Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Presidential Decree No. 1096, Also Known As The National Building Code of The Philippines Is
Uploaded by
MigaeaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Presidential Decree No. 1096, Also Known As The National Building Code of The Philippines Is
Uploaded by
MigaeaCopyright:
Available Formats
1. What is PD1096? And as a future civil engineer, what do you think is its importance?
Discuss your
answer.
Presidential Decree No. 1096, also known as the National Building Code of the Philippines is
a law created to provide a framework of minimum standards and guidelines for Philippine
Buildings. As a future engineer it is important to know and familiarize myself to the PD 1096
because this decree is created first and foremost to ensure public safety. We rely on the safety of
structures that surround us in our everyday living. The public need for protection from disaster due to
fire, structural collapse and general deterioration underscores the need for modern codes and their
administration. Building codes provide safeguards. Although no code can eliminate all risks, reducing
risks to an acceptable level helps.
2. Is it possible for Non-Issuance, Suspension or Revocation of Building Permits? Why? And what
should be done?
The Building Official may order or cause the non-issuance, suspension or revocation of building
permits on any or all of the following reasons or grounds:
(a) Errors found in the plans and specifications;
(b) Incorrect or inaccurate data of information supplied;
(c) Non-compliance with the provisions of this Code or of any rule or regulation.
Within fifteen (15) days from the date of receipt of advice of the non-issuance, suspension or
revocation of permits, the applicant/permittee may file an appeal with the Secretary who shall render
his decision within fifteen days from date of receipt of notice of appeal. The decision of the Secretary
shall be final subject only to review by the Office of the President.
3. Give at least 5 instances where application of Building permit is exempted.
a) Public buildings
b) Traditional indigenous family dwellings – a dwelling intended for the use and occupancy by the
family of the owner only and constructed of native materials such as bamboo, nipa, logs, or
lumber, the total cost of which does not exceed fifteen thousand pesos.
c) minor construction – sheds, playhouse, greenhouses, poultry houses, not exceeding 6.0sq meters
in total area, provided they are completely detached from any other building and are only for
private use of the owner.
d) Addition of open terraces or patios resting directly on the ground, not exceeding 20.0 sq. meters
in total floor area, exclusively for private use of owner; Installation of window grilles; etc.
e) Repairs – repair works not affecting or involving any structural member, such as replacement of
deteriorated roofing sheets or tiles, gutters, downspouts, fascias, ceilings, and/or sidings.
*provided these shall not violate any provision of the Code.
4. Give at least 2 examples of violations which may be subjected to administrative fines. Discuss
briefly.
a) Construction of building without permit – it is forbidden to build a structure without building
permit unless the structure is a public building or traditional indigenous family dwellings.
b) Use or occupancy of a building/structure without Certificate of Occupancy/Use even if
constructed under valid permit.
c) Change in the type of construction of any building without any building/structure without an
amendatory permit.
d) Disregarding the standards for construction, and promulgate rules and regulations therefor,
relating to structural framework, exterior walls and openings, interior walls and enclosures,
floors, exits and stairs construction, and roofs. There are requirements or standards for
construction, for example requirements for fire safety, sanitation, light and ventilation,
occupancy, etc.
5. What is Boring test? Why do we need this test and when is it required?
Boring Test, as used by foundation engineers, is the act or process of sinking holes into the
overburden (sometimes to considerable depth into bedrock) with rotary or drive sampling equipment
for the purpose of recovering samples from which information on the physical characteristics of the
materials penetrated can be obtained; also applied to the sample or samples so obtained.
It is needed to determine if the soil is suitable to be used as a base area for a structure. Also, to
define if an underground obstruction exists (e.g., old foundation). It can also be done to determine
presence of underground water.
You might also like
- How to Build Shipping Container Homes With PlansFrom EverandHow to Build Shipping Container Homes With PlansRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (5)
- FHA 203-k Loan - Questions & Answers Rehab Loan ProgramDocument6 pagesFHA 203-k Loan - Questions & Answers Rehab Loan ProgramJudy LeonettiNo ratings yet
- 16th Edition IEE Wiring Regulations: Design and Verification of Electrical InstallationsFrom Everand16th Edition IEE Wiring Regulations: Design and Verification of Electrical InstallationsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Annex A of PD 1096 Illustrations: Joel M. Tesico ARC-2204 App 1Document20 pagesAnnex A of PD 1096 Illustrations: Joel M. Tesico ARC-2204 App 1Joel TesicoNo ratings yet
- National Building Code - PD 1096 SummaryDocument5 pagesNational Building Code - PD 1096 SummaryPrudencio Buco60% (5)
- Review - PD 957Document70 pagesReview - PD 957iloilocityNo ratings yet
- Soil Investigation and Foundation DesignFrom EverandSoil Investigation and Foundation DesignRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- National Building Code of The PhilippinesDocument52 pagesNational Building Code of The PhilippinesRetsyLa Porteza100% (6)
- Pharmacology Mind MapsDocument31 pagesPharmacology Mind MapsRaafat A. Issaq50% (2)
- Week 2 - Ce102p - NBCP - Rule 3Document51 pagesWeek 2 - Ce102p - NBCP - Rule 3JP EstacioNo ratings yet
- Policarpio 5 - Refresher SECDocument2 pagesPolicarpio 5 - Refresher SECMigaea100% (1)
- Best Practices Data Model Review ProcessDocument3 pagesBest Practices Data Model Review ProcesssagrawaNo ratings yet
- English For LogisticsDocument25 pagesEnglish For LogisticsRolando Nunez100% (1)
- PVM Training Presentation Session 1 - 2014 SecureDocument40 pagesPVM Training Presentation Session 1 - 2014 Securediaccessltd_17172961No ratings yet
- Reciprocating Compressor FeaturesDocument3 pagesReciprocating Compressor Featuresjk_iitkNo ratings yet
- National Building Code of the Philippines Key ProvisionsDocument54 pagesNational Building Code of the Philippines Key ProvisionsMichelle Pamaylaon100% (3)
- Lab 5: DMVPN - BGPDocument9 pagesLab 5: DMVPN - BGPDevdutt VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Unit I: CODES AND REGULATIONS - : Lesson 1: The National Building Code of The PhilippinesDocument27 pagesUnit I: CODES AND REGULATIONS - : Lesson 1: The National Building Code of The PhilippinesStevenNo ratings yet
- 50 TMSS 02 R0Document0 pages50 TMSS 02 R0renjithas20050% (1)
- Ucsp Reviewer FinalsDocument15 pagesUcsp Reviewer FinalsMigaeaNo ratings yet
- Support Spacing Requirements for Horizontal PipingDocument40 pagesSupport Spacing Requirements for Horizontal PipingAlvin TusiNo ratings yet
- Final Draft Irr Columbarium ProjectsDocument14 pagesFinal Draft Irr Columbarium ProjectsSteps Rols100% (1)
- 10-Storey Construction MethodologyDocument18 pages10-Storey Construction MethodologyShah Jignesh100% (3)
- iOS Security White Paper Feb 2014Document33 pagesiOS Security White Paper Feb 2014Mikey CampbellNo ratings yet
- Auminium SulphateDocument16 pagesAuminium SulphateJanith Saumya BandaraNo ratings yet
- Shipping Container Homes: The best guide to building a shipping container home, including plans, FAQs, and much more!From EverandShipping Container Homes: The best guide to building a shipping container home, including plans, FAQs, and much more!No ratings yet
- P.D. 1096 National Building Code of The PhilippinesDocument12 pagesP.D. 1096 National Building Code of The Philippineshobi jungNo ratings yet
- Python IteratorsDocument8 pagesPython Iteratorssaad_plivo0% (1)
- DGTECH User ManualDocument41 pagesDGTECH User ManualMonika PatelNo ratings yet
- Rumus Hiley Untuk Hammer D100Document5 pagesRumus Hiley Untuk Hammer D100Prapto bwiNo ratings yet
- BD Report - Chap. 1 To 6Document50 pagesBD Report - Chap. 1 To 6Maire Joy E. AzañaNo ratings yet
- Conservatory Foundations.Document12 pagesConservatory Foundations.Phillipe LysNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document10 pagesActivity 2Barrientos Lhea ShaineNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet For Temporary GreenhouesesDocument10 pagesFact Sheet For Temporary Greenhouesestimothy.yueNo ratings yet
- National Building Code - PD 1096 Summary - TOAZ - INFODocument6 pagesNational Building Code - PD 1096 Summary - TOAZ - INFOAlray GolisNo ratings yet
- National Building Code of the Philippines Questions AnsweredDocument2 pagesNational Building Code of the Philippines Questions AnsweredFrancis TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Town & Country Planning Act 1990 Planning (Listed Buildings and Conservation Areas) Act 1990Document7 pagesTown & Country Planning Act 1990 Planning (Listed Buildings and Conservation Areas) Act 1990Femi AdeosunNo ratings yet
- PD 1096 National Building CodeDocument12 pagesPD 1096 National Building CodejuliusmagonciaNo ratings yet
- RMA 1991.edited - EditedDocument16 pagesRMA 1991.edited - EditedOnesmus AlkalineNo ratings yet
- Building System Ch. 3 and 4Document8 pagesBuilding System Ch. 3 and 4POWER_RAaaaNGERzNo ratings yet
- Rule I Ii IiiDocument3 pagesRule I Ii IiiMary Jane MontebonNo ratings yet
- Building PermitDocument3 pagesBuilding PermitChristian NaguitNo ratings yet
- BUILDINGDocument2 pagesBUILDINGMark Velasco TomasNo ratings yet
- Laurence C. Fabiala: Prepared byDocument17 pagesLaurence C. Fabiala: Prepared byLaurenceFabialaNo ratings yet
- BSD NotesDocument8 pagesBSD NotesAira Mhae de LemosNo ratings yet
- Local Media1575913366997717719Document7 pagesLocal Media1575913366997717719MONETH CORTEZNo ratings yet
- Local OrdinancesDocument14 pagesLocal OrdinancesAlmer Tanudra Vineyard ConstructionNo ratings yet
- Building Systems Design MidTerm Lesson Rev.Document44 pagesBuilding Systems Design MidTerm Lesson Rev.Camille Antonette TabulaoNo ratings yet
- AD8_RSW#1Document14 pagesAD8_RSW#1Daeniele Rae LageraNo ratings yet
- NBC PP1Document13 pagesNBC PP121-07217No ratings yet
- Other Terms To RememberDocument5 pagesOther Terms To RememberRobert SacloloNo ratings yet
- Building Department: 157.01 BUILDING CODES ADOPTED - COPIES ON FILE. Pursuant To Published Notice andDocument13 pagesBuilding Department: 157.01 BUILDING CODES ADOPTED - COPIES ON FILE. Pursuant To Published Notice andapi-345893311No ratings yet
- Ce 11 Module 1Document13 pagesCe 11 Module 1Mang AwitNo ratings yet
- Vios Assignment1Document6 pagesVios Assignment1Vios, Allen Rafael M.No ratings yet
- MODULE-1-BSD (1)Document49 pagesMODULE-1-BSD (1)adaptheamaeNo ratings yet
- Vii. Environmental Impact AND Site Planning: Laws and Zoning RestrictionsDocument13 pagesVii. Environmental Impact AND Site Planning: Laws and Zoning RestrictionsDenmar BalbonaNo ratings yet
- Construction RulesDocument21 pagesConstruction RulesHarleyNo ratings yet
- Consructtion Ass.Document7 pagesConsructtion Ass.Shem HaElohim EjemNo ratings yet
- Rule IiiDocument56 pagesRule IiiKhyrwin O HidalgoNo ratings yet
- National Building CodeDocument42 pagesNational Building Codehannah AyengNo ratings yet
- Summaryreport Nbcp.Document8 pagesSummaryreport Nbcp.Ferly May Zabala VillezaNo ratings yet
- 389506143-building-code-midterm-examsDocument4 pages389506143-building-code-midterm-examseloisaaquinoNo ratings yet
- SetbackDocument7 pagesSetbackVincent RanoaNo ratings yet
- Epcot Building Codes 2015 Edition Code Change Submittals Effective 10/01/2015Document48 pagesEpcot Building Codes 2015 Edition Code Change Submittals Effective 10/01/2015LALA0% (1)
- BSD LongDocument11 pagesBSD LongkkkNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - National Building Code of The Philippines - Part 1Document37 pagesModule 1 - National Building Code of The Philippines - Part 1Rovic VincentNo ratings yet
- Black White Yellow Corporate Photo Architecture PresentationDocument32 pagesBlack White Yellow Corporate Photo Architecture PresentationMarshall james G. RamirezNo ratings yet
- Noida Bye LawsDocument15 pagesNoida Bye LawsBhuvan PancholiNo ratings yet
- NBCP Part 1Document37 pagesNBCP Part 1ZhebyNo ratings yet
- 0-2022-07-12 - Tall Ship Design Review Application InstructionsDocument11 pages0-2022-07-12 - Tall Ship Design Review Application Instructionsapi-119493862No ratings yet
- Building PermitDocument30 pagesBuilding PermitChristine Lyza DinamlingNo ratings yet
- BP 01 When Is A Building Permit Required Updated Oct 22Document6 pagesBP 01 When Is A Building Permit Required Updated Oct 22BradNo ratings yet
- COCOSDE Homework 3 by LEE, Elixabeth S. (Leeleebeth)Document6 pagesCOCOSDE Homework 3 by LEE, Elixabeth S. (Leeleebeth)ELIXABETH LEENo ratings yet
- Textbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 5, Business Formation and Entity StructuringFrom EverandTextbook of Urgent Care Management: Chapter 5, Business Formation and Entity StructuringNo ratings yet
- Dirty Dustbins and Sloppy Streets: A Practical Treatise on the Scavenging and Cleansing of Cities and TownsFrom EverandDirty Dustbins and Sloppy Streets: A Practical Treatise on the Scavenging and Cleansing of Cities and TownsNo ratings yet
- Logarithmic Exponential Review 3-15Document5 pagesLogarithmic Exponential Review 3-15MigaeaNo ratings yet
- Alvarez 4 - Refresher SECDocument2 pagesAlvarez 4 - Refresher SECMigaeaNo ratings yet
- Rendon 4 - Refresher HYDDocument2 pagesRendon 4 - Refresher HYDMigaeaNo ratings yet
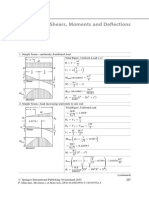
- Appendix A. Shears, Moments and Deflections: X L WLDocument13 pagesAppendix A. Shears, Moments and Deflections: X L WLMigaeaNo ratings yet
- Hiring for Project Managers, Engineers, Safety Officers and other roles in Mandaluyong CityDocument1 pageHiring for Project Managers, Engineers, Safety Officers and other roles in Mandaluyong CityMigaeaNo ratings yet
- Ra 104442 Civil Engineer Tuguegarao 11 2022Document28 pagesRa 104442 Civil Engineer Tuguegarao 11 2022MigaeaNo ratings yet
- Base Shear and Moment Calculations for Frame DesignDocument23 pagesBase Shear and Moment Calculations for Frame DesignMigaeaNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1670826954550 7007956178779713717Document4 pagesOrca Share Media1670826954550 7007956178779713717MigaeaNo ratings yet
- Women's Rights Issues and Breaking BarriersDocument2 pagesWomen's Rights Issues and Breaking BarriersMigaeaNo ratings yet
- Portfolio - Brigid1Document20 pagesPortfolio - Brigid1MigaeaNo ratings yet
- List of those who PASSED the CPE for Technical PositionsDocument4 pagesList of those who PASSED the CPE for Technical PositionsMigaeaNo ratings yet
- A Lesson Plan in Introduction To Phychological First Aid: Show The Video ClipDocument2 pagesA Lesson Plan in Introduction To Phychological First Aid: Show The Video ClipMigaeaNo ratings yet
- Using The Inverted Pyramid Style of Writing: Example # 1: Yale Library CelebrationDocument3 pagesUsing The Inverted Pyramid Style of Writing: Example # 1: Yale Library CelebrationJohn KarlNo ratings yet
- Master Full Contact SkillsDocument1 pageMaster Full Contact SkillsMigaeaNo ratings yet
- MAAP eTest Permit Sign Up for Exam on Feb 9Document1 pageMAAP eTest Permit Sign Up for Exam on Feb 9MigaeaNo ratings yet
- Ethics FinalsDocument1 pageEthics FinalsMigaeaNo ratings yet
- EDA1Document3 pagesEDA1MigaeaNo ratings yet
- Drinking in The WorkplaceDocument3 pagesDrinking in The WorkplaceMigaeaNo ratings yet
- Grouped Data Calculation PDFDocument14 pagesGrouped Data Calculation PDFNuelle NefielNo ratings yet
- 16 Bit MicropocessorDocument1 page16 Bit MicropocessorMigaeaNo ratings yet
- Selecting A Course v.2.0Document1 pageSelecting A Course v.2.0MigaeaNo ratings yet
- EDA1Document3 pagesEDA1MigaeaNo ratings yet
- SolucionarioDocument16 pagesSolucionariopedro75223No ratings yet
- Unit IV Social Control Social GroupsDocument15 pagesUnit IV Social Control Social GroupsMigaeaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6 Solns PDFDocument7 pagesTutorial 6 Solns PDFMigaeaNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal Parts GuideDocument4 pagesResearch Proposal Parts GuideMigaeaNo ratings yet
- ScaleDocument6 pagesScaleMigaeaNo ratings yet
- Marine Diesel Engine S60 Dimensions and SpecsDocument2 pagesMarine Diesel Engine S60 Dimensions and SpecsRomie HarieNo ratings yet
- (Common) Operation Guide For CME Script ExecutorDocument13 pages(Common) Operation Guide For CME Script ExecutorzyfanNo ratings yet
- M3 Tutorial - US - UK April 2013 V2Document48 pagesM3 Tutorial - US - UK April 2013 V2madelspNo ratings yet
- Lotus Domino About AdminPDocument12 pagesLotus Domino About AdminPSaravana Kumar100% (1)
- 8 4 6 - Nema SM24Document2 pages8 4 6 - Nema SM24cdsenthilNo ratings yet
- Planning 3G Netwrok With HSPA+ Service Base On 2G NetworkDocument59 pagesPlanning 3G Netwrok With HSPA+ Service Base On 2G NetworkBoby SharifNo ratings yet
- Vol-II Reinforced Cement Concrete WorkDocument70 pagesVol-II Reinforced Cement Concrete WorkAnudeep RamagiriNo ratings yet
- Java Card PlatformDocument35 pagesJava Card PlatformmmpfNo ratings yet
- MSN MSGRDocument808 pagesMSN MSGRfrigopunkerNo ratings yet
- Andritz Vertical Line Shaft PumpsDocument6 pagesAndritz Vertical Line Shaft PumpsVictor VignolaNo ratings yet
- Firesheep Side Jacking AttacksDocument5 pagesFiresheep Side Jacking AttacksPMNo ratings yet
- Electrical Motor Control TrainingDocument4 pagesElectrical Motor Control TrainingdenramrNo ratings yet
- Radio Shack Remote ManualDocument18 pagesRadio Shack Remote ManualJoeNo ratings yet
- Sony Ericsson t700, w890Document119 pagesSony Ericsson t700, w890drunk65No ratings yet
- AD OverviewDocument16 pagesAD OverviewChandan ChandanNo ratings yet
- Manish SrivastavaDocument3 pagesManish SrivastavaTammie LittleNo ratings yet