Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Species.: The Living World
Uploaded by
John DoeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Species.: The Living World
Uploaded by
John DoeCopyright:
Available Formats
THE LIVING WORLD
Notes for KITE Victers Zoology Class (Class :2) 25/11/2020
For viewing the class click the link below
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y4IO9p8-EVc
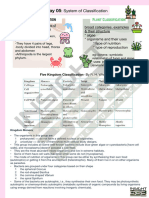
DIVERSITY IN THE LIVING WORLD
• Each different kind of plant, animal or organism that we see, represents a
species.
• The number of species that are known and described range between 1.7-
1.8 million.
• This refers to biodiversity or the number and types of organisms present on
earth.
Nomenclature
• Nomenclature is the standardization of naming of living things so that a
particular organism is known by the same name all over the world.
• The first step in nomenclature or naming is identification.
• International Code for Botanical Nomenclature (ICBN) provide
agreed principles and criteria for naming plants.
• International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) provide
agreed principles and criteria for naming animals.
Binomial nomenclature
• The system of providing a name to an organism with two components
is called Binomial nomenclature.
• Binomial nomenclature system is given by Carolus Linnaeus.
•
• Each name has two components –
The Generic name and the specific epithet.
Example
• The scientific name of mango is written as Mangifera indica.
• In this name Mangifera represents the genus
indica, is a particular species, or a specific epithet.
Universal Rules of Nomenclature
• Name of the author appears after the specific epithet, i.e., at the
end of the biological name and is written in an abbreviated form,
Example
Mangifera indica Linn.
It indicates that this species was first described by Linnaeus.
Classification
• Classification is the process by which anything is grouped into convenient
categories based on some easily observable characters.
Taxa
The scientific term for categories is taxa.
TAXONOMY
Based on characteristics, all living organisms can be classified into different taxa
(categories). This process of classification is taxonomy.
Basic processes of taxonomy
• Characterisation
• Identification
• Classification and
• Nomenclature
are the processes that are basic to taxonomy.
TAXON
It is the unit of classification which represents a rank in classification.
SPECIES
• A group of individual organisms with fundamental similarities are called as a
species.
GENUS
• Genus is a group of related species.
• Lion - Panthera leo
• Leopard - Panthera pardus
• Tiger – Panthera tigris
are all species of the genus Panthera.
•
FAMILY
Family, has a group of related genera with still less number of similarities as
compared to genus and species.
Among animals, genus Panthera, comprising lion, tiger, leopard is put along
with genus, Felis (cats) in the family Felidae.
Similarly, cat and a dog, are separated into two different families – Felidae
and Canidae, respectively.
Prepared by Biju TL,
GTHSS Poomala, Idukki
You might also like
- The Living WorldDocument4 pagesThe Living WorldBiju MylachalNo ratings yet
- +1 Biology Chapter 1 PDFDocument22 pages+1 Biology Chapter 1 PDFArjun v sNo ratings yet
- A Manual of the Mammalia: An Homage to Lawlor’s Handbook to the Orders and Families of Living MammalsFrom EverandA Manual of the Mammalia: An Homage to Lawlor’s Handbook to the Orders and Families of Living MammalsNo ratings yet
- The Living World and Biological ClassificationDocument8 pagesThe Living World and Biological ClassificationAmit RavindhraNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy and Classification ExplainedDocument27 pagesTaxonomy and Classification ExplainedShayvon Clarke100% (1)
- Essence Living WorldDocument5 pagesEssence Living WorldtarunNo ratings yet
- Binomial Nomenclature & Taxonomic ClassificationDocument19 pagesBinomial Nomenclature & Taxonomic ClassificationtiaraNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy Classification (1)Document48 pagesTaxonomy Classification (1)Dominic CorreaNo ratings yet
- 1st Bgy 1 Notes Classification of Living ThingsDocument34 pages1st Bgy 1 Notes Classification of Living ThingsnoreenasyikinNo ratings yet
- Components of Taxonomy BañasNaciloanDocument34 pagesComponents of Taxonomy BañasNaciloanmarielbustamante2002No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The living WorldDocument6 pagesChapter 1 The living WorldHimanshu TonkNo ratings yet
- ClassificationDocument29 pagesClassificationkaiya mollenthielNo ratings yet
- Biology Subject For Pre K Abilities and Characteristics of AnimalsDocument31 pagesBiology Subject For Pre K Abilities and Characteristics of Animalsmichaeljhoncamarin6No ratings yet
- Pre-Ig Unit 4Document39 pagesPre-Ig Unit 4myatthirisan2010No ratings yet
- Living WorldDocument4 pagesLiving WorldSuresh SNo ratings yet
- Principles of Classification: Understanding the Diversity of OrganismsDocument42 pagesPrinciples of Classification: Understanding the Diversity of OrganismsSandhya LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Cell in A BodyDocument11 pagesCell in A BodyRavi PrakashNo ratings yet
- Tal. Chikhali, Dist. Pune: Ganesh International School & Sr. SecondaryDocument34 pagesTal. Chikhali, Dist. Pune: Ganesh International School & Sr. SecondaryGanesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Life VarityDocument23 pagesLife VaritySubhan ullah TutorialNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument8 pagesUntitledTanmay GuptaNo ratings yet
- TaxonomyDocument26 pagesTaxonomynazNo ratings yet
- Essence: A) B) C) D) E) F)Document4 pagesEssence: A) B) C) D) E) F)tarunNo ratings yet
- Z P Cristobal TaxonomyDocument68 pagesZ P Cristobal Taxonomyleryc mdlNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 - ClassificationDocument26 pagesLecture 10 - Classificationnthinyal.2003No ratings yet
- Classifying Life with TaxonomyDocument51 pagesClassifying Life with Taxonomyichi senriNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Classification of Biodiversity NotesDocument6 pages5.3 Classification of Biodiversity NotesChristie NgNo ratings yet
- Classification of Living Things and Binomial NomenclatureDocument20 pagesClassification of Living Things and Binomial NomenclatureJaymark HisonaNo ratings yet
- Bio Short notes️_240403_221805Document169 pagesBio Short notes️_240403_221805munsifmohammed501No ratings yet
- Living World Class XiDocument32 pagesLiving World Class XivijithamuraliNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - ClassificationDocument84 pagesLecture 1 - ClassificationmuhdhazeeqNo ratings yet
- The Living World Notes RX AcademyDocument6 pagesThe Living World Notes RX Academychetandubey938No ratings yet
- Taxonomic ClassificationDocument40 pagesTaxonomic ClassificationReynald AntasoNo ratings yet
- The Survey of Plant KingdomDocument28 pagesThe Survey of Plant KingdomkerryNo ratings yet
- ClassificationDocument26 pagesClassificationapi-292439032100% (2)
- Scientific Names and Taxonomy ClassificationDocument16 pagesScientific Names and Taxonomy ClassificationChing DizonNo ratings yet
- Organizing MicroorganismsDocument16 pagesOrganizing MicroorganismsShahzad AslamNo ratings yet
- 1 The Living World-NotesDocument3 pages1 The Living World-NotesAnanth DharanidharanNo ratings yet
- Biology PDF XiDocument107 pagesBiology PDF XiSania 3003No ratings yet
- The Living WorldDocument3 pagesThe Living WorldSanjana AgarwalNo ratings yet
- A. Biological Classification - BIOLOGY4ISCDocument1 pageA. Biological Classification - BIOLOGY4ISCHannah 晗❾No ratings yet
- Classification of Living ThingsDocument44 pagesClassification of Living ThingsdacspinlacNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Linnaeus and ClassificationDocument41 pagesLecture 2 Linnaeus and Classificationhmin1805No ratings yet
- TAXONOMY KEYDocument35 pagesTAXONOMY KEYMuhammad Danial HasanNo ratings yet
- Classificationnotes2016 JosegDocument6 pagesClassificationnotes2016 Josegapi-319819727No ratings yet
- Plant Classification and Nomenclature: Spring 2014Document60 pagesPlant Classification and Nomenclature: Spring 2014CDB 1st Semester 2077No ratings yet
- Cds Day5Document4 pagesCds Day5Rajkamal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- BIO 101 DiversityDocument64 pagesBIO 101 DiversitysobamiwablossomNo ratings yet
- Week 24 BiologyDocument31 pagesWeek 24 Biologyjames gomezNo ratings yet
- Classification SystemsDocument14 pagesClassification SystemsSHEILA CLAUDNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Notes BiologyDocument144 pages1st Year Notes BiologyAkbar Dad BabarNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Classification Updated 2023Document52 pagesBiodiversity and Classification Updated 2023b0767212No ratings yet
- CH 1Document3 pagesCH 1Ruchika Kumari, VIII-A, 3956No ratings yet
- Living World Guide to Growth, Cells and ClassificationDocument2 pagesLiving World Guide to Growth, Cells and ClassificationGayathri Prathima GNo ratings yet
- Doctor Lennon T Mutyakureva - Classification of OrganismsDocument25 pagesDoctor Lennon T Mutyakureva - Classification of OrganismsleemutyakurevaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - ClassificationDocument59 pagesChapter 2 - ClassificationgoodmushroomsoupNo ratings yet
- 1 IGCSE Classification of Living Thing 2023Document61 pages1 IGCSE Classification of Living Thing 2023mohammed mahdy100% (1)
- Notes BiologyDocument144 pagesNotes BiologySrikanth VsrNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Plant SystematicsDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Plant SystematicsIzba SanaNo ratings yet
- CH 1bio MCQsDocument8 pagesCH 1bio MCQsrs9354614154No ratings yet
- Edible Forest Gardens2Document6 pagesEdible Forest Gardens2BettixNo ratings yet
- Strategy For Botany Optional in UPSC ExamsDocument21 pagesStrategy For Botany Optional in UPSC ExamsRiVa SinghNo ratings yet
- Weed ScienceDocument4 pagesWeed ScienceNURUL AIN HIDAYAH BINTI MOHD ZAHIR / UPMNo ratings yet
- Principles of Plant PathologyDocument58 pagesPrinciples of Plant Pathologyanon_310555357100% (1)
- New Records of 30 Wild Fungus Species and One Addition From Bangladesh-CompressedDocument22 pagesNew Records of 30 Wild Fungus Species and One Addition From Bangladesh-CompressedZinianasrin SumonNo ratings yet
- Prelab One-Flower IntroductionDocument29 pagesPrelab One-Flower IntroductionArwa ZayedNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION To Vegetable FarmingDocument2 pagesINTRODUCTION To Vegetable Farmingjim schaultzNo ratings yet
- BIOL1402 Fungi Study GuideDocument2 pagesBIOL1402 Fungi Study GuideMadeline JensenNo ratings yet
- TFSSvol1 3 PDFDocument1,551 pagesTFSSvol1 3 PDFNurul Farah AinNo ratings yet
- BS 03936-4-2007Document32 pagesBS 03936-4-2007Ali RayyaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Plants: Group 2: Joebert V. Delos Santos Rochelle B. Benavente Glydel F. Belencio Bse-1 FilipinoDocument14 pagesClassification of Plants: Group 2: Joebert V. Delos Santos Rochelle B. Benavente Glydel F. Belencio Bse-1 FilipinoMary rose AgorNo ratings yet
- Botany Paper-I: Morphology and Anatomy of Angiosperms: For Gondwana PapersDocument2 pagesBotany Paper-I: Morphology and Anatomy of Angiosperms: For Gondwana PapersPratiksha Baburao RajurkarNo ratings yet
- Anther Pollen Ovule Culture TechniquesDocument11 pagesAnther Pollen Ovule Culture TechniquesVARTIKA KHATI100% (1)
- Leaf Structure WorksheetDocument1 pageLeaf Structure Worksheetapi-309893409100% (1)
- Subject Link 1: Mid-Term Test: (1-5) Write The Correct Word For Each SentenceDocument6 pagesSubject Link 1: Mid-Term Test: (1-5) Write The Correct Word For Each SentenceYasser MohamedNo ratings yet
- Growing Guide for Brightly Colored Marigold FlowersDocument20 pagesGrowing Guide for Brightly Colored Marigold FlowersPrajakt RaulNo ratings yet
- Class 4 Science - How Plants Make Food 2 April - 20-21.docx 1Document3 pagesClass 4 Science - How Plants Make Food 2 April - 20-21.docx 1Ratheesh RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Plant and Garden Book PDFDocument534 pagesThe Ultimate Plant and Garden Book PDFEstee Gee100% (11)
- IndianLivestock PDFDocument255 pagesIndianLivestock PDFc sakthikumariNo ratings yet
- Monselise, Shaul P - CRC Handbook of Fruit Set and Development-1986Document579 pagesMonselise, Shaul P - CRC Handbook of Fruit Set and Development-1986Lili DomNo ratings yet
- Astika Dara PermadiDocument5 pagesAstika Dara PermadiItha Nurulmaidah Hi CangNo ratings yet
- Growing Hardy Soft Cane Dendrobium OrchidsDocument2 pagesGrowing Hardy Soft Cane Dendrobium OrchidsDheemanth BhandarkarNo ratings yet
- PRACTICAL MODULE ONLY 60320 - Unit 1Document4 pagesPRACTICAL MODULE ONLY 60320 - Unit 1Cemerlang StudiNo ratings yet
- Native Plant Propagation - MarinovaDocument21 pagesNative Plant Propagation - Marinovaapi-280363378100% (1)
- Chapter - 12 Reproduction in PlantsDocument5 pagesChapter - 12 Reproduction in Plantsanju singhNo ratings yet
- Frustulia Vulgaris (Thwaites) de Toni - AlgaebaseDocument2 pagesFrustulia Vulgaris (Thwaites) de Toni - AlgaebaseDario ŠakićNo ratings yet
- Story of Butterfly or Life Cycle of Butterfly in ArabicDocument21 pagesStory of Butterfly or Life Cycle of Butterfly in ArabicKUNNAMPALLIL GEJO JOHNNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 (Anmol)Document26 pagesAssignment 3 (Anmol)Anmol ChughNo ratings yet
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (378)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (515)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- Inside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowFrom EverandInside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (390)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- This Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyFrom EverandThis Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsFrom EverandWhy We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2083)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- The Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsFrom EverandThe Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsNo ratings yet
- The Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightFrom EverandThe Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)