Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Worksheet Pedia (Sanaani)
Uploaded by
Nur Sanaani0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views4 pagesjhjhjhjhjhjhjhjhhj
Original Title
worksheet pedia(sanaani)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentjhjhjhjhjhjhjhjhhj
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views4 pagesWorksheet Pedia (Sanaani)
Uploaded by
Nur Sanaanijhjhjhjhjhjhjhjhhj
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Ateneo de Zamboanga University
COLLEGE OF NURSING
Learning Worksheet (MOD 1 PED)
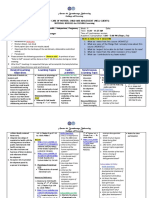
Directions: Complete the table by providing the most appropriate information.
Condition Signs & Symptoms Diagnostic test Management, Treatment Picture
Respiratory -This disease related to the Specific laboratory test Treatment:
Distress Syndrome immaturity of the lubgs tissue, must be carroed out to -institute thermoregulation-Prevent
this can also be classified as evaluate the neonatal for Hypotension
hyaline membraine disease, complication these test -Prevent Hypovolemia
this is a complex may include: -Correcr respiratory acidoses with
manifestation of sign of -Blood ventilatory support
respiratory.-who are the risk -urine -Correct metabolic acidoses by
factor of the respriatory -celerbral fliud(CSF) administrating sodium carbonate
distress syndrome:-premature- -cultures -blood glucose -administrator surfactant and other
maternal diabetes mellitus- -serume calcium-arterial drugs as order by physician
stress during delivery which blood gas(ABG)
produce acidoses(Sign and -radiographic evaluation
symptoms)-further increased
respiratory rate-labored
breathing-fine crackles on
ascultation-cyanosis-nasal
Flaring-expiratory grunting-
hypoxemia-hypercarbia-
acidosis
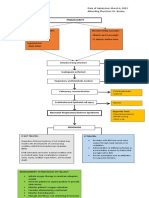
Meconium Involves aspiration of Diagnosis evaluation: Treatment:
Aspiration meconium into the lungs, -monitor fetal -immediately provide endicheal
Syndrome meconium aspiration respiration, such as suctioning and delivery
syndrome(MAS), result when presence of bradycardiac -offer respitatory assistance via
the neonatal inhaled the -assess for apgar score mechanical ventilation
meconium mixed with -ascultation of lungs -maintain a neutral thermal
amniotic fliud, typically -blood gas analysis environment
occurred with the first breath -chest X-ray -administer surfactant and an
or while the neonatal is in -urine color antibiotic
uteroRisk factors for (MAS)-
maternal diabetes-maternal
hypertension-difficult
delivery-fetal distress-
intrauterine hypoxia-advance
growth age(>42 week)-poor
intrauterine growthSign of
distress:-appearing limp-apgar
score <6-pallor-cyanosis-
coarse crackle when
auscultating neonatal lungs-
chest X-ray may show patches
or streaks of meconium in the
lungs air trapping or
hyperinflation
Condition Signs & Symptoms Diagnostic test Management, Treatment Picture
SIDS This is the typical death Observed infant: Educate pieces for patient:
occurring during age 12 -respiration of infant -Best sleep position”back”
months infant from unknow -breathing patterns of -Dress infant appropriately
reason and this tend occur infant “don’t over dress”
during sleep -assess for weight of -aviod exposing baby to tobacco
infant every now and smoke
then -Remove extra item from sleepin
-assess for proper area
position of infant -infact can sleep in the same
during sleep. room but not the same bed
–provide proper
ventilation.
–assess for
environmental
thermological humid
Hyperbilirubinemi This is also classified as Assess for: Treatment:
a pathologic “jaundice”, -assess for presences of -Provide an exchange transfuin
hyperbilirubunemia can be Jaundice -offer phototherapy
developed several ways: -assess for any -administration albumin
-certain drugs(such as presence of Elevated Nursing Intervention:
aspirin/tranquilizer/ serium bilirium -Clean the neonatal eye’s
sulfonamides) -assess for CBC periodically to removed
-this can cause -asess for urine drainage
(hypothermia/ anoxia/ -offer the neonatal extra water
hypoglycaemia to promote bilirium excretion
/hypoalbuminemia)
.
sign and symptoms:
-jaundice
-elevated serium biliruim
-hepatosplenomegaly
NAME: SANAANI, NUR-FATIMA, M.
Sec: BSN-2H
Date: 2/15/2021
You might also like
- 1 PEDIAII 2 - Neonatology 2Document20 pages1 PEDIAII 2 - Neonatology 2Andrassy Twinkle AlineaNo ratings yet
- Fetal DistressDocument10 pagesFetal DistressLady Jane CaguladaNo ratings yet
- Nasa QuizDocument4 pagesNasa QuizYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)No ratings yet
- Oral Revalida Day 2 PediaDocument10 pagesOral Revalida Day 2 PediaANGELICA JOY GATDULANo ratings yet
- Pre-Natal Care: Jennifer F. Aficial Man. RNDocument21 pagesPre-Natal Care: Jennifer F. Aficial Man. RNshana ferrerNo ratings yet
- High Risk NewbornDocument4 pagesHigh Risk NewbornHanna AligatoNo ratings yet
- GenitoDocument12 pagesGenitofatima_antonioNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 A Physiologic Problems of The NBDocument3 pagesNCM 109 A Physiologic Problems of The NBmaryelle conejarNo ratings yet
- 1.what Are The Possible Causes You Have To Consider?Document4 pages1.what Are The Possible Causes You Have To Consider?studio1234No ratings yet
- Neonatologi SMT 7Document39 pagesNeonatologi SMT 7Zulfikar RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Newborn Care LectureDocument65 pagesNewborn Care LectureNichole daFonsecaNo ratings yet
- 04 Pediatri Spotleri 2020Document104 pages04 Pediatri Spotleri 2020Osama E. ShamsNo ratings yet
- Ncma219 Lec MidtermDocument51 pagesNcma219 Lec MidtermMacababbad Joshua MiguelNo ratings yet
- Acute Conditions of The NewbornDocument5 pagesAcute Conditions of The NewbornCamille Joy BaliliNo ratings yet
- Ob Reviewer (Side Notes) : Most Common (Leading) Causes of Maternal Death Sa Pilipinas: 2019Document4 pagesOb Reviewer (Side Notes) : Most Common (Leading) Causes of Maternal Death Sa Pilipinas: 2019k76pk6brv9No ratings yet
- Fetal AssessmentDocument44 pagesFetal AssessmentmariallenNo ratings yet
- Meconium Aspiration SyndromeDocument10 pagesMeconium Aspiration SyndromeSampat KumawatNo ratings yet
- Special Neonatal ConditionsDocument37 pagesSpecial Neonatal ConditionsSanthosh.S.UNo ratings yet
- MCN NotesDocument5 pagesMCN NoteskistlerNo ratings yet
- Sample NCPDocument3 pagesSample NCPchenri1318No ratings yet
- Newborn Assessment PDFDocument51 pagesNewborn Assessment PDFMilca DavidNo ratings yet
- High Risk NewbornDocument4 pagesHigh Risk NewbornWenn Joyrenz ManeclangNo ratings yet
- Thermoregulation For The Maintenance of BodyDocument2 pagesThermoregulation For The Maintenance of BodyVince Matt BaguioNo ratings yet
- Summary of Obstetrics CasesDocument7 pagesSummary of Obstetrics CasesMahir AminNo ratings yet
- CASE PRESENTATION ON. Respiratory DistresssDocument13 pagesCASE PRESENTATION ON. Respiratory DistresssArchana Sahu78% (9)
- Eclampsia Pre EclampsiaDocument3 pagesEclampsia Pre EclampsiaOona Nicole Diorico100% (2)
- Toprank Review Pediatric Nursing NotesDocument12 pagesToprank Review Pediatric Nursing NotesCose online shopNo ratings yet
- Male and Female Radiographic ProceduresDocument5 pagesMale and Female Radiographic ProceduresKaye A. JardinicoNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 A Physiologic Problems of The NBDocument3 pagesNCM 109 A Physiologic Problems of The NBmaryelle conejarNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Distress Management in NewbornDocument5 pagesRespiratory Distress Management in Newbornagirl_9807100% (1)
- ROSIMO - AUG 2021 NB VomitingDocument5 pagesROSIMO - AUG 2021 NB VomitingcarlosNo ratings yet
- High Risk Newborn - Study GuideDocument10 pagesHigh Risk Newborn - Study GuideMalou Yap Buot100% (1)
- PED 1.6 Care of NewbornDocument5 pagesPED 1.6 Care of NewbornchristianNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis: Republic of The Philippines Bicol UniversityDocument7 pagesCase Analysis: Republic of The Philippines Bicol UniversityTrixia AlmendralNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Nursing Module 5Document4 pagesMaternal and Child Nursing Module 5Ezekiel John GarciaNo ratings yet
- Activity NCM 66 DARWINDocument8 pagesActivity NCM 66 DARWINLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- MCN ReviewerDocument4 pagesMCN ReviewerMaria Arabella LanacaNo ratings yet
- Adaptasi NeonatusDocument35 pagesAdaptasi NeonatusSyifa Dewi PrastikaNo ratings yet
- MALPRESENTATIONDocument13 pagesMALPRESENTATIONLady Jane CaguladaNo ratings yet
- BSN 2C MCN Lec Transes 1 1Document4 pagesBSN 2C MCN Lec Transes 1 1Shahina ShayneNo ratings yet
- Hot Topics of Pediatrics (Muhadharaty) PDFDocument577 pagesHot Topics of Pediatrics (Muhadharaty) PDFdr.sasikumarNo ratings yet
- Ob2 Sas 34Document6 pagesOb2 Sas 34????No ratings yet
- LM 3 Physiologic Adaptation of The MotherDocument8 pagesLM 3 Physiologic Adaptation of The MotherKiminatsu SyNo ratings yet
- Management of Respiratory Distress in The Newborn: Emergency MedicineDocument5 pagesManagement of Respiratory Distress in The Newborn: Emergency MedicineturigauNo ratings yet
- Medication and Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesMedication and Nursing Care PlanRubina MasihNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Newborn: ObjectivesDocument17 pagesDiseases of The Newborn: ObjectivesIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- BRONCHIOLITISDocument19 pagesBRONCHIOLITISKamilla AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Emergency Triage Assessment and Treatment: National Neonatology ForumDocument6 pagesEmergency Triage Assessment and Treatment: National Neonatology ForumSatya Prakash TiwariNo ratings yet
- UtsaDocument17 pagesUtsaCallie ParkNo ratings yet
- Group 2Document53 pagesGroup 2Cms CSUNo ratings yet
- Common Neonatal Disorders 4Document33 pagesCommon Neonatal Disorders 4Laishram Deeva ChanuNo ratings yet
- Labor Delivery NewbornDocument4 pagesLabor Delivery NewbornMello D. ConsulNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument13 pagesRespiratory Distress SyndromeKenneth UbaldeNo ratings yet
- High Risk Newborn and FamilyDocument93 pagesHigh Risk Newborn and FamilyJen IlaganNo ratings yet
- Midwifery 102 MaterialDocument11 pagesMidwifery 102 MaterialBai Norhamah HassanNo ratings yet
- DiagramDocument1 pageDiagramryanNo ratings yet
- NCM 109 SL Lesson 1Document3 pagesNCM 109 SL Lesson 1Martina Medrano100% (1)
- NS1 Case PresDocument8 pagesNS1 Case PresjoanaalpayNo ratings yet
- OB Nursing NotesDocument101 pagesOB Nursing NotesNur Sanaani100% (2)
- PediaDocument9 pagesPediaNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Notes THE SETTINGDocument2 pagesNotes THE SETTINGNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Code of Ethics For Filipino NursesDocument22 pagesCode of Ethics For Filipino NursesNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Code of Ethics For Filipino NursesDocument22 pagesCode of Ethics For Filipino NursesNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease NursingDocument22 pagesCommunicable Disease NursingNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Nursing Research - InitialDocument25 pagesNursing Research - InitialNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Management Quiz 1Document10 pagesManagement Quiz 1Reema100% (1)
- Management Quiz 1Document10 pagesManagement Quiz 1Reema100% (1)
- Management Quiz 1Document10 pagesManagement Quiz 1Reema100% (1)
- Answer Key.Document4 pagesAnswer Key.Nur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For SCIDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan For SCINur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Answer Key.Document4 pagesAnswer Key.Nur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Course Title Course Code Course Description Prerequisites Course Credit Placement Program OutcomeDocument10 pagesCourse Title Course Code Course Description Prerequisites Course Credit Placement Program OutcomeNur Sanaani100% (1)
- 3 Reflection Paper in One WordDocument3 pages3 Reflection Paper in One WordNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Answer Key.Document4 pagesAnswer Key.Nur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Module Content CHN113Document6 pagesModule Content CHN113Nur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Neurologic System Disorders: Ateneo de Zamboanga UniversityDocument2 pagesNeurologic System Disorders: Ateneo de Zamboanga UniversityNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Emergency NursingDocument56 pagesEmergency NursingNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- A-Module 2 - EVP, CommunicationRecords Mgt.Document7 pagesA-Module 2 - EVP, CommunicationRecords Mgt.Nur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Date/Week Learning Objectives Asynchronous Learning Topic Synchronous Learning TopicDocument6 pagesDate/Week Learning Objectives Asynchronous Learning Topic Synchronous Learning TopicNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- 3 Reflection Paper in One WordDocument3 pages3 Reflection Paper in One WordNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- 3 Reflection Paper in One WordDocument3 pages3 Reflection Paper in One WordNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Nephrons (Functional Unit)Document44 pagesNephrons (Functional Unit)Nur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Sanaani Nso AngioplastyDocument14 pagesSanaani Nso AngioplastyNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Nso Topics: INSTRUCTION: Using The Format Provided, Please Report On ThursdayDocument1 pageNso Topics: INSTRUCTION: Using The Format Provided, Please Report On ThursdayNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- MultisystemDocument19 pagesMultisystemNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Rationale: Answer: C. If A Patient HasDocument12 pagesRationale: Answer: C. If A Patient HasNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- RRL Mental Health Adjustment and Perceived Academic Performance of Senior Highschool StudentsDocument19 pagesRRL Mental Health Adjustment and Perceived Academic Performance of Senior Highschool StudentsNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument121 pagesUntitled DocumentNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- AbdomenDocument32 pagesAbdomenVirendra K. GajbhiyeNo ratings yet
- Normal Labour QuizDocument2 pagesNormal Labour QuizAsh_myNo ratings yet
- OBII - 16 Postterm Pregnancy - PDF Version 1Document6 pagesOBII - 16 Postterm Pregnancy - PDF Version 1Felina CabadingNo ratings yet
- 3rd Lecture On The Histology of Female Reproductive System by Dr. RoomiDocument19 pages3rd Lecture On The Histology of Female Reproductive System by Dr. RoomiMudassar RoomiNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 10354: The Responsible Parenthood and Reproductive Health Act of 2012Document29 pagesRepublic Act No. 10354: The Responsible Parenthood and Reproductive Health Act of 2012amy faith susonNo ratings yet
- REPRODocument48 pagesREPROARVIND KUMAR YADAVNo ratings yet
- Dyspareunia: Physical Therapy Evaluation and ManagementDocument27 pagesDyspareunia: Physical Therapy Evaluation and ManagementJohayra AbbasNo ratings yet
- Higlighted For FNCPSDocument55 pagesHiglighted For FNCPSCarey Jamille YadanNo ratings yet
- 2024 GPBDocument126 pages2024 GPBJessica CindyNo ratings yet
- Fucked Up FamilyDocument61 pagesFucked Up FamilyAamir KhanNo ratings yet
- (OB) 2B - Obstetrical Anesthesia (By Dr. Bretta Lucion)Document3 pages(OB) 2B - Obstetrical Anesthesia (By Dr. Bretta Lucion)CleoGomezNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing Royal PentagonDocument68 pagesPediatric Nursing Royal Pentagondcrisostomo8010100% (2)
- Fetal Distress 10: Suresh TharmaratnamDocument18 pagesFetal Distress 10: Suresh Tharmaratnamyenni anggrainiNo ratings yet
- 18 - Male Reproductive SystemDocument8 pages18 - Male Reproductive SystemGrace FloresNo ratings yet
- Extra Questions Chapter 2Document2 pagesExtra Questions Chapter 2Shriyanshi GarodiaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document36 pagesLecture 1Behar AbdurahemanNo ratings yet
- Abortion: By: Priyanka Sadafule 1 Year PBBSC Student SeminarDocument51 pagesAbortion: By: Priyanka Sadafule 1 Year PBBSC Student SeminarDigu SadafuleNo ratings yet
- Women Wellness CourseDocument69 pagesWomen Wellness CourseEktarayogaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 MAT Reproductive Sexual HealthDocument4 pagesMODULE 1 MAT Reproductive Sexual HealthHas SimNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Paper - Essay and LettersDocument96 pagesDescriptive Paper - Essay and LettersSRIPRASAD SATAPATHYNo ratings yet
- Participate IN Various Programmes VasectomyDocument6 pagesParticipate IN Various Programmes Vasectomyvenkat krishnanNo ratings yet
- Dentists' Knowledge of Oral Health During PregnancyDocument6 pagesDentists' Knowledge of Oral Health During PregnancyRubilu ResNo ratings yet
- Portfolio IN Community Health Nursing: Submitted byDocument5 pagesPortfolio IN Community Health Nursing: Submitted byJay Villasoto100% (1)
- Reaction Paper-In The WombDocument3 pagesReaction Paper-In The WombKuya Ericson71% (7)
- Review of Literature Related To Low Birth Weight BabiesDocument4 pagesReview of Literature Related To Low Birth Weight BabiesgwfdurbndNo ratings yet
- Efektifitas Pembelajaran Kelas Ibu Hamil Dalam Menurunkan Anemia Di Kecamatan Grogol SukoharjoDocument11 pagesEfektifitas Pembelajaran Kelas Ibu Hamil Dalam Menurunkan Anemia Di Kecamatan Grogol SukoharjoHarmoko Screamo D'sevenvoldNo ratings yet
- Answer-Goat and Sheep Lab2Document7 pagesAnswer-Goat and Sheep Lab2claire joy cabaseNo ratings yet
- Reaching The Age of AdolescenceDocument2 pagesReaching The Age of Adolescencernimlik668No ratings yet
- Save The Girl Child - Essay - Important IndiaDocument8 pagesSave The Girl Child - Essay - Important IndiaAnonymous 1b3ih8zg9100% (1)
- Midterm Coverage - NCM 108 Health Care Ethics NotesDocument10 pagesMidterm Coverage - NCM 108 Health Care Ethics NotesAudrie Allyson GabalesNo ratings yet