Professional Documents
Culture Documents
O.eiffel Tower PBA
Uploaded by
Anthony RelatorOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
O.eiffel Tower PBA
Uploaded by
Anthony RelatorCopyright:
Available Formats
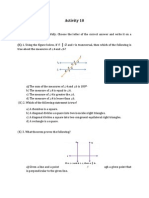
Name: __________________________ 11.
23 L’Eiffel Tower PBA Pd: ___
“C'est la Tour Eiffel. Il y a beaucoup de parallélogrammes dans sa conception” –Pierre, étudiant d’architecture
“This is the Eiffel Tower. There are many parallelograms in its design” – Pierre the Architect Student
The assembly of the 300 meter tower was a marvel of precision. Imagine a tower taller than 3 football fields, end to end. The
construction work began in January 1887 and was finished on March 31, 1889. How did they get it to be so beautifully symmetric
without modern construction techniques? Help Pierre the architect student understand the design.
Pierre’s Picture from the elevator As stated in the quote above, Pierre notices that the Eiffel Tower is made of many
parallelograms. Upon further investigation, he realizes that triangles are also a prominent
part of the design. Using his knowledge of triangles, he thinks he can determine the
measurements of all the angles. First he sketches a cross section of one of the support beams
as seen from the elevator:
####, 𝐵𝐺
####, 𝐵𝐶
In this figure, Pierre realizes that 𝐵𝐸 #### , and 𝐵𝐴
#### are all the same length. He also
realizes that #### #### are parallel.
𝐺𝑇 and 𝐸𝑂
1.) What types of triangle is ∆𝐸𝐵𝐶. Explain how you know.
2.) Determine the measures of the following angles. Explain your reasoning.
mÐBCE = _____ mÐEBC = _____ mÐABG = _____ mÐBGA = _____
3.) ∆𝐸𝐵𝐶, ∆𝐺𝐵𝐴, ∆𝐴𝐷𝑇, and ∆𝐶𝐷𝑂 are all congruent. Find the 𝑚∠𝐶𝐷𝑂 and 𝑚∠𝐶𝑂𝐷. Justify your answer.
mÐCDO = _____ mÐCOD = _____
4.) This shape looks like it’s symmetric… but is it? To be sure, Pierre looked at the blue print and drew a line down the middle. Use the
space below to prove that ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶 ≅ ∆𝐴𝐷𝐶
Given: The figure below
Prove: ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶 ≅ ∆𝐴𝐷𝐶
5.) Describe the transformation to get ∆𝐴𝐷𝐶 from ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶.
6.) Pierre wants to know more about the design at the left section of the tower, so he looked up a picture on the internet. He then drew
a blueprint.
a.) Pierre was able to determine that 𝑚∠𝐾𝐼𝑄 = 22° and 𝑚∠𝐼𝑄𝐾 = 22°. Find
the 𝑚∠𝑄𝐾𝑀 and explain your reasoning.
mÐQKM = _____
b.) Pierre thinks that all the triangles he sees in the figure are congruent. Is right or wrong? Justify your answer.
7.) The figure is drawn so all lines that appear to be parallel are parallel.
6 bisects ∠𝐻𝐼𝑀.
𝐿𝐼 Pierre visited the Eiffel Tower and measured the tilt of the left leg to the ground to be
##### bisects ∠𝐼𝐻𝐿.
𝑀𝐻 44 degrees to the ground. Because of security, he wasn’t able to get close enough to
∠𝐻𝐼𝑀 = 44° measure the angles where the pieces intersect. Help Pierre calculate the angles inside
∠𝐻𝐼𝑀 and ∠𝐼𝐻𝐿 are supplementary. the support beams.
mÐ1 mÐ2 mÐ3 mÐ4
mÐ5 mÐ6 mÐ7 mÐ8
Below is a sketch of a section near the top. IF HI=20 meters of steel. Calculate all of the steel used to make
this 2D section. Leave in simplified radical form or use the
calculator to evaluate your answer.
It is made from 4 squares with 2 diagonal support
beams in each square.
You might also like
- Chapter09 Geometric FiguresDocument32 pagesChapter09 Geometric Figureslen16328100% (4)
- Precalculus Q1 Mod1 Introduction of Conic Sections and The CircleDocument37 pagesPrecalculus Q1 Mod1 Introduction of Conic Sections and The CircleGene Ramirez75% (4)
- Hemh 103Document20 pagesHemh 103Narendra JadhavNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Trigonometry With Applications PDFDocument190 pagesEssentials of Trigonometry With Applications PDFcerbalzackguzmanNo ratings yet
- Third Periodical Test in Math 4Document3 pagesThird Periodical Test in Math 4irvin victoriaNo ratings yet
- Friction LossDocument5 pagesFriction LossNethajiNo ratings yet
- MATHDocument8 pagesMATHjoel paolo ramos100% (1)
- Third Periodical Test Mathematics 4Document3 pagesThird Periodical Test Mathematics 4GavzprinCessSalvadorNo ratings yet
- 08 - Trigonometric Functions, Identities and EquationsDocument3 pages08 - Trigonometric Functions, Identities and EquationsJASON_INGHAM100% (1)
- Kvs JR Maths OLympiad PapersDocument25 pagesKvs JR Maths OLympiad PapersNitinNo ratings yet
- Sine and Cosine Rule Problems (SL)Document22 pagesSine and Cosine Rule Problems (SL)Rudi Berlian100% (2)
- 5 5Document8 pages5 5spatel1972No ratings yet
- Triangles and Congruence Chapter With QtnsDocument40 pagesTriangles and Congruence Chapter With QtnsSishira PattanNo ratings yet
- PT - Mathematics 4 - Q3Document3 pagesPT - Mathematics 4 - Q3KM EtalsedNo ratings yet
- Math 4 3rd PT With TOSDocument7 pagesMath 4 3rd PT With TOSRuben100% (2)
- 3rd Periodical Test in Math 4Document7 pages3rd Periodical Test in Math 4mark jefferson borromeo100% (3)
- Geometry: Srimathi Sundaravalli Memorial School Chennai 2020-2021 Mathematics Class: Ix Topic: Gist of The ChapterDocument6 pagesGeometry: Srimathi Sundaravalli Memorial School Chennai 2020-2021 Mathematics Class: Ix Topic: Gist of The ChapterDhanya BalasundarrajNo ratings yet
- Corresponding AnglesDocument31 pagesCorresponding AnglesRaxie YacoNo ratings yet
- GCSE Mathematics 1MA1 Problem-Solving Questions 1: Higher TierDocument21 pagesGCSE Mathematics 1MA1 Problem-Solving Questions 1: Higher TierMorena PotenzaNo ratings yet
- Joy Activity 10Document7 pagesJoy Activity 10api-279213523No ratings yet
- EM g7 Maths 2021 WP 3rdDocument10 pagesEM g7 Maths 2021 WP 3rdNikila WeerasingheNo ratings yet
- SSC 2014 October GeometryDocument3 pagesSSC 2014 October GeometryLatif Ismail ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Geometry Final Exam ReviewDocument48 pagesGeometry Final Exam ReviewAngelo BoujaoudeNo ratings yet
- Math 8 LAW Q4docxDocument19 pagesMath 8 LAW Q4docxGirlie Mae FloresNo ratings yet
- Q4 - WEEK3 - WW - PT For G9Document5 pagesQ4 - WEEK3 - WW - PT For G9RC FerrerNo ratings yet
- Properties of ParallelogramDocument59 pagesProperties of ParallelogramJerson LumbreNo ratings yet
- MATHq3 ST2Document3 pagesMATHq3 ST2Ma Czarina Bardon - LavisteNo ratings yet
- BLM Square Metre: 1 CM 1 CM × 1 CMDocument10 pagesBLM Square Metre: 1 CM 1 CM × 1 CMJenonymouslyNo ratings yet
- 3-D Castle CreationsDocument12 pages3-D Castle CreationsLeila RobertsNo ratings yet
- Maths Progress International Year 8 Student Book SampleDocument35 pagesMaths Progress International Year 8 Student Book Samplessu371837No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 NotesDocument24 pagesChapter 6 NotesArchana RajuNo ratings yet
- 4th 1-2assessment Math8&esp8Document4 pages4th 1-2assessment Math8&esp8zye zhaNo ratings yet
- 2016 Regional Geometry Exam Final PDFDocument15 pages2016 Regional Geometry Exam Final PDFPartha SarathiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Guided NotesDocument22 pagesChapter 4 Guided NotesdevikaNo ratings yet
- Maths Grade 7 Mathematics 11 15 May 2020 English AREA AND PERIMETER OF 2D SHAPESDocument18 pagesMaths Grade 7 Mathematics 11 15 May 2020 English AREA AND PERIMETER OF 2D SHAPESJamal BhattiNo ratings yet
- Math 8 Q4 ModuleDocument40 pagesMath 8 Q4 ModulecesianeNo ratings yet
- Hemh 103Document16 pagesHemh 103Kartikey SinghNo ratings yet
- 09supp. Chapter 07Document4 pages09supp. Chapter 07Yadana1No ratings yet
- Board Question Paper: March 2018: GeometryDocument2 pagesBoard Question Paper: March 2018: Geometryjuthani100No ratings yet
- Study Guide Geometry Quarter 3 Test 12-13Document10 pagesStudy Guide Geometry Quarter 3 Test 12-13Sarra GrandeNo ratings yet
- Scale Drawing and Trigonometry Slides (With Notes)Document10 pagesScale Drawing and Trigonometry Slides (With Notes)SUE YIN100% (1)
- MA Sample Paper 10 UnsolvedDocument9 pagesMA Sample Paper 10 UnsolvedAarlio RohillaNo ratings yet
- DFMFullCoverage-PythagorasTheorem 2Document12 pagesDFMFullCoverage-PythagorasTheorem 2M MNo ratings yet
- DFMFullCoverage PythagorasTheoremDocument12 pagesDFMFullCoverage PythagorasTheoremeuphorian123No ratings yet
- The Quadrilateral Family Tree:: Do Well On This Test!Document6 pagesThe Quadrilateral Family Tree:: Do Well On This Test!jorgepayasayNo ratings yet
- PT - Mathematics 4 - Q3Document3 pagesPT - Mathematics 4 - Q3Jeline UyNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document6 pagesActivity 2Richelle MallillinNo ratings yet
- Review Homework 1Document2 pagesReview Homework 1api-368121935No ratings yet
- Estimating Square Roots and CubesDocument11 pagesEstimating Square Roots and CubesmanilaNo ratings yet
- Revision Sheet For EOY Grade 8Document16 pagesRevision Sheet For EOY Grade 8Subhashini ChandraNo ratings yet
- PT Mathematics-4 Q3Document5 pagesPT Mathematics-4 Q3marbin genayasNo ratings yet
- Higher Problem Solving Questions 1Document21 pagesHigher Problem Solving Questions 1shreyashahwigginsNo ratings yet
- 2023 2024 Class VI Mathematics Part 2 AWDocument64 pages2023 2024 Class VI Mathematics Part 2 AWRashmiSinghNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Notes: ReflectionsDocument13 pages3.1 Notes: ReflectionsffgfgfgffgNo ratings yet
- SLM - Math 8 Q4 WK 4 Module 4 Mary Ann M.diazDocument17 pagesSLM - Math 8 Q4 WK 4 Module 4 Mary Ann M.diazZia De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Math8 Summative Test q4Document5 pagesMath8 Summative Test q4Rhea DonaNo ratings yet
- Perimeter and AreaDocument20 pagesPerimeter and AreaBrigita Diny LaksitasariNo ratings yet
- Amity International School, Saket Math Worksheet - Class Vii Perimeter & Area and Visualizing Solid ShapesDocument2 pagesAmity International School, Saket Math Worksheet - Class Vii Perimeter & Area and Visualizing Solid ShapesPrisha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Full Student PacketDocument30 pagesChapter 1 Full Student PacketJillian MarceloNo ratings yet
- Homework 9.1 Ratios and ProportionsDocument10 pagesHomework 9.1 Ratios and ProportionsAliRazaNo ratings yet
- Theorems On Triangle Inequalities and Parallel Lines Cut by A TransversalDocument2 pagesTheorems On Triangle Inequalities and Parallel Lines Cut by A Transversal20100576No ratings yet
- GR 10 Euclidean Geometry Booklet SUE 2019Document18 pagesGR 10 Euclidean Geometry Booklet SUE 2019Desmond SmithNo ratings yet
- Assorted Trig Application ProblemsDocument9 pagesAssorted Trig Application ProblemsAnthony RelatorNo ratings yet
- Accelerated Algebra 2 Unit 6 Performance Task 2 - Ferris WheelDocument2 pagesAccelerated Algebra 2 Unit 6 Performance Task 2 - Ferris WheelAnthony RelatorNo ratings yet
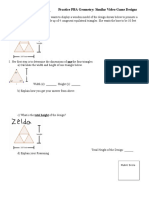
- Name: - Practice PBA Geometry: Similar Video Game DesignsDocument3 pagesName: - Practice PBA Geometry: Similar Video Game DesignsAnthony RelatorNo ratings yet
- Accelerated Algebra 2 Unit 6 Performance Task 2 - Ferris WheelDocument2 pagesAccelerated Algebra 2 Unit 6 Performance Task 2 - Ferris WheelAnthony RelatorNo ratings yet
- Assorted Trig Application ProblemsDocument9 pagesAssorted Trig Application ProblemsAnthony RelatorNo ratings yet
- Circular CurveDocument30 pagesCircular Curveqaiserkhan001No ratings yet
- Conic Sections OverviewDocument93 pagesConic Sections OverviewAkihiko SuzukiNo ratings yet
- Correlation 1 - Trigonometry NotesDocument7 pagesCorrelation 1 - Trigonometry Notesdoni poNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 GEOMETRYDocument26 pagesUnit 2 GEOMETRYHanif AshranNo ratings yet
- 9 THDocument32 pages9 THshinchan noharNo ratings yet
- Ramos Profed6 Output2Document13 pagesRamos Profed6 Output2Mark Anthony RamosNo ratings yet
- 1.𝐴𝑅≅𝑆𝑅, 𝑊𝑅≅𝐷𝑅 1. Given 2. ∠𝑊𝑅𝐴 and ∠𝐷𝑅𝑆 are vertical angles 2. Definition of vertical angles 3. ∠𝑊𝑅𝐴 ≅ ∠𝐷𝑅𝑆 3. Vertical Angle Theorem 4. Δ𝑅𝐴𝑊≅Δ𝑅𝑆𝐷 4. SAS Congruence PostulateDocument9 pages1.𝐴𝑅≅𝑆𝑅, 𝑊𝑅≅𝐷𝑅 1. Given 2. ∠𝑊𝑅𝐴 and ∠𝐷𝑅𝑆 are vertical angles 2. Definition of vertical angles 3. ∠𝑊𝑅𝐴 ≅ ∠𝐷𝑅𝑆 3. Vertical Angle Theorem 4. Δ𝑅𝐴𝑊≅Δ𝑅𝑆𝐷 4. SAS Congruence PostulatenowilNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Angle: IndexDocument16 pagesIntroduction of Angle: IndexRatay EvelynNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Standard 12 Chapter 4Document11 pagesCambridge Standard 12 Chapter 4Raymond ZhuNo ratings yet
- Coordinate Geometry of The Circle PDFDocument5 pagesCoordinate Geometry of The Circle PDFInspire The PeopleNo ratings yet
- Aus09 HW 17Document4 pagesAus09 HW 17Vea ValcorzaNo ratings yet
- Crosswords Puzzle 8C, 6CDocument24 pagesCrosswords Puzzle 8C, 6CmonicacorbusNo ratings yet
- Ce 2 Pre-Test 3 RationalizationDocument35 pagesCe 2 Pre-Test 3 Rationalizationkrystel basaNo ratings yet
- Individual Questions: Math League PressDocument2 pagesIndividual Questions: Math League PressFang GuoNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions For Class 8 Maths Chapter 4Document22 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 8 Maths Chapter 4ArchanaNo ratings yet
- ArMath 1 - Presentation1Document24 pagesArMath 1 - Presentation1Jayson RamirezNo ratings yet
- TYMCM Mass Points PDFDocument12 pagesTYMCM Mass Points PDFAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- MonkDocument121 pagesMonkCindy Yusseny Ayala MenjivarNo ratings yet
- Number:: One Two Three Four Five Six Seven Eight Nine TenDocument5 pagesNumber:: One Two Three Four Five Six Seven Eight Nine TenIndah Chairun AnnisaNo ratings yet
- Aim: What Are Cofunctions?: Do NowDocument5 pagesAim: What Are Cofunctions?: Do NowbwlomasNo ratings yet
- VedantuDocument2 pagesVedantuRishabhNo ratings yet
- International Islamic University Islamabad Schools Attock Campus 2 Term 1 BimonthlyDocument3 pagesInternational Islamic University Islamabad Schools Attock Campus 2 Term 1 BimonthlysalmanNo ratings yet
- Iterates of Brocardian Points and LinesDocument10 pagesIterates of Brocardian Points and Linescloz54No ratings yet
- Centroid of Triangle, Semicircle.Document11 pagesCentroid of Triangle, Semicircle.Shang Divina EbradaNo ratings yet