Professional Documents
Culture Documents
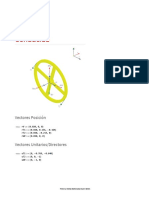
Polea Conducida: Vectores Posición
Uploaded by
Sebastian GomezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Polea Conducida: Vectores Posición
Uploaded by
Sebastian GomezCopyright:
Available Formats
Polea
Conducida
Vectores Posición
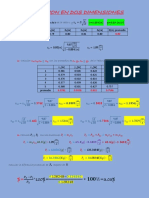
In[55]:= rV := {0.020, 0, 0}
rT1 := {0.020, 0.136, - 0.164}
rT2 := {0.020, - 0.213, 0}
rWV := {0.020, 0, 0}
Vectores Unitarios/Directores
In[59]:= uT1 := {0, - 0.769, - 0.640}
uT2 := {0, 0, - 1}
uWV := {0, - 1, 0}
Printed by Wolfram Mathematica Student Edition
2 Polea Conducida.nb
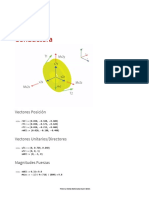
Magnitudes Fuerzas
In[62]:= nWV := 5.58 * 9.8
nT1 := 160.60585449697217`
nT2 := 51.753722896952596`
Vectores Fuerza/Momento
In[65]:= T1 := nT1 * uT1
T2 := nT2 * uT2
V := {Vx, Vy, Vz}
MV := {MVx, MVy, MVz}
WV := uWV * nWV
Sumatoría de Fuerzas/Momentos
In[70]:= SF := T1 + T2 + V + WV
SM := Cross[rWV, WV] + Cross[rT1, T1] + Cross[rT2, T2] + Cross[rV, V] + MV
Solucion
In[72]:= Solucion := Solve[SF ⩵ 0 && SM ⩵ 0, {Vx, Vy, Vz, MVx, MVy, MVz}]
Solucion[[1]][[1]]
Solucion[[1]][[2]]
Solucion[[1]][[3]]
Solucion[[1]][[4]]
Solucion[[1]][[5]]
Solucion[[1]][[6]]
Out[73]= Vx → 0.
Out[74]= Vy → 178.19
Out[75]= Vz → 154.541
Out[76]= MVx → 23.2106
Out[77]= MVy → - 4.44089 × 10-16
Out[78]= MVz → 0.
Printed by Wolfram Mathematica Student Edition
You might also like
- Vertical CurvesDocument25 pagesVertical CurvesMuhammad Iftikhar Ahmad100% (3)
- Thick Cylinder Lab ReportDocument12 pagesThick Cylinder Lab ReportTshepo Moloto100% (2)
- Digital Electronics For Engineering and Diploma CoursesFrom EverandDigital Electronics For Engineering and Diploma CoursesNo ratings yet
- Polea ConducidaDocument2 pagesPolea ConducidaSebastian GomezNo ratings yet
- Polea ConducidaDocument2 pagesPolea ConducidaSebastian GomezNo ratings yet
- Polea ConductoraDocument2 pagesPolea ConductoraSebastian GomezNo ratings yet
- Polea Conductora: Vectores PosiciónDocument2 pagesPolea Conductora: Vectores PosiciónSebastian GomezNo ratings yet
- Engranaje Pequeño: Vectores PosiciónDocument2 pagesEngranaje Pequeño: Vectores PosiciónSebastian GomezNo ratings yet
- Ecuacion Sistema GeneralDocument2 pagesEcuacion Sistema GeneralSebastian GomezNo ratings yet
- Ecuacion Sistema GeneralDocument2 pagesEcuacion Sistema GeneralSebastian GomezNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1Akash ShahNo ratings yet
- Assignment1 SolvedDocument4 pagesAssignment1 SolvedAkash ShahNo ratings yet
- Gaussian Mixture Model MLDocument5 pagesGaussian Mixture Model MLaswinhacker28No ratings yet
- Sistema General Sin Eje Ni TamborDocument3 pagesSistema General Sin Eje Ni TamborSebastian GomezNo ratings yet
- Timbunan Dan Konstruksi Penahan TanahDocument4 pagesTimbunan Dan Konstruksi Penahan TanahRAFIF AnandwikaNo ratings yet
- Advance Linear Control System Assignment No1: Completed By:shubham Agrawal.kDocument31 pagesAdvance Linear Control System Assignment No1: Completed By:shubham Agrawal.kShubham AgrawalNo ratings yet
- FINALDocument12 pagesFINALA Veces MirNo ratings yet
- Analisis de Sismico (Portico Plano) Ejemplo 1Document12 pagesAnalisis de Sismico (Portico Plano) Ejemplo 1Marco Antonio Marceliano SifuentesNo ratings yet
- U18ec038 Vlsi Lab 3Document8 pagesU18ec038 Vlsi Lab 3Timir PatelNo ratings yet
- Margarita Agudelo Rico: Taller # 1 Equilibrio de Partículas en El EspacioDocument3 pagesMargarita Agudelo Rico: Taller # 1 Equilibrio de Partículas en El EspacioMargarita Agudelo RicoNo ratings yet
- Velocidades y Aceleraciones MathematicaDocument5 pagesVelocidades y Aceleraciones Mathematicalameme990No ratings yet
- MD INC AZ TVD VS N/S E/W: EjercicioDocument9 pagesMD INC AZ TVD VS N/S E/W: EjerciciorodrigoNo ratings yet
- Σvx = -47.71281292 Σvy = 50.64101615 Sum Of Vector Y/Sum Of Vector X =Document3 pagesΣvx = -47.71281292 Σvy = 50.64101615 Sum Of Vector Y/Sum Of Vector X =MARIE GO ROUNDNo ratings yet
- ASIGNACIÓN VII ENVE 4460 Grupo 1 CORREGIDADocument11 pagesASIGNACIÓN VII ENVE 4460 Grupo 1 CORREGIDAtatistay6No ratings yet
- 20bce2251 VL2021220503859 Ast02Document10 pages20bce2251 VL2021220503859 Ast02TANMAY MEHROTRANo ratings yet
- Linear KinematicsDocument8 pagesLinear KinematicsJackson WangNo ratings yet
- Indorme Nº 6Document12 pagesIndorme Nº 6Daniel Escalera GarciaNo ratings yet
- 上机作业第六章Document7 pages上机作业第六章535277746No ratings yet
- Colision en Dos Dimensiones: 1x 1y 2x 2y 1 1 2 2Document2 pagesColision en Dos Dimensiones: 1x 1y 2x 2y 1 1 2 2luis marcaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Basic Sequences and Signal OperationDocument29 pagesLesson 3 Basic Sequences and Signal Operationpaulene panganNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 PDFDocument3 pagesLab 3 PDFSebastian CamachoNo ratings yet
- HW: Solve The Example ForDocument3 pagesHW: Solve The Example ForNarjes WalidNo ratings yet
- Introducción A Wolfram MathematicaDocument5 pagesIntroducción A Wolfram MathematicaECHEVERRIA BAUTISTA DANIELANo ratings yet
- Tutorial SolutionsDocument4 pagesTutorial Solutionscharlottekiel12No ratings yet
- Figure X 0:0.1:1 y X. Exp (2) Plot (X, Y) : p1 (U) (1-U) P P PDocument3 pagesFigure X 0:0.1:1 y X. Exp (2) Plot (X, Y) : p1 (U) (1-U) P P PLawrence WafulaNo ratings yet
- Directions: Analyze The Significant Difference Between Two MeansDocument3 pagesDirections: Analyze The Significant Difference Between Two MeansJohn Walter B. RonquilloNo ratings yet
- A Coder's Guide To Spline-Based Procedural GeometryDocument85 pagesA Coder's Guide To Spline-Based Procedural GeometrychessgeneralNo ratings yet
- MedpotDocument2 pagesMedpotDany JoséNo ratings yet
- Apparatus and MethodDocument10 pagesApparatus and MethodAli JafariNo ratings yet
- Desarrollo T4Document5 pagesDesarrollo T4ROMINA FORTUNATINo ratings yet
- Architectural Structure Final Project - Cantos, Talaisa, Villalobos - CompressedDocument25 pagesArchitectural Structure Final Project - Cantos, Talaisa, Villalobos - CompressedIvana Joyce VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Escriba Aquí La Ecuación.Document3 pagesEscriba Aquí La Ecuación.Josue Bernardi MaciasNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio 1: U 2 X (T) + TDocument9 pagesEjercicio 1: U 2 X (T) + TDaniela HoyosNo ratings yet
- Interpolatingfunction : Borra Resolvedor Diferencial Numérico Resolvedor Diferencial NuméricoDocument4 pagesInterpolatingfunction : Borra Resolvedor Diferencial Numérico Resolvedor Diferencial NuméricoSebastian CamachoNo ratings yet
- Gnphys+1+ +worktext+ +Week+2+Summative+TestDocument3 pagesGnphys+1+ +worktext+ +Week+2+Summative+TestJarissa GallazaNo ratings yet
- Thyristor Voltage ControllerDocument7 pagesThyristor Voltage Controllerkavish malakaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 7 Matrix Algebra For Homogeneous Linear Algebraic SystemDocument3 pagesTutorial 7 Matrix Algebra For Homogeneous Linear Algebraic System徐子裕No ratings yet
- Circular ShiftDocument4 pagesCircular ShiftTejhas KapoorNo ratings yet
- 2 ReportDocument9 pages2 Reportsvzdv asdqNo ratings yet
- QQQQDocument16 pagesQQQQbj66t68cdpNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 5Document7 pagesLab Report 5darren leeNo ratings yet
- Guia de Ejercitación #2 - Física I - 2020 Catedra: Fisica IDocument7 pagesGuia de Ejercitación #2 - Física I - 2020 Catedra: Fisica IAnonymous dEmimw3No ratings yet
- A) - Mencari, , .: Node IDocument12 pagesA) - Mencari, , .: Node Isudharma yogaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 SIZE REDUCTION 4 SOLUTIONDocument4 pagesTutorial 4 SIZE REDUCTION 4 SOLUTIONLondiwe NxumaloNo ratings yet
- Tarea4 Enrique PriegoDocument2 pagesTarea4 Enrique PriegoEnique PriegoNo ratings yet
- Transport Phenomena - 1 - Vector and Tensor 1 - FaceBookADocument42 pagesTransport Phenomena - 1 - Vector and Tensor 1 - FaceBookAHareritamNo ratings yet
- A Teacher Must Choose Five Monitors From A Class of 12 Students. How Many Different Ways Can The Teacher Choose The Monitors?Document11 pagesA Teacher Must Choose Five Monitors From A Class of 12 Students. How Many Different Ways Can The Teacher Choose The Monitors?Syed Ali HaiderNo ratings yet
- DILE NO A LA PLANCHA (Kim Jhon Phatti Satto)Document6 pagesDILE NO A LA PLANCHA (Kim Jhon Phatti Satto)Kimsito Al TlvNo ratings yet
- Laboratorio 1. Parte BDocument7 pagesLaboratorio 1. Parte BALEXANDRA CASTAÑEDA BARRIOSNo ratings yet