Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nerve Signal Triggers Muscle Contraction
Uploaded by
Syahrul HadikusumaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nerve Signal Triggers Muscle Contraction
Uploaded by
Syahrul HadikusumaCopyright:
Available Formats
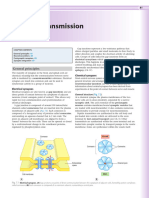
Nerve signal
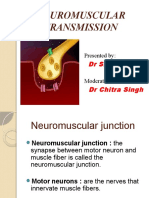
1 Neuromuscular Junction
Excitation of a skeletal muscle fiber
Axon 2b The EPP initiates an
Synaptic knob action potential
Ca2+ along sarcolemma
and T-tubules.
1a A nerve signal triggers
voltage-gated Ca2+ channels
to open—Ca2+ enters
synaptic knob and binds to
synaptic vesicles.
Voltage-gated
Ca2+ channel
ACh
Synaptic
1b ACh is released by vesicle
exocytosis into
synaptic cleft.
ACh
Synaptic cleft
2a ACh binding causes
Na+ to rapidly enter the
ACh skeletal muscle fiber
receptor K+ and K+ to slowly exit
the skeletal muscle
fiber, which may result
in an end-plate
potential (EPP).
Na+
1c ACh binds to
ACh receptors.
Motor end plate 3e Reset: ATP split and
myosin head is reset.
INTEGRATE CONCEPT OVERVIEW Pi
ADP
Figure 10.16 Skeletal Muscle Contraction. A summary
of skeletal muscle contraction, which includes the events at (1) the
neuromuscular junction, (2) the sarcolemma, T-tubules, and sarcoplasmic
reticulum, and (3) sarcomeres.
3d Release: ATP binds
to myosin head
releasing myosin
head from actin.
ATP
350
You might also like
- Introduction to Feynman Diagrams: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyFrom EverandIntroduction to Feynman Diagrams: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Neuromuscular Junction: Dr. Mustafa Al-Shehabat MSC, PH.DDocument32 pagesNeuromuscular Junction: Dr. Mustafa Al-Shehabat MSC, PH.Dمحمد السنجلاوي100% (1)
- The Mechanism of gated calcium Transport across Biological MembranesFrom EverandThe Mechanism of gated calcium Transport across Biological MembranesS. Tsuyoshi OhnishiNo ratings yet
- 06 Neuromuscular JunctionDocument17 pages06 Neuromuscular Junctionafzal sulemani100% (1)
- Neuromuscular Junction: Shannon Sanders Bishop O'ConnellDocument16 pagesNeuromuscular Junction: Shannon Sanders Bishop O'ConnellShannon SandersNo ratings yet
- 06 SynapseDocument22 pages06 SynapseJaydave PatelNo ratings yet
- NMJ Chemical Synapse Between Neurons and MuscleDocument21 pagesNMJ Chemical Synapse Between Neurons and Musclekunjbihari sulakhiyaNo ratings yet
- Synaptic Communication in Under 40Document61 pagesSynaptic Communication in Under 40namrata kar100% (1)
- Rob Bakels, PHD Section of Anatomy and R.Bakels@Umcg - NL: Medical Physiology Dept BscsDocument13 pagesRob Bakels, PHD Section of Anatomy and R.Bakels@Umcg - NL: Medical Physiology Dept BscsAli MuneerNo ratings yet
- L4 NeuromuscularJunctionDocument37 pagesL4 NeuromuscularJunctionM SNo ratings yet
- Muscle ContractionDocument48 pagesMuscle ContractionVikas VikiNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular Junction Physiology & Blocking Agents: Prof V K Bhatia Dept of Anaesthesiology KgmuDocument39 pagesNeuromuscular Junction Physiology & Blocking Agents: Prof V K Bhatia Dept of Anaesthesiology KgmuAthira S MadhuNo ratings yet
- Neurobiology Lectures 5-6Document58 pagesNeurobiology Lectures 5-6Saajid AmraNo ratings yet
- Calcium Control of Neurotransmitter Release PDFDocument15 pagesCalcium Control of Neurotransmitter Release PDFNisa Yulianti SuprahmanNo ratings yet
- Calcium Control of Neurotransmitter ReleaseDocument15 pagesCalcium Control of Neurotransmitter ReleaseNisa Yulianti SuprahmanNo ratings yet
- Neural Control and Coordination: Topic 1Document9 pagesNeural Control and Coordination: Topic 1Gautam KrishnaNo ratings yet
- M - PH: The Relationship Between Length and Active Force of A Skeletal MuscleDocument11 pagesM - PH: The Relationship Between Length and Active Force of A Skeletal MuscleFlowerNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Skeletal Muscle Contraction: Dr. Dinesh VeeraDocument42 pagesPhysiology of Skeletal Muscle Contraction: Dr. Dinesh VeeraArumpaavai PugazhiniNo ratings yet
- Neurobiology Lectures 5-6Document58 pagesNeurobiology Lectures 5-6Saajid AmraNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of Polysomnographic ChannelsDocument8 pagesBasic Concepts of Polysomnographic ChannelsGuenevere DamasinNo ratings yet
- Potential - Best Compatibility ModeDocument14 pagesPotential - Best Compatibility ModeDivya TripathyNo ratings yet
- Excitable TissueDocument8 pagesExcitable Tissueolayemi mariamNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular JunctionDocument23 pagesNeuromuscular Junctionkiedd_04100% (8)
- 1cns Basics - Redi (Nema)Document38 pages1cns Basics - Redi (Nema)Endre Shitaye KulkiNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmission and synaptic potentialsDocument2 pagesNeurotransmission and synaptic potentialsKarma iiiNo ratings yet
- Genesis of Resting Membrane PotentialDocument9 pagesGenesis of Resting Membrane PotentialSyauqat AthirNo ratings yet
- Neuromyal Junction2015Document52 pagesNeuromyal Junction2015Deling ManuabaNo ratings yet
- NMJ 1Document40 pagesNMJ 1Zainab AshroffNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Synaptic Transmission 2014 Clinical NeuroscienceDocument9 pagesChapter 7 Synaptic Transmission 2014 Clinical NeuroscienceMarta Casals CollNo ratings yet
- Modelling Bursting Pacemaker NeuronsDocument3 pagesModelling Bursting Pacemaker NeuronsRahul BatraNo ratings yet
- c10 Bioact (A) CoordinationDocument26 pagesc10 Bioact (A) CoordinationnurhasinahabrahimNo ratings yet
- Biophysics of Muscle ContractionDocument53 pagesBiophysics of Muscle ContractionMaitree UpadhayayNo ratings yet
- L3. Muscle Contraction Cycle - Sliding Filaments & Neurotransmission at NMJDocument9 pagesL3. Muscle Contraction Cycle - Sliding Filaments & Neurotransmission at NMJYolande ClothierNo ratings yet
- Synapse and action potential generationDocument4 pagesSynapse and action potential generationoguzNo ratings yet
- 6.2 Nervous CoordinationDocument1 page6.2 Nervous CoordinationRS JNo ratings yet
- L7 (Phy GM1)Document2 pagesL7 (Phy GM1)DANIA HUDA HUSNA ZULKIFLINo ratings yet
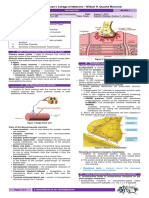
- St. Luke's College of Medicine - William H. Quasha Memorial: PhysiologyDocument3 pagesSt. Luke's College of Medicine - William H. Quasha Memorial: PhysiologyMavic Villanueva100% (1)
- Nerve Physiology PDFDocument31 pagesNerve Physiology PDFJunior AbdulcaderNo ratings yet
- Synapses, Neuro Muscular JunctionDocument13 pagesSynapses, Neuro Muscular Junctions vNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21Document4 pagesLecture 21vinnie0905No ratings yet
- NEUROMUSCULAR TRANSMISSION: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGYDocument45 pagesNEUROMUSCULAR TRANSMISSION: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGYparuNo ratings yet
- 2011 Cell Membranes - Signaling in Nerve CellsDocument13 pages2011 Cell Membranes - Signaling in Nerve CellsFidiya Septi Kusma WardaniNo ratings yet
- Synapse: Is The Point of Contact Between A Neuron andDocument31 pagesSynapse: Is The Point of Contact Between A Neuron andCharlie Mejos MercedNo ratings yet
- The Neuromuscular JunctionDocument9 pagesThe Neuromuscular JunctionKarthik VeeNo ratings yet
- The Hodgkin-Huxley Theory of Neuronal Excitation: 2.1 What Is A Neuron? Neuron Is A Signal ConverterDocument19 pagesThe Hodgkin-Huxley Theory of Neuronal Excitation: 2.1 What Is A Neuron? Neuron Is A Signal ConverterBoris ShalomovNo ratings yet
- Lesson# 10 - Synaptic TransmissionDocument2 pagesLesson# 10 - Synaptic TransmissionSmith PennanNo ratings yet
- Synapses: The Key Steps in Synaptic TransmissionDocument52 pagesSynapses: The Key Steps in Synaptic TransmissionilincaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology - For Nursing and Healthcare StudentsDocument6 pagesFundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology - For Nursing and Healthcare StudentsAbu BakrNo ratings yet
- Muscle ElectrophysiologyDocument2 pagesMuscle ElectrophysiologyAurelia AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Berne & Levy Physiology 7th - Emedicodiary-325-335Document11 pagesBerne & Levy Physiology 7th - Emedicodiary-325-335eb364a0319No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Assignment 4Document2 pagesChapter 1 Assignment 4nabihazonabNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRYDocument4 pagesBIOCHEMISTRYdominguezangela2002No ratings yet
- Electrophysiology Cardiovascular 2010Document77 pagesElectrophysiology Cardiovascular 2010Palupi Setyo HapsariNo ratings yet
- Week3-6pptcaridac MuscleDocument7 pagesWeek3-6pptcaridac MuscleSherida GibbsNo ratings yet
- NROSCI 1012 - Lecture 23Document3 pagesNROSCI 1012 - Lecture 23HonzaNo ratings yet
- Sketch NotesDocument3 pagesSketch NotesCyan KelleyNo ratings yet
- Instantaneous neural signal transmissionDocument78 pagesInstantaneous neural signal transmissionana luNo ratings yet
- NeuroDocument39 pagesNeuroJim XieNo ratings yet
- MSS Module Year One 2024Document43 pagesMSS Module Year One 2024Thaw Tar Noe WaiNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument29 pagesThe Cardiovascular Systemarif wicaksonoNo ratings yet
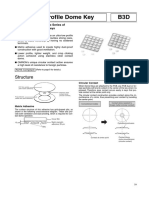
- Ultra-low Profile Dome Key Adds Single-key TypeDocument3 pagesUltra-low Profile Dome Key Adds Single-key TypeMuhamad PriyatnaNo ratings yet
- Astm E1973 - 1 (En)Document4 pagesAstm E1973 - 1 (En)Dinesh SaiNo ratings yet
- Recent Task 2 Essay Questions 2Document28 pagesRecent Task 2 Essay Questions 2esraaalhajNo ratings yet
- Senior Citizens and Human RightsDocument16 pagesSenior Citizens and Human RightsRiya SinghNo ratings yet
- Topic 3. Ecosystems (4 Marks) : Q. No. Option I Option II Option III Option IV Answer KeyDocument2 pagesTopic 3. Ecosystems (4 Marks) : Q. No. Option I Option II Option III Option IV Answer KeysakshiNo ratings yet
- 2.2.5 Respiration WorksheetDocument7 pages2.2.5 Respiration WorksheeterikabeltranNo ratings yet
- Sonotron NDTDocument3 pagesSonotron NDTNour MasmoudiNo ratings yet
- AV32D302 Service ManualDocument37 pagesAV32D302 Service ManualLuis MorenoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Troubleshoot - DynapacDocument37 pagesHydraulic Troubleshoot - DynapacMoazzam Ali0% (1)
- Pharmacy Service VA Design Guide: Final DraftDocument75 pagesPharmacy Service VA Design Guide: Final DraftAhmad Gamal Elden MAhanyNo ratings yet
- TheEconomist 2020 12 10Document296 pagesTheEconomist 2020 12 10merlindebergNo ratings yet
- The Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale I. Development, Use, and ReliabilityDocument6 pagesThe Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale I. Development, Use, and Reliabilitynurulhafizhah01No ratings yet
- What is Special EducationDocument2 pagesWhat is Special EducationImelda Nantin GarciaNo ratings yet
- Calculation of The Reorder Point For Items With Exponential and Poisson Distribution of Lead Time DemandDocument10 pagesCalculation of The Reorder Point For Items With Exponential and Poisson Distribution of Lead Time DemandRaj ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Irc 097-1987Document10 pagesIrc 097-1987kruttika_apNo ratings yet
- 15419Document29 pages15419Sadashiva SahooNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Life Insurance - Enrolment FormDocument1 pageSupplementary Life Insurance - Enrolment FormjeevaNo ratings yet
- Easy Tom Micro and NanoDocument2 pagesEasy Tom Micro and NanoMURALINo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Fringe & de Minimis BenefitsDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Fringe & de Minimis BenefitsNovelyn Hiso-anNo ratings yet
- Three Vital Elements of Qigong Exercise by Master Chunyi LinDocument3 pagesThree Vital Elements of Qigong Exercise by Master Chunyi LinTengriNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 08 Civics Confronting Marginalisation: Invoking Fundamental RightsDocument2 pagesChapter - 08 Civics Confronting Marginalisation: Invoking Fundamental Rightsnbs saraswathiNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet - BS6231 PVC Tri-Rated Flexible Cable - Cleveland CableDocument2 pagesData Sheet - BS6231 PVC Tri-Rated Flexible Cable - Cleveland CableCalum MartinNo ratings yet
- English Speaking BasicsDocument52 pagesEnglish Speaking BasicsMukesh Verma100% (1)
- Housekeeping in The Dental OfficeDocument45 pagesHousekeeping in The Dental OfficeJhaynerzz Padilla AcostaNo ratings yet
- Stress in The WorkplaceDocument10 pagesStress in The WorkplaceWendyLu32100% (1)
- Academic Procrastination, Self Efficacy and Anxiety of StudentsDocument7 pagesAcademic Procrastination, Self Efficacy and Anxiety of Studentscharvi didwania100% (3)
- CALIMOVEDocument46 pagesCALIMOVERasheedAladdinNGuiomala0% (1)
- Topic 3 BRUNEI The Oilfields LabourersDocument3 pagesTopic 3 BRUNEI The Oilfields LabourersRichmond BlancoNo ratings yet
- Mag-Gage The Superior Magnetic Level Gauge: Process Level Technology, Ltd. 281.332.6241Document12 pagesMag-Gage The Superior Magnetic Level Gauge: Process Level Technology, Ltd. 281.332.6241BYRON ENRIQUE AGUILERA CHIMARRONo ratings yet
- Optik 25Document6 pagesOptik 25z.umul9031No ratings yet
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Chair Yoga: Sit, Stretch, and Strengthen Your Way to a Happier, Healthier YouFrom EverandChair Yoga: Sit, Stretch, and Strengthen Your Way to a Happier, Healthier YouRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (5)
- Chakras and Yoga: Finding Inner Harmony Through Practice, Awaken the Energy Centers for Optimal Physical and Spiritual Health.From EverandChakras and Yoga: Finding Inner Harmony Through Practice, Awaken the Energy Centers for Optimal Physical and Spiritual Health.Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Boundless: Upgrade Your Brain, Optimize Your Body & Defy AgingFrom EverandBoundless: Upgrade Your Brain, Optimize Your Body & Defy AgingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (66)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Functional Training and Beyond: Building the Ultimate Superfunctional Body and MindFrom EverandFunctional Training and Beyond: Building the Ultimate Superfunctional Body and MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Power of 10: The Once-A-Week Slow Motion Fitness RevolutionFrom EverandPower of 10: The Once-A-Week Slow Motion Fitness RevolutionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (11)
- The Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineFrom EverandThe Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- This Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyFrom EverandThis Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Strong Is the New Beautiful: Embrace Your Natural Beauty, Eat Clean, and Harness Your PowerFrom EverandStrong Is the New Beautiful: Embrace Your Natural Beauty, Eat Clean, and Harness Your PowerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (515)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Eels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishFrom EverandEels: An Exploration, from New Zealand to the Sargasso, of the World's Most Mysterious FishRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (30)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (215)