0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views24 pagesObjective Type Question of Transmission and Distributio1
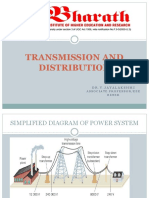
The document provides 100 multiple choice questions about transmission and distribution of electrical power. It covers topics like types of transmission lines, materials used, line constants, effects like Ferranti effect, voltage classifications of cables like low tension, high tension, super tension, extra high tension. Methods of laying underground cables like direct laying, solid system and draw-in system are discussed. Cable losses due to dielectric losses, conductor losses and sheath losses are also mentioned.
Uploaded by
krithikgokul selvamCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views24 pagesObjective Type Question of Transmission and Distributio1
The document provides 100 multiple choice questions about transmission and distribution of electrical power. It covers topics like types of transmission lines, materials used, line constants, effects like Ferranti effect, voltage classifications of cables like low tension, high tension, super tension, extra high tension. Methods of laying underground cables like direct laying, solid system and draw-in system are discussed. Cable losses due to dielectric losses, conductor losses and sheath losses are also mentioned.
Uploaded by
krithikgokul selvamCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd