Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Suppository
Suppository
Uploaded by
tiara0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views12 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views12 pagesSuppository
Suppository
Uploaded by
tiaraCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
CHAPTER 12
SUPPOSITORIES, INSERTS, AND STICKS
Suppositories generally have been employed for three STICKS
reasons, to - a convenient form for administering topical drugs.
1. promote defecation - their development involves the history of
2. introduce drugs into the body cosmetics, which parallels human history
3. treat anorectal diseases - it js cylindrical in shape and generally range from 5
SUPPOSITORIES (Cocoa butter as base = 2g) to 25 g.
- solid dosage forms intended for insertion into body - They are generally packaged in an applicator tube
orifices where they melt, soften, or dissolve and for topical administration
exert local or systemic effects.
- from the Latin supponere, meaning “to place The advantages of rectal administration:
under,” as derived from sub (under) and ponere (to 1. Avoiding, at least partially, the first-pass effect
place) that may result in higher blood levels for those
- usually about 32 mm (1.5 inch) long, are cylindrical, drugs subject to extensive first-pass metabolism
and have one or both ends tapered. upon oral administration.
- Some rectal suppositories are shaped like a bullet, a 2. Drug stability: Avoiding the breakdown of certain
torpedo, or the little finger. Depending on the drugs that are susceptible to gastric degradation.
density of the base and the medicaments in the 3. Ability to administer somewhat larger doses of
suppository, the weight may vary. drugs than using oral administration.
- Rectal suppositories for use by infants and children 4. Ability to administer drugs that may have an
are about half the weight and size of the adult irritating effect on the oral or gastrointestinal
suppositories and assume a more pencil-like shape. mucosa when administered orally.
5 TYPES: 5. Ability to administer unpleasant tasting or
(1) Rectal (2) Vaginal (3) Urethral smelling drugs whose oral administration is
(4) Nasal [Burginarium] (5) Aural [Ear Cones] limited.
6. In children, the rectal route is especially useful.
INSERT An ill child may refuse oral medication and may
- a solid dosage form that is inserted into a naturally fear injections.
occurring (nonsurgical) body cavity other than the 7. In patients experiencing nausea and vomiting or
mouth or rectum, including the vagina and urethra. when the patient is unconscious.
- Vaginal inserts (pessaries) are usually globular, 8. The presence of disease of the upper
oviform, or cone shaped gastrointestinal tract that may interfere with
- cocoa butter as base = 5g drug absorption.
9. Objectionable taste or odor of a drug (especially
- Urethral inserts (bougies) are pencil-shaped important in children).
suppositories intended for insertion into the male 10. Achievement of a rapid drug effect systemically
or female urethra. Male urethral suppositories may (as an alternate to injection).
be 3 to 6 mm in diameter and approximately 140
mm long, although this may vary. Female urethral Disadvantages of suppositories:
suppositories are about half the length and weight 1. A perceived lack of flexibility regarding dosage of
of the male urethral suppository. suppositories results in underuse and a lack of
- Cocoa butter as base = 4g availability.
2. If suppositories are made on demand, they may
be expensive.
3. Suppositories as a dosage form are safe, but they
exhibit variable effectiveness, including the
pathology of the anorectal lesions.
4. Different formulations of a drug with a narrow - Sticks are commonly used for local effect and
therapeutic margin, such as aminophylline, include hydration/emollient, antibacterial,
cannot be interchanged without risk of toxicity. sunscreen, antipruritic, and other uses.
5. The “bullet-shaped” suppository after insertion Systemic Action
can leave the anorectal site and ascend to the - the mucous membranes of the rectum and vagina
rectosigmoid and descending colon. Hence, one permit the absorption of many soluble drugs,
may consider that suppositories with this shape although the rectum is more frequently used.
possibly should not be used at bedtime. - Examples of drugs administered rectally in the form
6. Defecation may interrupt the absorption process of suppositories for their systemic effects include
of the drug; this may especially occur if the drug (a) prochlorperazine and chlorpromazine for the
is irritating. relief of nausea and vomiting and as a tranquilizer;
7. The absorbing surface area of the rectum is much (b) morphine and oxymorphone for opioid analgesia;
smaller than that of the small intestine. (c) ergotamine tartrate for the relief of migraine
8. The fluid content of the rectum is much less than syndrome;
that of the small intestine, which may affect (d) indomethacin, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory
dissolution rate, etc. analgesic and antipyretic; and
9. There is the possibility of degradation of some (e) ondansetron for the relief of nausea and
drugs by the microflora present in the rectum. vomiting
10. The dose of a drug required for rectal
administration may be greater than or less than Physiological Factors and Drug Effect that affect drug
the dose of the same drug given orally. This can absorption from the rectum:
be dependent upon such factors as the 1. Circulation Route
constitution and condition of the patient, the - drugs absorbed rectally can bypass the portal
physicochemical nature of the drug, and its ability circulation during their first pass into the general
to traverse the physiologic barriers to absorption. circulation. This enables drugs that are otherwise
11. The factors that affect the rectal absorption of a destroyed in the liver to exert systemic effects.
drug administered in the form of a suppository - Lymphatic circulation also assists in the absorption
may be divided into two main groups: of rectally administered drugs.
(a) anatomic and physiologic factors and (b) 2. pH and Lack of Buffering Capacity of the Rectal
physicochemical factors of the drug and the base. Fluids
- Rectal fluid pH ranges 7.2 to 7.4, in which the drug
Local Action administered will not generally be chemically
- Rectal suppositories intended for local action are changed by the rectal environment; therefore, the
most frequently used to relieve constipation or the pH of the medium may be determined by the
pain, irritation, itching, and inflammation associated characteristics of the drug
with hemorrhoids or other anorectal conditions. - The rectum contains three types of hemorrhoidal
- glycerin suppositories are a popular laxative where it veins:
promotes laxation by local irritation of the mucous • superior hemorrhoidal vein
membranes, probably by the dehydrating effect of • middle hemorrhoidal vein
the glycerin on those membranes. • inferior hemorrhoidal vein
- Vaginal suppositories or inserts intended for local - These veins act by transporting the active
effects are employed mainly as contraceptives, as principle absorbed in the rectum to the blood
antiseptics in feminine hygiene, and as specific system either directly by means of iliac veins and
agents to combat an invading pathogen. the vena cava or indirectly by means of the portal
- Urethral suppositories may be antibacterial or a vein and the liver
local anesthetic preparative for a urethral - it is generally accepted that at least 50% to 70%
examination. of the active ingredients administered rectally
take the direct pathway, thus bypassing the liver Cocoa butter base (theobroma oil)
and avoiding the first-pass effect. ✔ Fulfills the requirements of an ideal suppository
- The pH of the Vagina ranges 4-4.5 base
3. Colonic Content ✔ superior base when irritation or inflammation is
- greater absorption may be expected from a to be relieved
rectum that is void (absence of fecal matter) than x it is immiscible with body fluids
from one that is distended with fecal matter - fat-soluble drugs tend to remain in the oil and
- Other conditions such as diarrhea, colonic have little tendency to enter the aqueous
obstruction due to tumorous growths, and tissue physiologic fluids where the drug can release
dehydration can all influence the rate and degree its effect.
of drug absorption from the rectal site. - For water-soluble drugs in cocoa butter, the
reverse is usually true and results in good
Physicochemical Factors and Drug Effect release.
Physicochemical - relating to physics and chemistry
- Fat-soluble drugs seem to be released more
❖ Effects on Drug
readily from bases of glycerinated gelatin or
> Relative solubility of the drug in lipid and in
polyethylene glycol, both of which dissolve
water
slowly in body fluids.
> Particle size of the dispersed drug
Remarks:
❖ Effects on Suppository base
Cocoa butter melts quickly and non-irritatingly at
> Ability to melt, soften, and dissolve at body
body temperature and maintains solidity at room
temperature
temperature. In the treatment of anorectal disorders,
> Ability to release the drug substance
cocoa butter appears to be the superior base because of
> Its hydrophilic or hydrophobic character
its emollient or soothing, spreading action.
- The lipid–water partition coefficient of a
However, because of its triglyceride content,
drug is an important consideration in the
cocoa butter exhibits marked polymorphism or existence
selection of the suppository base and in
in several crystalline forms. Because of this, when cocoa
anticipating drug release from that base.
butter is hastily or carelessly melted at a temperature
▪ Lipid-water solubility
greatly exceeding the minimum required temperature
- A lipophilic drug distributed in a fatty
and is then quickly chilled, the result is a metastable
suppository base in low
crystalline form (alpha crystals) with a melting point
concentration has lesser tendency to
much lower than that of the original cocoa butter.
escape to the surrounding aqueous
fluids than a hydrophilic substance in
Nature of the Base
a fatty base.
Base - must be capable of melting, softening or
▪ Particle size
dissolving to release its drug for absorption.
- The smaller, the readily the
dissolution and chance for rapid
If base interacts with drug to inhibit its release, drug
absorption
absorption will be impaired or even prevented.
- It is preferable to avoid a too fine
If base irritates mucous membranes of rectum, it may
particle size because of the high
initiate a colonic response and prompt bowel
increase of the viscosity of the
movement, eliminating prospect of complete drug
melted excipient that can result from
release and absorption.
the use of excessively small particles
and possible difficulties in flow
Morphine Sulfate in Slow-Release Supp. - prepared in a
during production.
base that includes a material such as alginic acid, which
> Influences released and dissolved amount in
will prolong release of drug over several hours.
absorption
CLASSIFICATION OF BASES - because of its triglyceride content, cocoa butter
exhibits marked polymorphism or existence in
It is convenient to classify suppository bases according to several crystalline forms.
their physical characteristics into 2 main categories and a - Consequently, if suppositories that have been
3rd miscellaneous group: prepared by melting cocoa butter for the base do
a. Fatty or Oleaginous Bases not harden soon after molding, they will be
b. Water-soluble or Water-miscible Bases useless to the patient and a loss of time,
c. Miscellaneous Bases ( Combinations of Lipophilic materials, and prestige to the pharmacist.
and Hydrophilic Substances) - Substances such as phenol and chloral hydrate
Suppository Bases - should be physically and chemically have a tendency to lower the melting point of
stable, nonirritating, nonsensitizing, nontoxic, cocoa butter.
chemically and physiologically inert, compatible with a - If the melting point is low enough that it is not
variety of drugs, stable during storage, esthetically feasible to prepare a solid suppository using
acceptable (free from objectionable odor and a pleasing cocoa butter alone as the base, solidifying agents
appearance) like cetyl esters wax (about 20%) or beeswax
(about 4%) may be melted with the cocoa butter
Fatty or Oleaginous Bases to compensate for the softening effect of the
- the most frequently employed suppository bases added substance
- cocoa butter is a member of this group of - the addition of hardening agents must not be so
substances excessive as to prevent the base from melting in
- among the other fatty or oleaginous materials the body, nor must the waxy material interfere
used in suppository bases are many with the therapeutic agent in any way so as to
hydrogenated fatty acids of vegetable oils, such alter the efficacy of the product.
as palm kernel oil and cottonseed oil - Other bases in this category include commercial
- fat-based compounds containing compounds of products such as Fattibase (triglycerides from
glycerin with the higher–molecular-weight fatty palm, palm kernel, and coconut oils with
acids, such as palmitic and stearic acids, may be self-emulsifying glyceryl monostearate and
found in fatty bases polyoxyl stearate), the Wecobee bases
- Such compounds, such as glyceryl monostearate (triglycerides derived from coconut oil), and
and glyceryl monopalmitate, are examples of Witepsol bases (triglycerides of saturated fatty
this type of agent. acids C12–C18 with varied portions of the
- in many commercial products, they employ corresponding partial glycerides)
varied combinations of these types of materials Water-Soluble and Water-Miscible Bases
to achieve the desired hardness under conditions - The main members of this group are glycerinated
of shipment and storage and the desired quality gelatin and polyethylene glycols
of submitting to the temperature of the body to Glycerinated gelatin suppositories may be prepared by
release their medicaments dissolving granular gelatin (20%) in glycerin (70%) and
- some bases are prepared with the fatty materials adding water or a solution or suspension of the
emulsified or with an emulsifying agent medication (10%)
-It is most frequently used in the preparation of
Cocoa Butter, NF, - fat obtained from the roasted seed of vaginal suppositories, with which prolonged local action
Theobroma cacao. of the medicinal agent is usually desired
- At room temperature, it is a yellowish-white solid - It is slower to soften and mix with the
having a faint, agreeable chocolate-like odor physiologic fluids than is cocoa butter and therefore
- Chemically, it is a triglyceride (combination of provides a slower release
glycerin and one or different fatty acids) primarily - Because glycerinated gelatin–based
of oleopalmitostearin and oleodistearin. suppositories have a tendency to absorb moisture as a
result of the hygroscopic nature of glycerin, they must be
protected from atmospheric moisture if they are to molded with either a polyethylene glycol
maintain their shape and consistency base or a fatty acid base.
- Also as a result of the hygroscopicity of the - Polyethylene glycol suppositories do not
glycerin, the suppository may have a dehydrating effect melt at body temperature but rather
and irritate the tissues upon insertion. The water in the dissolve slowly in the body’s fluids.
formula for the suppositories minimizes this action; Therefore, the base need not be
however, if necessary, the suppositories may be formulated to melt at body temperature.
moistened with water prior to insertion to reduce the Thus, it is possible, in fact routine, to
initial tendency of the base to draw water from the prepare suppositories from polyethylene
mucous membranes and irritate the tissues. glycol mixtures having melting points
considerably higher than body
Urethral suppositories may be prepared from a temperature.
glycerinated gelatin base of a formula somewhat -This property permits a slower
different from the one indicated earlier release of the medication from the base
- For urethral suppositories, the gelatin once the suppository has been inserted
constitutes about 60% of the weight of and permits convenient storage of these
the formula, the glycerin about 20%, and suppositories without need for
the medicated aqueous portion about refrigeration and without danger of their
20% softening excessively in warm weather. -
- Urethral suppositories of glycerinated Further, their solid nature permits slow
gelatin are much more easily inserted insertion without fear that they will melt
than those with a cocoa butter base in the fingertips (as cocoa butter
owing to the brittleness of cocoa butter suppositories sometimes do). Because
and its rapid softening at body they do not melt at body temperature
temperature but mix with mucous secretions upon
- Various combinations of these dissolution, polyethylene glycol–based
polyethylene glycols may be combined by suppositories do not leak from the
fusion, using two or more of the various orifice, as do many cocoa butter–based
types to achieve a suppository base of suppositories
the desired consistency and -Polyethylene glycol
characteristics suppositories that do not contain at least
- Polyethylene glycols having average 20% water should be dipped in water just
molecular weights of 300, 400, and 600 before use to avoid irritation of the
are clear, colorless liquids. Those having mucous membranes after insertion. This
average molecular weights of greater procedure prevents moisture being
than 1,000 are waxlike white solids drawn from the tissues after insertion
whose hardness increases with an and the stinging sensation.
increase in the molecular weight - Poloxamers (Pluronics) are
- Melting ranges, for example, water-soluble, block copolymers with a
polyethylene glycols, are PEG 300 (−15°C wide range of uses. Pluronics L44, L62,
to 18°C), PEG 1000 (37°C to 40°C), PEG L64, and F68 are potential suppository
3350 (54°C to 58°C), and PEG 8000 (60°C bases.
to 63°C) -The poloxamers have practically
- Pharmacists have been called on in no odor or taste. An example of an
recent years to prepare progesterone aspirin suppository using a poloxamer
vaginal suppositories extemporaneously. base uses the following formula:
- These suppositories, used in Pluronic F68 - 6 .00 g
premenstrual syndrome, are commonly Pluronic L44 - 7.00 mL
Aspirin - 1.02 g affected by the nature of the suppository base.
Solubility
Formulation Variables - Increased solubility of the active in the base can
- Formulation variables that are generally improve product homogeneity; however, it may
considered include also delay the release of the active if there is too
(a) the nature and form of the active principle great an affinity of the drug for the suppository
(esters, salts, complexes, etc.), (b) the physical vehicle
state, particle dimensions, and the specific - If the active ingredient is insoluble in the base,
surface of the product, as is the case when a “suspension” or “emulsion”
© the solubility of the drug in various bases, is formed, this poses different problems.
(d) the presence or absence of adjuvants added - It is necessary to maintain homogeneity of the
to the active principle, total mixture; this can usually be obtained by
(e) the nature and type of dosage form in which constant agitation of the mixture during
the active principle is incorporated, and processing and filling.
:(f) pharmaceutical procedures used in the - Oftentimes, it is best to select a temperature
preparation of the dosage form. just above the melting point of the suppository
- Active drugs have a number of physical mixture where the mixture is thick but still
characteristics. In suppositories, those of interest pourable. Viscosity
involve the drug’s physical state, including - Viscosity considerations are also important in
physical state, particle size, solubility, dielectric the preparation of the suppositories and the
constant, and bulk density. release of the drug.
Physical State - If the viscosity of a base is low, it may be
- An active drug can be a solid, liquid, or semisolid necessary to add a suspending agent such as
in nature. silica gel to ensure that the drug is uniformly
- For solids, the drug’s particle size may be very dispersed until solidification occurs.
important, especially if the drug is not very water - When preparing the suppository, the
soluble; the increase in surface area resulting pharmacist should stir the melt constantly and
from decreased particle size can serve to keep it at the lowest possible temperature to
enhance its activity. maintain a high viscosity.
- For liquids, it is necessary to take up the liquid - After the suppository has been administered,
into the suppository base using one of several the release rate of the drug may be slowed if the
techniques such as forming an emulsion, adding a viscosity of the base is very high. This is because
drying powder, or adding a suitable thickening the viscosity causes the drug to diffuse more
agent when the liquid is mixed with the slowly through the base to reach the mucosal
suppository base. membrane for absorption.
- For the semisolids or paste-type drugs, it can be Brittleness
either mixed with a solid that will serve to thicken - Brittle suppositories can be difficult to
the drug prior to mixing with the base or mixed handle, wrap, and use. Cocoa butter
with the base to which a thickener is added. suppositories are usually not brittle
Particle Size unless the percentage of solids present is
- If a drug is readily soluble, the influence of high.
particle size may be minimal - In general, brittleness results when the
- For highly water-soluble drugs, the tendency will percentage of nonbase materials exceeds
be to dissolve and migrate to the rectal barrier. about 30%.
- For poorly water-soluble drugs, the dissolution - Synthetic fat bases with high stearate
rate will be slower, and a reduction in particle concentrations or those that are highly
size may increase the rate of dissolution by hydrogenated are typically more brittle.
exposing a greater surface area. This can also be
- S hock cooling also causes fat and cocoa
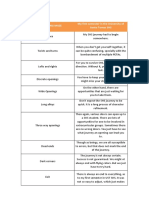
Oil-soluble drug: Moderate release
butter suppositories to crack. This Water-miscible base
condition can be prevented by ensuring
that the temperature of the mold is as Water-miscible drug: Moderate release; based
close to the temperature of the melted Water-miscible base on diffusion; all water
base as possible. soluble
- Suppositories should not be placed in a
freezer, which also causes shock cooling.
Volume Contraction Methods of preparing suppositories.
- Bases, excipients, and active ingredients 1. Hand molding/rolling/shaping
generally occupy less space at lower > a historic part of the art of the pharmacist
temperatures than at higher > useful when preparing a small number of
temperature. suppositories
- During the cooling process, the melt has > no heating required
a tendency to contract in size. This makes 2. Compression molding
it easier to release the suppository from > skips the task of hand rolling
the mold, but it may also produce a > more elegant than hand rolled preparation
cavity at the back, or open end, of the > air entrapment may take place, weight
mold. variation, drug may then be oxidized into this
- Such a cavity is undesirable and can be air
prevented if the melt is permitted to > compression methods comes with difficulties
approach its congealing temperature particularly to the required homogeneity of
immediately before it is poured into the the dosage from and its achievement of
mold. appropriate fracture strength.
- It is advisable to pour a small amount of > compression methods are less suitable for
excess melt at the open end of the mold fluid active ingredients
to allow for the slight contraction during a. Cold Compression
cooling. b. Compression in a tablet press
- Scraping with a blade or spatula dipped - occasionally, vaginal suppositories, such as
in warm water will remove the excess Metronidazol tablets, are prepared by
after solidification, but care must be compression in a tableting machine
taken not to remove the metal from the 3. Molding from a melt/Fusion method
mold. The heated instrument can also be > large or small-scale
used to smooth out the back of the > manufactured suppositories are generally
suppository prepared by this method
Drug Release Rates
General approximate drug release rates as they Preparation by molding
relate to the drug and base characteristics are 1) Melting of the base: preferably in water or steam
summarized as follows: bath to avoid local overheating
2) Incorporating the required medicament: either
emulsified or suspend
Drug:Base Characteristics Approximate Drug
Release Rate 3) Pouring the melt into the cooled metal mold:
4) Allowing the melt to cool and congeal thoroughly
Oil-soluble drug: Oily base Slow release; poor into suppositories: using refrigerator in a small
escaping tendency scale or refrigerated air on a larger scale
5) Removing the formed suppositories from the
Water-soluble drug: Oily Rapid release
mold
base
Remarks: - the pharmacist calculates the amounts of
Molds in common use today are made from stainless materials needed for the preparation of one or
steel, aluminum, brass, or plastic.
two more suppositories than the number
Along with Cocoa butter, glycerinated gelatin,
polyethylene glycol, and most other bases are suitable for prescribed to compensate for the inevitable
preparation by molding. loss of some material and to ensure having
enough material.
Lubrication of the Mold
- the pharmacist must be certain that the
● Suppository molds may require lubrication before
required amount of drug is provided in each
the melt is poured to facilitate clean and easy
suppository.
removal of the molded suppositories.
- Because the volume of the mold is known (from
● Cocoa butter or polyethylene glycol as base –
the determined volume of the melted
lubrication is seldom necessary as these materials
suppositories formed from the base), the volume
contract sufficiently on cooling to separate from
of the drug substances subtracted from the
the inner surfaces and allow easy removal
total volume of the mold will give the volume of
● Lubrication is necessary in Glycerinated gelatin
base required. If the added amounts of
suppositories - a thin coating of mineral oil
medicaments are slight, they may be considered
applied with the finger to the molding surfaces
to be negligible, and no deduction from the total
usually suffices
volume of base may be deemed necessary.
Calibration of the Mold
However, if considerable quantities of other
- The pharmacist should calibrate each suppository
substances are to be used, the volumes of these
mold for the usual base (generally cocoa butter and a
materials are important and should be used to
polyethylene glycol base) so as to prepare medicated
calculate the amount of base actually required to
suppositories each having the proper quantity of
fill the mold.
medicaments
Glycerin suppositories
METHOD FOR DETERMINATION ON THE AMOUNT OF
● Glycerin, a hygroscopic material, contributes to
BASE:
the laxative effect of the suppository by drawing
● The total volume of these materials is
water from the intestine and from its irritant
subtracted from the volume of the mold, and
action on the mucous lining.
the appropriate amount of base is added.
● promote laxation by local irritation of the mucous
Because the bases are solid at room temperature,
membranes, probably by the dehydrating effect
the volume of base may be converted to weight
of the glycerin on those membranes.
from the density of the material.
Determination of the Amount of Base Required
● The weight of the active ingredients subtracted
- the prescribing physician indicates the amount
from the weight of the suppository yields the
of medicinal substance desired in each
weight of the base. This amount of base
suppository but leaves the amount of base to
multiplied by the number of suppositories to be
the discretion of the pharmacist.
prepared in the mold is the total amount of base - stored at controlled room temperature (20°C to
required. 25°C or 68°F to 77°F)
● Third method is to place all of the required ● Suppositories prepared from a cocoa butter base
medicaments for the preparation of the total - usually individually wrapped or otherwise
number of suppositories (including one extra) in a separated in compartmentalized boxes to
calibrated beaker, add a portion of the melted prevent contact and adhesion.
base, and incorporate the drug substances. Then - stored below 30°C (86°F) and preferably in a
add sufficient melted base to reach the required refrigerator (2°C to 8°C or 36°F to 46°F)
volume of mixture based on the original ● Suppositories containing light sensitive drugs
calibration of the volume of the mold. - individually wrapped in an opaque material such
Info. patients need to know about suppositories as metallic foil.
● If they must be stored in the refrigerator, ❖ Suppositories made from a base of polyethylene glycol
suppositories should be allowed to warm to room may be stored at usual room temperatures.
temperature before insertion. ❖ Suppositories are also commonly packaged in slide
● Rub cocoa butter suppositories gently with the boxes or in plastic boxes.
fingers to melt the surface to provide lubrication Suppositories stored in high humidity may absorb
moisture and tend to become spongy, whereas
for insertion. Glycerinated gelatin or
suppositories stored in places of extreme dryness may
polyethylene glycol suppositories should be lose moisture and become brittle.
moistened with water to enhance lubrication.
● Bullet-shaped rectal suppositories should be
inserted point-end first.
● When using one-half suppository, the patient
should be told to cut the suppository in half
lengthwise with a clean razor blade.
● Most suppositories are dispensed in paper, foil,
or plastic wrappings, and the patient must be
instructed to completely remove the wrapping
before insertion.
Packaging and Storage
● Glycerin suppositories and glycerinated gelatin
suppositories
- packaged in tightly closed glass containers to
prevent a moisture change in the content of
the suppositories.
Other examples of suppositories given for
systemic results include diazepam, metronidazole, progesterone, aminophylline, morphine, prochlorperazine,
chlorpromazine, thiethylperazine, indomethacin, diclofenac, ketoprofen, naproxen, and ondansetron
You might also like
- PHARDOSE LAB Preparation 21-31Document2 pagesPHARDOSE LAB Preparation 21-31Czarina Barcelon Daos75% (4)
- Classification of Dosage FormsDocument25 pagesClassification of Dosage FormsNimit Jain100% (1)
- Phar 24 NotesDocument22 pagesPhar 24 NotesSherry LynnNo ratings yet
- IJPC 13 5 Veterinary CompoundingDocument100 pagesIJPC 13 5 Veterinary CompoundingMatiasNo ratings yet
- Fats and Fixed OilsDocument17 pagesFats and Fixed OilsMikay Barroga50% (2)
- Liquid Dosage FormsDocument9 pagesLiquid Dosage FormsRama MulyadiNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms Laboratory ManualDocument2 pagesPharmaceutical Dosage Forms Laboratory Manuallalag yanNo ratings yet
- Calamine LotionDocument2 pagesCalamine LotionHeba Ali100% (1)
- Experiment P'ceuticsDocument4 pagesExperiment P'ceuticsnigamnirupam50% (2)
- Phardose Lab Prep 1-6Document4 pagesPhardose Lab Prep 1-6Kimberley Anne SeeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PharmacologyDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Pharmacologyderic100% (12)
- Preparation No 12 - 15 PharLabDocument4 pagesPreparation No 12 - 15 PharLabKim Manlangit100% (4)
- PharDose Lab Prep 19-30Document4 pagesPharDose Lab Prep 19-30Angelyka Cabalo100% (1)
- Brex Manufacturing EditedDocument291 pagesBrex Manufacturing EditedMing MingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemDocument4 pagesChapter 11 - Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemYoreeNo ratings yet
- PharDose Lab PrelimsDocument8 pagesPharDose Lab PrelimsKimberley Anne SeeNo ratings yet
- Activity #1 - Physico-Chemical Properties of Drugs by Jasher Dave C. AcabalDocument9 pagesActivity #1 - Physico-Chemical Properties of Drugs by Jasher Dave C. AcabaldavenNo ratings yet
- Ointments Creams and Gels PhardoseDocument8 pagesOintments Creams and Gels PhardoseAlec LimNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Chemistry 1 - Full VersionDocument199 pagesMedicinal Chemistry 1 - Full Versionsaddamixo100% (2)
- Pha6111 Dispensing Lab Customer Service PDFDocument5 pagesPha6111 Dispensing Lab Customer Service PDFKATHLEEN CALALANGNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Dosage Form Lab Prep 6-18Document7 pagesPharmaceutical Dosage Form Lab Prep 6-18Jana EncaboNo ratings yet
- Dispensing Post LabDocument3 pagesDispensing Post LabYanni Bryan RegaladoNo ratings yet
- C 13 SolutionsDocument13 pagesC 13 SolutionsAli Uy100% (1)
- Preparation 19: Iso-Alcoholic Elixir: 3 GttsDocument16 pagesPreparation 19: Iso-Alcoholic Elixir: 3 GttsMikaela LaoNo ratings yet
- Preparation #: Effervescent Granules I. Objectives:: Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms Laboratory ManualDocument2 pagesPreparation #: Effervescent Granules I. Objectives:: Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms Laboratory Manuallalag yanNo ratings yet
- IPPP-II (Supp)Document85 pagesIPPP-II (Supp)Tinsaye HayileNo ratings yet
- Phardose Lab (Prep 6-10)Document3 pagesPhardose Lab (Prep 6-10)Jan Aira Almazan100% (1)
- DDS FINALS Compiled ReviewerDocument21 pagesDDS FINALS Compiled ReviewerChantelle Mea100% (1)
- 12 Special MethodsDocument45 pages12 Special MethodsnidsNo ratings yet
- Liworiz Chapter 1Document3 pagesLiworiz Chapter 1JAKE BENZYN TENo ratings yet
- Flexible Dominican Education (FDOME) Module BS Pharmacy ProgramDocument14 pagesFlexible Dominican Education (FDOME) Module BS Pharmacy ProgramSHEENA JOY HABITANNo ratings yet
- White Wax 50 G White Petrolatum 950 G To Make 1000 GDocument3 pagesWhite Wax 50 G White Petrolatum 950 G To Make 1000 GRoseanne Legaspi CasayuranNo ratings yet
- Preparation # I. Objectives:: Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms Laboratory ManualDocument2 pagesPreparation # I. Objectives:: Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms Laboratory Manuallalag yanNo ratings yet
- Monophasic Liquid Dosage Forms PDFDocument25 pagesMonophasic Liquid Dosage Forms PDFAamir KhanNo ratings yet
- PH 107 DDS Lab Midterm NotesDocument11 pagesPH 107 DDS Lab Midterm NotesKrsna NaveraNo ratings yet
- Dosage - Chapter 14Document57 pagesDosage - Chapter 14Kim Manlangit100% (1)
- Descriptive Statistics: Mathematics in The Modern World - Unit 4Document54 pagesDescriptive Statistics: Mathematics in The Modern World - Unit 4JAKE BENZYN TENo ratings yet
- Rajini Final Merged ThesisDocument89 pagesRajini Final Merged ThesispadminiNo ratings yet
- Physical Pharmacy Post-Lab Discussion For Preliminary PeriodDocument18 pagesPhysical Pharmacy Post-Lab Discussion For Preliminary PeriodKatryn Punsalang100% (2)
- Cold Cream USPDocument4 pagesCold Cream USPRon OlegarioNo ratings yet
- DdsDocument9 pagesDdsClaudette JunioNo ratings yet
- Emulsions: (A) Dilution TestDocument5 pagesEmulsions: (A) Dilution TestEman AzizNo ratings yet
- Aqueous PreparationsDocument15 pagesAqueous PreparationsAdiJoansyahNo ratings yet
- Dosage Lab FinalsDocument13 pagesDosage Lab FinalsKathleen CalalangNo ratings yet
- SolutionsDocument7 pagesSolutionsMARIE ERICKA ARONANo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Dosage Froms and Drug Delivery SystemsDocument14 pagesPharmaceutical Dosage Froms and Drug Delivery SystemsChantelle MeaNo ratings yet
- PHA6111LAB - Finals ReviewerDocument7 pagesPHA6111LAB - Finals ReviewerMarie Eloise BugayongNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical GranulesDocument55 pagesPharmaceutical GranulesWalaa abo foolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-3 LectureDocument9 pagesChapter 1-3 LectureAnalizaNo ratings yet
- Pcog Notes GlycosidesDocument8 pagesPcog Notes GlycosidesAlexandra Venice ChuaNo ratings yet
- DISPLABPreps1 20 2Document21 pagesDISPLABPreps1 20 2Alexa Joy C. InguilloNo ratings yet
- Preparation No. "17" "Liquid Petrolatum Emulsion" A. Wrap-Up Guide QuestionsDocument5 pagesPreparation No. "17" "Liquid Petrolatum Emulsion" A. Wrap-Up Guide QuestionsMEDELYN KEITH ESTANISLAONo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Incompatibility 1Document17 pagesPharmaceutical Incompatibility 1William FullerNo ratings yet
- Preparation OintmentDocument1 pagePreparation OintmentLyanlie MinamotoNo ratings yet
- Powders and GranulesDocument84 pagesPowders and GranulesMompati Letsweletse100% (2)
- Pharmacy Informatics Laboratory Activity 14Document1 pagePharmacy Informatics Laboratory Activity 14April Mergelle LapuzNo ratings yet
- Uniformity Dosage Unit USPDocument4 pagesUniformity Dosage Unit USPwike marelitaNo ratings yet
- Semi-Solid Dosage Forms: Ointments, Creams, Pastes & GelsDocument35 pagesSemi-Solid Dosage Forms: Ointments, Creams, Pastes & GelsAnaliza Kitongan LantayanNo ratings yet
- Topic 6: Hard and Soft Gelatin CapsulesDocument9 pagesTopic 6: Hard and Soft Gelatin CapsulesKate EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- PHA6111 Lab ACTIVITY 2 HERNANDEZDocument4 pagesPHA6111 Lab ACTIVITY 2 HERNANDEZGrace HernandezNo ratings yet
- PharCare NotesDocument9 pagesPharCare NotesJesza IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Philippine Alkaloids - PCOG PracticalDocument2 pagesPhilippine Alkaloids - PCOG Practicaltaengoo218No ratings yet
- Transdermal Drug Delivery SystemsDocument7 pagesTransdermal Drug Delivery SystemsMARIE ERICKA ARONANo ratings yet
- Suppositories and EnemasDocument35 pagesSuppositories and EnemasMr.ShazNo ratings yet
- Suppositories PHR308Document20 pagesSuppositories PHR308FeslyAnugerahAriestaPayungNo ratings yet
- Suppositories and PessariesDocument61 pagesSuppositories and PessariesAbera JamboNo ratings yet
- 2 SUPPOSITORIES&PESSARIEs 1 1Document79 pages2 SUPPOSITORIES&PESSARIEs 1 1Hinsarmu YerosanNo ratings yet
- Uses of SildenafilDocument1 pageUses of SildenafilJAKE BENZYN TENo ratings yet
- Individual Task #1 Jake Te HA-16Document1 pageIndividual Task #1 Jake Te HA-16JAKE BENZYN TENo ratings yet
- Review of Aas: Pharmaceutical Biochemistry (Pha 2116)Document41 pagesReview of Aas: Pharmaceutical Biochemistry (Pha 2116)JAKE BENZYN TENo ratings yet
- Botany ReproductionDocument5 pagesBotany ReproductionJAKE BENZYN TENo ratings yet
- Early Contacts in Neighboring CountriesDocument11 pagesEarly Contacts in Neighboring CountriesJAKE BENZYN TENo ratings yet
- Doctor-Patient Communication: A ReviewDocument8 pagesDoctor-Patient Communication: A ReviewJAKE BENZYN TENo ratings yet
- A Bewildering Maze My First Semester in The University of Santo Tomas SHSDocument2 pagesA Bewildering Maze My First Semester in The University of Santo Tomas SHSJAKE BENZYN TENo ratings yet
- NAME: Ang, Antivola, Silva, Te, Vizcarra GROUP: 2 - Targaryen TITLE OF ACTIVITY: Central Dogma of Molecular Biology DATE: 22 September 2017Document10 pagesNAME: Ang, Antivola, Silva, Te, Vizcarra GROUP: 2 - Targaryen TITLE OF ACTIVITY: Central Dogma of Molecular Biology DATE: 22 September 2017JAKE BENZYN TENo ratings yet
- Correa, Brian M. 11ha-16 History Performance TaskDocument2 pagesCorrea, Brian M. 11ha-16 History Performance TaskJAKE BENZYN TENo ratings yet
- NAME: Ang, Antivola, Silva, Te, Vizcarra GROUP: 2 - Targaryen TITLE OF ACTIVITY: Central Dogma of Molecular Biology DATE: 19 September 2017Document9 pagesNAME: Ang, Antivola, Silva, Te, Vizcarra GROUP: 2 - Targaryen TITLE OF ACTIVITY: Central Dogma of Molecular Biology DATE: 19 September 2017JAKE BENZYN TENo ratings yet
- Hard Drugs and Soft Drugs Drug Latentiation: (Prodrugs and Bioprecursor Prodrugs)Document17 pagesHard Drugs and Soft Drugs Drug Latentiation: (Prodrugs and Bioprecursor Prodrugs)مها عقديNo ratings yet
- Controlled Drug Delivery Systems - 1 PDFDocument6 pagesControlled Drug Delivery Systems - 1 PDFVikash Kushwaha100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Nursing: Ana Rebancos Guballa RM, RN, MANDocument129 pagesFundamentals of Nursing: Ana Rebancos Guballa RM, RN, MANmaica lectanaNo ratings yet
- US20200009067A1Document37 pagesUS20200009067A1M FNo ratings yet
- PSMB - Pink Pacop Mod4 6Document348 pagesPSMB - Pink Pacop Mod4 6Princess Rose GamboaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Chapter 4Document5 pagesPharmacology - Chapter 4GILLAN KIN ROBLESNo ratings yet
- Formulation and In-Vitro Characterization of Calcitriol Soft Gelatin CapsuleDocument23 pagesFormulation and In-Vitro Characterization of Calcitriol Soft Gelatin CapsuleArief Adi NugrohoNo ratings yet
- An Overview On Food & Drug Interactions: Pharma Times April 2017Document8 pagesAn Overview On Food & Drug Interactions: Pharma Times April 2017lisnallNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Notes (Introduction To Pharmacology)Document16 pagesPharmacology Notes (Introduction To Pharmacology)BRYCE WILLIAM GONo ratings yet
- CH 06Document7 pagesCH 06john mwangiNo ratings yet
- Dasar FarmakologiDocument102 pagesDasar FarmakologiAvivah Rohmatul JannahNo ratings yet
- Drugs & FoodDocument2 pagesDrugs & FoodRee AhmedNo ratings yet
- Percobaan 2 FarmakokinetikDocument12 pagesPercobaan 2 FarmakokinetikTaufik HidayatNo ratings yet
- W3 Lesson 1 PharmacokineticsDocument41 pagesW3 Lesson 1 PharmacokineticsThrecia RotaNo ratings yet
- Enteral and Parenteral RoutesDocument3 pagesEnteral and Parenteral RoutesKarla Karina Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Chitosan Nanoparticles and Its Application in Non-Parenteral Drug DeliveryDocument26 pagesAn Overview of Chitosan Nanoparticles and Its Application in Non-Parenteral Drug DeliveryAssyfa FiraNo ratings yet
- Ich m9Document22 pagesIch m9beNo ratings yet
- Sublingual Route For The Systemic Delivery of OndansetronDocument9 pagesSublingual Route For The Systemic Delivery of OndansetronDiny AnisaNo ratings yet
- DDS Glycerin Supp PostlabDocument33 pagesDDS Glycerin Supp PostlabGRACE MAR CABAHUGNo ratings yet
- GLIMEPIRIDE in DogsDocument10 pagesGLIMEPIRIDE in DogsHaroon RahimNo ratings yet
- Adverse Drug Reactions and InteractionsDocument6 pagesAdverse Drug Reactions and InteractionsAlvina HafidiatiNo ratings yet
- General Pharmacology 1Document59 pagesGeneral Pharmacology 1Ramadi PrameelaNo ratings yet
- Microspheresdocx 2021 03 25 16 55Document6 pagesMicrospheresdocx 2021 03 25 16 55Ravirajsinh GohilNo ratings yet
- Document (1) PharmaceuticsDocument14 pagesDocument (1) PharmaceuticsHanaa Abo SweirhNo ratings yet
- Q. Define Mean Absorption Time ? Illustrate The Relation Between MAT and MRT ?Document3 pagesQ. Define Mean Absorption Time ? Illustrate The Relation Between MAT and MRT ?arifur rahman tanzilNo ratings yet