Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thermodynamics HW
Uploaded by
Eser GülOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thermodynamics HW
Uploaded by
Eser GülCopyright:
Available Formats
I.T. U.
AERONAUTICAL AND ASTRONAUTICAL FACULTY
UCK212E THERMODYNAMICS
Prof. Dr. Ali Kodal
Homework 1
Due Date: March 8, 2017
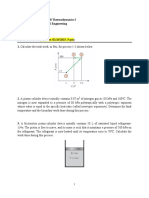
1. A gas is contained in a vertical, frictionless piston-cylinder device. The piston has a mass of
3.2 kg and a cross-sectional area of 35 cm2. A compressed spring above the piston exerts a
force of 150 N on the piston. If the atmospheric pressure is 95 kPa, determine the pressure
inside the cylinder.
2. A piston-cylinder device contains 0.85 kg of refrigerant-134a at -10°C. The piston that is free
to move has a mass of 12 kg and a diameter of 25 cm. The local atmospheric pressure is 88
kPa. Now, heat is transferred to refrigerant-134a until the temperature is 15°C. Determine
(a) the final pressure,
(b) the change in the volume of the cylinder, and
(c) the change in the enthalpy of the refrigerant-134a.
3. 100-kg of R-134a at 200 kPa are contained in a piston-cylinder device whose volume is
12.322 m3. The piston is now moved until the volume is one-half its original size. This is done
such that the pressure of the R-134a does not change. Determine the final temperature and
the change in the total internal energy of the R-134a.
4. A piston-cylinder device contains 0.15 kg of air initially at 2 MPa and 350°C. The air is first
expanded isothermally to 500 kPa, then compressed polytropically with a polytropic exponent
of 1.2 to the initial pressure, and finally compressed at the constant pressure to the initial state.
Determine the boundary work for each process and the net work of the cycle.
5. Refrigerant-134a at 600 kPa and 150°C is contained in a spring-loaded piston-cylinder device
with an initial volüme of 0.3 m3. The refrigerant is now cooled until its temperature is -30°C
and its volume is 0.1 m3. Determine the heat transferred to and the work produced by the
refrigerant during this process.
You might also like
- Thermo ProblemsDocument12 pagesThermo ProblemsElaineNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Prob Sheet Energy Analysis of Closed SystemsDocument3 pages1.1 Prob Sheet Energy Analysis of Closed SystemsAnonymous mXicTi8hBNo ratings yet
- Processes and Carnot CycleDocument4 pagesProcesses and Carnot CycleRagh AhmedNo ratings yet
- Sheet 3 Work CalculationDocument3 pagesSheet 3 Work CalculationHassan El SayedNo ratings yet
- Homework 4 Due Date: May 17, 2017Document1 pageHomework 4 Due Date: May 17, 2017Eser GülNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2 Dr. Gamal Nada Sheet 3 (Entropy), ContinuedDocument3 pagesThermodynamics 2 Dr. Gamal Nada Sheet 3 (Entropy), ContinuedEmptySilenceNo ratings yet
- KF 1Document19 pagesKF 1Diana Fitriani SurtikaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank-Thermal EngineeringDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank-Thermal EngineeringIrfan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument5 pagesUnit INallappan Rajj ANo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Work DoneDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 - Work DoneShubhenduGuptaNo ratings yet
- Cld20302 Thermodynamics Tutorial (Chapter 1.3)Document1 pageCld20302 Thermodynamics Tutorial (Chapter 1.3)Abdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (7th Edition)Document6 pagesChapter 3 (7th Edition)zaqbasalmau100% (1)
- EXAMDocument1 pageEXAMkelly evangelistaNo ratings yet
- In A Gas TurbineDocument7 pagesIn A Gas TurbineANBU RAJ ANo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument4 pagesThermowong zhi chengNo ratings yet
- Problem Set - Thermodynamics & ICEDocument2 pagesProblem Set - Thermodynamics & ICEBea Therese RadubanNo ratings yet
- Sheet #7Document4 pagesSheet #7Iam A gnoomNo ratings yet
- Our Official Android App - REJINPAUL NETWORK FromDocument2 pagesOur Official Android App - REJINPAUL NETWORK FromPradeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 First Law 2016Document8 pagesAssignment 1 First Law 2016PabitraBadhuk0% (1)
- Engineering Thermodynamics ProblemsDocument3 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics Problemsdhruv0010% (1)
- Etd Ti, T2.T3Document5 pagesEtd Ti, T2.T3Kumaran RNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument3 pagesQuestionsmonalNo ratings yet
- Assignment2 Btech Sem3 TD Mu207Document3 pagesAssignment2 Btech Sem3 TD Mu207nageshNo ratings yet
- ME214 BTD Tutorial QuestionsDocument2 pagesME214 BTD Tutorial QuestionsKONDALRAONo ratings yet
- Sample FinalDocument1 pageSample Finalroy 123No ratings yet
- RAC Numerical Question Bank Unit 1 NewDocument8 pagesRAC Numerical Question Bank Unit 1 NewHashmanNo ratings yet
- Instruction: Attempt All Questions. (ASSIGNMENT:-section A: Odd Numbers and Section B: Even Numbers) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9Document2 pagesInstruction: Attempt All Questions. (ASSIGNMENT:-section A: Odd Numbers and Section B: Even Numbers) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9Abi DemNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Questions 1111Document6 pagesTutorial Questions 1111Fahmy Muhd100% (1)
- Supplementary Problems For Practice: 1. A Mass of 0.15 KG of Air Is Initially Exists at 2 Mpa and 350Document1 pageSupplementary Problems For Practice: 1. A Mass of 0.15 KG of Air Is Initially Exists at 2 Mpa and 350physics a2No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Tut-3 - Problems - AnswersDocument5 pagesChapter 4 - Tut-3 - Problems - AnswersArchishman SinghNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Questions and AnswersDocument5 pagesThermodynamics Questions and AnswersMD SHOEBUDDIN0% (1)
- Additional Practice Problem (Mid-Sem)Document3 pagesAdditional Practice Problem (Mid-Sem)djdivyesh102No ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Examples (Quest) Part 4.1Document1 pageIdeal Gas Examples (Quest) Part 4.1Chloe OlazoNo ratings yet
- Homework 4 - MEEN 2300 - Spring 2015Document3 pagesHomework 4 - MEEN 2300 - Spring 2015MichaelNo ratings yet
- Thermo Finals - Questionnaire Quizzes and Sample Probs With AnswersDocument21 pagesThermo Finals - Questionnaire Quizzes and Sample Probs With Answersmarc rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Mid - Tearm - Indusf - PDF Filename - UTF-8''mid Tearm Indusf PDFDocument8 pagesMid - Tearm - Indusf - PDF Filename - UTF-8''mid Tearm Indusf PDFAhmed Rabie Abd ElazeemNo ratings yet
- Mid - Tearm - Indusf - PDF Filename - UTF-8''mid Tearm IndusfDocument8 pagesMid - Tearm - Indusf - PDF Filename - UTF-8''mid Tearm IndusfAhmed Rabie Abd ElazeemNo ratings yet
- Termodinamik 1 - Uygulama 2Document38 pagesTermodinamik 1 - Uygulama 2david tennantNo ratings yet
- Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument21 pagesEngineering Thermodynamicsrkrajesh86No ratings yet
- MI-106 Tut ThermoDocument37 pagesMI-106 Tut ThermoDhananjayLekshmiNarayan100% (7)
- Tutorial Sheet 6Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 6Syed YousufuddinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document2 pagesTutorial 4tehpohkee50% (2)
- Thermodynamic Question BankDocument10 pagesThermodynamic Question BankRaj PratyushNo ratings yet
- Me8391 Important QuestionsDocument4 pagesMe8391 Important QuestionsMohsin EngrNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Thermal Engineering UPDATEDDocument6 pagesQuestion Bank Thermal Engineering UPDATEDIrfan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 ThermodyanamicsDocument1 pageTutorial 1 ThermodyanamicsKaustubh Mallik100% (1)
- Thermodynamics Exams PapersDocument23 pagesThermodynamics Exams PapersAbdul HafizNo ratings yet
- ChE 122 LE1 Samplex 2Document3 pagesChE 122 LE1 Samplex 2googley71No ratings yet
- Assignment Properties of GasesDocument1 pageAssignment Properties of Gasesvidhisuthar1162No ratings yet
- CHE 220-FALL23-Homework VDocument2 pagesCHE 220-FALL23-Homework Vsemikonino35No ratings yet
- Assg1 Jan 2023Document2 pagesAssg1 Jan 2023Nimesh BhagatNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet No2Document7 pagesTutorial Sheet No2عبدالله عمرNo ratings yet
- T 2Document1 pageT 2jfl2096No ratings yet
- 1st Law ProbDocument2 pages1st Law ProbShashank SinghNo ratings yet
- XXDocument1 pageXXGetachew TikueNo ratings yet
- CL255 PS2Document6 pagesCL255 PS2anjali sadaphuleNo ratings yet
- XXDocument1 pageXXGetachew TikueNo ratings yet
- HES2330 Thermo 1 Tutorial 2 BBDocument9 pagesHES2330 Thermo 1 Tutorial 2 BBMahesan SinthujanNo ratings yet