Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Communication System Block Diagram (Basic)
Communication System Block Diagram (Basic)
Uploaded by
AfzalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Communication System Block Diagram (Basic)
Communication System Block Diagram (Basic)
Uploaded by
AfzalCopyright:
Available Formats
Communication System Block Diagram
(Basic)
• Source encoder converts message into message signal (bits)
• Transmitter converts message signal into format appropriate for channel
transmission (analog/digital signal)
• Channel conveys signal but may introduce attenuation, distortion, noise,
interference
• Receiver decodes received signal back to message signal
• Source decoder decodes message signal back into original message
308201- Communication Systems 8
Communication System Block Diagram
(Advanced)
• Source encoder compresses message to remove redundancy
• Encryption protects against eavesdroppers and false messages
• Channel encoder adds redundancy for error protection
• Modulator converts digital inputs to signals suitable for physical channel
308201- Communication Systems 9
Communication Channels
• Communication systems convert information into a format appropriate for
the transmission medium
• The channel is central to operation of a communication system
– Linear (e.g., mobile radio) or nonlinear (e.g., satellite)
– Time invariant (e.g., fiber) or time varying (e.g., mobile radio)
• The information-carrying capacity of a communication system is
proportional to the channel bandwidth
• Pursuit for wider bandwidth
– Copper wire: 1 MHz
– Coaxial cable: 100 MHz
– Microwave: GHz
– Optical fiber: THz
• The process of creating a signal suitable for transmission is called
‘modulation’
308201- Communication Systems 10
AM and FM Modulation
308201- Communication Systems 11
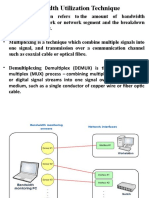
Multiplexing
• To combine multiple signals (analog or digital) for transmission over a
single line or media.
• A common type of multiplexing combines several low-speed signals for
transmission over a single high-speed connection.
• The following are several examples of different multiplexing methods:
– Space Division Multiplexing (SDM): each signal is assigned a different physical link
– Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) : each signal is assigned a different frequency
– Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) : each signal is assigned a fixed time slot in a fixed
rotation . A variant of it is the Statistical Time Division Multiplexing (STDM) where time
slots are assigned to signals dynamically to make better use of bandwidth
– Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) : each signal is assigned a particular
wavelength; used on optical fiber.
– Code Division Multiplexing (CDM) :The signals can be transmitted at the same time and
frequency band , but they can be made orthogonal by using special coding.
308201- Communication Systems 12
You might also like
- Integrated Electronics by Millman Halkias Solution ManualDocument5 pagesIntegrated Electronics by Millman Halkias Solution ManualPawan Nayak0% (2)
- Lecture No 2Document5 pagesLecture No 2Hadia RashidNo ratings yet
- 30820-Communication Systems: Week 1 - Lecture 1-3 (Ref: Chapter 1 of Text Book)Document26 pages30820-Communication Systems: Week 1 - Lecture 1-3 (Ref: Chapter 1 of Text Book)Furqan Ali CheemaNo ratings yet
- MultiplexingDocument42 pagesMultiplexingRijas RasheedNo ratings yet
- Electronic Communication: Recap and Way ForwardDocument45 pagesElectronic Communication: Recap and Way ForwardShawn MoyoNo ratings yet
- DemodulationDocument32 pagesDemodulationtuhafenijason05No ratings yet
- Chapter (2) : Introducing To Time-Division Multiplexing MultiplexingDocument55 pagesChapter (2) : Introducing To Time-Division Multiplexing MultiplexingIbrahim ElghawilNo ratings yet
- SonetsdhDocument66 pagesSonetsdhAbhishek gargNo ratings yet
- 30820-Communication Systems: Week 1 - Lecture 1-3 (Ref: Chapter 1 of Text Book)Document26 pages30820-Communication Systems: Week 1 - Lecture 1-3 (Ref: Chapter 1 of Text Book)Tooba SaharNo ratings yet
- Time Frequency MultiplexingDocument29 pagesTime Frequency MultiplexingNaheda ShkNo ratings yet
- SONETDocument35 pagesSONETfarjadarshadNo ratings yet
- Presented By:-: Dhrubajyoti AdakDocument26 pagesPresented By:-: Dhrubajyoti AdakJacob JacobNo ratings yet
- CH#5. MultiplexingDocument16 pagesCH#5. MultiplexingShining StarNo ratings yet
- Application of Multiplexing: Rio Aguilar, ECEDocument30 pagesApplication of Multiplexing: Rio Aguilar, ECERíõ EscanillaNo ratings yet
- Dcof Full Notes (Module 2)Document9 pagesDcof Full Notes (Module 2)Minhaj KmNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document55 pagesUnit 3Hema DarshanaNo ratings yet
- Data CommDocument5 pagesData CommShahbaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- ACN Unit2Document10 pagesACN Unit2Smit prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Physical LayerDocument46 pagesChapter 3 - Physical Layerhenok metaferiaNo ratings yet
- Multi-Channel Optical Systems LectureDocument20 pagesMulti-Channel Optical Systems Lecturebamlaku tekebaNo ratings yet
- Ec6004 Unit 4 PDFDocument44 pagesEc6004 Unit 4 PDFLaks hmiNo ratings yet
- 2 Overview CommunicationDocument46 pages2 Overview CommunicationFêyø Õrö MãñNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing: Principles of Communication Systems (PCS) EEE 351Document15 pagesMultiplexing: Principles of Communication Systems (PCS) EEE 351nabeel hasanNo ratings yet
- Digital Transmission: TE313: Introduction To Switching and TransmissionDocument24 pagesDigital Transmission: TE313: Introduction To Switching and TransmissionBaraka JungwaNo ratings yet
- DCC Chapter 2Document7 pagesDCC Chapter 2Khan Rahil AhmedNo ratings yet
- Multiple XingDocument34 pagesMultiple XingRafia ShoukatNo ratings yet
- RF ModulationDocument44 pagesRF Modulationanon_611424196No ratings yet
- Data CommunicationDocument114 pagesData CommunicationShikha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Data Communication - MultiplexingDocument42 pagesData Communication - MultiplexingAhmad Shdifat100% (1)
- Lecture-4: Data Communication and Computer NetworksDocument24 pagesLecture-4: Data Communication and Computer NetworksSaifuddin Mohammed TarekNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv Satellite Access 4.1 Modulation and Multiplexing: Voice, Data, VideoDocument22 pagesUnit Iv Satellite Access 4.1 Modulation and Multiplexing: Voice, Data, VideoBeuna.No ratings yet
- Multiplexing - Theory and ConceptDocument6 pagesMultiplexing - Theory and ConceptsolayanoNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument7 pagesINTRODUCTIONidatscribdNo ratings yet
- Articles: Time-Division Multiplexing 1 Frequency-Division Multiplexing 4 Multi-User MIMO 6Document14 pagesArticles: Time-Division Multiplexing 1 Frequency-Division Multiplexing 4 Multi-User MIMO 6Shirley HamamatsuNo ratings yet
- Chap1 Introd 2015Document19 pagesChap1 Introd 2015semakulaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document35 pagesChapter 01Syed Ariful Islam EmonNo ratings yet
- Com Chap 1 Lec 1Document33 pagesCom Chap 1 Lec 1Anwar MohammedNo ratings yet
- Natalie PresentationDocument13 pagesNatalie Presentationmilcentndhlovu251No ratings yet
- First Generation Optical NetworkDocument68 pagesFirst Generation Optical NetworkPonmalar Sivaraj50% (2)
- Multiple Access and Satellite CommunicationDocument72 pagesMultiple Access and Satellite CommunicationAnees KhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To TelecommunicationDocument14 pagesIntroduction To TelecommunicationUtkuNo ratings yet
- 4.0 Communication Systems (Basics) : Prepared By:-Ajay Kumar Kadel, Kathmandu Engg. CollegeDocument5 pages4.0 Communication Systems (Basics) : Prepared By:-Ajay Kumar Kadel, Kathmandu Engg. Collegeajaykumar988No ratings yet
- 6004 Week 1Document60 pages6004 Week 1Saifuddin Mohammed TarekNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 PDFDocument43 pagesLecture 1 PDF1saifulNo ratings yet
- Nepal Telecom Exam Preparation: (Level 7)Document38 pagesNepal Telecom Exam Preparation: (Level 7)Dipak Kumar NidhiNo ratings yet
- Time Division MuxDocument4 pagesTime Division MuxhardmanpersonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 NewDocument18 pagesChapter 3 NewCicie_RawkstarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document25 pagesLecture 01Danish ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- p1 - Pengantar Sistem Komunikasi 2022Document23 pagesp1 - Pengantar Sistem Komunikasi 2022Eyyad JamalNo ratings yet
- Chapter FourDocument33 pagesChapter FourAbrhamNo ratings yet
- Bandwidth Utilizations Technique.Document20 pagesBandwidth Utilizations Technique.chandaakhileshNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and Networking: Lecture - 6Document51 pagesData Communication and Networking: Lecture - 6HaroonĦammadiNo ratings yet
- GSM OptimizationDocument176 pagesGSM OptimizationAhmed YousryNo ratings yet
- DMRC ReportDocument22 pagesDMRC Reportprabal1234567No ratings yet
- Multiple XingDocument52 pagesMultiple XingDARRYL IVAN BODOLLONo ratings yet
- CHAP 2aDocument52 pagesCHAP 2aGANESAN ANo ratings yet
- Clase 2. Servicios WAN - Parte 1 PDFDocument71 pagesClase 2. Servicios WAN - Parte 1 PDFCarmita PinduisacaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Radio Access Technology: FrequencyDocument51 pagesMultiple Radio Access Technology: FrequencyaylateNo ratings yet
- Pspice Simulation of Feedback Control: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Document19 pagesPspice Simulation of Feedback Control: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- 2 PerceptionGDocument37 pages2 PerceptionGSyed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SignalsDocument53 pagesChapter 2 SignalsSyed AfzalNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductioDocument16 pages1 IntroductioSyed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Document20 pagesPower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- 7.13 Power Supply Control Input Voltage and Duty Ratio.: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Document12 pages7.13 Power Supply Control Input Voltage and Duty Ratio.: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Document18 pagesPower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Document25 pagesPower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Be Less Than The DC Term (Average Value)Document28 pagesBe Less Than The DC Term (Average Value)Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Creating A DC Voltage From An AC Source: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Document41 pagesCreating A DC Voltage From An AC Source: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Document25 pagesPower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 04Document4 pagesPower Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 04Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Pe 36 Ee17Document21 pagesPe 36 Ee17Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Assignment #02 - 15 Oct To 22 Oct 2021Document21 pagesAssignment #02 - 15 Oct To 22 Oct 2021Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 06Document19 pagesPower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 06Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
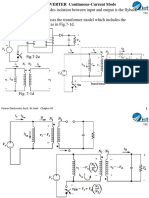
- Full-Wave Rectifier With RL-Source Load-Continuous Current: Power Electronics by D.W.Hart Chapter 04Document20 pagesFull-Wave Rectifier With RL-Source Load-Continuous Current: Power Electronics by D.W.Hart Chapter 04Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 06Document10 pagesPower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 06Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Continuous-Current Case: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 06Document20 pagesContinuous-Current Case: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 06Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Document13 pagesPower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- For Different Values of ALPHA: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Document16 pagesFor Different Values of ALPHA: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Document15 pagesPower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 01Document19 pagesPower Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 01Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Pe 26 Ee17Document23 pagesPe 26 Ee17Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D.W.Hart Chapter 04Document12 pagesPower Electronics by D.W.Hart Chapter 04Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 05Document20 pagesPower Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 05Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Resistive Load Creating A DC Component Using An Electronic SwitchDocument22 pagesResistive Load Creating A DC Component Using An Electronic SwitchSyed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 04Document13 pagesPower Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 04Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
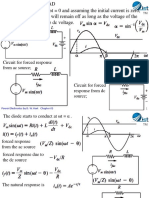
- Circuit For Forced Response From Ac Source : Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Document21 pagesCircuit For Forced Response From Ac Source : Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
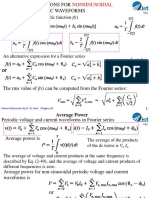
- Fourier Series For A Periodic Function F (T) : Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 02Document43 pagesFourier Series For A Periodic Function F (T) : Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 02Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
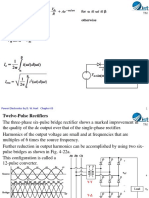
- Reducing Load Current Harmonics: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Document5 pagesReducing Load Current Harmonics: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Jara Exp-1Document9 pagesJara Exp-1diannesanjuan29No ratings yet
- PDFDocument31 pagesPDFAmit GhadeNo ratings yet
- Manual de Reparación Nikon fm2Document173 pagesManual de Reparación Nikon fm2JoseMiguelZerdosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To IoT (Internet of Thing)Document6 pagesIntroduction To IoT (Internet of Thing)Mohammad DerakhshaniNo ratings yet
- SAM ListDocument17 pagesSAM Listdundun92100% (3)
- Link Budget CalculatorDocument13 pagesLink Budget CalculatorYounesNo ratings yet
- Modbus Training PDFDocument75 pagesModbus Training PDFamruthkiranbabuji100% (4)
- Electrical Standards SLD Symbols Legend PDFDocument13 pagesElectrical Standards SLD Symbols Legend PDFBuyankhishig MonkhbaatarNo ratings yet
- BELINEA 101536 - Service ManualDocument41 pagesBELINEA 101536 - Service ManualAlexandru Daniel BuleuNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Physics NotesDocument100 pagesGrade 12 Physics NotesMemory SitambuliNo ratings yet
- Uec401 2017Document2 pagesUec401 2017g SinghNo ratings yet
- Integrated Deep Trench Capacitor in Si Interposer For CoWoS Heterogeneous Integration.Document4 pagesIntegrated Deep Trench Capacitor in Si Interposer For CoWoS Heterogeneous Integration.yifan zhaoNo ratings yet
- Huang D D 2014Document193 pagesHuang D D 2014Bala Subrahmanyam KNo ratings yet
- Energy Storage in Ceramic DielectricsDocument6 pagesEnergy Storage in Ceramic DielectricsJJ SerraltaNo ratings yet
- Digital Transformation Lab: by B.Nagasuman K.NarasimhaDocument10 pagesDigital Transformation Lab: by B.Nagasuman K.NarasimhaNarasimha KopparthiNo ratings yet
- Punkt MP02 Back Up ContactsDocument8 pagesPunkt MP02 Back Up Contactsqrillon2594No ratings yet
- PF Improvement On DG SetsDocument8 pagesPF Improvement On DG SetsAnupam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Vibration Transducer TRV-18 / 19: Technical DataDocument1 pageVibration Transducer TRV-18 / 19: Technical DataPiero Fernando Canales ValdezNo ratings yet
- E-Saksharta: Information Technology Resource CenterDocument4 pagesE-Saksharta: Information Technology Resource CenterAditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Common RailDocument3 pagesCommon RailKariem R Noweer100% (1)
- Experiment No. - 1 (E) Objective:-To Measure The Antenna Characteristics For Yagi-Uda AntennaDocument3 pagesExperiment No. - 1 (E) Objective:-To Measure The Antenna Characteristics For Yagi-Uda AntennaAvinash PariharNo ratings yet
- Chibo C300 Vs Degen DE 1102 Radio ReviewDocument10 pagesChibo C300 Vs Degen DE 1102 Radio ReviewZach Liang-No ratings yet
- Layout-Dependent Proximity Effects in Deep Nanoscale CMOSDocument8 pagesLayout-Dependent Proximity Effects in Deep Nanoscale CMOSVENKINo ratings yet
- E4201-810 HM100 PDFDocument10 pagesE4201-810 HM100 PDFMichael Robin B. SevillaNo ratings yet
- PD16 WiringDiagramDocument2 pagesPD16 WiringDiagramSpeedtuner IndonesiaNo ratings yet
- PSPICE Transient Simulation PlottingDocument7 pagesPSPICE Transient Simulation Plottingjae hak kimNo ratings yet
- Digital Comm Lab ManualDocument33 pagesDigital Comm Lab ManualroryNo ratings yet
- Re-640 Use en r1 - User ManualDocument140 pagesRe-640 Use en r1 - User ManualCláudio Luiz De PaulaNo ratings yet
- Black Box at F-86A Crash SiteDocument4 pagesBlack Box at F-86A Crash SitetrojandlNo ratings yet