Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Flower Structure and Function
Uploaded by
laila dhiya0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesThe flower is composed of four types of floral organs arranged in concentric whorls: carpels, stamens, petals, and sepals. Carpels and stamens are reproductive structures called sporophylls that contain ovules and produce pollen, respectively. Petals are typically brightly colored to attract pollinators, while sepals protect the inner floral parts before flowering. Carpels contain ovaries with ovules that can develop into seeds if fertilized by pollen from stamens. A pistil refers to a single carpel or multiple fused carpels.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe flower is composed of four types of floral organs arranged in concentric whorls: carpels, stamens, petals, and sepals. Carpels and stamens are reproductive structures called sporophylls that contain ovules and produce pollen, respectively. Petals are typically brightly colored to attract pollinators, while sepals protect the inner floral parts before flowering. Carpels contain ovaries with ovules that can develop into seeds if fertilized by pollen from stamens. A pistil refers to a single carpel or multiple fused carpels.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesFlower Structure and Function
Uploaded by
laila dhiyaThe flower is composed of four types of floral organs arranged in concentric whorls: carpels, stamens, petals, and sepals. Carpels and stamens are reproductive structures called sporophylls that contain ovules and produce pollen, respectively. Petals are typically brightly colored to attract pollinators, while sepals protect the inner floral parts before flowering. Carpels contain ovaries with ovules that can develop into seeds if fertilized by pollen from stamens. A pistil refers to a single carpel or multiple fused carpels.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Flower Structure and Function
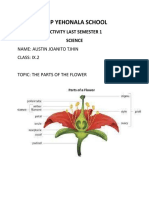
The flower, the sporophytic structure of angiosperms specialized
for sexual reproduction, is typically composed of four
types of floral organs: carpels, stamens, petals, and sepals
(Figure 38.2). When viewed from above, these organs take
the form of concentric whorls. Carpels form the first (innermost)
whorl, stamens the second, petals the third, and sepals
the fourth (outermost) whorl. All are attached to a part of the
stem called the receptacle. Flowers are determinate shoots;
they cease growing after the flower and fruit are formed.
Carpels and stamens are sporophylls—modified leaves
specialized for reproduction (see Concept 30.1); sepals and petals
are sterile modified leaves. A carpel (megasporophyll) has
an ovary at its base and a long, slender neck called the style.
At the top of the style is a sticky structure called the stigma
that captures pollen. Within the ovary are one or more ovules,
which become seeds if fertilized; the number of ovules depends
on the species. The flower in Figure 38.2 has a single carpel,
but many species have multiple carpels. In most species, the
carpels are fused, resulting in a compound ovary with two or
more chambers, each containing one or more ovules. The term
pistil is sometimes used to refer to a single carpel or two or
more fused carpels (Figure 38.3). A stamen (microsporophyll)
consists of a stalk called the filament and a terminal structure
called the anther; within the anther are chambers called
microsporangia (pollen sacs) that produce pollen. Petals are
typically more brightly colored than sepals and advertise the
flower to insects and other animal pollinators. Sepals, which
Figure 38.2 The structure of an idealized flower.
Figure 38.3 The relationship between the terms carpel
and pistil. A simple pistil consists of a single, unfused carpel. A
compound pistil consists of two or more fused carpels. Some types
of flowers have only a single pistil, while other types have many pistils.
In either case, the pistils may be simple or compound.
For example, most
grass flowers lack petals. Some incomplete flowers are sterile,
lacking functional stamens and carpels; others are unisexual
You might also like
- Reproductive Flowering Plants Magnoliophyta Angiosperms SpermDocument17 pagesReproductive Flowering Plants Magnoliophyta Angiosperms Spermfilan0fisteku-502158No ratings yet
- Terminology Used in Plant DescriptionDocument13 pagesTerminology Used in Plant DescriptionAli HamzaNo ratings yet
- Biology Sem 3Document13 pagesBiology Sem 3yondaimeredzuan0% (1)
- Flower: Jump To Navigation Jump To Search Flower (Disambiguation) Floral (Disambiguation)Document12 pagesFlower: Jump To Navigation Jump To Search Flower (Disambiguation) Floral (Disambiguation)jolinmartinNo ratings yet
- FlowerDocument22 pagesFlowerGrety IancuNo ratings yet
- Flower: Navigation Search Flower (Disambiguation) Floral (Disambiguation)Document18 pagesFlower: Navigation Search Flower (Disambiguation) Floral (Disambiguation)devakikris1985No ratings yet
- Flower - WikipediaDocument96 pagesFlower - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Phylum Magnoliophyta: AngiospermsDocument7 pagesPhylum Magnoliophyta: Angiospermskell73kNo ratings yet
- 4.8 Sexual Reproductive System of Flowering PlantsDocument16 pages4.8 Sexual Reproductive System of Flowering PlantsYu HasNo ratings yet
- Blossom: StructureDocument3 pagesBlossom: StructuremedicusNo ratings yet
- Morphology: Floral PartsDocument8 pagesMorphology: Floral PartsKiana DouglasNo ratings yet
- Flower: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument14 pagesFlower: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaBibithaNo ratings yet
- Flower: For Other Uses, See - "Floral" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeDocument18 pagesFlower: For Other Uses, See - "Floral" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeLakshanmayaNo ratings yet
- Parts of A FlowerDocument10 pagesParts of A FlowerAnaly CNo ratings yet
- Flower: Blossom, Is The Reproductive Structure Found inDocument29 pagesFlower: Blossom, Is The Reproductive Structure Found inMaya AlessiaNo ratings yet
- Project On Flower v1.0Document10 pagesProject On Flower v1.0powerleader50% (2)
- Structure: Plant Reproductive Morphology Androecium GynoeciumDocument2 pagesStructure: Plant Reproductive Morphology Androecium Gynoeciummegawhat115No ratings yet
- Morphology of FlowerDocument3 pagesMorphology of FlowerDeepakNo ratings yet
- Inflorescence, Pollination and FertilizationDocument16 pagesInflorescence, Pollination and Fertilizationniswati zahroNo ratings yet
- Floral Parts: Whorl ReceptacleDocument2 pagesFloral Parts: Whorl ReceptacleaartistjobNo ratings yet
- Flower DrugsDocument5 pagesFlower DrugsHarish KakraniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Plant Science Flower and Inflorescence StructureDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Plant Science Flower and Inflorescence StructureAlan ReidNo ratings yet
- Flower: Flower (Disambiguation) Floral (Disambiguation)Document6 pagesFlower: Flower (Disambiguation) Floral (Disambiguation)Cptcafecpt CptcafeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - MorphologyDocument27 pagesChapter 5 - Morphologyavishank584No ratings yet
- Morphology: Floral PartsDocument2 pagesMorphology: Floral PartsNovember RolfNo ratings yet
- A Flower01Document8 pagesA Flower01LOUISE ELIJAH GACUANNo ratings yet
- Angiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and SeedsDocument5 pagesAngiosperm Reproduction: Flowers, Fruits, and SeedsAurora ÇizmjaNo ratings yet
- FlowerDocument11 pagesFlowerKristoff Bryan BermacheaNo ratings yet
- Botany (Flower)Document15 pagesBotany (Flower)Louis Fetilo FabunanNo ratings yet
- 03 Reproductive Morphology VegetalDocument25 pages03 Reproductive Morphology VegetalbordinessrineNo ratings yet
- Flowers, Fruits and SeedsDocument2 pagesFlowers, Fruits and SeedsChessNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument8 pagesReproduction in Plantsdwi rahmaNo ratings yet
- Flower StructureDocument16 pagesFlower Structurevaishnavi100% (1)
- Flower: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument13 pagesFlower: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRakesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Flower: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument5 pagesFlower: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDanny FentomNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Flower MorphologyDocument39 pagesLecture 5 Flower MorphologyNur SabrinaNo ratings yet
- Flower Description Glossary PDFDocument5 pagesFlower Description Glossary PDFbekoNo ratings yet
- The Flower 4.1Document2 pagesThe Flower 4.1Study SuccessNo ratings yet
- (179751155) FlowerDocument17 pages(179751155) FlowersujithasNo ratings yet
- Flower - WikipediaDocument180 pagesFlower - WikipediaBiology ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Morphology: Floral PartsDocument2 pagesMorphology: Floral PartsyosephineikaaNo ratings yet
- B L R D P: F, F, S: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesB L R D P: F, F, S: ObjectivesJorelyn Giron NaniongNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The FlowerDocument10 pagesThe Structure of The FlowerGerald BenjaminNo ratings yet
- FlowerDocument5 pagesFlowerEiren QuimsonNo ratings yet
- Flower Anatomy 1Document36 pagesFlower Anatomy 1Iram Tahir100% (1)
- FlowerDocument5 pagesFlowerReambillo FamilyNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity Lecture 8-AngiospermsDocument22 pagesPlant Diversity Lecture 8-AngiospermsLebohang MakhanyaNo ratings yet
- Parts of The FlowerDocument4 pagesParts of The FlowerAustin Joanito TjhinNo ratings yet
- Plant Flower 01 ButtercupDocument1 pagePlant Flower 01 ButtercupwhatNo ratings yet
- Stamen - WikipediaDocument14 pagesStamen - Wikipediamae mahiyaNo ratings yet
- Plant Parts - Flowers: PistilDocument8 pagesPlant Parts - Flowers: PistilDiana Marie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1645490440596 6901687136957622992Document6 pagesOrca Share Media1645490440596 6901687136957622992Kelly CasterNo ratings yet
- 4 Flower of Different FamiliesDocument48 pages4 Flower of Different FamiliesGuru temp id-04 for Sekolah-8252 MoeNo ratings yet
- Bio Report6Document27 pagesBio Report6myvi3213No ratings yet
- Plants and People: FlowersDocument28 pagesPlants and People: FlowersSabrina Naila DastianaNo ratings yet
- Flower: BlossomDocument22 pagesFlower: BlossomEmpire kingNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System in Plants SS2Document7 pagesReproductive System in Plants SS2Ezeh PrincessNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants Class11Document15 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants Class11Ashok KumarNo ratings yet
- Plants and People: FlowersDocument28 pagesPlants and People: FlowersYuan ShengNo ratings yet