yet
- Milling Cutter NomenclatureDocument3 pagesMilling Cutter NomenclatureKhabir Islam50% (4)
- Motion in Two DimensionsDocument14 pagesMotion in Two Dimensionselchappoo kalboNo ratings yet
- Homework Class 4 21 Dec 2019 1576914976Document3 pagesHomework Class 4 21 Dec 2019 1576914976sudhamblrNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry WS3 PDFDocument6 pagesTrigonometry WS3 PDFTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Line Lines PDFDocument10 pagesMathematics Line Lines PDFKaranveer DhingraNo ratings yet