0% found this document useful (0 votes)
632 views13 pagesWorksheet 1
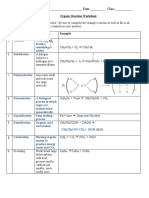
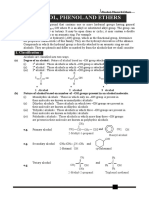
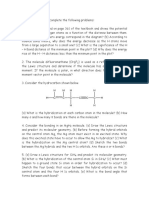
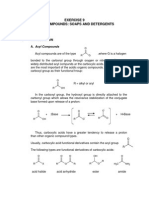
This document contains a 30 question worksheet about organic chemistry fundamentals and principles. The questions cover topics such as aromatic compounds, properties of organic compounds, polar and nonpolar molecules, isomerism (including geometric and optical isomers), IUPAC naming conventions, functional groups, and reaction types.
Uploaded by
Hamza NaeemCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
632 views13 pagesWorksheet 1
This document contains a 30 question worksheet about organic chemistry fundamentals and principles. The questions cover topics such as aromatic compounds, properties of organic compounds, polar and nonpolar molecules, isomerism (including geometric and optical isomers), IUPAC naming conventions, functional groups, and reaction types.
Uploaded by
Hamza NaeemCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd