Professional Documents
Culture Documents
'Biomass Conversion Technologies
Uploaded by
Irfan ShaikOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
'Biomass Conversion Technologies
Uploaded by
Irfan ShaikCopyright:
Available Formats
`Biomass conversion technologies
Biomass can be converted into different forms of energy by using various processes. Many
factors affect the choice of the process like quantity of biomass feedstock, desired energy form,
environmental standards, economic conditions, and project specific factors. Biomass can be
converted into three main products: power or heat generation, transportation fuels and chemica l
feedstock.
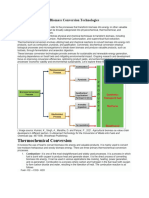
Biomass conversion technologies are shown in tree following chart.
Conversion
processes
Thermo-Chemical Bio-Chemical
Digestion
Combustion
Pyrolysis
Fermentation
Gasification
Liquefaction
Diagram. 1. Biomass conversion processes.
1. Thermo-chemical conversion
In thermo-chemical conversion, energy is produces by applying heat and chemical processes.
There are four thermo-chemical conversion processes, which are given below.
1.1 Combustion process
Combustion is an exothermic chemical reaction, in which biomass is burned in the presence of
air. In this process chemical energy which is stored in the biomass is converted in the
mechanical and electrical energies. This process is suitable for dry biomass containing moisture
less than 50%. Biomass is burned at the temperature of 800-1000 °C. This process is used for
domestic applications as well as commercially in biomass power plants in order to produce
electricity.
The typical efficiencies for stand-alone biomass combustion power plants (using wood and
forest residue as a fuel) range between 20-50 MWe, with related the electrical efficiencies in
the 25-30%. These power plants are suitable where fuels are available at low costs. In recent
years advanced combustion technology is being used. The application of fluid bed system and
advanced gas cleaning allows for production of electricity from biomass, on scale of 50-80
MWe, with 30-40% electrical efficiencies [14].
Pollution Control
Biomass Combustion Steam Boiler
Chamber
Pump
Steam Steam
Condenser
Valve
Steam
Turbin
e
AC Power Synchronous
Generator
Flow chart.2. Production of electricity by combustion of Biomass
1.2 Pyrolysis Process
It is the process of conversion of biomass to liquid (bio-oil), solid (charcoal) and gaseous (fuel
gases) products by heating in the absence of air at 500 °C. There are two types of pyrolysis :
Fast pyrolysis, conventional (Carbonization) pyrolysis and slow pyrolysis. Fast pyrolys is
process has high heating value and heat transfer rate and completes within seconds. Fast
pyrolysis yields 60% bio-oil, 20% bio-char and 20% biogas. Conventional pyrolysis process is
the process in which mostly carbon (35%) is leaved as residue. Slow pyrolysis takes more time
than fast pyrolysis, it also has low temperature and heating values. Flash pyrolysis is the type
of fast pyrolysis, in which 80% bio-oil is obtained at keeping temperature low. If flash pyrolys is
is used for converting biomass to bio-crude, it has up to 80% efficiency [15][16].
Biomass
Pyrolysis
Bio-oil Char Fuel gas
Storage Storage
Engine
Charcoal Turbine
Electricity Electricity
Flow chart. 3. Production of electricity by pyrolysis of Biomass
1.3 Gasification process
In biomass gasification, charcoal, wood chips, energy crops, forestry residues, agricultur a l
waste and other wastes are transformed into flammable gases at high temperature (800-1000°C.
In this process fuel (biomass) reacts with a gasifying medium such as oxygen enriched air, pure
oxygen, steam or a combination of both. The product gas composition and energy content
depends upon the gasifying media’s nature and amount of it. Low calorific Value (CV) gas
obtained by gasification about 4-6 MJ/N m³. The product gas can be used as a feedstock
(syngas) in the production of chemicals like methanol. One promising concept is the biomass
integrated gasification/ combined cycle (BIG/CC), in which gas turbines convert the gaseous
fuel to electricity with a high overall conversion efficiency. The integration of gasification and
combustion/ heat recovery ensures 40-50% conversion efficiency for a 30-60 MW. The syngas
can be converted into hydrogen gas, and it may have a future as fuel for transportation [15].
Biomass Pretreatment Gasification
Fischer-Tropsch
Syngas purification
Reactor
Product separation Gas
Diesel fuel
Lighter
hydrocarbons
Turbine
Diesel engine
Electricity
Electricity
Flow chart. 4. Production of electricity by Gasification of Biomass
1.4 Liquefaction process
It is the process in which biomass is converted into liquid phase at low temperatures (250-350
°C) and high pressures (100-200 bar), usually with a high hydrogen partial pressure and
catalysts to increase the rate of reaction. This process is used to get maximum liquid yields
with higher quality than from the pyrolysis process. The product have higher heating value and
lower oxygen content which makes the fuel chemically stable. The main purpose of the
liquefaction is to obtain high H/C ratio of the product oil [16].
Biomass Pretreatment Liquefaction Phase separation
Water
CO 2
Fermentation
Waste water Oil
Yeasts
Green electric power
Combustion
Bio-oil
Bio- Up-grading
fuel
Flow chart. 5. Liquefaction process of Biomass
2. Bio-Chemical conversion
Biochemical conversion makes use of the enzymes of bacteria and other living organisms to
break down biomass and convert it into fuels. This conversion process includes anaerobic
digestion and fermentation.
2.1. Anaerobic digestion process
This is a process in which organic material directly converted to a gas which is termed as
biogas. It is mixture of methane, carbon dioxide and other gases like hydrogen sulphide in
small quantities. Biomass is converted in anaerobic environment by bacteria, which produces
a gas having an energy of 20-40% of lower heating value of the feedstock. This process is
suitable for organic wastes having high moisture about 80-90%. This biogas can be directly
used in spark ignition gas engines and gas turbines and can be upgraded to higher quality
natural gas by removing carbon dioxide. The overall conversion efficiency of this process is
21%. Waste heat from engines and turbines can be recovered by using combined heat and
power system [17].
Biomass Digester Biogas
Transport use Biogas
Vehicle fuel
Compressor Storage
vessel
Electricity Turbine /
generator
Process heat for digester
Gas
boiler
2.2. Fermentation process
Fermentation is an anaerobic process that breaks down the glucose within organic materials. It
is a series of chemical reactions that convert sugars to ethanol. The basic fermentation process
involves the conversion of a plant’s glucose (or carbohydrate) into an alcohol or acid. Yeast or
bacteria are added to the biomass material, which feed on the sugars to produce ethanol and
carbon dioxide. The ethanol is distilled and dehydrated to obtain a higher concentration of
alcohol to achieve the required purity for the use as automotive fuel. The solid residue from
the fermentation process can be used as cattle-feed and in the case of sugar cane; the bagasse
can be used as a fuel for boilers or for subsequent gasification [18].
Biomass
Pre-treatment
Fermentation Solid residue
Animal
Feed
Distillation
Dehydration
Ethanol
You might also like
- BioMass Conversion TechnologiesDocument5 pagesBioMass Conversion Technologiessanthoshi durgaNo ratings yet
- Lignocellulose Biorefinery Product EngineeringDocument41 pagesLignocellulose Biorefinery Product EngineeringQuinta EsenciaNo ratings yet
- Artículo II ParcialDocument27 pagesArtículo II ParcialGabriel GómezNo ratings yet
- Biomass Pyrolysis and GasificationDocument5 pagesBiomass Pyrolysis and Gasificationaminabutt4524No ratings yet
- Biomass Energy Technologies: Conversion ProcessesDocument55 pagesBiomass Energy Technologies: Conversion Processessujit kcNo ratings yet
- Biofuel and Green BiotechnologyDocument4 pagesBiofuel and Green BiotechnologynavneetNo ratings yet
- Biomass Gasification LectureDocument32 pagesBiomass Gasification Lectureaz33mNo ratings yet
- Thermochemical ConversionDocument31 pagesThermochemical ConversionerkiruthirajNo ratings yet
- Thermo Chemical DegradationDocument32 pagesThermo Chemical DegradationN.R. RishiNo ratings yet
- Energy From Biogas: Presented By: Bharath S Chandan S Pavan Kalyan K SathishDocument34 pagesEnergy From Biogas: Presented By: Bharath S Chandan S Pavan Kalyan K SathishSatish KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Biomass AssignmentDocument8 pagesBiomass AssignmentAfsa NilaNo ratings yet
- 4 Biomass Energy Technologies: 4.1 Biomass and Its PotentialDocument4 pages4 Biomass Energy Technologies: 4.1 Biomass and Its PotentialErna SeptyaningrumNo ratings yet
- AEG Lecture - 3Document6 pagesAEG Lecture - 3maliniguru2003No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 2Document20 pagesChapter 2 2prashant_cool_4_uNo ratings yet
- Biomass Conversion Technologies for Biofuel and Green EnergyDocument7 pagesBiomass Conversion Technologies for Biofuel and Green EnergynavneetNo ratings yet
- MEng/PG Dip in Energy Technology OverviewDocument18 pagesMEng/PG Dip in Energy Technology OverviewNidas SameeraNo ratings yet
- PTBE Minggu 14 LainDocument42 pagesPTBE Minggu 14 LainDhia DhiNo ratings yet
- King Saud University Biomass Group IntroductionDocument50 pagesKing Saud University Biomass Group IntroductionWessam EssamNo ratings yet
- Biomass NotesDocument3 pagesBiomass NotesRafia Rayana btbcNo ratings yet
- Waste To EnergyDocument25 pagesWaste To EnergyDeepak Agarwal100% (1)
- Clase 1 MGarciaDocument69 pagesClase 1 MGarciaDiego Hernán Peláez ArangoNo ratings yet
- Harus Selesai Hari IniDocument11 pagesHarus Selesai Hari IniZefanya Maranatha MangunsongNo ratings yet
- Methanol ASPEN PlusDocument23 pagesMethanol ASPEN PlusAravind BudarajuNo ratings yet
- Biomassenergy Power PlantDocument24 pagesBiomassenergy Power PlantIrfan ShaikNo ratings yet
- Fast Pyrolysis of Lignocellulosic Biomass: Guide: DR Panneerselvam RanganathanDocument2 pagesFast Pyrolysis of Lignocellulosic Biomass: Guide: DR Panneerselvam RanganathanVikram ReddyNo ratings yet
- University of Engineering & Technology KSK New Campus: BiomassDocument11 pagesUniversity of Engineering & Technology KSK New Campus: BiomassAli Raza100% (1)
- A Presentation On BioenergyDocument30 pagesA Presentation On BioenergyDaniel DadzieNo ratings yet
- Problems and Solutions - Renewable EnergyDocument101 pagesProblems and Solutions - Renewable EnergyShashank Tripathi100% (3)
- Port Said University Mechanical Power Engineering Course on BiofuelsDocument28 pagesPort Said University Mechanical Power Engineering Course on BiofuelsMohamed HammamNo ratings yet
- Biomass Conversion Technologies OutlineDocument49 pagesBiomass Conversion Technologies OutlineVIDHARSHANA JNo ratings yet
- Biomass PyrolysisDocument36 pagesBiomass PyrolysisRajiyung Sun100% (2)
- Thermochemical conversion of biomass: combustion, CHP, and co-firingDocument47 pagesThermochemical conversion of biomass: combustion, CHP, and co-firingKhoi HoangNo ratings yet
- 4.1 - AWM Conversion and UtilizationDocument29 pages4.1 - AWM Conversion and UtilizationPEARL ANGELIE UMBANo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics-Ii Lab Oel: Submitted ToDocument13 pagesThermodynamics-Ii Lab Oel: Submitted Toharis khalilNo ratings yet
- Power Plants Lab: Department of Mechanical, Mechatronics and Manufacturing EngineeringDocument5 pagesPower Plants Lab: Department of Mechanical, Mechatronics and Manufacturing EngineeringFalcon KingdomNo ratings yet
- Estimating Cost of Fast Pyrolysis Bio-oil ProductionDocument10 pagesEstimating Cost of Fast Pyrolysis Bio-oil Productionrussell_mahmoodNo ratings yet
- Biomass to Bioenergy Conversion ProcessesDocument22 pagesBiomass to Bioenergy Conversion Processescharbel jabbourNo ratings yet
- Biomass in Boilers: An Efficient Renewable Energy SourceDocument11 pagesBiomass in Boilers: An Efficient Renewable Energy Sourceshah shakeel rssNo ratings yet
- Biogas IntroductionDocument75 pagesBiogas IntroductionRohan JindalNo ratings yet
- Rice Husk Gasification Technology Generates Renewable EnergyDocument4 pagesRice Husk Gasification Technology Generates Renewable EnergyRasoulNo ratings yet
- Community Biogas PlantDocument19 pagesCommunity Biogas PlantYashdeep SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Bioenergy Symposium TakeharaDocument29 pagesBioenergy Symposium TakeharaJurarut MinmuninNo ratings yet
- JMI ESc BiomassDocument33 pagesJMI ESc BiomassAJKNo ratings yet
- Biomass JCV 2017Document49 pagesBiomass JCV 2017Kevin Carmona Toral100% (1)
- Factsheet - Thermochemical Gasification of BiomassDocument8 pagesFactsheet - Thermochemical Gasification of BiomassFlorin LunguNo ratings yet
- Pyrolysis: Biochar (BC) ProductionDocument7 pagesPyrolysis: Biochar (BC) ProductionrohithNo ratings yet
- What Makes A Biorefinery Carbon Negative?: Webinar Presentation March 31, 2011Document31 pagesWhat Makes A Biorefinery Carbon Negative?: Webinar Presentation March 31, 2011Southern Alliance for Clean EnergyNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Biochar With An Emphasis On Its PropertiesDocument40 pagesAn Introduction To Biochar With An Emphasis On Its Propertiesjan_soNo ratings yet
- SessionII Uzun PDFDocument26 pagesSessionII Uzun PDFElizabeth VerdianaNo ratings yet
- Production of Hydrogen From Biomass-Derived LiquidsDocument10 pagesProduction of Hydrogen From Biomass-Derived LiquidsVoinea MarianNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: 1 Bio-Oil Plant DesignDocument55 pagesChapter One: 1 Bio-Oil Plant DesignJomed Barallas100% (1)
- 288 PyrolysisDocument3 pages288 Pyrolysisaminabutt4524No ratings yet
- Biogas Power PlantDocument130 pagesBiogas Power PlantRahul Tomar100% (3)
- Biomass Technology For Electricity Generation in CommunityDocument10 pagesBiomass Technology For Electricity Generation in CommunitySAKDA MAPRADITKULNo ratings yet
- A Review On Energy From Biomass: (Non Conventional Energy Sources)Document19 pagesA Review On Energy From Biomass: (Non Conventional Energy Sources)Juzer ShabbirNo ratings yet
- A Review On Energy From Biomass: (Non Conventional Energy Sources)Document19 pagesA Review On Energy From Biomass: (Non Conventional Energy Sources)Sathiya NathanNo ratings yet
- Process Integration Study of A Biorefinery Producing Ethylene From Lignocellulosic Feedstock For A Chemical ClusterDocument23 pagesProcess Integration Study of A Biorefinery Producing Ethylene From Lignocellulosic Feedstock For A Chemical ClusterMiguel PardoNo ratings yet
- Bio EnergyDocument67 pagesBio EnergyMuhammad Javed IqbalNo ratings yet
- Thermochemical Processing of Biomass: Conversion into Fuels, Chemicals and PowerFrom EverandThermochemical Processing of Biomass: Conversion into Fuels, Chemicals and PowerNo ratings yet
- Advances in Biofeedstocks and Biofuels, Volume 2: Production Technologies for BiofuelsFrom EverandAdvances in Biofeedstocks and Biofuels, Volume 2: Production Technologies for BiofuelsLalit Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- UnderstandingEthereumviaGraphAnalysis_toitDocument32 pagesUnderstandingEthereumviaGraphAnalysis_toitIrfan ShaikNo ratings yet
- Y-16 Detained List: SR No Id Number Student Name Dept DisciplineDocument12 pagesY-16 Detained List: SR No Id Number Student Name Dept DisciplineIrfan ShaikNo ratings yet
- MAT Sample Paper 5Document7 pagesMAT Sample Paper 5abhijitkashyep1990No ratings yet
- EducationUSA Session 100 in 100 - KL University Jan 28Document1 pageEducationUSA Session 100 in 100 - KL University Jan 28Irfan ShaikNo ratings yet
- GRE and IELTS ScheduleDocument7 pagesGRE and IELTS ScheduleIrfan ShaikNo ratings yet
- Iv Year Me TT BlendedDocument10 pagesIv Year Me TT BlendedIrfan ShaikNo ratings yet
- Certificate Course As Per SpecialisationDocument3 pagesCertificate Course As Per SpecialisationIrfan ShaikNo ratings yet
- MAT Sample Paper 2Document14 pagesMAT Sample Paper 2abhijitkashyep1990No ratings yet
- MAT 2007 entrance exam analysisDocument7 pagesMAT 2007 entrance exam analysisKshitij ZutshiNo ratings yet
- MAT Sample Paper 5Document7 pagesMAT Sample Paper 5abhijitkashyep1990No ratings yet
- Bitsler Double BTC ScriptDocument56 pagesBitsler Double BTC Scriptpro alshamesi02No ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper: Post Graduate Management Managerialability Test - Paper-IiDocument14 pagesSample Question Paper: Post Graduate Management Managerialability Test - Paper-IiIrfan Shaik100% (1)
- Sample Question Paper: Post Graduate Management Managerialability Test - Paper-IiDocument14 pagesSample Question Paper: Post Graduate Management Managerialability Test - Paper-IiIrfan Shaik100% (1)
- MAT Sample Paper 5Document7 pagesMAT Sample Paper 5abhijitkashyep1990No ratings yet
- KLEF IV/IV B.Tech Regular END SEMESTER Exams March 2021 Open Elective Courses Time TableDocument1 pageKLEF IV/IV B.Tech Regular END SEMESTER Exams March 2021 Open Elective Courses Time TableIrfan ShaikNo ratings yet
- Url Shortner in Blogger CodeDocument32 pagesUrl Shortner in Blogger CodeIrfan ShaikNo ratings yet
- 17ME4056-Advanced Strength of Materials Intelligence, 17BT40A1 - Ipr & Patent LawsDocument8 pages17ME4056-Advanced Strength of Materials Intelligence, 17BT40A1 - Ipr & Patent LawsIrfan ShaikNo ratings yet
- KLEF IV BTech Regular Semester Exam Time TableDocument1 pageKLEF IV BTech Regular Semester Exam Time TableIrfan ShaikNo ratings yet
- BiomassDocument36 pagesBiomassSaurabh MishraNo ratings yet
- Bitsler Double BTC ScriptDocument44 pagesBitsler Double BTC Scriptaryan malhotraNo ratings yet
- Iv Year Me TT BlendedDocument12 pagesIv Year Me TT BlendedIrfan ShaikNo ratings yet
- Univ - Reg.Number: 170070207 Name of Candidate: Tulluru Jaya Sai Krishna Month & Year of Exam: MAR-2021 Program: B.Tech Branch:ME Scheme:RegularDocument1 pageUniv - Reg.Number: 170070207 Name of Candidate: Tulluru Jaya Sai Krishna Month & Year of Exam: MAR-2021 Program: B.Tech Branch:ME Scheme:RegularIrfan ShaikNo ratings yet
- Reamning Life in Present Notches JournalDocument11 pagesReamning Life in Present Notches JournalIrfan ShaikNo ratings yet
- Abstract 1Document1 pageAbstract 1Irfan ShaikNo ratings yet
- Presentation: NAME-Md Imran ID No-170070184 Sec 4 NAME - MD Imran ID No-170070184 Sec 4Document15 pagesPresentation: NAME-Md Imran ID No-170070184 Sec 4 NAME - MD Imran ID No-170070184 Sec 4Irfan ShaikNo ratings yet
- Unified Package ComponentsDocument2 pagesUnified Package ComponentsIrfan ShaikNo ratings yet
- Readme!Document1 pageReadme!Irfan ShaikNo ratings yet
- Biomassenergy Power PlantDocument24 pagesBiomassenergy Power PlantIrfan ShaikNo ratings yet
- Ocean Thermal Energy ConversionDocument4 pagesOcean Thermal Energy ConversionIrfan ShaikNo ratings yet
- Gas Safety Regulation 103 - 2004Document28 pagesGas Safety Regulation 103 - 2004demaks011No ratings yet
- PGI in Brief 2016Document14 pagesPGI in Brief 2016ERICANo ratings yet
- AGT Exam With AnswersDocument4 pagesAGT Exam With Answersreda mesbahNo ratings yet
- Welding Variables Guide: Effects of Current, Voltage, Speed & MoreDocument34 pagesWelding Variables Guide: Effects of Current, Voltage, Speed & MoremilindNo ratings yet
- Flue Gas AnalysisDocument12 pagesFlue Gas AnalysisMadhavanIceNo ratings yet
- K Factor For Several GasesDocument3 pagesK Factor For Several Gasesaldaadrina100% (1)
- Floating LNG FLNG Technical Challenges and Future TrendsDocument12 pagesFloating LNG FLNG Technical Challenges and Future TrendsIsioma1100% (1)
- Pressure Swing AdsorptionDocument10 pagesPressure Swing Adsorptionradhika.rdtNo ratings yet
- (A1, 2019) Thermochemical Waste-Heat Recuperation by Steam Methane Reforming With Flue Gas AdditionDocument11 pages(A1, 2019) Thermochemical Waste-Heat Recuperation by Steam Methane Reforming With Flue Gas AdditionAsdrubolNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Synthesis GasDocument109 pagesReactions of Synthesis Gasapi-379986180% (5)
- Tech Bulletin Comparing Oxygen Source OptionsDocument3 pagesTech Bulletin Comparing Oxygen Source OptionsRaydoon SadeqNo ratings yet
- Flashback Arrestor E460 UkDocument2 pagesFlashback Arrestor E460 UkAgusNo ratings yet
- Gas Law WorksheetDocument2 pagesGas Law WorksheetMJ VergaraNo ratings yet
- Fuels Combustion PDFDocument11 pagesFuels Combustion PDFnaman shahNo ratings yet
- Boiler NG CalculationDocument9 pagesBoiler NG CalculationChirag DarjiNo ratings yet
- Peng-Robinson Equation: C C R RDocument4 pagesPeng-Robinson Equation: C C R RBagus ArfNo ratings yet
- ME385 Internal Combustion Engines Lecture NotesDocument53 pagesME385 Internal Combustion Engines Lecture Notes01094255175 01094255175No ratings yet
- "Green Gas" As SNG (Synthetic Natural Gas) A Renewable Fuel With Conventional QualityDocument17 pages"Green Gas" As SNG (Synthetic Natural Gas) A Renewable Fuel With Conventional QualityRobin ZwartNo ratings yet
- Mq2-Sensitivity Chars Withlog WithgraphDocument7 pagesMq2-Sensitivity Chars Withlog WithgraphAnil NaikNo ratings yet
- SCH 2200 Comparative Study of S and P Block Elements: 2.0 Hydrogen 2.1 OccurrenceDocument3 pagesSCH 2200 Comparative Study of S and P Block Elements: 2.0 Hydrogen 2.1 OccurrenceBrian NyagaNo ratings yet
- ME 21012 Fuels and Combustion CurriculumDocument2 pagesME 21012 Fuels and Combustion Curriculumsameer gaikwadNo ratings yet
- ReportFileDocument31 pagesReportFileRohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- 5.4 Science Form 1Document20 pages5.4 Science Form 1norsalimahNo ratings yet
- 2006 IPCC V3 3 Ch3 Chemical IndustryDocument110 pages2006 IPCC V3 3 Ch3 Chemical IndustryNour Saad EdweekNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficiency of Hydrogen from Natural Gas via SMRDocument21 pagesEnergy Efficiency of Hydrogen from Natural Gas via SMRgharibi.ali98486No ratings yet
- Ozone Depletion Assignment-FinalDocument17 pagesOzone Depletion Assignment-FinalAsad Zahid50% (2)
- 3830 Lecture Notes Part5 2008 Noble GasesDocument6 pages3830 Lecture Notes Part5 2008 Noble GasesYashitGarg100% (1)
- Weekly Weld Repair AnalysisDocument1 pageWeekly Weld Repair AnalysisknocknocknockNo ratings yet
- Tas Institute of OilDocument7 pagesTas Institute of OilSheena DovenantNo ratings yet
- Trainings For 2021Document14 pagesTrainings For 2021greatcenter registrarNo ratings yet