Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Capital Budgeting Process and Techniques
Uploaded by
Maha HamdyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Capital Budgeting Process and Techniques
Uploaded by
Maha HamdyCopyright:
Available Formats
31.
Which of the following involves significant financial investments in projects to develop
new products, expand production capacity, or remodel current production facilities?
a. capital budgeting
b. working capital
c. master budgeting
d. project-cost budgeting
Answer: a Difficulty: 1 Objective: 1
Terms to Learn: capital budgeting
32. The accounting system that corresponds to the project dimension in capital budgeting is
the:
a. net present value method
b. internal rate of return
c. accrual accounting rate of return
d. life-cycle costing
Answer: d Difficulty: 1 Objective: 1
Terms to Learn: capital budgeting
33. The stage of the capital budgeting process that distinguishes which types of capital
expenditure projects are necessary to accomplish organization objectives is the:
a. identification stage
b. search stage
c. information-acquisition stage
d. selection stage
Answer: a Difficulty: 1 Objective: 2
Terms to Learn: capital budgeting
34. The stage of the capital budgeting process which explores alternative capital
investments that will achieve organization objectives is the:
a. identification stage
b. search stage
c. information-acquisition stage
d. selection stage
Answer: b Difficulty: 1 Objective: 2
Terms to Learn: capital budgeting
35. The stage of the capital budgeting process which considers the expected costs and the
expected benefits of alternative capital investments is the:
a. identification stage
b. search stage
c. information-acquisition stage
d. selection stage
Answer: c Difficulty: 1 Objective: 2
Terms to Learn: capital budgeting
36. The stage of the capital budgeting process which chooses projects for implementation is
the:
a. selection stage
b. search stage
c. identification stage
d. management-control stage
Answer: a Difficulty: 1 Objective: 2
Terms to Learn: capital budgeting
37. The stage of the capital-budgeting process in which projects get underway and
performance is monitored is the:
a. implementation and control stage
b. search stage.
c. identification stage
d. management-control stage
Answer: a Difficulty: 1 Objective: 2
Terms to Learn: capital budgeting
38. The two factors capital budgeting emphasizes are:
a. qualitative and nonfinancial
b. quantitative and nonfinancial
c. quantitative and financial
d. qualitative and financial
Answer: c Difficulty: 1 Objective: 2
Terms to Learn: capital budgeting
39. Which of the following are NOT included in the formal financial analysis of a capital
budgeting program?
a. quality of the output
b. safety of employees
c. cash flow
d. Neither a nor b are included.
Answer: d Difficulty: 2 Objective: 2
Terms to Learn: capital budgeting
40. The stage of the capital budgeting process in which a firm obtains funding for the
project is the:
a. identification stage
b. search stage
c. information-acquisition stage
d. financing stage
Answer: d Difficulty: 1 Objective: 2
Terms to Learn: net present value (NPV) method
41. Which capital budgeting technique(s) measure all expected future cash inflows and
outflows as if they occurred at a single point in time?
a. net present value
b. internal rate of return
c. payback
d. Both a and b are correct.
Answer: d Difficulty: 2 Objective: 3
Terms to Learn: capital budgeting, net present value (NPV) method, internal rate-of-
return (IRR) method
42. Discounted cash flow methods for capital budgeting focus on:
a. cash inflows
b. operating income
c. cash outflows
d. Both a and c are correct.
Answer: d Difficulty: 2 Objective: 3
Terms to Learn: discounted cash flow (DCF) methods
43. Net present value is calculated using the:
a. internal rate of return
b. required rate of return
c. rate of return required by the investment bankers
d. None of these answers is correct.
Answer: b Difficulty: 2 Objective: 3
Terms to Learn: net present value (NPV) method
44. All of the following are methods that aid management in analyzing the expected results
of capital budgeting decisions EXCEPT:
a. accrual accounting rate-of-return method
b. discounted cash-flow method
c. future-value cash-flow method
d. payback method
Answer: c Difficulty: 2 Objective: 3
Terms to Learn: capital budgeting
45. The capital budgeting method which calculates the expected monetary gain or loss from
a project by discounting all expected future cash inflows and outflows to the present
point in time using the required rate of return is the:
a. payback method
b. accrual accounting rate-of-return method
c. sensitivity method
d. net present value method
Answer: d Difficulty: 2 Objective: 3
Terms to Learn: net present value (NPV) method
46. Assume your goal in life is to retire with one million dollars. How much would you
need to save at the end of each year if interest rates average 6% and you have a 20-year
work life?
a. $14,565
b. $27,184
c. $120,102
d. $376,476
Answer: b Difficulty: 3 Objective: 3
Terms to Learn: net present value (NPV) method
S (36.786) = $1,000,000
S = $ 27,184.25
THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION APPLIES TO QUESTIONS 47 AND 48:
47. Hawkeye Cleaners has been considering the purchase of an industrial dry-cleaning
machine. The existing machine is operable for three more years and will have a zero
disposal price. If the machine is disposed now, it may be sold for $60,000. The new
machine will cost $200,000 and an additional cash investment in working capital of
$60,000 will be required. The new machine will reduce the average amount of time
required to wash clothing and will decrease labor costs. The investment is expected to
net $50,000 in additional cash inflows during the year of acquisition and $150,000 each
additional year of use. The new machine has a three-year life, and zero disposal value.
These cash flows will generally occur throughout the year and are recognized at the end
of each year. Income taxes are not considered in this problem. The working capital
investment will not be recovered at the end of the asset's life.
What is the net present value of the investment, assuming the required rate of return is
10%? Would the company want to purchase the new machine?
a. $82,000; yes
b. $50,000; no
c. $(50,000); yes
d. $(82,000); no
Answer: a Difficulty: 3 Objective: 3
Terms to Learn: net present value (NPV) method
Yr. 0 ($60,000 – $200,000 - $60,000) x 1.000 = $(200,000)
Yr. 1 $50,000 x 0.909 = 45,450
Yr. 2 $150,000 x 0.826 = 123,900
Yr. 3 $150,000 x 0.751 = 112,650
$ 82,000
48. What is the net present value of the investment, assuming the required rate of return is
24%? Would the company want to purchase the new machine?
a. $(32,800); yes
b. $(16,400); no
c. $16,400; yes
d. $32,800; no
Answer: c Difficulty: 3 Objective: 3
Terms to Learn: net present value (NPV) method, required rate of return (RRR)
Yr. 0 ($60,000 – $200,000 – $60,000) x 1.000 = $(200,000)
Yr. 1 $ 50,000 x 0.806 = 40,300
Yr. 2 $150,000 x 0.650 = 97,500
Yr. 3 $150,000 x 0.524 = 78,600
$ 16,400
49. In using the net present value method, only projects with a zero or positive net present
value are acceptable because:
a. the return from these projects equals or exceeds the cost of capital
b. a positive net present value on a particular project guarantees company
profitability
c. the company will be able to pay the necessary payments on any loans secured to
finance the project
d. Both a and b are correct.
Answer: a Difficulty: 2 Objective: 3
Terms to Learn: net present value (NPV) method
50. Which of the following is NOT an appropriate term for the required rate of return?
a. discount rate
b. hurdle rate
c. cost of capital
d. All of these answers are correct.
Answer: d Difficulty: 2 Objective: 3
Terms to Learn: required rate of return (RRR), discount rate, hurdle rate, opportunity
cost of capital
51. Which of the following results of the net present value method in capital budgeting is
the LEAST acceptable?
a. $(10,000)
b. $(7,000)
c. $(18,000)
d. $0
Answer: c Difficulty: 2 Objective: 3
Terms to Learn: net present value (NPV) method
52. The definition of an annuity is:
a. similar to the definition of a life insurance policy
b. a series of equal cash flows at intervals
c. an investment product whose funds are invested in the stock market
d. Both a and b are correct.
Answer: b Difficulty: 2 Objective: 3
Terms to Learn: net present value (NPV) method
53. The net present value method focuses on:
a. cash inflows
b. accrual-accounting net income
c. cash outflows
d. Both a and c are correct.
Answer: d Difficulty: 2 Objective: 3
Terms to Learn: net present value (NPV) method
54. If the net present value for a project is zero or positive, this means that the:
a. project should be accepted
b. project should not be accepted
c. expected rate of return is below the required rate of return
d. Both a and c are correct.
Answer: a Difficulty: 2 Objective: 3
Terms to Learn: net present value (NPV) method
55. Upper Darby Park Department is considering a new capital investment. The following
information is available on the investment. The cost of the machine will be $150,000.
The annual cost savings if the new machine is acquired will be $40,000. The machine
will have a 5-year life, at which time the terminal disposal value is expected to be
$20,000. Upper Darby Park Department is assuming no tax consequences. If Upper
Darby Park Department has a required rate of return of 10%, which of the following is
closest to the present value of the project?
a. $1,632
b. $12,418
c. $14,060
d. $150,000
Answer: c Difficulty: 3 Objective: 3
Terms to Learn: net present value (NPV) method
($40,000 x 3.791) + ($20,000 x .621) – $150,000 = $14,050.
56. Shirt Company wants to purchase a new cutting machine for its sewing plant. The
investment is expected to generate annual cash inflows of $300,000. The required rate
of return is 12% and the current machine is expected to last for four years. What is the
maximum dollar amount Shirt Company would be willing to spend for the machine,
assuming its life is also four years? Income taxes are not considered.
a. $507,000
b. $720,600
c. $791,740
d. $911,100
Answer: d Difficulty: 3 Objective: 3
Terms to Learn: net present value (NPV) method
X = $300,000 x PV Ann 4 (12%) = $300,000 x 3.037
X= $911,100
57. The Zeron Corporation wants to purchase a new machine for its factory operations at a
cost of $950,000. The investment is expected to generate $350,000 in annual cash flows
for a period of four years. The required rate of return is 14%. The old machine can be
sold for $50,000. The machine is expected to have zero value at the end of the four-year
period. What is the net present value of the investment? Would the company want to
purchase the new machine? Income taxes are not considered.
a. $119,550; yes
b. $69,550; no
c. $1,019,550; yes
d. $326,750; no
Answer: a Difficulty: 3 Objective: 3
Terms to Learn: net present value (NPV) method
Year 0 = ($50,000 - $950,000) = $(900,000)
Year 1 = $350,000 x 0.877 = 306,950
Year 2 = $350,000 x 0.769 = 269,150
Year 3 = $350,000 x 0.675 = 236,250
Year 4 = $350,000 x 0.592 = 207,200
$ 119,550
58. Wet and Wild Water Company drills small commercial water wells. The company is in
the process of analyzing the purchase of a new drill. Information on the proposal is
provided below.
Initial investment:
Asset $160,000
Working capital $ 32,000
Operations (per year for four years):
Cash receipts $160,000
Cash expenditures $ 88,000
Disinvestment:
Salvage value of drill (existing) $ 16,000
Discount rate 20%
What is the net present value of the investment? Assume there is no recovery of
working capital.
a. $(62,140)
b. $10,336
c. $42,362
d. $186,336
Answer: b Difficulty: 3 Objective: 3
Terms to Learn: net present value (NPV) method
– $32,000 – $160,000 + $16,000 = $(176,000)
Yr 1 = $72,000 x 0.833 = 59,976
Yr 2 = $72,000 x 0.694 = 49,968
Yr 3 = $72,000 x 0.579 = 41,688
Yr 4 = $72,000 x 0.482 = 34,704
$ 10,336
59. The capital budgeting method that calculates the discount rate at which the present
value of expected cash inflows from a project equals the present value of expected cash
outflows is the:
a. net present value method
b. accrual accounting rate-of-return method
c. payback method
d. internal rate of return
Answer: d Difficulty: 2 Objective: 3
Terms to Learn: internal rate-of-return (IRR) method
60. In capital budgeting, a project is accepted only if the internal rate of return equals or:
a. exceeds the required rate of return
b. is less than the required rate of return
c. exceeds the net present value
d. exceeds the accrual accounting rate of return
Answer: a Difficulty: 2 Objective: 3
Terms to Learn: internal rate-of-return (IRR) method, required rate of return (RRR)
You might also like
- Cost Accounting Chapter 21 Capital BudgetingDocument16 pagesCost Accounting Chapter 21 Capital BudgetingDick RodiNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting Test Bank CompressDocument30 pagesCapital Budgeting Test Bank CompressBiancaNo ratings yet
- Calculate Internal Rate of Return for New Factory Machine Investment/TITLEDocument7 pagesCalculate Internal Rate of Return for New Factory Machine Investment/TITLEMaha HamdyNo ratings yet
- 9Document16 pages9edmarian0% (1)
- Ch23-PERFORMANCE MEASUREMENT, COMPENSATION, AND MULTINATIONAL CONSIDERATIONSDocument17 pagesCh23-PERFORMANCE MEASUREMENT, COMPENSATION, AND MULTINATIONAL CONSIDERATIONSRommel CruzNo ratings yet
- PM0012 MQP Keys PDFDocument16 pagesPM0012 MQP Keys PDFJoshi DhvanitNo ratings yet
- Budgeting, Finance, and Risk Management in Project ManagementDocument16 pagesBudgeting, Finance, and Risk Management in Project ManagementJoshi DhvanitNo ratings yet
- Assignments For Chapter 2 Project Selection - BABAWE13276Document4 pagesAssignments For Chapter 2 Project Selection - BABAWE13276Thi Khanh Linh PhamNo ratings yet
- CF MCQ ShareDocument17 pagesCF MCQ ShareMadhav RajbanshiNo ratings yet
- Mas Capital Budgeting ReviewersDocument16 pagesMas Capital Budgeting ReviewersNo Mi ViNo ratings yet
- E CommerceDocument11 pagesE CommerceToản NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: Answer: B. Wealth MaximisationDocument20 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: Answer: B. Wealth MaximisationArchana Neppolian100% (1)
- Financial Management Credit OfficerDocument11 pagesFinancial Management Credit OfficerMonika ChhatwaniNo ratings yet
- True/FalseDocument5 pagesTrue/FalseMaha HamdyNo ratings yet
- ch02 PDFDocument5 pagesch02 PDFPualNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2Document3 pagesQuiz 2Dhiraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Financial Management: Code: MB0045 Marks (140) Time (2 HRS) Section-A 1mark 50 50 MarksDocument21 pagesFinancial Management: Code: MB0045 Marks (140) Time (2 HRS) Section-A 1mark 50 50 Marksmrahul29_400215311No ratings yet
- Project Cost Management QuestionsDocument69 pagesProject Cost Management QuestionsAndreea DeeaNo ratings yet
- Budgeting CTRLDocument9 pagesBudgeting CTRLJoseph PamaongNo ratings yet
- Bba502 b1850 MQP Answer KeysDocument16 pagesBba502 b1850 MQP Answer KeysSarah SajjadNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Financial Statements Solved MCQs (Set-3)Document6 pagesAnalysis of Financial Statements Solved MCQs (Set-3)VenkataRamana IkkurthiNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice: Performance Measurement, Compensation, and Multinational ConsiderationsDocument13 pagesMultiple Choice: Performance Measurement, Compensation, and Multinational ConsiderationsJEP WalwalNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 - Corporate Finance QuestionsDocument7 pagesQuiz 2 - Corporate Finance QuestionsYasir RahimNo ratings yet
- Assignments For Chapter 2 Project SelectionDocument3 pagesAssignments For Chapter 2 Project SelectionThi Khanh Linh PhamNo ratings yet
- MAS Handout - QuantechDocument4 pagesMAS Handout - QuantechDivine VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Quiz Capital Budgeting 2018 2019 1st SemDocument6 pagesQuiz Capital Budgeting 2018 2019 1st Semjethro carlobosNo ratings yet
- Examination Paper: Instruction To CandidatesDocument11 pagesExamination Paper: Instruction To CandidatesNikesh MunankarmiNo ratings yet
- Quizzes 1 14Document29 pagesQuizzes 1 14Sieggy Bennicoff YundtNo ratings yet
- Financial Management MCQsDocument11 pagesFinancial Management MCQsmadihaadnan150% (2)
- Mbaln 622Document10 pagesMbaln 622dale2741830100% (2)
- R32 Capital Budgeting - AnswersDocument30 pagesR32 Capital Budgeting - AnswersVipul 663No ratings yet
- Project Management A Managerial Approach 8th Edition Meredith Test BankDocument12 pagesProject Management A Managerial Approach 8th Edition Meredith Test Banktheodoreeugenef2j100% (35)
- Practice Exam - Part 3: Multiple ChoiceDocument4 pagesPractice Exam - Part 3: Multiple ChoiceAzeem TalibNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Practice MCQ - S Financial Management by BrighamDocument49 pagesCH 11 Practice MCQ - S Financial Management by BrighamShahmir AliNo ratings yet
- 605A-Management Accounting PDFDocument21 pages605A-Management Accounting PDFMD Shuhel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Work in The 21st Century An Introduction To Industrial and Organizational Psychology 6th Edition Frank J Landy Jeffrey M Conte Isbn 9781118976272 DownloadDocument10 pagesTest Bank For Work in The 21st Century An Introduction To Industrial and Organizational Psychology 6th Edition Frank J Landy Jeffrey M Conte Isbn 9781118976272 Downloadadrienneturnerkpqowgcymz100% (13)
- MAC Material 2Document33 pagesMAC Material 2Blessy Zedlav LacbainNo ratings yet
- Strategy and Analysis in Using Net Present Value: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument12 pagesStrategy and Analysis in Using Net Present Value: Multiple Choice Questionsphantom ceilNo ratings yet
- Financial Management - SmuDocument0 pagesFinancial Management - SmusirajrNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument16 pagesCapital Budgetingjayson100% (3)
- FULL Source FIN202Document277 pagesFULL Source FIN202Nguyen Hoang Phuong Nam (K16HCM)No ratings yet
- FM Recollected QuestionsDocument8 pagesFM Recollected Questionsmevrick_guyNo ratings yet
- Management Advisory Services Made EasyDocument18 pagesManagement Advisory Services Made EasyRyan Christian M. Coral0% (1)
- Financial Management For Decision Makers Canadian 2nd Edition Atrill Test BankDocument17 pagesFinancial Management For Decision Makers Canadian 2nd Edition Atrill Test Bankodiledominicmyfmf100% (28)
- 28560550Document29 pages28560550Hanabusa Kawaii IdouNo ratings yet
- 100 Sample Questions of MCQ Project ManagementDocument10 pages100 Sample Questions of MCQ Project ManagementmaheshNo ratings yet
- I M.com Cost May 21Document3 pagesI M.com Cost May 21VISHAGAN MNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 PDFDocument77 pagesChapter 13 PDFMaureen ToledoNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Financial Management For UGC NET With AnswersDocument9 pagesMCQ On Financial Management For UGC NET With AnswersRajendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Engg Econ GRP 3&4 Quiz (Economics, Study, Method)Document5 pagesEngg Econ GRP 3&4 Quiz (Economics, Study, Method)Maria AndresNo ratings yet
- Calculate Capital Budgeting Project NPV and IRRDocument17 pagesCalculate Capital Budgeting Project NPV and IRRFredy Msamiati100% (1)
- AccountingDocument16 pagesAccountingClassicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Answer SheetDocument7 pagesChapter 6 Answer SheetJoan Gayle BalisiNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Financial Management For Decision Makers Second Canadian Edition 2 e 2nd Edition Peter Atrill Paul Hurley DownloadDocument18 pagesTest Bank For Financial Management For Decision Makers Second Canadian Edition 2 e 2nd Edition Peter Atrill Paul Hurley Downloadbriannacochrankaoesqinxw100% (19)
- Gitman Ch.5Document14 pagesGitman Ch.5Doni SujanaNo ratings yet
- 19Document3 pages19Maha HamdyNo ratings yet
- 16Document3 pages16Maha HamdyNo ratings yet
- 18Document4 pages18Maha HamdyNo ratings yet
- A) True B) FalseDocument3 pagesA) True B) FalseMaha HamdyNo ratings yet
- 16Document3 pages16Maha HamdyNo ratings yet
- (Introduction) A-Answer The Following QuestionsDocument2 pages(Introduction) A-Answer The Following QuestionsMaha HamdyNo ratings yet
- in The Necessary Corrective Actions (In Case of Deviations From The Expected Performance) Must Be Taken Into Account From The Beginning of The InputDocument4 pagesin The Necessary Corrective Actions (In Case of Deviations From The Expected Performance) Must Be Taken Into Account From The Beginning of The InputMaha HamdyNo ratings yet
- A) Marketing B) Marketing System C) Marketing Mix D) Product Life CycleDocument6 pagesA) Marketing B) Marketing System C) Marketing Mix D) Product Life CycleMaha HamdyNo ratings yet
- Solution: Profitability Analysis, When The Jacket " Gale " Is DroppedDocument2 pagesSolution: Profitability Analysis, When The Jacket " Gale " Is DroppedMaha HamdyNo ratings yet
- 13Document4 pages13Maha HamdyNo ratings yet
- Exercises On Chapter (1)Document5 pagesExercises On Chapter (1)Maha HamdyNo ratings yet
- Special Order Decision: I. Relevant Cost AnalysisDocument2 pagesSpecial Order Decision: I. Relevant Cost AnalysisMaha HamdyNo ratings yet
- 6.profitability Analysis: A. Keep or Drop A Product Line DecisionsDocument2 pages6.profitability Analysis: A. Keep or Drop A Product Line DecisionsMaha HamdyNo ratings yet
- 12Document4 pages12Maha HamdyNo ratings yet
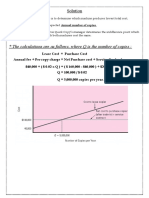
- The Calculations Are As Follows, Where Q Is The Number of CopiesDocument2 pagesThe Calculations Are As Follows, Where Q Is The Number of CopiesMaha HamdyNo ratings yet
- Lease-Or-Buy Decision: I. Relevant Cost AnalysisDocument2 pagesLease-Or-Buy Decision: I. Relevant Cost AnalysisMaha HamdyNo ratings yet
- 12 AaDocument1 page12 AaMaha HamdyNo ratings yet
- Table Presents TTS's Analysis of The Relevant CostsDocument2 pagesTable Presents TTS's Analysis of The Relevant CostsMaha HamdyNo ratings yet
- F-MCQ (Choose Only One Correct Answer in Each Question)Document2 pagesF-MCQ (Choose Only One Correct Answer in Each Question)Maha HamdyNo ratings yet
- B. Excessive Relevant Cost Pricing: Value StreamDocument1 pageB. Excessive Relevant Cost Pricing: Value StreamMaha HamdyNo ratings yet
- 32 AaDocument2 pages32 AaMaha HamdyNo ratings yet
- Equipment-Replacement Decision: Consider The Following ExampleDocument2 pagesEquipment-Replacement Decision: Consider The Following ExampleMaha HamdyNo ratings yet
- II. Strategic Analysis: A. Is TTS Now Operating at Full Capacity ?Document2 pagesII. Strategic Analysis: A. Is TTS Now Operating at Full Capacity ?Maha HamdyNo ratings yet
- Make-or-Buy Decision: I. Relevant Cost AnalysisDocument2 pagesMake-or-Buy Decision: I. Relevant Cost AnalysisMaha HamdyNo ratings yet
- To Show That The Analysis Based On The Total Cost Provides The Same AnswerDocument2 pagesTo Show That The Analysis Based On The Total Cost Provides The Same AnswerMaha HamdyNo ratings yet
- 33 AaDocument2 pages33 AaMaha HamdyNo ratings yet
- 31 AaDocument2 pages31 AaMaha HamdyNo ratings yet
- A-Answer The Following QuestionsDocument2 pagesA-Answer The Following QuestionsMaha HamdyNo ratings yet
- 34AADocument2 pages34AAMaha HamdyNo ratings yet
- 35AADocument2 pages35AAMaha HamdyNo ratings yet
- At.2505 Planning The AuditDocument28 pagesAt.2505 Planning The Auditawesome bloggersNo ratings yet
- Preparing For The CIC Certified Insurance CounselorDocument17 pagesPreparing For The CIC Certified Insurance CounselorHeidi LueckNo ratings yet
- CH 12 P1Document2 pagesCH 12 P1GlaizzaNo ratings yet
- ReceiptDocument1 pageReceiptAbdul Hadi Rashid100% (1)
- Opening Saving Account in HDFC BankDocument31 pagesOpening Saving Account in HDFC BankSukhchain AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Statement - 50291311034 - 20230529 - 123959 (4) ADITIDocument12 pagesStatement - 50291311034 - 20230529 - 123959 (4) ADITIRajeev kumar AgarwalNo ratings yet
- SBH Bank Form PDFDocument1 pageSBH Bank Form PDFdsNo ratings yet
- Treasury ManagementDocument15 pagesTreasury Managementharrykey John100% (3)
- Simple Interest: Learning ObjectivesDocument37 pagesSimple Interest: Learning ObjectivesJhon Vincent Buraga100% (1)
- Soneri Bank PresentationDocument9 pagesSoneri Bank PresentationAsadNo ratings yet
- Starbucks vs Caribou Coffee Company AnalysisDocument17 pagesStarbucks vs Caribou Coffee Company AnalysisJake FavreNo ratings yet
- Financial Asset at Fair Value Problem 21-1 (IFRS) : Solution 21-1 Answer CDocument15 pagesFinancial Asset at Fair Value Problem 21-1 (IFRS) : Solution 21-1 Answer CEngel QuimsonNo ratings yet
- KCC Bank Project ReportDocument2 pagesKCC Bank Project ReportANSHULNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Preparation for Faculty of Economics and BusinessDocument3 pagesFinal Exam Preparation for Faculty of Economics and BusinessAlvira FajriNo ratings yet
- Govt. of West Bengal Transport Department Grips Echallan: (Identifiction No)Document1 pageGovt. of West Bengal Transport Department Grips Echallan: (Identifiction No)Monojit MondalNo ratings yet
- Customer statement summary for September 2022Document7 pagesCustomer statement summary for September 2022OluwarotimiNo ratings yet
- Adjsuting EntriesDocument3 pagesAdjsuting Entrieshs927071No ratings yet
- List of Urban SchoolDocument90 pagesList of Urban SchoolAbhi RicNo ratings yet
- Soon After Beginning The Year End Audit Work On March 10Document2 pagesSoon After Beginning The Year End Audit Work On March 10M Bilal SaleemNo ratings yet
- SAA Versus TAA 2009-01Document5 pagesSAA Versus TAA 2009-01domomwambiNo ratings yet
- N CY5 DAwg 4 GQSJ JQuDocument12 pagesN CY5 DAwg 4 GQSJ JQuVinod SharmaNo ratings yet
- ACCT4110 Advanced Accounting PRACTICE Exam 2 KEY v2Document14 pagesACCT4110 Advanced Accounting PRACTICE Exam 2 KEY v2accounts 3 lifeNo ratings yet
- Intacc Quiz1Document15 pagesIntacc Quiz1Armina BagsicNo ratings yet
- Financial Management On Catfish Farms (PDFDrive)Document61 pagesFinancial Management On Catfish Farms (PDFDrive)AmiibahNo ratings yet
- Mortgage and Amortization: Business MathematicsDocument8 pagesMortgage and Amortization: Business MathematicsAthinaNo ratings yet
- ABM Fundamentals Accounting HistoryDocument37 pagesABM Fundamentals Accounting HistoryMylene CandidoNo ratings yet
- P-6 Aset TetapDocument65 pagesP-6 Aset TetapRaehan RaesaNo ratings yet
- Moniepoint Document 2023-12-27T10 30Document20 pagesMoniepoint Document 2023-12-27T10 30miracleikeaNo ratings yet
- Level 1 CISIDocument26 pagesLevel 1 CISISukruth GupthaNo ratings yet
- 2980 Daf1206 LendingDocument118 pages2980 Daf1206 Lendingmargaret kurgatNo ratings yet