Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MIN-534 Tut 1
Uploaded by
ABHIRAM K BCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MIN-534 Tut 1
Uploaded by
ABHIRAM K BCopyright:
Available Formats
Air-conditioning and
Mechanical & Industrial Ventilation-MIN-534
Engineering Department
Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee
Tutorial
MIN – 106: Engineering -1
Thermodynamics
Tutorial 6: Gas-Vapour Mixtures and Air Conditioning
1. Atmospheric air with a relative humidity of 40 percent is held at 35oC and 970
mbar. Determine (a) the specific humidity, (b) the dew point temperature, (c)
the enthalpy in kJ/kg dry air, where h = 0 at 0oC, and (d) the specific volume
in m3/kg dry air.
2. Atmospheric air at 1 bar has a dry bulb temperature of 27°C and a wet bulb
temperature of 20oC. Determine, through the use of steam- table and
equations (a) the humidity ratio, (b) the relative humidity, and (c) enthalpy, in
kJ/k. (based on h = 0 at 0oC for dry air).
3. By use of a psychrornetric chart, estimate the missing information in the table
below. The system is a mixture of water vapour and dry air, and the total
pressure is 1 bar.
Dry bulb Wet bulb Relative Sp. Sp. Enthalpy Sp. Volume
temp. C temp. C humidity Humidity kJ/kg dry air m3/kg dry air
o o
DBT WBT ϕ kg/kg dry
air
ω
(a) 27 21 - - - -
(b) 28 19 - - - -
(c) 24 - - 0.012 - -
(d) - - 60 0.010 - -
(e) 26 - - - 65 -
4. Atmospheric air at 101 kPa, 30oC and 60 percent relative humidity flows over
a set of cooling coils at an inlet flow rate of 1500 m 3/min. The liquid which
condenses is removed from the system at 17oC. Subsequently heating of the
air results in a final state of 25oC and 60% relative humidity. Determine (a) the
heat removed in the cooling section, (b) the heat added in the heating section
and (c) the amount of vapour condensed, in kg/min.
5. Atmospheric air at 34°C and 20 percent relative humidity passes through an
evaporative cooler until the final temperature is 21°C. Calculate (a) the
amount of liquid water added in kg/kg dry air, (b) the final relative humidity,
and (c) the minimum possible final temperature. Calculate the required
property data, and check these values against the psychrometric chart.
6. Atmospheric air at 28°C and 10 percent relative humidity passes through an
evaporative cooler until the final relative humidity is 80 percent. Find the
amount of water added to the air and the final dry bulb temperature by
employing the psychrometric chart.
7. Atmospheric air at 36°C and 10 percent relative humidity passes through an
evaporative cooler.
(a) On the basis of the psychrometric chart, what is the minimum temperature
that could be reached by this process?
(b) If the final dew point temperature is 14°C, estimate from psychrometric
chart how much water is added in the cooler and what the final
temperature is.
8. An air stream at 8°C and 30 percent relative humidity is first heated to 32°C.
Steam at 10 bar is then introduced into a humidification section until the air
reaches a state of 30°C and 50 percent relative humidity at 1 bar. Determine
(a) the heat added in kJ/kg dry air, (b) the mass of steam required, in kg
steam/kg dry air, and (c) the temperature of the steam added, in °C.
9. An atmospheric air stream at 10°C and 40 percent relative humidity is first
heated to 33°C and then passed through an evaporative cooler until the
temperature reaches 20°C. Calculate the required property data, using steam
table data, and determine (a) the heat added, (b) the water added, and (c) the
final relative humidity. Check calculations by employing the psychrometric
chart.
10. In an air conditioning process 50 m3/min of outside air at 29°C and 80 percent
relative humidity is mixed adiabatically with 100 m3/min of inside air initially at
20°C and 30 percent relative humidity. Determine for the resultant mixture (a)
the dry bulb temperature, (b) the wet bulb temperature, (c) the humidity ratio,
and (d) the relative humidity. Compute initial property values required, using
steam table data where necessary, and compare values with the
psychrometric chart if the pressure is 0.10 MPa.
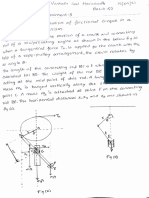
11. Water enters a cooling tower at 33°C and leaves at 22°C. The tower receives
10,000 m3/min of atmospheric air at 1 bar, 20°C and 40 percent relative
humidity. The air exit condition is 32oC and 90 percent relative humidity.
Determine (a) the mass flow rate of dry air passing through the tower, in
kg/min, (b) the mass flow rate of entering water in kg/min, and (c) the amount
of water evaporated in kg/min.
12. It is desired to cool water from 40 to 26°C . The cooling tower receives 800
m3/min of atmospheric air at 1 bar with dry bulb and wet bulb temperatures of
29 and 21oC. The outlet water rate is 1250 kg/mm, and the exit air relative
humidity is 100 percent. Determine (a) the outlet temperature of the air, and
(b) the evaporation rate of the water.
You might also like
- Atomic Structure and Periodicity TutorialDocument188 pagesAtomic Structure and Periodicity TutorialCayo Farias100% (2)
- ME 405 Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Question BankDocument6 pagesME 405 Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Question BankDeepakNo ratings yet
- Global Warming and Climate ChangeDocument617 pagesGlobal Warming and Climate Changefasolăi100% (6)
- Grade 10-12 Geography Pamphlet on Solar System, Earth, Latitudes & LongitudesDocument80 pagesGrade 10-12 Geography Pamphlet on Solar System, Earth, Latitudes & LongitudesBøßß PrîñçéNo ratings yet
- Keshe - Message in A BottleDocument21 pagesKeshe - Message in A BottleD.Domenico100% (2)
- Technological Institute of the Philippines Heat and Mass Transfer Problem SetDocument6 pagesTechnological Institute of the Philippines Heat and Mass Transfer Problem SetBia TordecillasNo ratings yet
- R&AC Assigment-cum-Turorial Questions - Unit-V - 2017Document6 pagesR&AC Assigment-cum-Turorial Questions - Unit-V - 2017sivakrishna100% (1)
- Chapter 08Document14 pagesChapter 08Gianne Karl AlmarinesNo ratings yet
- Episode 3: Production of Synthesis Gas by Steam Methane ReformingDocument31 pagesEpisode 3: Production of Synthesis Gas by Steam Methane ReformingSAJJAD KHUDHUR ABBASNo ratings yet
- HW-6, Ch-14Document9 pagesHW-6, Ch-14Natalie NinachuuNo ratings yet
- GEM 447E VENTILATION AND AIR-CONDITIONING SYSTEMSDocument2 pagesGEM 447E VENTILATION AND AIR-CONDITIONING SYSTEMSIzzah HzmhNo ratings yet
- Air Con Past Exam QuestionsDocument5 pagesAir Con Past Exam QuestionsSamarth PatelNo ratings yet
- Etd 2mechDocument2 pagesEtd 2mechgsudhanta1604No ratings yet
- Tut 5Document1 pageTut 5me21b105No ratings yet
- Tutorial 6 Mixtures BDA 3043 - Thermodynamics II Winardi SaniDocument3 pagesTutorial 6 Mixtures BDA 3043 - Thermodynamics II Winardi SaniwanpudinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial PsychrometryDocument2 pagesTutorial PsychrometryKaran Kumawat0% (2)
- ThermodynamicsDocument1 pageThermodynamicsBong AlgaNo ratings yet
- Gas MixDocument2 pagesGas MixLena BshnaweNo ratings yet
- Problem Set - MidtermDocument3 pagesProblem Set - MidtermJohn Paul JacalanNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems On Air Conditioning SystemDocument1 pagePractice Problems On Air Conditioning Systemsushil.vgiNo ratings yet
- SH - No.1 ACDocument3 pagesSH - No.1 ACيوسف عبيد خليفةNo ratings yet
- Q13&14Document2 pagesQ13&14Duaa GadoraaNo ratings yet
- Gas Mixture Chapter ProblemsDocument2 pagesGas Mixture Chapter ProblemsDhenil ManubatNo ratings yet
- Q13&14Document2 pagesQ13&14Izzah HzmhNo ratings yet
- Unit VDocument4 pagesUnit VNallappan Rajj ANo ratings yet
- Assignment OneDocument1 pageAssignment Oneabenezer gezahegnNo ratings yet
- AIRCONDITIONING ProblemsDocument28 pagesAIRCONDITIONING Problemsعبدالرحمن منصورNo ratings yet
- Mixtures and Solutions Review QuestionsDocument5 pagesMixtures and Solutions Review Questionsmozam haqNo ratings yet
- Energy ProblemsDocument7 pagesEnergy ProblemsprpunkskaterNo ratings yet
- Internal II Question Paper Etd Set IIDocument2 pagesInternal II Question Paper Etd Set IItagoreboopathyNo ratings yet
- Problems 1 0100103304 2-59Document1 pageProblems 1 0100103304 2-59Jj LewandyNo ratings yet
- Psych ExercisDocument2 pagesPsych ExercisJohn Jonel CasupananNo ratings yet
- Psych Rome TryDocument2 pagesPsych Rome TryAaditya VijayNo ratings yet
- Energy Conservation in BuildingsDocument2 pagesEnergy Conservation in BuildingsAlex MarkNo ratings yet
- Airconditioning KnecDocument7 pagesAirconditioning KnecManfred GithinjiNo ratings yet
- MEC551 Tutorial 5 (Aircondition)Document2 pagesMEC551 Tutorial 5 (Aircondition)Imhaziq ZamriNo ratings yet
- Instructions:: No of Pages: 2 Course Code: 12M504Document2 pagesInstructions:: No of Pages: 2 Course Code: 12M504CRAZY PIANO PLAYERNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Air Conditioning (Chapter 7 - Mec551) : APRIL 2009Document2 pagesTutorial - Air Conditioning (Chapter 7 - Mec551) : APRIL 2009Muhammad FirdawsNo ratings yet
- ME132 Thermodynamics Nov Dec 2007Document4 pagesME132 Thermodynamics Nov Dec 2007ARUNGREESMANo ratings yet
- Thermal Engineering AssignmentsDocument8 pagesThermal Engineering Assignmentsnims1964No ratings yet
- SMP Cooling Towers QUESTIONs-AssignedDocument2 pagesSMP Cooling Towers QUESTIONs-AssignedEsther0% (2)
- Assignment 3Document2 pagesAssignment 3HajiasifAliNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument3 pagesDepartment of Mechanical EngineeringJames Patrick TorresNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning (ERE411) Faculty of Eng. (EECE) Energy Resources Eng. Dept. Sheet Chapter 15 4 Year EREDocument1 pageRefrigeration and Air Conditioning (ERE411) Faculty of Eng. (EECE) Energy Resources Eng. Dept. Sheet Chapter 15 4 Year EREHamdy AboaliNo ratings yet
- AC Problems-1Document1 pageAC Problems-1SjsinssjNo ratings yet
- 2 - Air Conditioning Processes QuestionsDocument2 pages2 - Air Conditioning Processes QuestionswhaleeNo ratings yet
- Rac Problems Set 1Document6 pagesRac Problems Set 1Mohammad Umair100% (1)
- I.E.S-(Conv.)-2000 Air Conditioning Design CalculationsDocument6 pagesI.E.S-(Conv.)-2000 Air Conditioning Design CalculationsYogesh DanekarNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument16 pagesThermoİBRAHİM HAZAR AYTULUNNo ratings yet
- Gas Vapors Mixtures Sample Problems Easiest Problems of Your LifeDocument2 pagesGas Vapors Mixtures Sample Problems Easiest Problems of Your LifeSam DyNo ratings yet
- RAC Tutorial Sheet 5Document2 pagesRAC Tutorial Sheet 5Ankur SachdevaNo ratings yet
- SESSION 10 - TAKE HOME EXAMDocument1 pageSESSION 10 - TAKE HOME EXAMExy DelgadoNo ratings yet
- CL 321 Separation Processes Assignment 6 Psychrometric PropertiesDocument1 pageCL 321 Separation Processes Assignment 6 Psychrometric PropertiesPinjala AnoopNo ratings yet
- Tugas RSKT 1 Kelas ADocument1 pageTugas RSKT 1 Kelas ADimas AnandaNo ratings yet
- Me40 Final Exam PracticeDocument4 pagesMe40 Final Exam Practicegrinci76No ratings yet
- CHEM 111 Physical Chemistry I Problem Set 1 - GasesDocument1 pageCHEM 111 Physical Chemistry I Problem Set 1 - Gasesjulia cortezNo ratings yet
- HW #4: Psychrometric properties and processesDocument2 pagesHW #4: Psychrometric properties and processesshum kennethNo ratings yet
- HW04 PDFDocument2 pagesHW04 PDFOhh YeckokiwiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 - RefrigerationDocument2 pagesAssignment 4 - RefrigerationJade PurezaNo ratings yet
- 13qus DME KecDocument4 pages13qus DME KecstrombornNo ratings yet
- 1418395957089Document3 pages1418395957089MahendraMeenaNo ratings yet
- Copy of Assign Chap 6 Version 2Document6 pagesCopy of Assign Chap 6 Version 2Khairul HishamNo ratings yet
- INDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ROORKEE Mail - Resume Verification - Information of Project Undertaken in MIN-303 During Autum Semester 2020-2021Document6 pagesINDIAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ROORKEE Mail - Resume Verification - Information of Project Undertaken in MIN-303 During Autum Semester 2020-2021ABHIRAM K BNo ratings yet
- BTP Notice-I Finalization of Supervisor, Title & BatchDocument1 pageBTP Notice-I Finalization of Supervisor, Title & BatchABHIRAM K BNo ratings yet
- Conversion Percentage FormulaDocument1 pageConversion Percentage FormulaABHIRAM K BNo ratings yet
- 2021-22 AutumnDocument5 pages2021-22 AutumnABHIRAM K BNo ratings yet
- Me PDFDocument340 pagesMe PDFeklavya koshtaNo ratings yet
- MIN-300 Inventory First AssessmentDocument2 pagesMIN-300 Inventory First AssessmentABHIRAM K BNo ratings yet
- Me PDFDocument340 pagesMe PDFeklavya koshtaNo ratings yet
- Development of a real-world inventory management model for a hospital pharmacyDocument5 pagesDevelopment of a real-world inventory management model for a hospital pharmacyABHIRAM K BNo ratings yet
- MIN - 301 Experiment-3 18117045Document4 pagesMIN - 301 Experiment-3 18117045ABHIRAM K BNo ratings yet
- MIN-534 Tut 1Document2 pagesMIN-534 Tut 1ABHIRAM K BNo ratings yet
- Module 1: FireDocument8 pagesModule 1: FireMarielle CaralipioNo ratings yet
- Rain DescriptionDocument3 pagesRain DescriptionAnonymous WGtE7JNo ratings yet
- Fortnightly Test Series: (For NEET-2022)Document8 pagesFortnightly Test Series: (For NEET-2022)Shekhar JainNo ratings yet
- DRRR Unit 3 L1-L3Document4 pagesDRRR Unit 3 L1-L3Mary Rose TuburanNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Lecture NoteDocument4 pagesWeek 1 Lecture Notealibaba011No ratings yet
- Zainal (2001) - Prediction of Performance of A Downdraft Gasifier Using Equilibrium Modeling For Different Biomass Materials PDFDocument17 pagesZainal (2001) - Prediction of Performance of A Downdraft Gasifier Using Equilibrium Modeling For Different Biomass Materials PDFHotib PerwiraNo ratings yet
- 9A03604 Refrigeration & Air ConditioningDocument4 pages9A03604 Refrigeration & Air ConditioningsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Section One Introduction To Radioactive MaterialsDocument20 pagesSection One Introduction To Radioactive MaterialsSalkoNo ratings yet
- Dryness FractionDocument3 pagesDryness FractionNavpreet KumarNo ratings yet
- Famous Early ChemistsDocument6 pagesFamous Early ChemistsAHMAD FAHRUDIN100% (1)
- Electric Vehicles A SmartDocument5 pagesElectric Vehicles A SmarthahaNo ratings yet
- Reading Report Student's Name: Junior Cardenas Colana Teacher's NameDocument2 pagesReading Report Student's Name: Junior Cardenas Colana Teacher's NameJuniorCardenasNo ratings yet
- The Early History of Quantum Tunneling - Merzbacher - Phys Today 2002-08Document6 pagesThe Early History of Quantum Tunneling - Merzbacher - Phys Today 2002-08Carlos AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Highway Materials: ASPHALT CONCRETE-PropertiesDocument8 pagesChapter 2: Highway Materials: ASPHALT CONCRETE-PropertiesUnknown_unknown_unknownNo ratings yet
- Sustainability AssessmentDocument9 pagesSustainability AssessmentEbrahim AminiNo ratings yet
- Production, Activation, and Applications of Biochar in Recent TimesDocument33 pagesProduction, Activation, and Applications of Biochar in Recent TimesNelson SouzaNo ratings yet
- Geotech 1 Lecture 2 StructureDocument38 pagesGeotech 1 Lecture 2 StructureAli AsadNo ratings yet
- Corrections - Food WebDocument6 pagesCorrections - Food WebTopNo ratings yet
- WatershedDocument7 pagesWatersheddivyakalpaNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - Rtu Lab ReportDocument19 pagesGroup 3 - Rtu Lab ReportUI Career ExpoNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCSE Physics P2 Final Exam 15 - 16 PDFDocument19 pagesEdexcel GCSE Physics P2 Final Exam 15 - 16 PDFPaul BurgessNo ratings yet
- DNV Alternative Fuels For Containerships Methanol-Ammonia Web FinalDocument100 pagesDNV Alternative Fuels For Containerships Methanol-Ammonia Web Finalbjarne9800No ratings yet
- 6-Overview of Radiation Practices IndusrialDocument59 pages6-Overview of Radiation Practices Indusrialkirandevi1981No ratings yet
- Grammar - Attempt Review - OkDocument15 pagesGrammar - Attempt Review - OkAnas SumarhadiNo ratings yet
- Biology Syllabus 2009Document4 pagesBiology Syllabus 2009Samuel EshunNo ratings yet