Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Standards and specifications for e-learning systems
Uploaded by
Shahnoor AliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Standards and specifications for e-learning systems
Uploaded by
Shahnoor AliCopyright:
Available Formats
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.
net/publication/224085435
Standards and specifications for e-learning systems
Conference Paper · October 2009
Source: IEEE Xplore
CITATION READS
1 2,682
2 authors, including:
Slavomir Stankov
The Faculty of Science University of Split - Croatia
86 PUBLICATIONS 541 CITATIONS
SEE PROFILE
Some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects:
Upotrebljivost i prilagodljivost sučelja inteligentnih autorskih ljuski View project
Enhancing Adaptive Courseware based on Natural Language Processing, Office of Naval Research grant N00014-20-1-2066 View project
All content following this page was uploaded by Slavomir Stankov on 28 March 2015.
The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file.
Standards and Specifications for E-Learning Systems
Divna Krpan 1, Slavomir Stankov 2
1
Faculty of Science, Teslina 12, Split, 21000 Croatia
2
Faculty of Science, Teslina 12, Split, 21000 Croatia
E-mail: divna.krpan@pmfst.hr
Abstract - This paper presents a brief description of Shareable Content Object Reference Model (SCORM), a
set of standards and specifications intended to be used in e-learning for the purpose of sharing content across
different e-learning systems. SCORM has gone through changes since its origin to keep up with technology
development and growing demands on e-learning systems. Since these standards are being used in practice,
practical issues arose which finally led to the divergence of developmental directions for the two new future
versions of SCORM.
Keywords – e-learning standard, SCORM
1. INTRODUCTION Organization for Standardization (ISO)
(http://www.iso.org).
There is increase in interest for e-learning with There is obvious need for standardization of
rapid development of computers and high speed learning content, which is more complex then
Internet access. On high level, components of e- electrical plug. Such need was recognized by United
learning may be divided into two categories: States White House Office of Technology, the
conceptual and physical [1]. Department of Defense (DoD) and the Department
Physical components include learning content of Labor which founded Advanced Distributed
files, database and management software, which Learning Initiative (ADL) in 1997 [2]. ADL
have physical (electronic) existence. collected existing specifications and standards for
Conceptual components include courses and content from different organizations, and formed set
lessons. Smallest part of learning content is often of standards known as Sharable Content Object
called learning object (LO). The best practice for Reference Model (SCORM).
determining the size of LO is mapping it with In next chapters we are going to describe current
concept or learning objective. Learning objects are SCORM specification, its application in practice and
building blocks for learning content. Very often, work in progress on future directions.
same concepts or learning objectives appear across
different courses, and also in different organizations.
It would be waste of time and money to create the 2. FORMER VERSIONS OF SCORM
same LO from scratch each time when
corresponding concept or learning objective appears SCORM as "Reference Model" is more like a
in different context. Obviously, it would be more roadmap for standards because it contains references
convenient to reuse already created LO. In that case, for existing standards and specifications made by
such LO should be independent from any other other organizations (IMS, AICC, IEEE, ARIADNE).
learning content in order to make it possible to SCORM provides support for requirements known
extract that LO from one environment and import it as ADL’s "ilities" [3]: reusability, interoperability,
somewhere else. accessibility, adaptability, durability and
However, such LO may not be compatible with affordability. All ADL’s "ilities" are combined with
some other system. Standards are part of our "the Web-based assumption" which claims that the
everyday life that we sometimes don't notice. Clocks Web provides the best opportunity for maximum
(analog or digital) show time all over the world, access and reuse of learning content.
electrical plugs only fit one way into their sockets, SCORM version 1.0 was released in January
ISBN number on cover of each book, screws in the 2000 [4]. Latest official version of SCORM is
chair we are sitting on, etc. A standard is a "SCORM 2004 3rd Edition" released in November
documented agreement which contains technical 2006. which consists of five “technical books”, but
specifications which should be used consistently as to simplify, these books are grouped under three
rules, guidelines, or definitions of characteristics to main topics: "SCORM Content Aggregation Model
ensure that products, processes and services are (CAM)", "SCORM Run-time Environment (RTE)"
appropriate for their purpose. Largest developer and and "SCORM Sequencing and Navigation (SN)".
publisher of International Standards is International This version brings changes from previous editions.
These changes are about clarification of concepts
and requirements, considering best practices from SCOs and content aggregation packages. LMS or
ADL Community, bug fixes and other content which passes such test is referred to as
improvements. SCORM conformant, but it is also possible to get
SCORM is based on series of software elements. SCORM Certification through process of third party
On top level, there is Learning Management System testing. The term “conformant” is used when a
(LMS), a system that manages content and tracks product follows the SCORM specifications, and
learner progress and interactions. LMS may be more "SCORM certified" is used for product which passed
or less complex with different implementations. All testing by one of the ADL Certification Testing
other parts of SCORM content hierarchy are Centers.
contained in LMS.
SCORM Content Aggregation Model (CAM)
book describes instructional components or objects 3. SCORM IN PRACTICE
used in content aggregation. Content aggregation
may represent course, but it is possible to form In practice, there could be many different
smaller content aggregations as long as they are problems which interfere with interoperability. The
independent of other content and may be used in results may be interpreted differently then
different context. CAM book also describes the way determined by specification because some LMSs
content aggregations are packed in content packages. report that course is completed which differs from
Sharable content object (SCO) is actually the pass or fail condition. Some bugs and character
SCORM’s LO, or conceptual component. Learner encoding may interfere in communication between
interacts with learning content at this level [1]. A content and LMS.
SCO is the smallest unit of content that a LMS is SCORM is technical document written for
able to load and track and which may communicate toolmakers and vendors and not directly intended for
with LMS [3]. SCO is a set of one or more Assets. content designers and developers. It does not
Assets are learning resources or physical files such consider what makes good learning or how to create
as graphics, sounds, and movies, although there are learning experiences. But, it does affect design of
no restrictions on the type. SCO should be LMS because designers must consider all ADL
independent of its learning context to enable "ilities", design of learning object and context where
reusability. There is no restriction on size of SCO, that object is present [5].
but it is recommended that SCO should represent SCORM should be used when there is a need for
smallest logical unit or concept. SCOs and Assets reusable and durable content which may be shared in
are grouped in Learning Activities which represent many different contexts with large number of
meaningful and structured units of instruction. learners and courses.
Learning Activity may consist of several sub- According to http://adlnet.gov/, until March 15,
activities. 2009 ADL has certified a total of 268 products, and
SCORM Run-Time Environment (RTE) book 154 of those products are LMSs. There are also 295
describes communication between SCO and LMS, SCORM conformant products, and 159 of them are
and gives high-level information how an LMS LMSs. In next chapter, we briefly present two LMSs
determines which SCO will be delivered at any as example of certified and conformant LMSs.
given time. SCO and LMS communicate using
standardized communication mechanisms as well as 3.1. Blackboard
standard model for data which is transferred between
them. RTE book is important for interoperability Blackboard is Web-based Learning Management
between SCOs and LMSs. System (LMS) used all over the world
SCORM Sequencing and Navigation (SN) book (http://www.blackboard.com/). It allows students
defines a method for representing the behavior of a and faculty to participate in classes delivered online
instructional components. SCORM conformant LMS or to use online materials and activities to
will sequence content in standard and consistent complement face-to-face teaching. With Blackboard,
way. Learning Activities are grouped into Activity instructors can provide students with course
Tree, and SN book describes the branching and flow materials, discussion boards, virtual chat, online
of those Learning Activities. Both, learner and LMS quizzes, an academic resource center, and more.
may initiate navigational events which should be Courses may be conducted entirely through
processed as triggers for determining appropriate Blackboard, without any face-to-face sessions.
learning activity. The CAM book describes how to Blackboard Academic Suite 8.0 is a certified
build sequencing rules, and SN book describes in SCORM LMS for SCORM 2004 3rd Edition.
more detail those rules and how to process their
behavior. 3.2. Moodle
For each version of SCORM, there is also
SCORM Conformance Test Suite which contains Moodle (Modular Object-Oriented Dynamic
software and documents for self-testing of LMSs, Learning Environment) is LMS provided freely as
Open Source under GNU Public License. It may be 2. Sharing additional objective data between SCOs
installed on any computer which supports PHP and – Some SCOs report objective information (like
SQL type database; it can run on different Windows min, max and raw scores), which can be shared
and Mac operating systems, as well as some versions between SCOs in same activity tree, but also
of Linux. across different activity trees, which also
Moodle enables teachers to create web pages for enables easier sequencing.
their courses by entering HTML code, or using 3. Jump Navigation Request – This improvement
WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) word allows content developers more sequencing
processor online, so it is possible to develop content options and separates branching within a SCO
online, including lessons. It also contains the from what learner is allowed to do.
SCORM module which allows upload of any 4. Rolling-up partial completion information –
standard SCORM package, but it is not possible to There is more accurate evaluation of partial
create or export SCORM content. completion of some activity tree then previously
For testing purposes, we uploaded official relying on the boolean complete/incomplete
SCORM ADL object: SCORM 2004 3rd Edition values.
Data Model Content Example (DMCE) Version 1.1 ADL listed those four features as improvements,
from http://www.adlnet.gov/. DMCE is a SCORM but some authors, disagree [8]. There is confusion
2004 3rd Edition Conformant Content Aggregation about successfully completing activity with learning
Content Package. The content package can be objectives. Rolling-up does not work on learning
imported into any SCORM 2004 3rd Edition objectives, but only on status of activity. This means
conformant LMS and explored. Although there was that this SCORM model is focused on series of
a warning on ADL site that it will not work with a activities and not on achieving competency or
SCORM Version 1.2 conformant LMS, we did not learning outcomes. Objective roll-up rules should be
encounter any difficulties using it with Moodle computed at the completion of each activity.
1.9.2. It is officially reported from Moodle that Some e-learning systems just deliver content to
SCORM 1.2 is supported in Moodle 1.9.3 and learners and acknowledge that they read it, which is
Moodle 1.8.7 which pass all the tests in the ADL marked as completion of some content, since scores
Conformance test suite for SCORM 1.2 [6]. are more complicated. There is also complaint about
Moodle is partially SCORM conformant because SCORM's notion of global and local. Global really
some specifications such as Navigation and refers to persistence in one LMS for one course for
Sequencing have not yet been implemented. one learner. It is suggested that activity objectives
Therefore, Moodle cannot be SCORM certified should be related to activity and disappear when that
either. activity is completed, and should persist only when
that activity was interrupted before completion.
Aggregation objectives should be related to
4. SCORM IN PROCESS single user in course (or aggregation) and should be
available to any SCO in that course, but also
Changes in standards and specification are not persistent for all attempts on that course. The first
very desirable because their purpose is to be stable two types are local objectives, and global objectives
and provide common environment, but progress is should potentially exist across different LMSs.
also inevitable. If there are technology advances Robson also suggested multi-user SCOs to allow
they should be considered as well. So, SCORM is objectives to be related to multiple learner IDs,
still in process. which may be interpreted as aggregation of learner
models into team models. Each team model may be
4.1. SCORM 2004 4th edition considered as single learner, and also team
competence may be distributed among team
ADL announced development of SCORM 2004 members [9]. SCORM confuses instructional model
4th edition in December, 2008 with Beta release of based on completions and performance with
software which includes Test Suite and Sample Run- intelligent instructional model which is based on
Time Environment (SRTE) [7]. The 4th edition objectives and mapping of completions and
brings some bug fixes from earlier versions, but performance to objective states.
there are no drastic changes. The main part of the paper may consist of several
There are four new features: chapters.
1. Sharing generic run-time data between SCOs –
ADL defined new run-time data model element 4.2. SCORM 2.0
to enable sharing and storing learner tracking
information between different SCOs within The development of the next SCORM 2.0, is
same activity tree. This facilitates better now mission for new international federation for
sequencing. Learning Education Training Systems
Interoperability (LETSI), while ADL continues to
work on SCORM 2004 [10]. LETSI was formed by complexity, Intelligent Tutoring systems, simulation
ADL and eleven other organizations. interfaces, sources outside LMS, Web 2.0, etc. In
SCORM has become international software [12] there is discussion about problems in team
standard for learning systems interoperability. based training and difficulties in assessing their
According to ADL, goal of SCORM 2.0 is to performance, but additionally everything gets more
become open, or free from restrictions such as complicated with assessment of "teams of
patents or licenses, so LETSI is aimed to develop individuals" by taking into account contributions of
open source software community to support each individual.
SCORM adopters and product developers. LETSI
itself does not develop the component standards
which are part of SCORM. Call for participation was REFERENCES
announced in June, 2008.
SCORM 2.0 should have two major components: [1] C. Fallon and S. Brown, E-learning standards:
(i) general reference model (Core SCORM), based a guide to purchasing, developing, and
on learning standards that support basic deploying standards-conformant e-learning, St.
interoperability, and (ii) additional components that Lucie Press, New York, 2003.
support instructional capabilities, based on [2] C. Ostyn, The Eye of the SCORM,
specifications which are not yet part of standard. http://www.ostyn.com/resscormtech.htm
There were 98 submitted papers with suggestions (Accessed: 11.03.2009.), 2006.
about what to do next, and what to fix. All [3] Advanced Distributed Learning (ADL),
suggestions were analyzed and greatest number of Sharable Content Object Reference Model
papers points out the need for support with Web (SCORM) 2004 3rd Edition Documentation
services and fixes to SCORM 2004. Only two papers Suite, Available online:
referred to support for Intelligent Tutoring Systems http://www.adlnet.gov/downloads/DownloadPa
and agents wondering will SCORM 2.0 address ge.aspx?ID=237, 2006.
those issues, how and when. [4] K. Johnson and S. Slosser, "SCORM Status
In Fig.1, there is a summary of major suggestions and Evolution", International Pugfest II, 2006.
from all 98 submitted white papers which most [5] D. Rehak, ADL/SCORM - What Does it Mean
directly address the topic [11]. for Developers of ICT Projects, PowerPoint
Sequencing 15
presentation on Reusable Learning Designs
Web service interfaces 17 conference, UTS, Sydney, 2002.
Fixes to SCORM 2004 17 [6] Moodle.org, SCORM module,
Content agreggation and format 13
http://docs.moodle.org/en/SCORM, (Accessed:
Assesment and compentencies 13
10.03.2009), 2009.
Team training and shared data 12
Market 8
[7] Advanced Distributed Learning (ADL), ADL
Support for insructors 14
Releases SCORM 2004 4th Edition Beta
Intelligent systems 2 Software,
Content lifecycle management 2 http://www.adlnet.gov/News/articles/index.asp
Accessibility an usability 6
x?ID=508 (Accessed: 14.03.2009.), 2008.
[8] R. Robson, "SCORM 2004 4th Edition
Fig. 1. Summary of white papers suggestions for Thoughts", Learning Education Training
SCORM 2.0. Systems Interoperability (LETSI), SCORM 2.0
White Papers, 2008.
5. SCORM EXPECTATIONS [9] V. A. Goodkovsky, "Content Aggregation
Model and Recursive Manifest for SCORM 2"
In the past, SCORM provided standards and Learning Education Training Systems
specifications for aggregations, but not as much for Interoperability (LETSI), SCORM 2.0 White
its structure. Previous versions of SCORM provided Papers, 2008.
simple communication between SCO and LMS, but [10] Advanced Distributed Learning (ADL),
with service oriented approach, there are more SCORM 2.0: LETSI Announces a Call for
things for consideration. SCORM objective to Participation,
remain pedagogy neutral has been argued. Previous http://www.adlnet.gov/News/articles/index.asp
models are taking into account adaptation of x?ID=476 (Accessed: 14.03.2009.), 2008.
learning activities based on learner progress in [11] F. Polster, "Topic Descriptions," Learning
Sequencing and Navigation book, but that was Education Training Systems Interoperability
problematic to implement and also was not what (LETSI), SCORM 2.0 White Papers, 2008.
many communities wanted. [12] T. Archibald and P. Berking, "Team-Based
Many other things emerge which were not Learning", Learning Education Training
discussed enough: collaborative learning, different Systems Interoperability (LETSI), SCORM 2.0
White Papers, 2008.
View publication stats
You might also like
- Cit 427 Database Systems and ManagementDocument171 pagesCit 427 Database Systems and Managementimamashraf1100% (1)
- Training Plan SampleDocument4 pagesTraining Plan SampleMelanie Tongol Gonzales100% (1)
- Natural Language ProcessingDocument309 pagesNatural Language Processingsillypolo100% (3)
- Crack WPA2Document9 pagesCrack WPA2hero_trojanNo ratings yet
- SQL Advanced SQL Query Optimization Techniques B09978MXWXDocument125 pagesSQL Advanced SQL Query Optimization Techniques B09978MXWXmoon26100% (1)
- Shiny DashboardDocument27 pagesShiny DashboardAnna VargováNo ratings yet
- XML-based Content Management: Integration, Methodologies and ToolsFrom EverandXML-based Content Management: Integration, Methodologies and ToolsNo ratings yet
- IntroQADEA UG v2016EE PDFDocument210 pagesIntroQADEA UG v2016EE PDFShaik AzharuddinNo ratings yet
- The ADL SCORM Specification V 1.2Document11 pagesThe ADL SCORM Specification V 1.2Iván Garrido MorillasNo ratings yet
- SCORM ExplainedDocument3 pagesSCORM ExplainedHAZEEM_ALRA3DNo ratings yet
- IncreasinglyDocument3 pagesIncreasinglyVanee SanNo ratings yet
- Knowledge Base For Automatic Generation of OnlineDocument23 pagesKnowledge Base For Automatic Generation of OnlinedalnerNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 6 PDFDocument10 pagesKelompok 6 PDFeri 1262No ratings yet
- XML XSLT - KhorDocument15 pagesXML XSLT - KhorSantosh DasNo ratings yet
- The Sharable Content Object Reference Model (SCORM) - A Critical ReviewDocument2 pagesThe Sharable Content Object Reference Model (SCORM) - A Critical ReviewIvetNo ratings yet
- Building A Learning Object Content Management SystemDocument8 pagesBuilding A Learning Object Content Management SystemzandreeNo ratings yet
- E-Content StandardsDocument39 pagesE-Content StandardsYazhini VenkatesanNo ratings yet
- SCORM in Practice Email VersionDocument19 pagesSCORM in Practice Email Versionapi-3770163No ratings yet
- SCORM 1.1: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesSCORM 1.1: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediamekehetehNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To SCORMDocument25 pagesAn Introduction To SCORMAfshan_Amin_8556No ratings yet
- E LearnDocument10 pagesE LearnarjNo ratings yet
- Study of The Scorm Model For Online Education and TrainingDocument1 pageStudy of The Scorm Model For Online Education and TrainingnassimNo ratings yet
- Review of Lms Literature For Aut Lms Review CommitteeDocument44 pagesReview of Lms Literature For Aut Lms Review CommitteeRui Guimarães LimaNo ratings yet
- Organizing E-Learning Standards and SpecificationsDocument7 pagesOrganizing E-Learning Standards and Specifications7390840No ratings yet
- A New Software Architecture For Learning Management Systems With Scorm SupportDocument4 pagesA New Software Architecture For Learning Management Systems With Scorm SupportalexNo ratings yet
- Implementable ElearningDocument5 pagesImplementable ElearningAsif IqbalNo ratings yet
- HG ThesisDocument128 pagesHG Thesisimane nourNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 2 EnggresDocument10 pagesJurnal 2 EnggresEbenezer ManullangNo ratings yet
- PCI2015pp055 056sid090Document3 pagesPCI2015pp055 056sid090cafexarmaniNo ratings yet
- Supporting Collaborative Learning Activities With ScormDocument10 pagesSupporting Collaborative Learning Activities With ScormPhilstar JillNo ratings yet
- An Implementable Architecture of An E-Learning System: Xiaofei Liu, Abdulmotaleb El Saddik and Nicolas D. GeorganasDocument4 pagesAn Implementable Architecture of An E-Learning System: Xiaofei Liu, Abdulmotaleb El Saddik and Nicolas D. Georganaschandru1908No ratings yet
- E-Learning: Emerging Tools & TechnologiesDocument7 pagesE-Learning: Emerging Tools & TechnologiesPrachi MahajanNo ratings yet
- ScormDocument6 pagesScormDalia KadousNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Instructional Research and Instructional TechnologyDocument19 pagesHandbook of Instructional Research and Instructional TechnologynirmalarothinamNo ratings yet
- Geeky Banker CAIIB IT MODULE C COMPLETEDocument54 pagesGeeky Banker CAIIB IT MODULE C COMPLETErutesh2021No ratings yet
- Ontology-Oriented Inference-Based Learning Content Management SystemDocument12 pagesOntology-Oriented Inference-Based Learning Content Management SystemijwestNo ratings yet
- ITEC2007 JavaBasedSimulationContentInE-Learning GiordanoDocument8 pagesITEC2007 JavaBasedSimulationContentInE-Learning GiordanoXuan ThuNo ratings yet
- SCORM - My PresentationDocument42 pagesSCORM - My PresentationrubinibalaNo ratings yet
- Intro To LBP Schema - MDDocument3 pagesIntro To LBP Schema - MDNicolas CaroNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering Bloom TaxonomyDocument8 pagesSoftware Engineering Bloom TaxonomyAntonio Maria P. ResendeNo ratings yet
- XML Simplified 3Document259 pagesXML Simplified 3V BunNo ratings yet
- Comparing Open edX and Moodle MOOC PlatformsDocument8 pagesComparing Open edX and Moodle MOOC PlatformsMark_Black_BeliciusNo ratings yet
- Technical and Pedagogical Usability Criteria for Digital LearningDocument11 pagesTechnical and Pedagogical Usability Criteria for Digital LearningHaniAzzahraNo ratings yet
- Challenges in Search and Usage of Multi-Media Learning ObjectsDocument9 pagesChallenges in Search and Usage of Multi-Media Learning ObjectsCarsten UllrichNo ratings yet
- Learning Objects On The Semantic WebDocument5 pagesLearning Objects On The Semantic WebDulaj PasqualNo ratings yet
- Work in Progress - Using A Collaborative Content Management System For Ethics EducationDocument2 pagesWork in Progress - Using A Collaborative Content Management System For Ethics EducationHimanshu SethNo ratings yet
- Ontology Based Semantic Web Technologies in E-Learning Environment Using ProtégéDocument4 pagesOntology Based Semantic Web Technologies in E-Learning Environment Using ProtégéPetter PNo ratings yet
- OOP Concepts in C#Document22 pagesOOP Concepts in C#Indumini DilshaniNo ratings yet
- SCORM Technology, Xblock and scorm shellDocument7 pagesSCORM Technology, Xblock and scorm shellNaeem IlyasNo ratings yet
- Alfaro-Garcia Contentanalysis-1Document6 pagesAlfaro-Garcia Contentanalysis-1api-695953173No ratings yet
- Study Cloud Computing ServicesDocument36 pagesStudy Cloud Computing Servicesharisimp100% (1)
- Testing Objectives for e-Learning Interoperability & ConformanceDocument19 pagesTesting Objectives for e-Learning Interoperability & ConformanceAmanuel KassaNo ratings yet
- Cubric - A Semantic Web Framework For Generating Collaborative E-Learning EnvironmentsDocument4 pagesCubric - A Semantic Web Framework For Generating Collaborative E-Learning EnvironmentsJoaquim SilvaNo ratings yet
- DCOMSDocument40 pagesDCOMSLTashjain FamNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Ontology in Intelligent E-Learning System Development Based On Semantic WebDocument6 pagesImplementation of Ontology in Intelligent E-Learning System Development Based On Semantic WebevoNo ratings yet
- Challenges of Transitioning To An E-Learning System With Learning Objects CapabilitiesDocument25 pagesChallenges of Transitioning To An E-Learning System With Learning Objects CapabilitiesNayNo ratings yet
- Next Gen POS Case Study OOADDocument4 pagesNext Gen POS Case Study OOADvijiNo ratings yet
- TESDADocument50 pagesTESDAfarmbaluzoNo ratings yet
- E-Learning Resource LocatorDocument53 pagesE-Learning Resource LocatorGellanka LavanyaNo ratings yet
- Systems: Adaptation in E-Learning Content Specifications With Dynamic Sharable ObjectsDocument11 pagesSystems: Adaptation in E-Learning Content Specifications With Dynamic Sharable ObjectsIvetNo ratings yet
- Learning Design Implementation in SCORMDocument5 pagesLearning Design Implementation in SCORMTrang Ngo Nguyen ThuyNo ratings yet
- p72 TsiakmakiDocument6 pagesp72 TsiakmakicafexarmaniNo ratings yet
- User Context Aware Delivery of E-Learning Material: Approach and ArchitectureDocument9 pagesUser Context Aware Delivery of E-Learning Material: Approach and ArchitecturePriya MahajanNo ratings yet
- Federal Tvet Institute (Ftveti) : Course DescriptionDocument5 pagesFederal Tvet Institute (Ftveti) : Course DescriptionMatwos AregaNo ratings yet
- Information Extraction Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesInformation Extraction Literature Reviewaflstfcap100% (1)
- Comparison of Moodle and Atutor LMSS: Péter Lengyel, Miklós Herdon, Róbert SzilágyiDocument8 pagesComparison of Moodle and Atutor LMSS: Péter Lengyel, Miklós Herdon, Róbert SzilágyiLatifah MamatNo ratings yet
- TDT4136 Introduction To Artificial Intelligence: Lecture 1: Introduction (Chapter 1 in The Textbook)Document40 pagesTDT4136 Introduction To Artificial Intelligence: Lecture 1: Introduction (Chapter 1 in The Textbook)Shahnoor AliNo ratings yet
- Discrete Mathematics Math 6A: Homework 9 SolutionDocument11 pagesDiscrete Mathematics Math 6A: Homework 9 SolutionShahnoor AliNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic and DesignDocument54 pagesDigital Logic and DesignShahnoor AliNo ratings yet
- Class Xi PracticalsDocument12 pagesClass Xi PracticalsShahnoor AliNo ratings yet
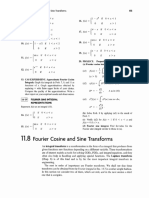
- Fourier Cosine and Sine Transforms ExplainedDocument1 pageFourier Cosine and Sine Transforms ExplainedShahnoor AliNo ratings yet
- Endeavour Leadership Program Guidelines 2019 Round PDFDocument31 pagesEndeavour Leadership Program Guidelines 2019 Round PDFeduardo cabocloNo ratings yet
- HEC Scholarship Aptitude Test Sample Paper GuideDocument340 pagesHEC Scholarship Aptitude Test Sample Paper GuideMuhammad Faiz Ur Rehman0% (2)
- HEC Scholarship Aptitude Test Sample Paper GuideDocument340 pagesHEC Scholarship Aptitude Test Sample Paper GuideCharag E ZindgiNo ratings yet
- Flip The Page: National Textile University, FaisalabadDocument4 pagesFlip The Page: National Textile University, FaisalabadShahnoor AliNo ratings yet
- Shahnoor Et Al. Yamama Conf PDFDocument6 pagesShahnoor Et Al. Yamama Conf PDFShahnoor AliNo ratings yet
- Standards and specifications for e-learning systemsDocument5 pagesStandards and specifications for e-learning systemsShahnoor AliNo ratings yet
- Research Paper PresentationDocument16 pagesResearch Paper PresentationShahnoor AliNo ratings yet
- Fortisiem: Unified Event Correlation and Risk Management For Modern NetworksDocument7 pagesFortisiem: Unified Event Correlation and Risk Management For Modern Networksdhazh007No ratings yet
- Computer Networks LabDocument49 pagesComputer Networks LabKumar KumarNo ratings yet
- Web-based SIWES management systemDocument8 pagesWeb-based SIWES management systemjibrin ahamaduNo ratings yet
- ABPP3 Programmers Reference Part3 6.2.8 RevADocument121 pagesABPP3 Programmers Reference Part3 6.2.8 RevAmiitianNo ratings yet
- Michelin OTR UserGuide Android INCENTERDocument39 pagesMichelin OTR UserGuide Android INCENTERThe Lonious MonkNo ratings yet
- SAP Master Data Governance For Financial Data - OverviewDocument40 pagesSAP Master Data Governance For Financial Data - OverviewDamodar Naidu PaladuguNo ratings yet
- 11th Gen Core Processors v1.4.10100 Ipm User GuideDocument26 pages11th Gen Core Processors v1.4.10100 Ipm User GuideDavid SatterfieldNo ratings yet
- 6AV66467BA220HN0 Datasheet enDocument3 pages6AV66467BA220HN0 Datasheet enlaurentiu floreaNo ratings yet
- InstructionsDocument5 pagesInstructionsKayee GohNo ratings yet
- Oracle® Transportation Management: Installation Guide Release 6.4.3 Part No. E92124-06Document118 pagesOracle® Transportation Management: Installation Guide Release 6.4.3 Part No. E92124-06Sai BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Sinar Mutiara HP Agustus 2022-1Document44 pagesSinar Mutiara HP Agustus 2022-1My GadgetNo ratings yet
- 2006 Daceasy Year-End GuideDocument82 pages2006 Daceasy Year-End GuideJean Rene KisisaNo ratings yet
- 02 Vsphere Services Consultant FAQDocument69 pages02 Vsphere Services Consultant FAQNateadorNaterNo ratings yet
- 3DSystems Metal AM Software Ebook 3DXpertDocument18 pages3DSystems Metal AM Software Ebook 3DXpertMário CoutoNo ratings yet
- Advanced CSSDocument22 pagesAdvanced CSSraj4rajNo ratings yet
- Technology Proficiency Assessment Tool - Google FormsDocument5 pagesTechnology Proficiency Assessment Tool - Google Formsapi-583514395No ratings yet
- 0501 Storage DevicesDocument11 pages0501 Storage DevicesAttitude BeboNo ratings yet
- Police Officer Exam 7326Document97 pagesPolice Officer Exam 7326tomacholsrpNo ratings yet
- POSPac MMS GNSS-Inertial ToolsDocument246 pagesPOSPac MMS GNSS-Inertial Tools渕上翔No ratings yet
- Logo 8.3 - System - Manual - en-US - en-USDocument369 pagesLogo 8.3 - System - Manual - en-US - en-USJirawan SirinNo ratings yet
- World's Smallest: Up To 48 ZonesDocument16 pagesWorld's Smallest: Up To 48 ZonesPedroGomes2No ratings yet
- FTV - Lab ManualDocument304 pagesFTV - Lab ManualraulcarballedaNo ratings yet
- You Created This PDF From An Application That Is Not Licensed To Print To Novapdf PrinterDocument5 pagesYou Created This PDF From An Application That Is Not Licensed To Print To Novapdf PrinterCristian Fabian Pacherres SanchezNo ratings yet
- Course Outline For ProgrammingDocument4 pagesCourse Outline For ProgrammingChrysler PanaguitonNo ratings yet