Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHEM 111 Physical Chemistry I Problem Set 1-Gases
Uploaded by
julia cortezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CHEM 111 Physical Chemistry I Problem Set 1-Gases
Uploaded by
julia cortezCopyright:
Available Formats
CHEM 111
Physical Chemistry I
Problem Set 1- Gases
1. Biogas produced by anaerobic fermentation of pig manure at 30 °C and 1 atm pressure has
the following mole percent composition: 65% CH4, 34% CO2 and 1% H2. Calculate the
a. apparent molar mass;
b. weight percent of CH4 in the gas;
c. density of the gas; and
d. density of the gas which is saturated with water vapor at 30 °C and 1 atm pressure.
The vapor pressure of water at 30 °C is 31.8 mmHg.
2. A typical composition of natural gas at 30 °C and 1 atm (in mol%) is 96.0% CH4, 3.2% N2 and
0.8% CO2.
a. Calculate the apparent molar mass and the density of the gas.
b. Calculate the maximum load that can be carried by a 100-liter balloon filled with the gas
(Assume that the atmosphere is dry air with molar mass of 28.9 g/mol)
c. If the gas is saturated with water vapor at 30 °C, calculate the apparent molar mass
and density of the gas (the vapor pressure of water at 30 °C is 31.8 mm Hg).
3. What mass can be supported by a balloon containing 1000 L of helium at 27°C and 1 atm
pressure if the atmosphere is dry and composed (in mole percent) of 75% N2 and 25% O2?
4. Calculate the water vapor that will condense per cubic meter of wet air at 80% relative
humidity and 40 °C when it passes through an air conditioner at 10 °C. The vapor pressures of
water at 10 °C and 40 °C are 9.2 and 55.3 mmHg. Assume that the air coming out of the air
conditioner at 10 °C is at 50% relative humidity.
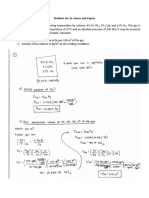
5. Starting with the Berthelot equation:
a. derive the power series expansion for the compression factor Z in terms of 1/ .
b. derive the equation for the Boyle temperature in terms of a, b and R.
c. write down the mathematical implications of an inflection point for the pressure-volume
plot.
d. derive the equations for the critical parameters c, Tc and Pc in terms of a, b and R.
e. derive the reduced form of the given equation of state.
You might also like
- PS5 Gases-and-Vapors SaturationDocument2 pagesPS5 Gases-and-Vapors SaturationLizvel Keith TorresNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - HumidificationDocument2 pagesTutorial 1 - HumidificationwafinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6 Mixtures BDA 3043 - Thermodynamics II Winardi SaniDocument3 pagesTutorial 6 Mixtures BDA 3043 - Thermodynamics II Winardi SaniwanpudinNo ratings yet
- ChE ReviewerDocument27 pagesChE ReviewerJohn Paul Rodriguez100% (2)
- CHE 202 Tutorial QuestionDocument6 pagesCHE 202 Tutorial QuestionFawziyyah AgboolaNo ratings yet
- Gases and Vapors (Part 1)Document2 pagesGases and Vapors (Part 1)Khristel PenoliarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SheetsDocument10 pagesChemistry Sheetshebaneyar74No ratings yet
- Avs-Activity No.1 DIRECTIONS: Copy and Solve The Following Problems CorrectlyDocument1 pageAvs-Activity No.1 DIRECTIONS: Copy and Solve The Following Problems CorrectlyJoseph MondragonNo ratings yet
- MIN-534 Tut 1Document2 pagesMIN-534 Tut 1ABHIRAM K BNo ratings yet
- MEC551 Tutorial 5 (Aircondition)Document2 pagesMEC551 Tutorial 5 (Aircondition)Imhaziq ZamriNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Fr3 Test BankDocument9 pagesAP Chemistry Fr3 Test BankzeustamNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 3a: Gases and VaporsDocument8 pagesProblem Set 3a: Gases and VaporsShane PatulotNo ratings yet
- Exercise GasesDocument4 pagesExercise GasesAri AdiantariNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 5A - Single-Phase System Exercise 1Document26 pagesLecture Notes 5A - Single-Phase System Exercise 1TaanzNo ratings yet
- ChE CalculationsDocument39 pagesChE Calculationsneil loNo ratings yet
- Solucionario Maron Capítulo 1Document8 pagesSolucionario Maron Capítulo 1anon_788159847No ratings yet
- r050210803 Chemical Process CalculationsDocument8 pagesr050210803 Chemical Process CalculationsSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Process Calculation Py Qs by Dev SirDocument97 pagesProcess Calculation Py Qs by Dev SirVIKAS SINGHNo ratings yet
- Phase Equilibrium ProblemsDocument2 pagesPhase Equilibrium ProblemsAravind Rajesh100% (1)
- 07a30802 Chemical Process CalculationsDocument8 pages07a30802 Chemical Process CalculationsAshwin Nandagiri100% (1)
- Internal II Question Paper Etd Set IIDocument2 pagesInternal II Question Paper Etd Set IItagoreboopathyNo ratings yet
- Problemario B.E. Segundo ParcialDocument4 pagesProblemario B.E. Segundo ParcialjorgeNo ratings yet
- Gases & The Kinetic-Molecular TheoryDocument20 pagesGases & The Kinetic-Molecular TheoryAshley Marie ChildersNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 QDocument4 pagesTutorial 2 QRicky SaputraNo ratings yet
- Problems 1 0100103304 2-59Document1 pageProblems 1 0100103304 2-59Jj LewandyNo ratings yet
- CPC QB Full 2013Document7 pagesCPC QB Full 2013Arul KamalakumarNo ratings yet
- CPCDocument39 pagesCPCNaresh NaniNo ratings yet
- Homework #2 For Chemical Process Calculation PDFDocument2 pagesHomework #2 For Chemical Process Calculation PDFUrgen TamangNo ratings yet
- Chem 1Document3 pagesChem 1Lovey ChandiNo ratings yet
- Question PART 2 (2023)Document6 pagesQuestion PART 2 (2023)01khanh26No ratings yet
- Asignment - Chapter 1 PDFDocument3 pagesAsignment - Chapter 1 PDFDo Cong Minh100% (1)
- Test Bank Chapter 5Document7 pagesTest Bank Chapter 5Ahmed ZakiNo ratings yet
- End Sem Questions CLPC 11 Process CalculationsDocument2 pagesEnd Sem Questions CLPC 11 Process CalculationsSujalNo ratings yet
- Cpe 420 Tutorial 2Document3 pagesCpe 420 Tutorial 2Muhamad Baihakhi ShamsudinNo ratings yet
- Assisgnment-I - Material and Energy Balance - Autumn 2022Document2 pagesAssisgnment-I - Material and Energy Balance - Autumn 2022Konain Raza AnsariNo ratings yet
- ME132 Thermodynamics Nov Dec 2007Document4 pagesME132 Thermodynamics Nov Dec 2007ARUNGREESMANo ratings yet
- AIRCONDITIONING ProblemsDocument28 pagesAIRCONDITIONING Problemsعبدالرحمن منصورNo ratings yet
- CHEM 2820 Problem Set 1Document3 pagesCHEM 2820 Problem Set 1Vicente JonathanNo ratings yet
- Gas MixDocument2 pagesGas MixLena BshnaweNo ratings yet
- Chang Chemistry - Assessment Chapter 5Document8 pagesChang Chemistry - Assessment Chapter 5haha_le12No ratings yet
- Ejercicios FisicoquimicaDocument5 pagesEjercicios FisicoquimicaLuiz MarquezineNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Chapter 5Document9 pagesTest Bank Chapter 5geenah111No ratings yet
- 2020 Dec. CHT203-ADocument3 pages2020 Dec. CHT203-AjainsNo ratings yet
- Paper On StoichometryDocument6 pagesPaper On StoichometryanupzodNo ratings yet
- GASES Free Response WorksheetDocument4 pagesGASES Free Response WorksheetJJNo ratings yet
- Azucar HojaDocument9 pagesAzucar HojaJorge PerezNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument4 pagesUnit VNallappan Rajj ANo ratings yet
- Day 2 1 PDFDocument17 pagesDay 2 1 PDFChristianNo ratings yet
- Chemical Process CalculationsDocument8 pagesChemical Process Calculationsbhaskar5377No ratings yet
- CHE 111P Seatwork 1Document3 pagesCHE 111P Seatwork 1Dodjie MaestrecampoNo ratings yet
- Assignment OneDocument1 pageAssignment Oneabenezer gezahegnNo ratings yet
- PHYCHEMDocument12 pagesPHYCHEM22-00248No ratings yet
- Tut 5Document1 pageTut 5me21b105No ratings yet
- PC Question Paper Nov 2021Document4 pagesPC Question Paper Nov 2021venkatesan sivaramuNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document15 pagesProblem Set 1YanYan Carpio25% (4)
- States of Matter - Entrance Exam Model Question Paper 2012Document3 pagesStates of Matter - Entrance Exam Model Question Paper 2012Vinod BhaskarNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)