Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Time 75 Minutes Che611A Endsem-Part2 Total Marks
Uploaded by
Pankaj Kumar SainiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Time 75 Minutes Che611A Endsem-Part2 Total Marks
Uploaded by
Pankaj Kumar SainiCopyright:
Available Formats
Time 75 Minutes CHE611A EndSem-Part2 Total Marks (35)
Question 2.1 (20 Marks)
Consider the plane shear flow between two infinitely large and wide plates. The gap between the
plates is b in y direction. The plate at y=b moves with a velocity V in the x direction. The plate at
y=0 is receiving a constant heat flux q0 and the plate at y=b is insulated. Assume that the fluid
properties do not change significantly with the temperature and that both velocity and temperature
profiles are fully developed. Obtain the velocity and temperature profiles. Calculate the Nusselt
number for this case.
Question 2.2. (15 Marks)
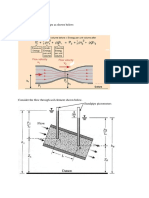
Presence of a lubricating fluid between bearing and shafts (at a slight offset) permits supporting a
large amount of load. For small gap between the two, the problem is very well approximated by a
fast moving tapered plane over a flat plate, mimicking a converging channel. A crude model of the
converging channel of length L=(L1+L2) and heights h1 and h2 at the two ends can be assumed to
be consisting of a step channel of lengths L1 & L2 with heights h1 and h2 as shown in figure below.
The lower plate moving at V mimics the relative motion of the plates. Both ends of the channel are
open to atmosphere. Assume steady, fully developed flow in both the channels and that the regions
of non-fully developed flow at the two ends and at the junction of the channels will have negligible
influence (reasonable if L >>h1). To keep it consistent with the ramp angle of converging channel,
we need to make sure that h2/h1=L2/(L1+L2).
A. Obtain the pressure at the location of the step for the case L2/L1= last digit of your roll number
(second last digit incase last digit is 0).
B. Sketch the pressure profiles neatly.
C. Calculate the load that the step channel of width W can support on it due to the pressure
distribution in the channel over its entire length L using h2=1mm and L=10cm if the fluid is
water (viscosity 10-3 Pa.s) for W=10 cm and V=10m/s.
L1
L2
h1
h2
Page 1 of 1
You might also like
- TUTORIAL 1 - Solutions: SolutionDocument12 pagesTUTORIAL 1 - Solutions: SolutionMahesh Ramesh TapasNo ratings yet
- Additional Reading Materials For Lectures 07 & 11: Lecturer: Dr. HF DuanDocument7 pagesAdditional Reading Materials For Lectures 07 & 11: Lecturer: Dr. HF Duanminervini markNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 OPCHDocument7 pagesChapter 1 OPCHgemadogelgaluNo ratings yet
- Topic 4c Minor Losses Turbulent Flow in Circular Pipes 2021Document23 pagesTopic 4c Minor Losses Turbulent Flow in Circular Pipes 2021Nor SyamimiNo ratings yet
- Fall2023 HPR 2Document2 pagesFall2023 HPR 2qesemNo ratings yet
- Midterm SolutionsDocument6 pagesMidterm SolutionsCengiz KöseoğluNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics II (Chapter 1)Document14 pagesHydraulics II (Chapter 1)Abduljebar HussienNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Formulas of The Flow Rate Coefficient of A Broad-Crested SpillwayDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Formulas of The Flow Rate Coefficient of A Broad-Crested SpillwaymmirelesNo ratings yet
- Assignment Transport FenomenaDocument2 pagesAssignment Transport FenomenaSiti Mastura Abdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Oktober 2017Document2 pagesAssignment 1 Oktober 2017FatinnnnnnNo ratings yet
- Binani HydraulicgradientDocument5 pagesBinani HydraulicgradientJimmy ThomasNo ratings yet
- Two Dimensional Hydrodynamic Model For Complex Channel NetworksDocument12 pagesTwo Dimensional Hydrodynamic Model For Complex Channel NetworksEdgar ChuquipiondoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics (Lecture 17)Document41 pagesFluid Mechanics (Lecture 17)Andrew ChikuselaNo ratings yet
- Open Channel Flows - Fluid MechanicsDocument47 pagesOpen Channel Flows - Fluid Mechanicsnaeema_58No ratings yet
- Penstock Presentation - PpsDocument42 pagesPenstock Presentation - PpsGourav KhudasiaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics II Chapter-1Document13 pagesHydraulics II Chapter-1Kefene GurmessaNo ratings yet
- Seepage in Soils PDFDocument6 pagesSeepage in Soils PDFfr3chillNo ratings yet
- MODULE 5.7 WeirsDocument17 pagesMODULE 5.7 WeirsFrancis Hernandez100% (2)
- FlowLabEOC2e CH10Document6 pagesFlowLabEOC2e CH10Bernardo BenzecryNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics - Chapter 3Document8 pagesHydraulics - Chapter 3thuaiyaalhinaiNo ratings yet
- MIT2 06S13 Pracprbquiz1Document5 pagesMIT2 06S13 Pracprbquiz1dbNo ratings yet
- Lecturenote - 295567744open Channel Hydraulics Chapter SixDocument10 pagesLecturenote - 295567744open Channel Hydraulics Chapter SixAlfatah muhumedNo ratings yet
- Unsteady Flow in PipesDocument15 pagesUnsteady Flow in PipeschileNo ratings yet
- Open Channel Flow IntroductionDocument28 pagesOpen Channel Flow IntroductionBIRUK ABATENo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 2Document15 pagesLecture 5 2IbrahimDewaliNo ratings yet
- Matriz - Asistente Administrativo RegionalDocument27 pagesMatriz - Asistente Administrativo RegionalCliver Amanqui UminaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Engineering - Lec - 7-UpdatedDocument18 pagesHydraulic Engineering - Lec - 7-UpdatedUsman AliNo ratings yet
- MEEG 630, Intermediate Fluid Mechanics: R U R If A Pressure GradientDocument2 pagesMEEG 630, Intermediate Fluid Mechanics: R U R If A Pressure GradientAditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Couette Flow, Steady Laminar Flow in Circular Tube & Steady Axial Flow in An AnnulasDocument6 pagesCouette Flow, Steady Laminar Flow in Circular Tube & Steady Axial Flow in An AnnulasAbdul Hafeez100% (1)
- Hydraulics Engineering - Lec - 7Document19 pagesHydraulics Engineering - Lec - 7Kamran JUTTNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Subjective QuestionsDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics Subjective QuestionsCrewdex ProNo ratings yet
- Uniform & Gradually Varied Open-Channel FlowDocument46 pagesUniform & Gradually Varied Open-Channel FlowFelix HabarugiraNo ratings yet
- Ch3 2023-J0xDocument20 pagesCh3 2023-J0xNguyễn Hồng Minh ThưNo ratings yet
- Focal LengthDocument5 pagesFocal LengthWayneNo ratings yet
- Classification of Flow in Open Channels: Prepared By: Suripin Jurusan Teknik Sipil FT UndipDocument30 pagesClassification of Flow in Open Channels: Prepared By: Suripin Jurusan Teknik Sipil FT Undipria ramadhinnyNo ratings yet
- Internal Flows (Pipe Flow) Internal Flows (Pipe Flow)Document58 pagesInternal Flows (Pipe Flow) Internal Flows (Pipe Flow)Theødřøš ÄbNo ratings yet
- Flow Through Porous Mediums IIIDocument29 pagesFlow Through Porous Mediums IIIJanith ChamilkaNo ratings yet
- Dr. R. N. Sankhua Director, NWA: Modelling With Hec-RasDocument15 pagesDr. R. N. Sankhua Director, NWA: Modelling With Hec-RasEphrem GizachewNo ratings yet
- Lecture-5 ThermofluidEngineering and Microsystems DesignDocument25 pagesLecture-5 ThermofluidEngineering and Microsystems DesignSairam.KNo ratings yet
- Flow Conditions and Critical DepthDocument8 pagesFlow Conditions and Critical Depthtroll warlordsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 FlownetDocument10 pagesChapter 2 FlownetAndrian AgengNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2012 2nd Year Mechanical EngineeringDocument17 pagesAssignment 2012 2nd Year Mechanical EngineeringFiseha Bogale KibNo ratings yet
- Fluid Friction in Pipes and Losses From Fittings: ObjectivesDocument4 pagesFluid Friction in Pipes and Losses From Fittings: ObjectivesOsamaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document28 pagesLecture 4CHOWDHURY SAMINo ratings yet
- Lec-2specific Enrgy-Rapidly Varying Flow PDFDocument133 pagesLec-2specific Enrgy-Rapidly Varying Flow PDFNoman Tariq Malkani100% (1)
- ATP Unidirectional FlowDocument2 pagesATP Unidirectional FlowLikhithNo ratings yet
- 225 Fall 2013 PDFDocument518 pages225 Fall 2013 PDFcombatps1No ratings yet
- 流體力學Document30 pages流體力學sonkuas100% (1)
- 8 Two-D Seepage - Handouts - ColourDocument48 pages8 Two-D Seepage - Handouts - ColourtobyforsomereasonNo ratings yet
- Hyd N Hyd Machines-Compiled-NBSDocument55 pagesHyd N Hyd Machines-Compiled-NBSSbs Smrt LtaNo ratings yet
- Graduate Transport (CBE)Document3 pagesGraduate Transport (CBE)elmoNo ratings yet
- 5 6226615153610197310Document10 pages5 6226615153610197310Amiya Kumar DasNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document27 pagesCH 1RABIN KHADKANo ratings yet
- Xi Physics - Mechanical Properties of Fluids (Part Ii)Document10 pagesXi Physics - Mechanical Properties of Fluids (Part Ii)adarshdarasinghNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 PDFDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 PDFharrisNo ratings yet
- LabDocument4 pagesLabnidhalsaadaNo ratings yet
- Flow Measurement 1Document17 pagesFlow Measurement 1hiuNo ratings yet
- 2014-01-Open Channel FlowDocument42 pages2014-01-Open Channel FlowKrmt Goji SamaratunggadewaNo ratings yet
- Anti-Ragging FormDocument1 pageAnti-Ragging FormPankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Academic Calendar For 2020 21 II SemesterDocument3 pagesIndian Institute of Technology Kanpur Academic Calendar For 2020 21 II SemesterHarshit TiwariNo ratings yet
- Corrosion and Degradation of Materials: Issues To Address..Document12 pagesCorrosion and Degradation of Materials: Issues To Address..Pankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- Academic Calendar - 2020-21-IDocument1 pageAcademic Calendar - 2020-21-IYash VarunNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: What Is It About?: This Is An Equilibrium Diagram: Phases Present Here Had All The Time They Needed To FormDocument30 pagesChapter 10: What Is It About?: This Is An Equilibrium Diagram: Phases Present Here Had All The Time They Needed To FormPankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology KanpurDocument1 pageIndian Institute of Technology KanpurbingoNo ratings yet
- Approval of Revised Fee Structure 29 07 20Document4 pagesApproval of Revised Fee Structure 29 07 20Pankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur Academic Calendar For 2021 22 I SemesterDocument1 pageIndian Institute of Technology Kanpur Academic Calendar For 2021 22 I SemesterPankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- Phase DiagramsDocument99 pagesPhase DiagramsPankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- Elevation View of Baseplate Plan View of BaseplateDocument1 pageElevation View of Baseplate Plan View of BaseplatePankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: Structures & Properties Of: CeramicsDocument106 pagesChapter 12: Structures & Properties Of: CeramicsPankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- Topics List - CHE 621ADocument2 pagesTopics List - CHE 621APankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Materials - MergedDocument247 pagesLecture 9 Materials - MergedPankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- CHE621A - Assignment 3Document9 pagesCHE621A - Assignment 3Pankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- Che659a Assign#5 20102033Document1 pageChe659a Assign#5 20102033Pankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- CHE621A - Assignment 2Document10 pagesCHE621A - Assignment 2Pankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- Topics List - CHE 621ADocument2 pagesTopics List - CHE 621APankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- Topics List - CHE 621ADocument2 pagesTopics List - CHE 621APankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- Mid Sem ExamDocument3 pagesMid Sem ExamPankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- Topics List - CHE 621ADocument2 pagesTopics List - CHE 621APankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- CHE621A - Assignment 1Document9 pagesCHE621A - Assignment 1Pankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- Topics List - CHE 621ADocument1 pageTopics List - CHE 621APankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- Topics List - CHE 621ADocument1 pageTopics List - CHE 621APankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- T T 0 Y L T: Time 75 Minutes Che611A Endsem-Part3 Total MarksDocument1 pageT T 0 Y L T: Time 75 Minutes Che611A Endsem-Part3 Total MarksPankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- Transport Anurag Kanpur: TripathiDocument9 pagesTransport Anurag Kanpur: TripathiPankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- Transport Anurag Kanpur: TripathiDocument18 pagesTransport Anurag Kanpur: TripathiPankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- CHE 659A: Process Engineering Principles in MicrofabricationDocument2 pagesCHE 659A: Process Engineering Principles in MicrofabricationPankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- Student Add - Drop ApplicationDocument2 pagesStudent Add - Drop ApplicationPankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet
- Transport Anurag Kanpur: TripathiDocument10 pagesTransport Anurag Kanpur: TripathiPankaj Kumar SainiNo ratings yet