Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Multiple Sclerosis - Is An Immune-Mediated, Progressive Demyelinating Disease of The CNS
Uploaded by
Jarod Hembrador0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views4 pagesPatho
Original Title
Multiple Sclerosis CM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPatho
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views4 pagesMultiple Sclerosis - Is An Immune-Mediated, Progressive Demyelinating Disease of The CNS
Uploaded by
Jarod HembradorPatho
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
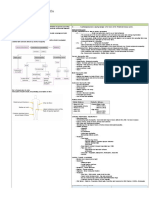
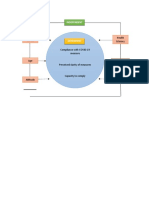
Multiple Sclerosis - is an immune-mediated, progressive demyelinating disease of the CNS.
Predisposing Factors:
• Age (20-35 y.o) Precipitating Factors:
• Gender (Female) • Exposure to:
• Geographic Location o Epstein-Barr Virus (most common)
• Genetic Susceptibility o Measles Virus
• Smoking o Human Herpes Virus-6
• Low levels of Vit. D
Sensitized T & B lymphocyte passes blood brain barrier
Sensitized T cell remain in CNS and promote infiltration
Interferon gamma T-cells attach to T cells attach to myelin sheath receptor
activates macrophages macrophages
T cells release cytokines
Macrophage release of tissue necrosis factor
Inflammatory response is started
Myelin sheath is attacked
Destruction of Myelin Sheath
Oligodendrocytes attempts to repair damaged
myeline
T cells, macrophages and interferon gamma
attack the myelin sheath, oligodendrocytes,
axon as they were identified as foreign
Axon becomes demyelinated Primary S&S
Degeneration of axons • Fatigue
• Depression
Plaques of sclerotic tissue appear to • Loss of Balance
demyelinated sheath • Difficulty in
coordination
Permanent irreversible
• Pain
damage Interruption if impulse transmission
Manifestation depending on involves neurons
Urinary Tract Infection
Sensorimotor Optic nerves:
Bladder Nerve:
nerves: • Blurring of vision
• Incontinence
• Weakness • Diplopia
• Urgency
Impaired physical • Difficulty in • Scotoma
coordination • Frequency of
mobility r/t weakness • Blindness urination
and spasticity • Numbness
• Pain
• Spasticity Impaired urinary
elimination r/t nervous
Risk for injury r/t visual system dysfunction
impairments
• Assist patient in for muscles • Assess voiding pattern
exercises as able or allowed out • Ensure adequate hydration to
of bed • Recommend to make use of an prevent urinary tract infection and
• Present a safe environment: bed eye patch if experiencing double stones.
rails up, bed in a down position, vision. • Use a catheter to expel retained
important items close by. • Orient to the surroundings; keep urine.
• Provide analgesics as prescribed personal belongings and furniture • Set up on a bladder training
• Evaluate need for assistive on fixed arrangement. program to lessen incontinence
devices • Advise making use of other episodes
• Teach patient or family in senses to compensate for • Encourage proper hand hygiene
maintaining home atmosphere reduced sensation. and perineal care
hazard-free and safe • Provide a clutter-free and safe • Administer medications as
• Let the patient accomplish tasks environment. prescribed
at his or her own pace • Obtain periodic urinalysis, urine
culture and sensitivity as indicated
• Electrophoresis – the cerebrospinal fluid is
being studied to check for the presence of
IgG antibodies.
• Magnetic Resonance Imaging – helpful in
visualization of the lesions on the white
matter of the central nervous system
• Visual, auditory and somatosensory
evoked potentials – can help define the
extent of the disease process and monitor
changes.
• Neuropsychological testing - may be
indicated to assess cognitive impairment.
• Urodynamic Studies – for underlying
bladder dysfunctions
Disease-Modifying Medications:
• Interferon beta-1a (Rebif) and interferon beta-1b
(Betaseron)
• Glatiramer acetate (Copaxone)
• IV methylprednisolone
• Novantrone
Symptoms Management Medications:
• Baclofen (Lioresal)
• Benzodiazepines (Valium), tizanidine (Zanaflex), and
dantrolene (Dantrium)
• amantadine (Symmetrel), pemoline (Cylert), or
fluoxetine (Prozac
• beta-adrenergic blockers (Inderal), antiseizure agents
(Neurontin), and benzodiazepines (Klonopin)
• anticholinergic agents, alpha-adrenergic blockers,
antispasmodic agents
• Ascorbic Acid & Antibiotics
Legend:
Predisposing Factors Complication Nursing Diagnosis
Precipitating Factors Disease Process Nursing Management Diagnostics
Disease Signs & Symptoms Medical Management
You might also like
- 111 Peripheral NeuropathyDocument17 pages111 Peripheral NeuropathyjassbhanguNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Neuropathy Clinical ApproachDocument19 pagesPeripheral Neuropathy Clinical ApproachNur Nadzifah Zainal AbidinNo ratings yet
- Slides Introduction To MyopathyDocument18 pagesSlides Introduction To Myopathypaxivas131No ratings yet
- Cornea 4Document27 pagesCornea 4Rana AhmedNo ratings yet
- AtaxiaDocument10 pagesAtaxiaosakaNo ratings yet
- High Fever Stiff Neck Severe HeadacheDocument3 pagesHigh Fever Stiff Neck Severe HeadacheDiana Jane LauretaNo ratings yet
- Neuro NotesDocument15 pagesNeuro NotesClyde CapapasNo ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestation Diagnostic Investigations TreatmentDocument2 pagesClinical Manifestation Diagnostic Investigations TreatmentAyeNo ratings yet
- The Lab: - Katie ProvostDocument13 pagesThe Lab: - Katie ProvostTransverse Myelitis AssociationNo ratings yet
- Revision 21.7.23-Y3Document7 pagesRevision 21.7.23-Y3leexinyiNo ratings yet
- Group 3: Clinicopathological ConferenceDocument31 pagesGroup 3: Clinicopathological ConferenceNathanielTalibongNo ratings yet
- Atypical Benign Melanocytic LesionsDocument23 pagesAtypical Benign Melanocytic Lesionsghitza80No ratings yet
- Leukocytes AbnormalitiesDocument5 pagesLeukocytes AbnormalitiesJezzah Mae CañeteNo ratings yet
- Peripheral NeuropathiesDocument10 pagesPeripheral NeuropathiesFergieNo ratings yet
- CNS PathologyDocument10 pagesCNS Pathologysarguss1483% (6)
- P and C Cont - VdsDocument4 pagesP and C Cont - VdsAchilles YbarraNo ratings yet
- MeningitisDocument17 pagesMeningitisKyla Marie TejadaNo ratings yet
- Diseases 2Document11 pagesDiseases 2Kristy CostelloNo ratings yet
- MRAT 211 - Thoracic Rehabilitation TRANSDocument10 pagesMRAT 211 - Thoracic Rehabilitation TRANSLovely GopezNo ratings yet
- Nervo US Syste M: Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesNervo US Syste M: Endocrine SystemEric A Colinares Jr.No ratings yet
- Acute Flaccid Paralysis-1Document20 pagesAcute Flaccid Paralysis-1Peterson Wachira HscNo ratings yet
- Genetic and Metabolic DisordersDocument16 pagesGenetic and Metabolic DisordersErin HillNo ratings yet
- Geria MidtermsDocument4 pagesGeria Midtermswieka mawieNo ratings yet
- 18 Nevi and Malignant MelanomaDocument7 pages18 Nevi and Malignant MelanomaWaiwit KritayakiranaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Sclerosis (Medicalstudyzone - Com)Document21 pagesMultiple Sclerosis (Medicalstudyzone - Com)WaleedNo ratings yet
- Bacterial MeningitisDocument2 pagesBacterial Meningitisjennielunay00No ratings yet
- PEDIA Neuromuscular DisorderDocument3 pagesPEDIA Neuromuscular DisorderThakoon TtsNo ratings yet
- NeuroSlidesDocument1,097 pagesNeuroSlidesThy DavidNo ratings yet
- Gyne - Benign LesionsDocument4 pagesGyne - Benign LesionsIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- L10.3-OPHTHA-Uvea (Sept3022)Document5 pagesL10.3-OPHTHA-Uvea (Sept3022)Erald PaderangaNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Neuropathy AidaDocument36 pagesPeripheral Neuropathy AidaAdlina ArifinNo ratings yet
- Lens: Anatomy, Pathology, and Mechanisms of Toxicity Lens DevelopmentDocument6 pagesLens: Anatomy, Pathology, and Mechanisms of Toxicity Lens DevelopmentAmit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Guillain Barre Syndrome PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesGuillain Barre Syndrome Pathophysiologykathy100% (13)
- Lymph Node PathologyDocument4 pagesLymph Node PathologyGerardLum0% (1)
- 6.CEREBRAL PALSY An OverviewDocument60 pages6.CEREBRAL PALSY An Overviewita oktafia nainggolanNo ratings yet
- Fi Bro OsseousDocument23 pagesFi Bro OsseousyuniNo ratings yet
- Generic Name:: M@Bile ScanneDocument1 pageGeneric Name:: M@Bile ScanneWinnie AriolaNo ratings yet
- Disease and Health - Presentation - Pranav Y9ADocument13 pagesDisease and Health - Presentation - Pranav Y9APranav PatchaNo ratings yet
- LeprosyDocument22 pagesLeprosyvisweswar030406No ratings yet
- Clinical Significance of Demyelinating Lesions of The CNSDocument5 pagesClinical Significance of Demyelinating Lesions of The CNSTransverse Myelitis AssociationNo ratings yet
- 14 PDFDocument3 pages14 PDFavvaNo ratings yet
- School NewsletterDocument3 pagesSchool Newsletterapi-351642214No ratings yet
- Hair and Nail DisordersDocument14 pagesHair and Nail DisorderskateverdadNo ratings yet
- UMNLand AHCDocument27 pagesUMNLand AHCdrmamodoNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue Neoplasms 2011Document36 pagesEpithelial Tissue Neoplasms 2011Salma HelmyNo ratings yet
- 10-4 Melanocytic LesionsDocument40 pages10-4 Melanocytic LesionsSorin DeacuNo ratings yet
- Management of Snake BiteDocument1 pageManagement of Snake BiteAfri AdiNo ratings yet
- Small BowelDocument4 pagesSmall Bowelsarguss14100% (1)
- Basic SuturingDocument4 pagesBasic SuturingMian SimporiosNo ratings yet
- Skin Disorders 4-2-08Document14 pagesSkin Disorders 4-2-08api-3822433No ratings yet
- Cervical Disc Disease and Spondylosis: Rabia Qureshi, Jason A. Horowitz, Hamid HassanzadehDocument7 pagesCervical Disc Disease and Spondylosis: Rabia Qureshi, Jason A. Horowitz, Hamid HassanzadehMasithaNo ratings yet
- Rheumatology I 02 Seronegative SpondylarthropathiesDocument21 pagesRheumatology I 02 Seronegative SpondylarthropathiesWen Jie LauNo ratings yet
- KERATOCONUSDocument22 pagesKERATOCONUSAarush DeoraNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue Neoplasms 2011-2012Document36 pagesEpithelial Tissue Neoplasms 2011-2012Salma HelmyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Clients With Oncological DisordersDocument7 pagesNursing Care of Clients With Oncological DisordersLuna MarieNo ratings yet
- NURSING 21 Sensory PerceptionDocument2 pagesNURSING 21 Sensory PerceptionKareen SornitoNo ratings yet
- Cell-Cell Signaling in Vertebrate DevelopmentFrom EverandCell-Cell Signaling in Vertebrate DevelopmentE.J. RobertsonRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Hidden Disabilities and Conditions: Creating an Inclusive WorkplaceFrom EverandHidden Disabilities and Conditions: Creating an Inclusive WorkplaceNo ratings yet
- Transverse Myelitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandTransverse Myelitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CERAE September 5Document2 pagesCERAE September 5Jarod HembradorNo ratings yet
- FigureDocument1 pageFigureJarod HembradorNo ratings yet
- OB Narrative AssessmentDocument4 pagesOB Narrative AssessmentJarod HembradorNo ratings yet
- Concept of Pregnancy Final NCM 107 07172019Document6 pagesConcept of Pregnancy Final NCM 107 07172019Jarod Hembrador100% (1)
- East Vs WestDocument3 pagesEast Vs WestJarod Hembrador100% (1)
- Procedure Checklist On OxygenationDocument2 pagesProcedure Checklist On OxygenationKhatlen BagaresNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Rural Water, Sanitation and Hygiene Project PROPOSALDocument13 pagesSustainable Rural Water, Sanitation and Hygiene Project PROPOSALLawrence WatssonNo ratings yet
- Proforma Curriculum VitaeDocument4 pagesProforma Curriculum VitaeSohail IqbalNo ratings yet
- Nzmail 18821014Document26 pagesNzmail 18821014zeljkogrNo ratings yet
- PHC Assignment 1Document5 pagesPHC Assignment 1Florenze Laiza Donor Lucas100% (1)
- Crane Workbox 4398Document4 pagesCrane Workbox 4398hazopman100% (1)
- SES Presentation FinalDocument65 pagesSES Presentation FinalCurtis YehNo ratings yet
- Cancer Treatment - Capsaicin - Oil RecipeDocument4 pagesCancer Treatment - Capsaicin - Oil RecipeJESUS IS RETURNING DURING OUR GENERATIONNo ratings yet
- Body Image: Marika Tiggemann, Kristy HageDocument7 pagesBody Image: Marika Tiggemann, Kristy HageRachel VictorianaNo ratings yet
- AH1N1 PPT PresentationDocument28 pagesAH1N1 PPT PresentationIna Isabela CostiboloNo ratings yet
- Sets FITT Goals: Lesso NDocument7 pagesSets FITT Goals: Lesso NJA DENo ratings yet
- 10 1007@s00068-mfjrbtDocument14 pages10 1007@s00068-mfjrbtJGunar VasquezNo ratings yet
- Rdramirez Aota 2018 Poster For PortfolioDocument1 pageRdramirez Aota 2018 Poster For Portfolioapi-437843157No ratings yet
- Reactive Hyperplastic Lesions of The Oral CavityDocument8 pagesReactive Hyperplastic Lesions of The Oral CavityMarïsa CastellonNo ratings yet
- Intermittent Positive Pressure BreathingDocument12 pagesIntermittent Positive Pressure BreathingHitesh RohitNo ratings yet
- Behavior ResourcesDocument6 pagesBehavior ResourcesBrook Farm Veterinary CenterNo ratings yet
- BotulismeDocument36 pagesBotulismeDienjhe Love BunzNo ratings yet
- Fractures NoteDocument31 pagesFractures NoteNoor AlblushiNo ratings yet
- Causal DiagaramDocument2 pagesCausal DiagaramBelcena, Emily Faith D.No ratings yet
- How To File A Claim-For GSISDocument2 pagesHow To File A Claim-For GSISZainal Abidin AliNo ratings yet
- Treatment and Prognosis of Febrile Seizures - UpToDateDocument14 pagesTreatment and Prognosis of Febrile Seizures - UpToDateDinointernosNo ratings yet
- Bleeding During Pregnancy and Nursing Care PlanDocument17 pagesBleeding During Pregnancy and Nursing Care PlanLizcelle Bihasa86% (7)
- Lab 11 AntianginalDocument4 pagesLab 11 AntianginalanaNo ratings yet
- 60 Substance Abuse Group Therapy ActivitiesDocument7 pages60 Substance Abuse Group Therapy ActivitiesHanes Labajos100% (1)
- A Comparison Between Indirect and Objective Wear-Time Assessment of Removable Orthodontic AppliancesDocument6 pagesA Comparison Between Indirect and Objective Wear-Time Assessment of Removable Orthodontic ApplianceshelmysiswantoNo ratings yet
- JHU Press Fall 2013 CatalogDocument99 pagesJHU Press Fall 2013 CatalogjhupressNo ratings yet
- Resume - EportfolioDocument3 pagesResume - Eportfolioapi-337162374No ratings yet
- ETW-2013 Amma PDFDocument100 pagesETW-2013 Amma PDFRosalete LimaNo ratings yet
- National Health Policy in India: Dr. Kanupriya ChaturvediDocument38 pagesNational Health Policy in India: Dr. Kanupriya ChaturvediRadhakrishnan TherivilaNo ratings yet
- Bkerzay Wellness BrochureDocument1 pageBkerzay Wellness BrochureSandra Abou JaoudehNo ratings yet