Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Units
Uploaded by
semarasik_651536604Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Units
Uploaded by
semarasik_651536604Copyright:
Available Formats
Commonly used units in CE319F (Elementary Fluid Mechanics) - S.A.
Kinnas
(to be continuously enhanced and improved!)
Remember also multiples of units: h(ecto)=100; k(ilo)=103; M(ega)=106; G(iga)=109; T(era)=1012; Peta=1015, and
sub-multiples of units: c(enti)=10-2; m(illi)=10-3; m (micro)=10-6; n(ano)=10-9; pico=10-12
Quantity SI units U.S. customary units Definitions/equations
L (Length) m (=100 cm=1000 mm) ft (=12 inches=0.3048 m)
M (Mass) kg slug [=32.2 lbm(pound mass)=14.59 kg]
T (time) sec or s sec or s
v (velocity) m/sec ft/sec Velocity=Distance/Time
a (acceleration) m/sec2 ft/sec2 Acceleration=Velocity/Time
w (angular velocity) rad(ians)/sec or sec -1
rad/sec or sec -1
v(elocity)=w*r(adius)
f (frequency) cycles/sec = Hz (Hertz) = RPS (Revs Per Sec) [often RPM (Revs Per Min)] w=2 p f=2 p/T
T (period) sec sec T=1/f
F (Force) N(ewton)=1kg*1m/sec2 lbf (pound force)=1slug*1ft/sec2 Force=Mass*Acceleration
W (Weight) 1kg (on earth) weighs: 1 slug (on earth) weighs: Weight=M*g(accel. of gravity)
1kg*9.81 m/sec2=9.81 N (=1 kp or kilopond) 1slug*32.2 ft/sec2=32.2 lbf
g (accel. of gravity) g=9.81 m/sec2 g=32.2 ft/sec2
M(Moment) or Q(Torque) N.m lbf.ft Moment=Force*Arm(distance)
W (Work) J(oule)=N.m lbf.ft Work=Force*Distance
P (Power) W(att)=J/sec hp=550 lbf.ft/sec (1hp=0.746 kW) Power=Work/Time
T (Temperature) K(elvin)=273 + oC(elcius)
o o
R(ankine)=460 + oF(ahrenheit) F=9/5*oC+32 ; oC=(oF-32)*5/9
o
p (pressure) Pa(scal)=N/m ; 1bar=10 Pa; 1mbar=100Pa=1hPa;
2 5
psi (lbf/in ) or psf (lbf/ft )
2 2
pressure=Normal Force/Area
1 atm = 101.3 kPa; 1 Torr=1 mmHg
p (standard atm pressure) patm=101.3 kPa=1,013 mbar=760mmHg patm=14.696 psi =29.92 inHg
t (shear stress) Pa(scal)=N/m2 psi (lbf/in2) or psf (lbf/ft2) shear stress=Shear Force/Area
r (density) kg/m 3
slugs/ft 3
r=Mass/Volume
g (specific weight) N/m3 lbf/ft3 g=Weight/Volume=r g
S.G. (specific gravity) unitless! unitless! S.G.=g/gwater.=r/r water
m (dynamic viscosity) Pa.sec = N.sec/m2 (1 poise= 10-1 Pa.sec) lbf.sec/ft2 t=m dv/dy
n (kinematic viscosity) m2/sec (1 stokes=10-4 m2/sec) ft2/sec n=/m/r
s (surface tension) N/m lbf/ft Force=s * Length
Last updated: SAK 2/11/08
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- UnitsDocument1 pageUnitssemarasik_651536604No ratings yet
- Three-Piece Ball Valves: With Integral ISO Mounting FlangeDocument4 pagesThree-Piece Ball Valves: With Integral ISO Mounting Flangesemarasik_651536604No ratings yet
- Calculation For Reinforcement PadDocument1 pageCalculation For Reinforcement Padsemarasik_651536604No ratings yet
- Birmingham Wire Gauge System For Wall ThicknessDocument1 pageBirmingham Wire Gauge System For Wall Thicknesssemarasik_651536604No ratings yet
- Piping Tech QuesDocument2 pagesPiping Tech QuescristhianNo ratings yet
- Piping Loss Calculations: Input Values Head Loss, Given Piping and FlowDocument1 pagePiping Loss Calculations: Input Values Head Loss, Given Piping and Flowsemarasik_651536604No ratings yet
- Report of Sales To Cool Saddle Traders: Date Quantity Product RevenueDocument1 pageReport of Sales To Cool Saddle Traders: Date Quantity Product Revenuesemarasik_651536604No ratings yet
- ENTHALPY CALCULATION OF LPG, n-C3H8 60%, n-C4H10 40% W/W: Component Temper Pressure Vapor Pres KJ/KGDocument1 pageENTHALPY CALCULATION OF LPG, n-C3H8 60%, n-C4H10 40% W/W: Component Temper Pressure Vapor Pres KJ/KGsemarasik_651536604No ratings yet
- ThreadsDocument2 pagesThreadssemarasik_651536604No ratings yet
- Rigours Preheater: Feed - 1694.44 2.85 21.14 792.89 0.05 0.00Document14 pagesRigours Preheater: Feed - 1694.44 2.85 21.14 792.89 0.05 0.00semarasik_651536604100% (1)
- HollowBar SANDVIKDocument2 pagesHollowBar SANDVIKBudijono WinotoNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Stress and Strain On High Pressure Steam Turbine Steam Turbine Shaft Due To Mechanical Loading-ReviewDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Stress and Strain On High Pressure Steam Turbine Steam Turbine Shaft Due To Mechanical Loading-Reviewsemarasik_651536604No ratings yet
- Piping CodesDocument3 pagesPiping Codessemarasik_651536604No ratings yet
- ELAN Detector Minimum Head/Shell Thickness Estimates: in in ExDocument1 pageELAN Detector Minimum Head/Shell Thickness Estimates: in in Exsemarasik_651536604No ratings yet
- Slug Loads Calc SheetDocument1 pageSlug Loads Calc Sheetsemarasik_651536604No ratings yet
- BS en 60045-1 - 1993Document32 pagesBS en 60045-1 - 1993semarasik_651536604No ratings yet
- Investigating Theme Park Service Quality by Using Modified Themequal ModelDocument15 pagesInvestigating Theme Park Service Quality by Using Modified Themequal Modelsemarasik_651536604No ratings yet
- Safety - Report Disney LandDocument9 pagesSafety - Report Disney Landsemarasik_651536604No ratings yet
- CJ 20-PD-0027 Road Crossing DesignDocument1 pageCJ 20-PD-0027 Road Crossing Designsemarasik_651536604No ratings yet
- Evaporation Loss Measurement PDFDocument8 pagesEvaporation Loss Measurement PDFAli ShahNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Stress and Strain On High Pressure Steam Turbine Steam Turbine Shaft Due To Mechanical Loading-ReviewDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Stress and Strain On High Pressure Steam Turbine Steam Turbine Shaft Due To Mechanical Loading-Reviewsemarasik_651536604No ratings yet
- Fault-Tolerant Computing: Dealing With High-Level ImpairmentsDocument19 pagesFault-Tolerant Computing: Dealing With High-Level Impairmentssemarasik_651536604No ratings yet
- CJ 20-PD-0027 Road Crossing DesignDocument1 pageCJ 20-PD-0027 Road Crossing Designsemarasik_651536604No ratings yet
- Seperator Design, K C Foong PDFDocument7 pagesSeperator Design, K C Foong PDFpomaukNo ratings yet
- Summary of Roland ProjectDocument3 pagesSummary of Roland Projectsemarasik_651536604No ratings yet
- Guidelines For Lifting Operations by Floating Vessels CranesDocument36 pagesGuidelines For Lifting Operations by Floating Vessels CranesKin Lai KongNo ratings yet
- WSA 2P10S 1843P ModelDocument1 pageWSA 2P10S 1843P Modelsemarasik_651536604No ratings yet
- CODESDocument3 pagesCODESsemarasik_651536604No ratings yet
- SDTA Engineer (Mechanical & Instrument) Scope of WorkDocument2 pagesSDTA Engineer (Mechanical & Instrument) Scope of Worksemarasik_651536604No ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Dayton Tech StampingDocument78 pagesDayton Tech StampingRaghu VenkatNo ratings yet
- Maag Gear Shaper CutterDocument3 pagesMaag Gear Shaper CutterBrandoNo ratings yet
- Discussions On IE Irodov S Problems in General Physics Arihant Books ArihantBooks PDFDocument2 pagesDiscussions On IE Irodov S Problems in General Physics Arihant Books ArihantBooks PDFRajiv VermaNo ratings yet
- Description of MaterialsDocument4 pagesDescription of MaterialsArjun Kj100% (1)
- Mokveld-Product Sheet Angle ChokeDocument2 pagesMokveld-Product Sheet Angle Chokeyulianus_sr100% (1)
- Telephone: Based On Book - Design For People by Henry DreyfussDocument14 pagesTelephone: Based On Book - Design For People by Henry Dreyfussbhushan manjunathNo ratings yet
- ABS - Sales PitchDocument22 pagesABS - Sales PitchyasirsaitNo ratings yet
- Operation and Maintenance Manual-C140-18 PDFDocument271 pagesOperation and Maintenance Manual-C140-18 PDFYusroni Nainggolan0% (1)
- Grating For Catch BasinDocument5 pagesGrating For Catch Basinnoto.sugiartoNo ratings yet
- Ariel Corporation - Arielcorp - Com15Document1 pageAriel Corporation - Arielcorp - Com15Anwar Sadat100% (1)
- Simulacion Numérica de Cuchara PeltonDocument5 pagesSimulacion Numérica de Cuchara PeltonOscar Choque JaqquehuaNo ratings yet
- Hitachi Hiacs Multi3000Document10 pagesHitachi Hiacs Multi3000a_596No ratings yet
- 01) Machine Design I PDFDocument24 pages01) Machine Design I PDFDebasis soorNo ratings yet
- Company Profile - PretechDocument26 pagesCompany Profile - PretechanandivmNo ratings yet
- Pds 62-Sin Ds En-MeggerDocument2 pagesPds 62-Sin Ds En-MeggerAdhy PrastyoNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Peroxide Gas GeneratorsDocument17 pagesHydrogen Peroxide Gas GeneratorsCliff ThriveNo ratings yet
- Ugc Net: General Paper On Teaching & Research AptitudeDocument6 pagesUgc Net: General Paper On Teaching & Research AptitudeAkarshika pandeyNo ratings yet
- Despiece SUSP. DEL 930EDocument2 pagesDespiece SUSP. DEL 930EAndersson Campos VásquezNo ratings yet
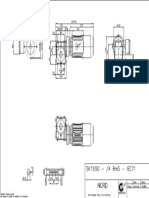
- SK1SI50 - /4 Bre5 - IEC71: Date Name Drawn SystemDocument1 pageSK1SI50 - /4 Bre5 - IEC71: Date Name Drawn SystemHugo AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Plantation Tree ProjectsDocument15 pagesPlantation Tree Projectsmahnoor cheemaNo ratings yet
- M/S Rajaram Constrution: Government of MadhyapradeshDocument7 pagesM/S Rajaram Constrution: Government of Madhyapradeshfevahe756No ratings yet
- WeldingDocument752 pagesWeldingAndres_Pastor1987100% (3)
- Business Systems Analyst Information Technology in NYC Resume Len KhatsernovDocument3 pagesBusiness Systems Analyst Information Technology in NYC Resume Len KhatsernovLenKhatsernovNo ratings yet
- NTU Learning Hub, SingaporeDocument53 pagesNTU Learning Hub, SingaporeDarcy stylesNo ratings yet
- Cap 8 Livro PDFDocument36 pagesCap 8 Livro PDFDiogo FonaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Question PaperDocument17 pagesChemical Reaction Question PapershivamNo ratings yet
- Visual Foxpro DOCUMENTDocument98 pagesVisual Foxpro DOCUMENTAndronache Andreea100% (2)
- BS 50128Document3 pagesBS 50128Jeffrey HoNo ratings yet
- Fortigate Logging ReportingDocument68 pagesFortigate Logging Reportingzulhelmi2010No ratings yet
- Lifting Lug Calculation - Concrete BucketDocument3 pagesLifting Lug Calculation - Concrete Bucketali akbarNo ratings yet