Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Poster Microwave Transport Network V1.1
Uploaded by
Aung Aung OoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Poster Microwave Transport Network V1.1
Uploaded by
Aung Aung OoCopyright:
Available Formats
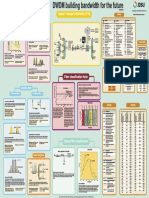
Frequency
80 GHz E-Band
Frequency
Feature Application Policy 60 GHz V-Band
Band
40 GHz
License To improve frequency utilization and License band
Deficient resources
band total air-interface bandwidth 6 GHz
Flexible Evolution SubLink SubLink
Ultra-large Short-distance large-capacity backhaul
E-Band 500 m 1 km 5 km 15 km 50 km Distance CC
bandwidth Link aggregation
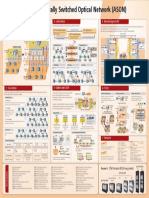
Start Diagnosis Report Topology
LM
Large Bandwidth Very-short distance backhaul for mass DM
V-Band License-free small cell deployment, with low CAPEX Throughput test
and low OPEX Path
Easy Maintenance
SubLink License-free N-LOS/n-LOS backhaul
Report
Multi-service transport with throughput of 10 Gbit/s level
Continuity check (CC)
Ch1: STM-1
Ch2: STM-1 Remote defect indication Proactive
Fronthaul Backhaul Backbone Ch3: STM-1+Ethernet (RDI) OAM
Ch4: Ethernet
... Fault Alarm indication signal
Ch16: Ethernet management (AIS)
2G 2G+3G 2G+3G+LTE LTE‐A
Space diversity and IF-combination technologies, Loopback test (LB)
TDM MW Hybrid MW Packet MW Routing MW
TDM PWE3 PWE3 to fight against multi-path fading
TDM Link trace (LT)
Ethernet Ethernet IP routing Tx On-demand
Rx-SD
OAM
Packet loss measurement
Main Performance (LM)
Combiner
monitoring
Delay measurement (DM)
SD
Native E1/STM-1 Expansible branching unit
E1 tributary board TDM Antenna
Branching unit (BU)
SDH board cross- port BU 1
connection CES E1
EoS/EoP
MPLS Cascading
tunnel port
processing board
Universal ATM Microwave
CES processing Packet frame
switching
IF board PWE3 BU 2
board
Native
Ethernet interface
IP Ethernet BU 3
board
forwarding
L3VPN MPLS
IP tunnel
BU 4
Ch 1 Ch 2 Ch 3 Ch 4
Easy-to-install: on poles, walls, lampposts
E-Band
Frequency Band 71–76/81–86 GHz
ERPS multi-ring protection 1+1 protection (HSB switching)
Easy-to-maintain: configuration-free, Wi-Fi access, and co-
management of base stations Small Cell
Easy-to-network: multiple interfaces, built-in switching units protection Spanning tree protection
Macro Cell
Macro cell Large capacity: 400+ Mbit/s capacity
Aggregation Site
Modem/IF RF RF Modem/IF
Macro cell Throughput
Main Features
V-Band
protection Hierarchical L3VPN protection
Protection mechanism (6-42 GHz)
Small CSG1 ASG1 (6-11 GHz)
Small Small 0 3 4 1 2 TE hot standby
cell cell cell 2 1 2 RSG1 3 4 VPN FRR
eNodeB 5 5 5 VRRP
Sublink
Sublink
V-Band
V-Band
V-Band
3 1
4 Legend
MME/S-GW 0 Working Path
n Protection path
eNodeB CSG2 ASG2 for fault n
Large Bandwidth Multiple Services High Precision
*: Maximum value when frame header compression is enabled
High Reliability
Ethernet
ERPS
LAG
35% Principle 3G NodeB traffic model EPLA example STP
20% User data frame
2048QAM PHY header 64 128
1024QAM f2 f4 L1 (20 bytes) 512 1518
256QAM f1 f2
f1 f3 MAC header
L2
(18 bytes) Data frame in
More About E-band and
30% 35%
IP header
air interface Huawei MW Solutions
L3 Compression
(20-48 bytes) indication 20% 15% 800 Mbit/s service 800 Mbit/s pipe
Principle (160 Mbit/s per flow) (200 Mbit/s per link)
Without drop AM Adaptive Modulation MPLS MultiProtocol Label Switching
Modem Payload Payload ASG Aggregation Site Gateway MW Microwave
TRX CES Circuit Emulation Service PLA Physical Link Aggregation
LAG example
CPRI Common Public Radio Interface PW Pseudo Wire
Capacity Availability Equivalent throughput diagram CSG Cell Site Gateway QAM Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
99.999% f1 V E2E End-to-End QPSK Quadrature Phase Shift Keying
500M
EPLA Enhanced Physical Link Aggregation RSG RNC Site Gateway
H ERPS Ethernet Ring Protection Switching SD Space Diversity
f2 Drop IMA Inverse Multiplexing over ATM SNCP Subnetwork Connection Protection
99.9%
100M
TRX LAG Link Aggregation Group XPIC Cross Polarization Interference
M
800 Mbit/s service 800 Mbit/s pipe
M AM M SK Air Some drop LMSP Linear Multiplex Section Protection Cancellation
QA QA AM QA Modem (160 Mbit/s per flow) (200 Mbit/s per link)
48 24 6Q
64
Q 6 QP NodeB UNI interface UNI RNC
20 10 25 1
V1.1 (2014-03-15)
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Optical Transport Module (OTM) OTN Encryption: Encrypt OTN Payloads for Network SecurityDocument1 pageOptical Transport Module (OTM) OTN Encryption: Encrypt OTN Payloads for Network SecuritykapakdoonNo ratings yet
- Optical AmpDocument25 pagesOptical AmpSimrandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Surpass Hix 56Xx Multiservice Dslam Broadband AccessDocument18 pagesSurpass Hix 56Xx Multiservice Dslam Broadband AccessNyàssouh Kh100% (1)
- Brkopt 2102Document69 pagesBrkopt 2102cool dude911No ratings yet
- Understanding Optical Time Domain Reflectometry Poster PDFDocument1 pageUnderstanding Optical Time Domain Reflectometry Poster PDFyouvsyou100% (1)
- Huanetwork XDSL Solution - Huawei ADSL2+ and VDSL2 Solution)Document9 pagesHuanetwork XDSL Solution - Huawei ADSL2+ and VDSL2 Solution)Elizabeth RichNo ratings yet
- 01-29 Spectrum Analyzer BoardDocument18 pages01-29 Spectrum Analyzer BoardGhallab AlsadehNo ratings yet
- Huawei Optix Osn 9800 m24 DatasheetDocument4 pagesHuawei Optix Osn 9800 m24 DatasheetAli Rajabzadeh dezfuliNo ratings yet
- Cisco ONS 15216 SeriesDocument38 pagesCisco ONS 15216 SeriesPavleObradovicNo ratings yet
- Introduction To WDM Systems and OpticalDocument2 pagesIntroduction To WDM Systems and OpticalKallie FokkerNo ratings yet
- Huawei Cloud Computing Data Center Security Solution For Petroleum IndustryDocument2 pagesHuawei Cloud Computing Data Center Security Solution For Petroleum IndustrySandhya Rani PadhyNo ratings yet
- Cisco Monitor Performance NCS 2000 DWDMDocument100 pagesCisco Monitor Performance NCS 2000 DWDMp4i9e8r5No ratings yet
- Technologies: Radio Network Planning ProcessDocument14 pagesTechnologies: Radio Network Planning Processnkapnangluther3099No ratings yet
- DWDM Impairments Optical Transport Networks (OTN) : Linear EffectsDocument1 pageDWDM Impairments Optical Transport Networks (OTN) : Linear Effectskapil dev pandeyNo ratings yet
- Radcom LTE Poster 2011Document1 pageRadcom LTE Poster 2011Sergiy RipskyyNo ratings yet
- Ronald Talisay CV Telecom EngineerDocument6 pagesRonald Talisay CV Telecom EngineerRonald AllanNo ratings yet
- DWDM Basics: Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing ExplainedDocument18 pagesDWDM Basics: Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing Explainedpriyanka joshiNo ratings yet
- Apsfl Brochure Web PurposeDocument16 pagesApsfl Brochure Web PurposeBharath CNWNo ratings yet
- 01 HCIA 5G Motivação e Progresso Da IndustriaDocument52 pages01 HCIA 5G Motivação e Progresso Da IndustriaEvaldo JuniorNo ratings yet
- Ason v1 2 PDFDocument1 pageAson v1 2 PDFGiorgio Valtolina100% (1)
- 3GPP 36 Series Specifications GuideDocument5 pages3GPP 36 Series Specifications GuideSonu TiwariNo ratings yet
- Telefonica Tests Huawei 100G Transmission Over 1,000kmDocument3 pagesTelefonica Tests Huawei 100G Transmission Over 1,000kmvictoriovegaNo ratings yet
- WDM networking technologies overviewDocument22 pagesWDM networking technologies overviewAbhishek SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Basic IP PDFDocument276 pagesBasic IP PDFfalberto08No ratings yet
- Planning for Radio Coverage and CapacityDocument18 pagesPlanning for Radio Coverage and CapacityLintong AldironNo ratings yet
- OTC119204 OptiX OSN 9800 Common Data Configuration ISSUE18.00Document37 pagesOTC119204 OptiX OSN 9800 Common Data Configuration ISSUE18.00Ernesto GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Ofc 1Document76 pagesOfc 1kaushaltrivedi46No ratings yet
- Telecommunication PosterDocument3 pagesTelecommunication PosterWan HaziqNo ratings yet
- Optical Network Monitoring System Onmsi Ensures Municipality Fiber Network Availability Case StudiesDocument2 pagesOptical Network Monitoring System Onmsi Ensures Municipality Fiber Network Availability Case StudiesgagaNo ratings yet
- Planning Radio Coverage and CapacityDocument26 pagesPlanning Radio Coverage and CapacitynaveedalishaNo ratings yet
- 19 - Network Planning PDFDocument7 pages19 - Network Planning PDFhasNo ratings yet
- Huawei OSN1800 Pre-Sale Training Slide For Agent (2012) PDFDocument43 pagesHuawei OSN1800 Pre-Sale Training Slide For Agent (2012) PDFS. M. Arifinul KarimNo ratings yet
- FTTH ProfileDocument28 pagesFTTH Profilesandeepmishra100% (1)
- BT Comparing Azure PIM WhitepaperDocument11 pagesBT Comparing Azure PIM WhitepaperBen BadjiNo ratings yet
- Icon Library: Current As of 3-15-2007Document69 pagesIcon Library: Current As of 3-15-2007jure.denkNo ratings yet
- Nokia Wavefabric Portfolio Brochure PDFDocument19 pagesNokia Wavefabric Portfolio Brochure PDFSNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Cut-Off Shifted Single-Mode Optical Fibre and CableDocument24 pagesCharacteristics of Cut-Off Shifted Single-Mode Optical Fibre and CableDan BuruianaNo ratings yet
- Microwave Design FormulaDocument1 pageMicrowave Design FormulagvdomingoNo ratings yet
- Section 6 B2H SOPDocument91 pagesSection 6 B2H SOPDayaram SahNo ratings yet
- Triple Play For Subscriber Services Feature Guide - 13.3Document374 pagesTriple Play For Subscriber Services Feature Guide - 13.3openid_dr4OPAdENo ratings yet
- 40-Channel Single Mudule ROADMDocument8 pages40-Channel Single Mudule ROADMAmos MakhubeleNo ratings yet
- DWDM / DCI - Discovery: SP OpticalDocument21 pagesDWDM / DCI - Discovery: SP OpticalMakusNo ratings yet
- 2 - BF000010 GPON Fundamentals ISSUE1.05 (S+N)Document68 pages2 - BF000010 GPON Fundamentals ISSUE1.05 (S+N)Jonathan MolinaNo ratings yet
- Hdmi™ (High-Defi Nition Multimedia Interface) : Connectors and Pin AssignmentDocument2 pagesHdmi™ (High-Defi Nition Multimedia Interface) : Connectors and Pin AssignmentmattgirvNo ratings yet
- Ip Over DMDWDocument19 pagesIp Over DMDWammezzNo ratings yet
- 3-OTC107403 OptiX NG WDM ASON Application ISSUE1.03Document102 pages3-OTC107403 OptiX NG WDM ASON Application ISSUE1.03HachidSofianeNo ratings yet
- Gpon and OpticalDocument67 pagesGpon and Opticalkhanhvt50No ratings yet
- 3KC29562AAAATQZZA - V1 - 1850 Transport Service Switch 5R (TSS-5R) Release 4.0 Installation and System Turn-Up Guide PDFDocument234 pages3KC29562AAAATQZZA - V1 - 1850 Transport Service Switch 5R (TSS-5R) Release 4.0 Installation and System Turn-Up Guide PDFrafiq_machoNo ratings yet
- I&M OTN Sept2016 PDFDocument64 pagesI&M OTN Sept2016 PDFnoircyNo ratings yet
- OSN 9800 V100R001C01 Product Overview 01 REVISADO PDFDocument52 pagesOSN 9800 V100R001C01 Product Overview 01 REVISADO PDFplinio_de_paulaNo ratings yet
- Selection of Different ITU-T G.652-FinalDocument8 pagesSelection of Different ITU-T G.652-FinalanjanivaishNo ratings yet
- BRKSPG 2116Document104 pagesBRKSPG 2116Daniel VieceliNo ratings yet
- WDM Technologies: Passive Optical ComponentsFrom EverandWDM Technologies: Passive Optical ComponentsAchyut K. DuttaNo ratings yet
- Cisco Icon LibraryDocument6 pagesCisco Icon LibraryYunow MendozaNo ratings yet
- Presentacion CHI NOG18 Tabata Materan Revised 050318Document40 pagesPresentacion CHI NOG18 Tabata Materan Revised 050318Najeeb Ur Rehman LashariNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic CommunicationDocument4 pagesFiber Optic Communicationeaglett100% (1)
- FTTx Industry Overview and Next Generation PON TechnologiesDocument44 pagesFTTx Industry Overview and Next Generation PON Technologieseugene123No ratings yet
- MW Link IssuesDocument18 pagesMW Link IssuesEditson Jiovanny Garzon OjedaNo ratings yet
- RTN 900 v100r019c10 Mimo Site Commissioning (Ism8+Xmc-5d Odu) 02Document9 pagesRTN 900 v100r019c10 Mimo Site Commissioning (Ism8+Xmc-5d Odu) 02Aung Aung OoNo ratings yet
- RTN 900 v100r019c10 Mimo Site Commissioning (Ism8+Xmc-5d Odu) 02Document9 pagesRTN 900 v100r019c10 Mimo Site Commissioning (Ism8+Xmc-5d Odu) 02Aung Aung OoNo ratings yet
- Carrier Aggregation (CA) TechnologyDocument5 pagesCarrier Aggregation (CA) TechnologyAung Aung OoNo ratings yet
- RTN 950 Product BrochureDocument2 pagesRTN 950 Product BrochureAung Aung OoNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) TechnologyDocument3 pagesMultiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) TechnologyAung Aung OoNo ratings yet
- TDMA scheduling solution divides timeslots to control hidden node interferenceDocument2 pagesTDMA scheduling solution divides timeslots to control hidden node interferenceAung Aung OoNo ratings yet
- TDMA scheduling solution divides timeslots to control hidden node interferenceDocument2 pagesTDMA scheduling solution divides timeslots to control hidden node interferenceAung Aung OoNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) TechnologyDocument3 pagesMultiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) TechnologyAung Aung OoNo ratings yet
- Microwave Backhaul Solution in B2Bú A New Field With Great PotentialDocument2 pagesMicrowave Backhaul Solution in B2Bú A New Field With Great PotentialAung Aung OoNo ratings yet
- Anti Interference TechnologiesDocument2 pagesAnti Interference TechnologiesEduardo Garcia PerezNo ratings yet
- Microwave Backhaul Solution in B2Bú A New Field With Great PotentialDocument2 pagesMicrowave Backhaul Solution in B2Bú A New Field With Great PotentialAung Aung OoNo ratings yet
- RBS 6601 PDFDocument47 pagesRBS 6601 PDFDebayan ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- RTN 900 Product Family PosterDocument1 pageRTN 900 Product Family PosterAung Aung OoNo ratings yet
- Maintenance (Technical) - WikipediaDocument44 pagesMaintenance (Technical) - WikipediaAung Aung OoNo ratings yet
- Maintenance (Technical) - WikipediaDocument44 pagesMaintenance (Technical) - WikipediaAung Aung OoNo ratings yet
- ServiceNow KB - Upgrade Best Practices (KB0547245)Document12 pagesServiceNow KB - Upgrade Best Practices (KB0547245)Abhishek MishraNo ratings yet
- User Plan & Control PlanDocument4 pagesUser Plan & Control PlanUsman ArshadNo ratings yet
- Dell Inspiron 1545 Wistron Dr1 Roberts Uma 48 4aq01 031 08212 3 PDFDocument59 pagesDell Inspiron 1545 Wistron Dr1 Roberts Uma 48 4aq01 031 08212 3 PDFrafael vidalNo ratings yet
- SY0-601 - Dumpsbase 45Document143 pagesSY0-601 - Dumpsbase 45DripNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument16 pagesProjectPriyanka GautamNo ratings yet
- Cisco RoadmDocument73 pagesCisco Roadmhas samNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Wiring Scheme: RegistrationDocument2 pages3 Phase Wiring Scheme: RegistrationMihai MargineanuNo ratings yet
- Eflash: Contractual Information For Partners: Phase-OutDocument3 pagesEflash: Contractual Information For Partners: Phase-OutMoises ReznikNo ratings yet
- Coaxial Cable GuideDocument7 pagesCoaxial Cable Guidesundars_sriNo ratings yet
- Game Development Using Panda 3D Game EngineDocument3 pagesGame Development Using Panda 3D Game EngineEditor IJRITCCNo ratings yet
- An IOT Approach For Motion Detection Using Raspberry PiDocument4 pagesAn IOT Approach For Motion Detection Using Raspberry PiInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- CPU Protection Queue ConfigurationDocument232 pagesCPU Protection Queue ConfigurationErnestoDelgadoNo ratings yet
- Java Web Component EE6 OCEWCDDocument5 pagesJava Web Component EE6 OCEWCDjigyansu prustyNo ratings yet
- EM GS 4210 24P2S - v1.0Document346 pagesEM GS 4210 24P2S - v1.0huyvt3No ratings yet
- Power Distribution System Reconfiguration For Loss Reduction by Using Heuristic MethodDocument6 pagesPower Distribution System Reconfiguration For Loss Reduction by Using Heuristic MethodATSNo ratings yet
- AdrielDocument3 pagesAdrielalylanuzaNo ratings yet
- Manual Ups Forza Sl762Document52 pagesManual Ups Forza Sl762josedavid2898980No ratings yet
- NSE7 - EFW-7.0 Exam - Free Actual Q&As, Page 1 - ExamTopicsDocument35 pagesNSE7 - EFW-7.0 Exam - Free Actual Q&As, Page 1 - ExamTopicsMalik SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- Hadoop TestDocument8 pagesHadoop Testbig_fir100% (1)
- Data Exchange Between S7-1200 and Sentron Pac Via Modbus TCP (Set 22)Document55 pagesData Exchange Between S7-1200 and Sentron Pac Via Modbus TCP (Set 22)Denza_666No ratings yet
- CPRI IntroductionDocument26 pagesCPRI Introductionsyahrul rizalNo ratings yet
- Unix Programming Important QuestionsDocument6 pagesUnix Programming Important QuestionsDronavalli GayathriNo ratings yet
- Icnd230 - Student Guide v4Document652 pagesIcnd230 - Student Guide v4Ulises MandujanoNo ratings yet
- Submit Your Site To Free Directories, With 9dir Free Directories List3Document3 pagesSubmit Your Site To Free Directories, With 9dir Free Directories List3Sarayu Sannajaji0% (1)
- Restful WebServicesDocument60 pagesRestful WebServicesNavi Bharat100% (1)
- SNA Bullet 10 MCQS-50: Which Types of Network Hardware Does Linux Support ?Document11 pagesSNA Bullet 10 MCQS-50: Which Types of Network Hardware Does Linux Support ?Mursaleen UmerNo ratings yet
- Nokia PDFDocument11 pagesNokia PDFNivyaNo ratings yet
- S5570S-EI Series High Performance Intelligent Ethernet Switch DatasheetDocument23 pagesS5570S-EI Series High Performance Intelligent Ethernet Switch DatasheetroiNo ratings yet
- Jncis SecDocument177 pagesJncis Secarvin3060100% (4)
- Spatialnet: End-To-End Physical Network Inventory ManagementDocument3 pagesSpatialnet: End-To-End Physical Network Inventory ManagementDoraoraNo ratings yet