Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Asthma Signs and Syptoms: Pathophysiology
Uploaded by
Lu BeibeiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Asthma Signs and Syptoms: Pathophysiology
Uploaded by
Lu BeibeiCopyright:
Available Formats
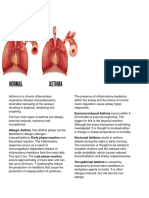
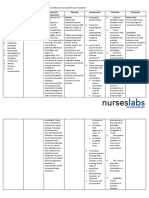
SIGNS AND SYPTOMS ASTHMA
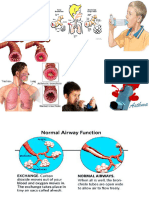
- cough, wheeze (sound of airflow through BACKGROUND INFORMATION
narrowed airways), sensation of chest tightness, - a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airway, leads
dyspnea (most common) to varied degree of obstruction in the airways, leads
- diaphoresis, tachycardia, widen pulse pressure to recurrent episodes of wheezing, breathlessness,
can occur w/ hypoxemia & central cyanosis ( late sensation of chest tightness, cough, more so in the
sign of poor oxygenation) PATHOPHYSIOLOGY morning & night
- hypoxemia is a secondary to a ventilation- - exposure to allergen leads to airway inflammation, Key characteristic of asthma: episodic & reversible
perfusion mismatch & readily responds to bronchoconstriction, causing mucosal edema & airway obstruction
supplemental oxygenation mucus production
- some ppl have exaggerated IgE response to certain
allergen, by attaching to IgE receptors on mast cell.
The IgE mast cell complexes remaing for ling time, COMPLICATIONS
thus a 2 exposure to allergen triggers mast cel to - status asthmaticus: severe & persistent asthma that does not respond to
nd
CAUSES degranulate conventional therapy
- enironmetnal exposures, triggering response ALLERGY is the STRONGEST predisposing factor for - respiratory failure, pneumonia, atelectasis, pneumothorax, acute cor
of the immune ssytem asthma pulmonale
EARLY-PHASE REPSONSE: charac. by bronchospasm, - airway obstruction during acute asthmatic episodes, often result in
hypoxemia, requiring O2 & monitoring pulse oximetry & ABG
this response is triggered when an allergen or
Fluid are administered, becoz ppl w/ asthma are frequently dehydrated from
irritant attaches to IgE receptors on mast cells found
diaphoresis & insensible fluid loss from hyperventilation
beneath the basement membrane of the bronchial
wall, mast cells are activated & releases granules,
phospholipids cellmembranes are disrupted. Both
process results in release of inflammatory mediators,
histamaines, bradykinin, leukotrienes,
prostaglandins, platelet activating factors, Diagnostic
chemotatctic factors, cytokines ( IL4, 5) -Acute episode: sputum & blood tests may disclose
- causing bronchial smooth muscle contriction, ↑ eosinopjilia (↑eosinophils)
vasodilation, permeability, epithelial damages - ABG & pulse oximetry reveal hypoxemia during
Clinical effects: bronchospasm, ↑ mucus acute attacks
secretion,edema formation, ↑ amount of tenacious - During an exacerbation, the FEV1 & FVC are
sputum, causing wheeze, cough, sensation of chest markedly ↓ but improve w/ bronchodilator
tightness, SOB administration( demonstrating reversibility)
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT
- immediate intervention may be necessary, PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
becoz continuing and progressive dyspnea -LATE-PHASE RESPONSE: peaks at 5-12 hours after exposure, last hours to days
leads to ↑anxiety, aggravating the situation Primary charac: inflammation, as opposed to bronchial smooth muscle contraction,
- short-acting beta 2-adrenergic agonists eosinophils, neutrophils inflammatory cells are involved, release mediators that
( albuterol (Ventolin) are medications of choice induce further inflammation & cause mast cells to degranulate, causing release of
of relief of acute symptoms & prevention of histamine & other mediators & initiating self-sustaining cycles
exercise- induced asthma - - reduced airway diameter, ↑airway resistance RT mucosal inflammation of the
(used to relax smooth muscle) airway, constriction of bronchial sooth muscle, excess production of mucus
hypertrophy of the bronchial smooth muscle cell, thickening of basement
membrane, hypertrophy of mucus glands, secretion of thick & tenacious
sputume, hyperinflation, air trapping of alveoli
COMPLICATIONS
- anticholinergics (ex/. Ipratropium bromide ASTHMA
(Atrovent) inhibit muscarinic cholinergic receptors
&↓intrinsic vagal tone of the airway
- may be used in pt who do not tolerate short acting
beta2 adrenergic agoanist
NURSING MANAGEMENT
- Corticosteroids are most potent & effective
- calm approach to provide care becoz pt & family are often
inflammatory medications currently available
frightened & anxious
- broadly effective in alleviating symptoms, &
-obtain Hx of allergic rxn before adminstration of medications
improving airway function
- identifies medication the pt is currently taking
Educate the adverse effect: cough & thrush
- Administers med as prescribed & monitors the pt’ response to those
medications. These meds may include an Ab if the pt has an
underlying respiratory infection
- administer fluids if the pt is dehydrated
- recognize & avoids asthma triggers
p. 2165 Drug therapies Table: 31.6
You might also like
- Status Asthmatic UsDocument1 pageStatus Asthmatic UskhadzxNo ratings yet
- Vih MT#2Document8 pagesVih MT#2cjNo ratings yet
- (PULMO) - Asthma PDFDocument5 pages(PULMO) - Asthma PDFKeith LajotNo ratings yet
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument19 pagesBronchial AsthmaAnushri ManeNo ratings yet
- NCM 112: Oxygen Exchange and Utilization: Bambam2017Document25 pagesNCM 112: Oxygen Exchange and Utilization: Bambam2017Alyssa Claire TumulakNo ratings yet
- Drugs For AsthmaDocument3 pagesDrugs For AsthmaTerepe CrimsonNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Document16 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Kimberly Abella CabreraNo ratings yet
- Asthma: Definition by GINA (Global Initiative For Asthma)Document10 pagesAsthma: Definition by GINA (Global Initiative For Asthma)Miszwanee DarwisyNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledTruptilata SahooNo ratings yet
- 50 DiseasesDocument44 pages50 DiseasesJewenson SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Concept Map AsthmaDocument3 pagesConcept Map AsthmaKaren HutchinsonNo ratings yet
- Allergy: Initial ExposureDocument4 pagesAllergy: Initial ExposureElle RosalesNo ratings yet
- k12, Pa, Pathology of Copd - rts1-k12Document46 pagesk12, Pa, Pathology of Copd - rts1-k12ashtridNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument9 pagesPneumoniaKenneth UbaldeNo ratings yet
- Lower Respiratory DisorderDocument27 pagesLower Respiratory DisorderMark OngNo ratings yet
- Asthma 1Document79 pagesAsthma 1DanishMandiNo ratings yet
- Asthma - English VersionDocument2 pagesAsthma - English VersionjoeNo ratings yet
- The System: RespiDocument219 pagesThe System: Respilalaine22dale100% (1)
- A Child Presenting With Breathing Difficulties (Asthma)Document54 pagesA Child Presenting With Breathing Difficulties (Asthma)Sindhu BabuNo ratings yet
- Respiratory AcidosisDocument5 pagesRespiratory Acidosisapi-376421583% (6)
- Copd Omc Class - BB PDFDocument29 pagesCopd Omc Class - BB PDFafaq alismailiNo ratings yet
- 5 - Drugs For AsthmaDocument75 pages5 - Drugs For Asthmanica velano100% (1)
- COPDDocument4 pagesCOPDitsmailbbkNo ratings yet
- PULMO OB TransDocument8 pagesPULMO OB TransMichelle Vera GabunNo ratings yet
- Childhood Asthma: DR - Rodman Tarigan, Spa.,MkesDocument35 pagesChildhood Asthma: DR - Rodman Tarigan, Spa.,MkesBambang IrwansyahNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory Failure Concept MapDocument1 pageAcute Respiratory Failure Concept Mapjenievysenerez100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studyboxed juiceNo ratings yet
- Care of Patients With Asthma: Peak Flow MonitoringDocument2 pagesCare of Patients With Asthma: Peak Flow MonitoringBelle MakinanoNo ratings yet
- Asthma: Exercise-Induced Asthma Occurs Within 5Document4 pagesAsthma: Exercise-Induced Asthma Occurs Within 5April PunzalanNo ratings yet
- 316 Revalida ReviewerDocument28 pages316 Revalida ReviewerSOPHIA PILLENANo ratings yet
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument45 pagesBronchial Asthmamuluken mulatieNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument6 pagesCase StudyJA BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities CnsDocument3 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities CnsNichole BenbenenNo ratings yet
- ARDS (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome) : EarlyDocument1 pageARDS (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome) : EarlyDora Elena HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument34 pagesBronchial AsthmaFabb NelsonNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument4 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCPkimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- Pcap - PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesPcap - PathophysiologyAyla Mar100% (1)
- Curriculum Vitae: Dr. Muh - Ilyas, SP - PD, KP, SP.P (K), FINASIMDocument51 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Dr. Muh - Ilyas, SP - PD, KP, SP.P (K), FINASIMMuhammad ZakkiNo ratings yet
- 2023 UsDocument10 pages2023 UswisgeorgekwokNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis ReactionsDocument25 pagesAnaphylaxis ReactionsLucila LugoNo ratings yet
- Asphyxia NeonatorumDocument28 pagesAsphyxia NeonatorumAsha jilu100% (1)
- Bronchial Asthma FixDocument23 pagesBronchial Asthma FixAprilia KambeyNo ratings yet
- Bronchial AsthmaDocument20 pagesBronchial AsthmaJuliet De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting Respiratory SystemDocument20 pagesDrugs Affecting Respiratory SystemClaire LibatNo ratings yet
- Anaphylactic Shock ReaderDocument3 pagesAnaphylactic Shock ReaderzipheleleNo ratings yet
- 1.11 Hypersensitivity (Dr. Dacula)Document5 pages1.11 Hypersensitivity (Dr. Dacula)John Benedict BondocNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 6 - S1 - PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF LUNG DISEASESDocument11 pagesLecture - 6 - S1 - PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF LUNG DISEASESgrigoras ilincaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Bronchitis and EmphesemaDocument2 pagesChronic Bronchitis and Emphesemanursing concept maps100% (2)
- Drug Study Lab, NCP - Bronchial AsthmaDocument6 pagesDrug Study Lab, NCP - Bronchial AsthmaRichelle Sandriel C. de CastroNo ratings yet
- Asthma 2Document14 pagesAsthma 2Salman KhanNo ratings yet
- Levofloxac in (Levox)Document2 pagesLevofloxac in (Levox)jbespirituNo ratings yet
- Anaphylactic, Clinical Manifestation &management PKB PontianDocument9 pagesAnaphylactic, Clinical Manifestation &management PKB Pontianandi darul aqsaNo ratings yet
- Penyakit Asma Dan MekanismenyaDocument15 pagesPenyakit Asma Dan MekanismenyaTutde SedanaNo ratings yet
- Askep Asthma BronchialDocument13 pagesAskep Asthma BronchialrinawahyuniNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaSystem DisorderDocument1 pagePneumoniaSystem DisorderAA DDNo ratings yet
- Asthma Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesAsthma Ineffective Airway ClearanceEdmr SlzarNo ratings yet
- Kez NCPDocument12 pagesKez NCPShizuka Marycris AmaneNo ratings yet
- Anaphylaxis: A Practical GuideFrom EverandAnaphylaxis: A Practical GuideAnne K. EllisNo ratings yet
- Medical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesFrom EverandMedical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Familial Dilated Cardiomyopathy of Young Portuguese Water DogsDocument9 pagesFamilial Dilated Cardiomyopathy of Young Portuguese Water DogsJessareth Atilano CapacioNo ratings yet
- Pre - Assessment: Directions: Complete Each Statement by Writing The Missing Word On Your HealthDocument3 pagesPre - Assessment: Directions: Complete Each Statement by Writing The Missing Word On Your HealthMary Rose QuimanjanNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Guidelines For AdultsDocument9 pagesAntibiotic Guidelines For AdultsVarshini Tamil SelvanNo ratings yet
- Blood and Tissue Flagellates BSCDocument27 pagesBlood and Tissue Flagellates BSCSisay FentaNo ratings yet
- Boli Cauzate de Factori BioticiDocument130 pagesBoli Cauzate de Factori BioticiLaviniaLaavyNo ratings yet
- The National Strategic Plan For Mental Health 2020-2025Document82 pagesThe National Strategic Plan For Mental Health 2020-2025immanuel immanNo ratings yet
- COVID Response by Metro HealthDocument12 pagesCOVID Response by Metro HealthDavid Ibanez100% (1)
- Study of Sociodemographic Profile, Maternal, Fetal Outcome in Preeclamptic and Eclamptic Women A Prospective StudyDocument6 pagesStudy of Sociodemographic Profile, Maternal, Fetal Outcome in Preeclamptic and Eclamptic Women A Prospective StudyHarvey MatbaganNo ratings yet
- Management Guide: For Laying Hens in Deep Litter, Perchery and Free-Range SystemsDocument34 pagesManagement Guide: For Laying Hens in Deep Litter, Perchery and Free-Range SystemsSri PurwantiNo ratings yet
- LoperamideDocument4 pagesLoperamideMazen MamdouhNo ratings yet
- High Yield Cardiology Internal Medicine Shelf PDFDocument44 pagesHigh Yield Cardiology Internal Medicine Shelf PDFsaja fuadNo ratings yet
- A 17 Year Old With Becker Muscular Dystrophy and UDocument5 pagesA 17 Year Old With Becker Muscular Dystrophy and UagamerocallejasNo ratings yet
- 2019 European League Against Rheumatism American College of Rheumatology Classification Criteria For Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument9 pages2019 European League Against Rheumatism American College of Rheumatology Classification Criteria For Systemic Lupus Erythematosusnacxit6No ratings yet
- NEUROGENIC BLADDER Nov 2021Document100 pagesNEUROGENIC BLADDER Nov 2021Ranjit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Notes 231022 202713-2Document13 pagesNotes 231022 202713-2Mary Franhz EspirituNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry Made EasyDocument14 pagesPsychiatry Made EasyD. W. S JayarathnaNo ratings yet
- Adenoidectomy and Tonsillectomy 2Document27 pagesAdenoidectomy and Tonsillectomy 2DR AAMNo ratings yet
- I-Clear Ang PiniliDocument21 pagesI-Clear Ang PiniliNurse HoomanNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus Disease (Covid-19) : Mandatory QuarantineDocument2 pagesCoronavirus Disease (Covid-19) : Mandatory QuarantineNinya PileNo ratings yet
- CT and MRI of Abdomen and PelvicDocument1,691 pagesCT and MRI of Abdomen and PelvicĐức Khang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- BIOEN 345: Failure Analysis of Physiology: Lecture 4 May 4, 2020: Vessel PathologiesDocument45 pagesBIOEN 345: Failure Analysis of Physiology: Lecture 4 May 4, 2020: Vessel PathologiesasdfghjklNo ratings yet
- A Read The Questions Carefully. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocument6 pagesA Read The Questions Carefully. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerJenielyn SadoNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesChronic Kidney Disease: A. Pathophysiology A. Schematic DiagramDaniel GeduquioNo ratings yet
- Common Cold 1Document17 pagesCommon Cold 1anandshaw000No ratings yet
- Disorders of Esophagus and StomachDocument29 pagesDisorders of Esophagus and StomachSamuel kuriaNo ratings yet
- Phthiraptera: Johari Jalinas Medical and Urban EntomologyDocument15 pagesPhthiraptera: Johari Jalinas Medical and Urban EntomologyjoharijalinasNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk For Activity IntoleranceDocument4 pagesNCP Risk For Activity IntoleranceBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Hematologic DisorderDocument8 pagesHematologic DisorderRayan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Prescription Analysis and InterpretationDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 Prescription Analysis and InterpretationShannen CostoNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Mini-OSCEDocument322 pagesDermatology Mini-OSCEMarrkNo ratings yet