Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 3.3: Hardscapes.: Class Notes: Landscape Architecture
Uploaded by
Sejal RankaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module 3.3: Hardscapes.: Class Notes: Landscape Architecture
Uploaded by
Sejal RankaCopyright:
Available Formats
MODULE 3.3: HARDSCAPES.
1. Write a note of Hardscape OR Explain the following terms
a) Paving
b) Retaining walls
c) Shelters
d) Seating
e) Tree guard
f) Planters
g) Lighting
h) Traffic control and protection
i) Signage
j) Sculptures
k) Fences
ANSWER: Hardscape consist of elements such as
a) Paving:
Paving is the method of creating durable surfaces laid
down on an area intended to sustain traffic (vehicular
or foot traffic). The most common modern paving
methods are stone and concrete. In the past, brick was
extensively used. Today, permeable paving methods
are beginning to be used more for low-impact
roadways and walkways.
(c) Smitha Navda,BMSCE,2012
b) Retaining walls: They are used to create
relatively level areas at different elevations,
where changes in elevation can’t be
accomplished by grading because of limited
horizontal distances or where changes of grade
must be accomplished with least disturbance to
topography.
CLASS NOTES: LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTURE
th
5 Semester ‘A’ Section
• c) Shelters: Shelters are often
major elements of a site. They
can be used as a visual
reference to the historical or
cultural character of a place.
The choice of an appropriate
design idiom should reflect an
understanding of the social and
cultural forces that have given
the place its unique identity.
Shelters often serve as focal
points of a site they should be:
1. Readily visible
2. Easily accessible
3. Sited to take advantage of
views
4. Sited adjacent to major
pedestrian routes
TYPES:
• Tensile Fabric Structures
• Pergolas: A pergola is a garden
feature forming a shaded walk
or passageway of pillars that
support cross-beams and a sturdy open lattice, upon which woody vines are trained.
• Trellis: An open framework, latticework, or design of wood or steel in a vertical wall
or horizontal overhead. Vegetation supported vertically or horizontally.
• Canopies: A covered shelter for protection from sun, rain, snow, tree-litter, etc., that
generally projects over a sidewalk, driveway, entry, window or similar area.
• Gazebos: A gazebo is a pavilion structure, sometimes octagonal, in parks, gardens,
and spacious public areas.
(c) Smitha Navda,BMSCE,2012
d) Seating: Seating should be sited so as to:
• Be sheltered from wind
• Take advantage of site views
• Be situated back of circulation paths
• Provide a variety of options for pedestrians such as sunlight, shade, multitude,
activity, formality, informality etc.
CLASS NOTES: LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTURE
th
5 Semester ‘A’ Section
They include benches, stoops, ledges, seat
walls, steps etc.
e) Tree guard:
Tree guard: An element used for the protection
of tree growth in the younger stage and it is also
(c) Smitha Navda,BMSCE,2012
used to maintain nutrients and moisture levels in
cold area.
f) Planters:
Planters: small containers
for growth of plants.
Standard sizes are
diameter 12”, 18”22”, 24”
and 30”.
CLASS NOTES: LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTURE
th
5 Semester ‘A’ Section
g) Lighting: The height of light standards is
the single factor that most directly
determines the quality of the light and the
consequent ambience of the site.
• Exterior lighting can be generally
categorised as:
1. Decorative lighting
2. Vehicular use lighting
3. General site lighting
4. Pedestrian use lighting
5. Feature lighting
Bollards: Bollards are low profile
sturdy posts embedded in the floor to
protect some other fragile structures or
to exclude vehicles from pedestrian
precincts.
The message they convey here is
not of `STAY OUT' but that of `COME IN
ON YOUR FEET'.
Where vehicular traffic is to be
restricted for a few hours only, light
weight temporary bollards are also used.
Bollards unlike railings do not
form visually barriers.
(c) Smitha Navda,BMSCE,2012
CLASS NOTES: LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTURE
th
5 Semester ‘A’ Section
H) Traffic control and protection:
(c) Smitha Navda,BMSCE,2012
CLASS NOTES: LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTURE
th
5 Semester ‘A’ Section
i) Signage’s: Signage is any kind of visual graphics created
to display information to a particular audience.
This is typically manifested in the form of way finding
information in places such as streets or outside of buildings
j) Sculpture: Sculpture is three-dimensional artwork
created by shaping or combining different materials.
• Materials may be worked by removal such as carving; or they may be assembled
such as by welding.
• Different materials like stone,wood,steel,marbel etc. can be used.
(c) Smitha Navda,BMSCE,2012
k) Fences: Fences, screens & walls are used for a variety of reasons:
• Visual privacy
• Physical inclusion
• Control of people & animals
• Modification of environmental factors like noise, wind,
sunlight etc.
• Purely aesthetic reasons
CLASS NOTES: LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTURE
th
5 Semester ‘A’ Section
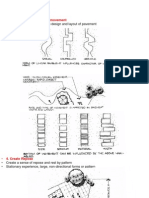
DESIGN INFORMATION
• An integral part of the architecture of the entire site.
• Should be compatible with adjacent buildings and fences or walls.
• should be of durable material such as brick, wood, wrought iron, decorative concrete
block or similar
• Fences should generally be stepped up or down to accommodate changes in
topography rather than sloping with the ground.
• Fences adjacent to sidewalks should be at least 12” or 1’ (30 cms) from the sidewalk.
INSTALLATION MATERIAL
• Limited Solid Material. All fences which have 50% or less solid material will be
considered limited solid material fences.
• Less than 50% solid material may be spaced eight feet (8’) on centre.
Example: chain link or split rail fences.
• Solid Material. All fences which have more than 50% solid materials will be
considered solid material fences.
• Types:Momumentalmetal,wooden,PVC,wire fence.
• All fences must be installed within or on the property lines. It is the property owner’s
responsibility to locate the property lines.
• A fence, a hedge or a wall located in a side yard or rear yard area adjacent to a
driveway, alley or street, must comply with the visibility triangle requirements.
(c) Smitha Navda,BMSCE,2012
CLASS NOTES: LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTURE
th
5 Semester ‘A’ Section
You might also like
- Hyper Shell RoofingDocument18 pagesHyper Shell Roofingವಿನಯ್ ಎಮ್. ಆರ್No ratings yet
- HardscapeDocument46 pagesHardscapeSindhu Swetha100% (1)
- Hillside Guidelines May202008Document51 pagesHillside Guidelines May202008ongkingcozarijaneNo ratings yet
- BUILDING MATERIALSDocument82 pagesBUILDING MATERIALSAleena AsifNo ratings yet
- Landscape Architecture: An IntroductionDocument19 pagesLandscape Architecture: An IntroductionAli WAHEEDNo ratings yet
- LANDSCAPE ARCHITECTURE CaspDocument11 pagesLANDSCAPE ARCHITECTURE CasptejasNo ratings yet
- Rural School FacilitiesDocument23 pagesRural School FacilitiesEducation JusticeNo ratings yet
- Food Court CriteriaDocument7 pagesFood Court CriteriaEzec OolNo ratings yet
- VennerDocument17 pagesVennerswathi sathupalliNo ratings yet
- Principles of Landscape DesignDocument17 pagesPrinciples of Landscape DesignAreeba Parvez100% (1)
- Glass and Glazing (Document)Document10 pagesGlass and Glazing (Document)maygracedigolNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet Shopping MallDocument4 pagesProblem Sheet Shopping Mallapi-3754256100% (2)
- Soft LandscapeDocument9 pagesSoft LandscapeAmal AmranNo ratings yet
- Industrial Design Guidelines PDFDocument76 pagesIndustrial Design Guidelines PDFjavier rangel argoteNo ratings yet
- Elective Report - Radhika KhandelwalDocument7 pagesElective Report - Radhika KhandelwalRadhika KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Site Planning and Landscape Design Course OverviewDocument114 pagesSite Planning and Landscape Design Course OverviewAnitha M RNo ratings yet
- Hardscape, Softscape and Waterscape Design ElementsDocument32 pagesHardscape, Softscape and Waterscape Design ElementsRojayneNo ratings yet
- FutureArc Crosswaters-3Q2007Document6 pagesFutureArc Crosswaters-3Q2007Leonardo MerardNo ratings yet
- Pioneer Landscape Architect Ravindra BhanDocument11 pagesPioneer Landscape Architect Ravindra BhanSuryNo ratings yet
- Plaza: Access To Features: The Design Team Must Ensure That Landscaping, Level Changes, or OtherDocument9 pagesPlaza: Access To Features: The Design Team Must Ensure That Landscaping, Level Changes, or OtherJavier PereiraNo ratings yet
- Ar8701 Landscape DesignDocument2 pagesAr8701 Landscape Designsiva raman100% (1)
- Jayasudha 2014 VernacularDwellingsThanjavur-SustainablePrinciplesDocument9 pagesJayasudha 2014 VernacularDwellingsThanjavur-SustainablePrinciplesshivaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Landscape DesignDocument10 pagesAdvanced Landscape DesignSomhita DasNo ratings yet
- Lighting in LandscapeDocument23 pagesLighting in LandscapeAksa RajanNo ratings yet
- HUGHES - Cator and Cribbage Construction of Northern PakistanDocument12 pagesHUGHES - Cator and Cribbage Construction of Northern PakistanFayaz JerovNo ratings yet
- Types of Flooring MaterialsDocument26 pagesTypes of Flooring MaterialsSanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Landscape Drainage Systems GuideDocument9 pagesLandscape Drainage Systems GuideDashuNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To Landscape Architecture PDFDocument31 pages1.introduction To Landscape Architecture PDFnaina100% (1)
- Introduction To Site Planning - 1 PDFDocument157 pagesIntroduction To Site Planning - 1 PDFXylish ReyesNo ratings yet
- Dampness in Buildings: Su Bmitted To: A R. Da Ma N D Eep KDocument26 pagesDampness in Buildings: Su Bmitted To: A R. Da Ma N D Eep Kaanchal jainNo ratings yet
- Contemporary GardenDocument5 pagesContemporary GardenShubhangi SinghNo ratings yet
- Institutional Framework For MGMT of Disasters in IndiaDocument55 pagesInstitutional Framework For MGMT of Disasters in Indiasaksham111No ratings yet
- Landscape Role in Hindu TemplesDocument12 pagesLandscape Role in Hindu Templesaishwarya ramakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Shading Devices VaishaliDocument12 pagesShading Devices VaishalivaishaliNo ratings yet
- Design Brief 2nd Year 4th Sem ADDocument8 pagesDesign Brief 2nd Year 4th Sem ADChinmay KumtakarNo ratings yet
- Macea GuidelinesDocument15 pagesMacea Guidelinesallendy valdezNo ratings yet
- Biophilic Synopsis PDFDocument57 pagesBiophilic Synopsis PDFAmirunnisaNo ratings yet
- 7 Ways To Enhance Indoor Environments With Biophilic DesignDocument5 pages7 Ways To Enhance Indoor Environments With Biophilic DesignTim KengNo ratings yet
- Water As A Design ElementDocument26 pagesWater As A Design ElementAkshita Saklani100% (1)
- 03 Landscape Study - Thoery For SlidesDocument24 pages03 Landscape Study - Thoery For SlidesMirnaalini SekarNo ratings yet
- Low Cost Housing Concrete Jacketed Earth Wall BuildingDocument18 pagesLow Cost Housing Concrete Jacketed Earth Wall BuildingramNo ratings yet
- Landscaping PDFDocument45 pagesLandscaping PDFDianaMocodeanNo ratings yet
- Roofing Materials Guide: Types, Specs & Installation for Rib RoofDocument54 pagesRoofing Materials Guide: Types, Specs & Installation for Rib RoofIntsik LvnNo ratings yet
- Landscaping Elements GuideDocument62 pagesLandscaping Elements GuideNitin Agarwal0% (1)
- Natural - Manmade Urban-Rural LandscapeDocument23 pagesNatural - Manmade Urban-Rural LandscapeSrishti MuruganNo ratings yet
- Grooming Standard Novotel BJB PDFDocument28 pagesGrooming Standard Novotel BJB PDFAriestya HandokoNo ratings yet
- Roof Garden Construction - Step by Step Details PDFDocument3 pagesRoof Garden Construction - Step by Step Details PDFNirbhay SinghNo ratings yet
- Chosen Journal-Biophilic Design Impact On Healthcare Facilities Interior Design in EgyptDocument12 pagesChosen Journal-Biophilic Design Impact On Healthcare Facilities Interior Design in Egyptvicky kosasihNo ratings yet
- Public, Semi-Public, and Private Spaces - Incite Architecture PDFDocument2 pagesPublic, Semi-Public, and Private Spaces - Incite Architecture PDFHildebrando Labrador0% (2)
- IX. TRUSS and ROOF SYSTEMSDocument38 pagesIX. TRUSS and ROOF SYSTEMSkriengsak ruangdechNo ratings yet
- 16.sustainable Landscape Case StudiesDocument77 pages16.sustainable Landscape Case StudiesBhanu Shankar SinghNo ratings yet
- Cost Effective Building Techniques ArchitectureDocument13 pagesCost Effective Building Techniques Architecturekit sparkNo ratings yet
- High Density FibreboardDocument10 pagesHigh Density FibreboardSanjay ShettyNo ratings yet
- Landscape PPT 02Document13 pagesLandscape PPT 02Ayon SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Our Jungle Camp Eco Resort Case StudyDocument8 pagesOur Jungle Camp Eco Resort Case StudyRITHWIK DINESH MADARIYILNo ratings yet
- Site Analysis Document SummaryDocument69 pagesSite Analysis Document SummaryZULKEFLE ISMAIL100% (2)
- Section 1 The Principles of Landscaping PDFDocument63 pagesSection 1 The Principles of Landscaping PDFUsama ZafarNo ratings yet
- Bamboo Construction & TechniquesDocument43 pagesBamboo Construction & TechniquesCzNo ratings yet
- Landscape Design Course OverviewDocument2 pagesLandscape Design Course OverviewAyeesha ANo ratings yet
- Exposé Mur de SoutenementDocument22 pagesExposé Mur de SoutenementJunior LNo ratings yet
- Guideline - Site Planning and DesignDocument9 pagesGuideline - Site Planning and DesignJosielynNo ratings yet
- Water in Landscape4Document19 pagesWater in Landscape4Sejal RankaNo ratings yet
- Elements of Landscape1Document36 pagesElements of Landscape1Sejal RankaNo ratings yet
- Plant Material and Their ApplicationDocument6 pagesPlant Material and Their ApplicationSejal RankaNo ratings yet
- Site Analysis Book FIA - 3Document15 pagesSite Analysis Book FIA - 3Sejal RankaNo ratings yet
- Final Last-A3 Landscape - EleDocument1 pageFinal Last-A3 Landscape - EleSejal RankaNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Pregnancy and Childbirth at the RVIDocument124 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Pregnancy and Childbirth at the RVIIcha KartichaNo ratings yet
- Systematic Technical Analysis Level 1Document199 pagesSystematic Technical Analysis Level 1Sejal RankaNo ratings yet
- Cmt1 Sample 2018Document44 pagesCmt1 Sample 2018ธรรม จักษ์100% (1)
- Practice Questions For CMT Level 1 Set 2Document24 pagesPractice Questions For CMT Level 1 Set 2gaurav67% (3)
- 5 Day Alaska Itinerary ADFTS 40Document1 page5 Day Alaska Itinerary ADFTS 40Sejal RankaNo ratings yet
- Landscape DrainDocument9 pagesLandscape DrainshaNo ratings yet
- Hard LandscapeDocument52 pagesHard LandscapeDharani Gowd100% (2)
- Landscape Architecture ResearchDocument58 pagesLandscape Architecture ResearchAr Meena JadounNo ratings yet
- Site Planning and Space ProgramDocument65 pagesSite Planning and Space ProgramJerzy Mae GloriosoNo ratings yet
- Landscape Design Elements and PrinciplesDocument45 pagesLandscape Design Elements and PrinciplesFirman MustariNo ratings yet
- Himalaya LandscapeDocument41 pagesHimalaya LandscapeHimalya HarryNo ratings yet
- Landscape and Hardscape Project ScheduleDocument5 pagesLandscape and Hardscape Project ScheduleIlham Januar SistiawanNo ratings yet
- Landscape: University of Tennessee, KnoxvilleDocument25 pagesLandscape: University of Tennessee, KnoxvilleThiviya BabuNo ratings yet
- Landscape DesignDocument200 pagesLandscape DesignDeepti ShiwakotiNo ratings yet
- Dayananda Sagar School of Architecture: 09 Arc 7.7 Landscape Architecture NotesDocument4 pagesDayananda Sagar School of Architecture: 09 Arc 7.7 Landscape Architecture NotesPrajwal PrakashNo ratings yet
- Site Planning and Landscape DesignDocument49 pagesSite Planning and Landscape DesignAnitha M RNo ratings yet
- 2 Updated Notes AR 803 Landscape Design & Site PlanningDocument142 pages2 Updated Notes AR 803 Landscape Design & Site PlanningNishma GuragaiNo ratings yet
- Landscape DesignDocument21 pagesLandscape DesignRuthNo ratings yet
- Landscape Architectural Design SoWDocument3 pagesLandscape Architectural Design SoWMaan BarmadaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Landscape Design 10092020Document19 pagesModule 1 Landscape Design 10092020Ar Jitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Hardscapes and Hardscapes ElementsDocument4 pagesHardscapes and Hardscapes ElementsineeNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Hardscape and SoftscapeDocument2 pagesThe Difference Between Hardscape and SoftscapeShubha100% (1)
- LANDSCAPEDocument66 pagesLANDSCAPEchaplinNo ratings yet
- Company Profile-2Document2 pagesCompany Profile-2Nisamudeen H KklNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Land Scapedesign (Autosaved) NewDocument14 pagesModule 1 Land Scapedesign (Autosaved) NewAr Jitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Module 3.3: Hardscapes.: Class Notes: Landscape ArchitectureDocument7 pagesModule 3.3: Hardscapes.: Class Notes: Landscape ArchitectureSejal Ranka100% (1)
- Hardscape Landscape ArchitectureDocument7 pagesHardscape Landscape Architectureangelfelix28No ratings yet
- Parliament Annexe Extension New Delhi: Submited By-Name - Chandan Kumar ROLL NO. - 1705026 B-Arch. Sem. - ViiiDocument15 pagesParliament Annexe Extension New Delhi: Submited By-Name - Chandan Kumar ROLL NO. - 1705026 B-Arch. Sem. - ViiiCHANDAN KUMARNo ratings yet
- Write Up of OxyzoneDocument17 pagesWrite Up of OxyzoneSINTU100% (1)
- Lecture 3 Softscaping Vs HardscapingDocument16 pagesLecture 3 Softscaping Vs Hardscapingkokoaldali2001No ratings yet
- Observations:: Residential Navyug Society, AhmedabadDocument5 pagesObservations:: Residential Navyug Society, AhmedabadRavnish BatthNo ratings yet
- 4.9.15 Elements of Landscape Architecture PDFDocument24 pages4.9.15 Elements of Landscape Architecture PDFShubhaNo ratings yet
- Landscaping For Beginners Step by Step Planning Your Outdoor Space Design Walkways Edges PatiosDocument96 pagesLandscaping For Beginners Step by Step Planning Your Outdoor Space Design Walkways Edges PatiosMustafa MalikNo ratings yet
- Application of Ecobrick As A Garden Hardscape Material: EcobricksDocument4 pagesApplication of Ecobrick As A Garden Hardscape Material: EcobricksTessya Raulia MeiraniNo ratings yet