Professional Documents
Culture Documents
T 2
Uploaded by
jfl2096Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
T 2
Uploaded by
jfl2096Copyright:
Available Formats
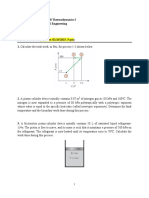
SME 1413 Tutorial 2
1. A mass of 5 kg of saturated water vapor at 300 kPa is heated at constant pressure until the temperature reaches 200 oC.
Calculate the work done by the steam during this process. (165.9 kJ).
2. A frictionless piston-cylinder device initially contains 200 L of saturated liquid refrigerant-134a. The piston is free to
move, and its mass is such that it maintains a pressure of 900 Pa on the refrigerant. The refrigerant is now heated until its
temperature rises to 70 oC. Calculate the work done during this process. (5571 kJ).
3. A mass of 2.4 kg of air at 150 kPa and 12 oC is contained in a gas-tight, frictionless piston-cylinder device. The air is now
compressed to a final pressure of 600 kPa. During the process, heat is transferred from the air such that the temperature inside
the cylinder remains constant. Calculate the work input during this process. (272 kJ).
4. During an expansion process, the pressure of a gas changes from 100 to 700 kPa according to the relation P = aV + b,
where a = 1220 kPa/m3 and b is a constant. If the initial volume of the gas is 0.2 m3, calculate the work done during this
process. (197 kJ).
5. A frictionless piston-cylinder device contains 2 kg of nitrogen at 100 kPa and 300 K. Nitrogen is now compressed slowly
according to the relation PV 1.4 constant until it reaches a final temperature of 360 K. Calculate the work input during
this process. (89 kJ).
6. Carbon dioxide contained in a piston-cylinder device is compressed from 0.3 to 0.1 m 3. During the process, the pressure
and volume are related by P aV 2 where a = 8 kPa.m6. Calculate the work done on the carbon dioxide during this
process. (53.3 kJ).
7. A piston-cylinder device initially contains 0.25 kg of nitrogen gas at 130 kPa and 120 oC. The nitrogen is now expanded
isothermally to a pressure of 100 kPa. Determine the boundary work done during this process. ( 7.65 kJ).
8. A piston-cylinder device initially contains 0.8 m3 of saturated water vapor at 250 kPa. At this state, the piston is resting on
a set of stops, and the mass of the piston is such that a pressure of 300 kPa is required to move it. Heat is now slowly
transferred to the steam until the volume doubles. Show the process on a P-v diagram with respect to saturation lines and
determine (a) the final temperature, (b) the work done during this process, and (c) the total heat transfer. (662 oC, 240 kJ,
1213 kJ).
9. A rigid tank contains 10 kg of air at 350 kPa and 27oC. The air is now heated until its pressure doubles. Determine (a) the
volume of the tank and (b) the amount of heat transfer. (2.46 m3, 2207 kJ).
10. A mass of 15 kg of air in a piston-cylinder device is heated from 25 to 77 oC by passing a current through a resistance
heater inside the cylinder. The pressure inside the cylinder is held constant at 300 kPa during the process, and a heat loss of
60 kJ occurs. Determine the electric energy supplied, in kWh. (0.235 kWh).
11. A piston-cylinder device, whose piston is resting on a set of stops, initially contains 3 kg of air at 200 kPa and 27 oC. The
mass of the piston is such that a pressure of 400 kPa is required to move it. Heat is now transferred to the air until its volume
doubles. Determine the work done by the air and the total heat transferred to the air during this process. Also show the
process on a P-V diagram. (516 kJ, 2674 kJ).
12. A frictionless piston-cylinder device initially contains air at 200 kPa and 0.2 m 3. At this state, a linear spring ( F x ) is
touching the piston but exerts no force on it. The air is now heated to a final state of 0.5 m 3 and 800 kPa. Determine (a) the
total work done by the air and (b) the work done against the spring. Also, show the process on a P-V diagram. (150 kJ, 90 kJ).
13. A spherical balloon contains 5 kg of air at 200 kPa and 450 K. The balloon material is such that the pressure inside is
always proportional to the square of the diameter. Determine the work done when the volume of the balloon doubles as a
result of heat transfer. (843 kJ).
14. A piston-cylinder device contains helium gas initially at 150 kPa, 20 oC, and 0.5 m3. The helium is now compressed in a
polytropic process ( PVn = constant) to 400 kPa and 140oC. Determine the heat loss or gain during this process. (11.2 kJ
loss).
15. Two rigid tanks are connected by a valve. Tank A contains 0.2 m 3 of water at 400 kPa and 80 percent quality. Tank B
contains 0.5 m3 of water at 200 kPa and 250oC. The valve is now opened, and the two tanks eventually come to the same
state. Determine the pressure and the amount of heat transfer when the system reaches thermal equilibrium with the
surroundings at 25oC. (3.17 kPa, 2170 kJ).
16. An insulated rigid tank initially contains 1.4 kg saturated liquid water and water vapor at 200 oC. At this state, 25 percent
of the volume is occupied by liquid water and the rest by vapor. Now an electric resistor place in the tank is turned on, and
the tank is observed to contain saturated water vapor after 20 min. Determine (a) the volume of the tank, (b) the final
temperature, and (c) the electric power rating of the resistor. (0.00648 m 3, 371oC, 1.58 kW).
You might also like
- Closed System ExercisesDocument2 pagesClosed System ExercisesMareta DanarNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems On First Law For Closed SystemDocument3 pagesPractice Problems On First Law For Closed SystemNetra PujarNo ratings yet
- ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMSDocument3 pagesENERGY ANALYSIS OF CLOSED SYSTEMSAnonymous mXicTi8hBNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument4 pagesThermowong zhi chengNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual ThermodynamicsDocument10 pagesSolution Manual ThermodynamicsNur HanifahNo ratings yet
- ME331 Thermodynamics: PS #3 Solutions: Numeric 1Document14 pagesME331 Thermodynamics: PS #3 Solutions: Numeric 1Crimson MorangeNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Principles Tutorial First Law Closed SystemsDocument2 pagesThermodynamics Principles Tutorial First Law Closed Systemstehpohkee50% (2)
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2Nayli SorfinaNo ratings yet
- QB Unit 1Document6 pagesQB Unit 1Gaurav GadhesariaNo ratings yet
- Taller 2 2023-1Document8 pagesTaller 2 2023-1anderson ortizNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics QuestionsDocument4 pagesThermodynamics Questionsprateek vyasNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 2 Dr. Gamal Nada Sheet 3 (Entropy), ContinuedDocument3 pagesThermodynamics 2 Dr. Gamal Nada Sheet 3 (Entropy), ContinuedEmptySilenceNo ratings yet
- 11me201 Thermodynamics QuestionsDocument12 pages11me201 Thermodynamics QuestionsramsastryNo ratings yet
- Engineering Thermodynamics Worksheet AnalysisDocument13 pagesEngineering Thermodynamics Worksheet Analysisroba angasuNo ratings yet
- CHE 220-FALL23-Homework VDocument2 pagesCHE 220-FALL23-Homework Vsemikonino35No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Review ProblemsDocument3 pagesThermodynamics Review ProblemssayanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 6Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 6Syed YousufuddinNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Homework Solutions Dr Alizadeh"TITLE"Dr Alizadeh Thermodynamic Calculations Homework ProblemsDocument5 pagesThermodynamic Homework Solutions Dr Alizadeh"TITLE"Dr Alizadeh Thermodynamic Calculations Homework ProblemsTerry Clarice DecatoriaNo ratings yet
- TH-005-Examples of Chapter Five PDFDocument7 pagesTH-005-Examples of Chapter Five PDFLinda LCNo ratings yet
- Sheet 3 - ME 211TDocument4 pagesSheet 3 - ME 211Tsophia haniNo ratings yet
- Sheet #7Document4 pagesSheet #7Iam A gnoomNo ratings yet
- 11me201 Thermodynamics QuestionsDocument12 pages11me201 Thermodynamics QuestionsJustin Cox0% (2)
- Problem Sheet-03 ME201 1st LawDocument2 pagesProblem Sheet-03 ME201 1st LawPratyusha SatpathyNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 5 ExamplesDocument26 pagesLecture - 5 ExamplesDimas Angga100% (7)
- ETD - Question BankDocument6 pagesETD - Question BankGopinath VNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Question Set ADocument4 pagesThermodynamics Question Set AVivek NegiNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems On EntropyDocument1 pagePractice Problems On EntropyNetra PujarNo ratings yet
- Assignment-EntropyDocument2 pagesAssignment-Entropyme22b009No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 (ME206)Document2 pagesTutorial 1 (ME206)deshrajNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Questions and AnswersDocument5 pagesThermodynamics Questions and AnswersMD SHOEBUDDIN0% (1)
- Exercise 4 - Analysis of Closed SystemDocument3 pagesExercise 4 - Analysis of Closed SystemPuviin VarmanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 3Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 3Syed YousufuddinNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Tutorial ProblemsDocument20 pagesThermodynamics Tutorial ProblemsRishabh Sharma100% (1)
- Assignment 1 First Law 2016Document8 pagesAssignment 1 First Law 2016PabitraBadhuk0% (1)
- Problemas TermoDocument3 pagesProblemas TermocleonardoeNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics An Engineering Approach: Thermo 1 (MEP 261)Document22 pagesThermodynamics An Engineering Approach: Thermo 1 (MEP 261)cwidiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document25 pagesChapter 7Nabeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Group Quiz ME 63 THYZ - WFWX EntropyDocument2 pagesGroup Quiz ME 63 THYZ - WFWX Entropyluvieduffy_13No ratings yet
- ME-1100 Thermodynamics tutorial problemsDocument2 pagesME-1100 Thermodynamics tutorial problemsKethavath Sunil ch21b047No ratings yet
- Assignment2 Btech Sem3 TD Mu207Document3 pagesAssignment2 Btech Sem3 TD Mu207nageshNo ratings yet
- Moving Boundary Work. 2015Document2 pagesMoving Boundary Work. 2015Brayan Steven Cubillos MorenoNo ratings yet
- T 5Document2 pagesT 5jfl2096No ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument3 pagesQuestionsmonalNo ratings yet
- Ned University of Engineering & Technology Department of Food Engineering Thermodynamics - Assignment SPRING SEMESTER 2020-2021Document4 pagesNed University of Engineering & Technology Department of Food Engineering Thermodynamics - Assignment SPRING SEMESTER 2020-2021Sahar Batool QaziNo ratings yet
- Tutorial MED205Document4 pagesTutorial MED205Anonymous V4jDKjUR6No ratings yet
- ME 63 Prob Set 2Document2 pagesME 63 Prob Set 2RamonVannCleffRaroNo ratings yet
- Sheet 4 First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument1 pageSheet 4 First Law of Thermodynamicsahmed kaedNo ratings yet
- More Thermo Problems..Document3 pagesMore Thermo Problems..bmz00000No ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Department Unit 1 NotesDocument5 pagesMechanical Engineering Department Unit 1 NotesNallappan Rajj ANo ratings yet
- Assignment # 4 (Chapter 5) Due 3:00 PM of February 07, 2008 1Document2 pagesAssignment # 4 (Chapter 5) Due 3:00 PM of February 07, 2008 1Adam SchellNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics I Homework ProblemsDocument3 pagesThermodynamics I Homework ProblemsMichaelNo ratings yet
- ChE 122 LE1 Samplex 2Document3 pagesChE 122 LE1 Samplex 2googley71No ratings yet
- Guía de Ejercicios ESS TermodinámicaDocument17 pagesGuía de Ejercicios ESS TermodinámicaLuis Ignacio Aguilera100% (1)
- MA2003 Thermo-Fluids Tutorial ProblemsDocument6 pagesMA2003 Thermo-Fluids Tutorial ProblemsLadnilrebNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Questions 1111Document6 pagesTutorial Questions 1111Fahmy Muhd100% (1)
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1atif irshadNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Work Calculations Mechanical EngineeringDocument3 pagesThermodynamics Work Calculations Mechanical EngineeringHassan El SayedNo ratings yet
- In A Gas TurbineDocument7 pagesIn A Gas TurbineANBU RAJ ANo ratings yet
- ME331 Thermodynamics: PS#5 SolutionsDocument12 pagesME331 Thermodynamics: PS#5 SolutionsCrimson MorangeNo ratings yet
- BOM Listing for PartsDocument1 pageBOM Listing for Partsjfl2096No ratings yet
- Piping PipeDocument18 pagesPiping Pipejfl2096No ratings yet
- UTMDigital Part Time Student Services 202020211Document4 pagesUTMDigital Part Time Student Services 202020211jfl2096No ratings yet
- Stiff NerDocument6 pagesStiff NerNiraj ShindeNo ratings yet
- Valve Material and Size ChartDocument444 pagesValve Material and Size Chartjfl2096No ratings yet
- Side Casing 2-1 of 2Document1 pageSide Casing 2-1 of 2jfl2096No ratings yet
- Ga-Sht 2 PDFDocument1 pageGa-Sht 2 PDFjfl2096No ratings yet
- Side Casing 1-2 of 2Document1 pageSide Casing 1-2 of 2jfl2096No ratings yet
- I So Creation LogDocument3 pagesI So Creation Logjfl2096No ratings yet
- Top Casing 3-1 of 1Document1 pageTop Casing 3-1 of 1jfl2096No ratings yet
- Front Casing - 2 of 2Document1 pageFront Casing - 2 of 2jfl2096No ratings yet
- Top Casing 2-2 of 2 PDFDocument1 pageTop Casing 2-2 of 2 PDFjfl2096No ratings yet
- Side Casing 1-1 of 2Document1 pageSide Casing 1-1 of 2jfl2096No ratings yet
- Top Casing 1-1 of 1Document1 pageTop Casing 1-1 of 1jfl2096No ratings yet
- Top Casing 2-2 of 2Document1 pageTop Casing 2-2 of 2jfl2096No ratings yet
- AVEVA Oracle Components Installation GuideDocument216 pagesAVEVA Oracle Components Installation Guidejfl2096No ratings yet
- Zavaruvanje BrosuraDocument28 pagesZavaruvanje BrosuraBlagoja Anna SotirovskiNo ratings yet
- Ga-Sht 2Document1 pageGa-Sht 2jfl2096No ratings yet
- AVEVA NET Dashboard User Guide 5.0.2Document127 pagesAVEVA NET Dashboard User Guide 5.0.2jfl2096No ratings yet
- CIDECT Design Guide 9Document213 pagesCIDECT Design Guide 9paris06250% (2)
- AVEVA NET Fundamentals GuideDocument152 pagesAVEVA NET Fundamentals Guidejfl2096No ratings yet
- Structural Steel Welding - Semih Genculu, P.EDocument18 pagesStructural Steel Welding - Semih Genculu, P.ErobersasmitaNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For SMAWDocument5 pagesGuidelines For SMAWjfl2096No ratings yet
- AISC Design Guide 02 Errata Steel and Composite Beams With Web Openings PDFDocument15 pagesAISC Design Guide 02 Errata Steel and Composite Beams With Web Openings PDFFernando Gutiérrez UrzúaNo ratings yet
- JOB-1904 - Panel Steel Structure Supports RevB 05042019-Layout4Document1 pageJOB-1904 - Panel Steel Structure Supports RevB 05042019-Layout4jfl2096No ratings yet
- AWS - Welding SymbolsDocument1 pageAWS - Welding SymbolsAli Saifullizan IsmailNo ratings yet
- Santos GLNG Project-Design & Construction Drawings PDFDocument209 pagesSantos GLNG Project-Design & Construction Drawings PDFjfl2096No ratings yet
- 30-Year Mortgage Loan SummaryDocument20 pages30-Year Mortgage Loan Summaryjfl2096No ratings yet
- DWG Ld21 2 WHPB T 4011 Ma 002 Rev A (Commented)Document3 pagesDWG Ld21 2 WHPB T 4011 Ma 002 Rev A (Commented)jfl2096No ratings yet
- Panel Steel Structure Supports RevB 05042019-Layout5Document1 pagePanel Steel Structure Supports RevB 05042019-Layout5jfl2096No ratings yet