Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ayurvedic Treatment of Stroke
Uploaded by
VENU B AOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ayurvedic Treatment of Stroke
Uploaded by
VENU B ACopyright:
Available Formats
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research
Vol.10; Issue: 1; January 2020
Website: www.ijhsr.org
Case Study ISSN: 2249-9571
Treatment Protocol of Stroke (Pakshaghata) Through Ayurveda Medicine -
A Case Study
Santosh Kumar Bhatted1, Uttamram Yadav2
1
Associate Professor & HOD, Department of Panchakarma, All India Institute of Ayurveda, New Delhi
2
PG Scholar, Department of Panchakarma, All India Institute of Ayurveda, New Delhi
Corresponding Author: Santosh Kumar Bhatted
ABSTRACT
Stroke is a common medical emergency and the second leading cause of death worldwide. In
Ayurveda stroke is described as Pakshaghata. The present study is a case report on management of
stroke of a male patient aged 40 years with chief complaints of loss of function of the left upper &
lower limb. He was a diagnosed case of stroke on the basis of clinical presentation and brain-
computed tomography-scan. The case treated with the Ayurveda medications was found to be
effective in providing relief in chief complain with improvement of overall health of the patient.
Treatment protocol was snehana, swedana, mridu virechana, basti karma, murdhani taila
(shirodhara) along with internal medication which is mentioned by Acharya Sushruta. Before
treatment NIH-Stroke Scale was 16 & Barthel index scale was 15 and after the treatment NIH-Stroke
Scale was 4 & Barthel index scale was 70 providing symptomatic relief too. This reveals that
Ayurveda treatment modalities can play a significant role in treatment of Stroke (Pakshaghata).
Keywords: Virechana, Snehana, Svedana, Basti karma, Shirodhara, Abhyanga, Pakshaghata
INTRODUCTION signs of focal (or global in case of coma)
Stroke is the sudden death of some disturbance of cerebral function lasting
brain cells due to lack of oxygen when the more than 24 hours or leading to death with
blood flow to the brain is lost by blockage no apparent cause other than a vascular
or rupture of an artery to the brain. [1] The origin. [2] The incidence rises steeply with
most common symptom of a stroke is age, and in many lower- and middle-
sudden weakness or numbness of the face, income countries it is rising in association
arm or leg, most often on one side of the with less healthy lifestyles. About one-fifth
body. Other symptoms include: confusion, of patients with an acute stroke die within a
difficulty in speaking difficulty in seeing month of the event and at least half of those
with one or both eyes; difficulty in walking, who survive are left with physical disability.
[3]
dizziness, loss of balance or coordination; According to update the global burden of
severe headache with no known cause; disease (GBD) study reported nearly 5.87
fainting or unconsciousness. million stroke deaths globally in 2010, as
Stroke is defined by the World compared to 4.66 million in 1990.
Health Organization as ‘a clinical syndrome Stroke can be correlated with the disease
consisting of rapidly developing clinical Pakshaghata described in Ayurveda. [4]
CASE REPORT
Table 1: History taking
Introductive UHID no. – 34948 IPD no. – 2439
history Name – Madan Gopal
Age/sex – 40/M
Marital status – married
Education – high school
Socioeconomic status – poor
Occupation – labor
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research (www.ijhsr.org) 111
Vol.10; Issue: 1; January 2020
Santosh Kumar Bhatted et.al. Treatment protocol of stroke (pakshaghata) through ayurveda medicine - a case
study
Table 1 to be continued...
Past history No HTN & diabetic
Chief Unable to stand & walk. Since 18 month
complaint Loss of function left upper & lower limb.
Incontinence of urine & stool.
Loss of sensation in left upper limb.
Slurred speech.
Difficulty in swallowing.
Unable to open eyes.
Swelling in left forearm.
Associated Insomnia Since 18 month
complaint Incomplete defecation
Loss of appetite
Treatment Ayurveda remedies
history
History of According to patient statement he was quite well 18 months back then he suddenly fell down. He had headache and body
Present illness pain as associated symptoms, so he took conservative treatment as prescribed by family physician. There was no relief in
associated symptoms moreover loss of function of the left upper & lower limb developed after 2 days become unable to
stand and walk without support. After that the patient took some Ayurvedic treatment but there was no such significant
relief. So the patient came to AIIA for better management.
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION –
Blood pressure - 110/80mmhg Edema – left wrist joint
Pulse rate – 76/min. Pallor – No
Temperature – Afebrile Icterus – No
Respiratory rate – 20/min. Clubbing – No
SYSTEMIC EXAMINATION –
NERVOUS SYSTEM:
Consciousness Conscious
Higher functions
Mental status MMSE score – 18
Cranial nerve examination Hyposmia
Olfactory Ptosis in both eye
Oculomotor Slurred speech
Hypoglossal (Rest of the cranial nerve status were normal)
Motor examination Diminished (left upper & lower limb)
Tone of muscles Grade – I (left upper & lower limb)
Power of muscles Swallowing – difficulty
Reflexes – superficial Lt. biceps jerk reflex – grade - 0
- Deep Lt. supinator jerk reflex – grade – 0
Lt. knee jerk reflex – grade – 1
Lt. planter jerk reflex – grade – 3
Gait Ataxic gait
Grade tendon reflexes as follows –
0 – Absent DIAGNOSIS
1 – present On the basis of clinical presentation and
2 – Brisk CT-Scan of the brain it was diagnosed as
3 – Very brisk case of Stroke (Pakshaghata).
4 – Clonus TREATMENT PROTOCOL
CLINICAL FINDINGS Patient was admitted in IPD AIIA, Plan for
Table 2: OBJECTIVE FINDING Snehana (Abhyanga), Swedana, Anuvasana
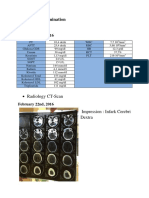
S.N. DATE INVESTIGATION FINDING
1 02/02/19 Brain CT-Scan Middle cerebral artery basti as Matra basti and Shirodhara along
Stroke with internal medication as detailed in table.
[5]
Table 3: SUBJECTIVE FINDING Table 4: Schedule of Sarvanga Abhyanga
S.N. SYMPTOMS OF PAKSHAGHAT S.N. Name of the Quantity Time Duratiom
1 Vama sandhibandhan vimokshyana Present drug
2 Dakshida sandhibandhan vimokshyana Absent 1 Ksheerbala 100 30 6 days
3 Cheshta nivritti Present taila ml/day minute/day
4 Ruja Present 2 Madhuyashti 100 30 7 days
5 Vakastambha Present taila ml/day minute/day
6 Akarmandyam Present
7 Achetnam Absent
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research (www.ijhsr.org) 112
Vol.10; Issue: 1; January 2020
Santosh Kumar Bhatted et.al. Treatment protocol of stroke (pakshaghata) through ayurveda medicine - a case
study
Table 5: Schedule of Mridu Sarvanga Bashpa Swedana Table 6: Plan for Anuvasan Basti as Matra Basti
S.N. Name of the drug Time Duration S.N. Name of the drug Dose
1 Dashmoola kwatha 7 minute/day 14 days 1 Ksheerbala taila 60ml
2 Shatpushpa kalka 2gm
3 Saindhav 1gm
Table 7: Schedule and observation of matra basti
Day Date Retention time of matra Observation
basti
1st 20/3/19 15 min Not significant changes.
2nd 22/3/19 20 min Not significant changes.
3rd 23/3/19 2 hours 30 min Not significant changes.
4th 25/3/19 3 hour Slight sensation of urge for micturition and defecation.
5th 26/3/19 2 hours 45 min Increase in Sensation of urge for micturition & defecation and increase in body strength.
6th 27/3/19 3 hours 30 min Patient able to inform of urge for micturition & defecation and he was complaining of
fever.
7th 30/3/19 4 hours Proper evacuation of stool & flatulence and increase body strength.
8th 01/4/19 4 hours 15 min Proper evacuation of stool & flatulence and increase body strength.
9th 02/4/19 6 hours Proper evacuation of stool & flatulence and lightness of the body.
10th 03/4/19 3 hours Lightness of the body & getting better.
11th 04/4/19 5 hours 20 min Improvement of sleep and speech.
12th 05/4/19 19 hours Patient able to swallow semisolid food and slight sense of sensation in left upper limb.
13th 06/4/19 6 hours 40 min Swapnaanuvritti (sound sleep) and lightness of the body.
14th 08/4/19 5 hours 30 min Swapnaanuvritti (sound sleep) and burning sensation in left upper limb.
15th 09/4/19 4 hours Patient able to stand with support and lightness of the body.
16th 10/4/19 8 hours 25 min Patient able to stand with support and increase body strength.
Table 8: Schedule of Shirodhara
Day Date Time Observation
1st 03/4/19 30 minute Not significant change.
2nd 04/4/19 30 minute Improve sleep and speech.
3rd 05/4/19 30 minute Sound sleep.
4th 06/4/19 30 minute Sound sleep and lightness of the head.
5th 08/4/19 30 minute Sound sleep and lightness of the head.
6th 09/4/19 30 minute Sound sleep and lightness of the head.
7th 10/4/19 30 minute Regular & Sound sleep and overall improvement.
Table 9: Internal medication
S.N. Name of medicine Dose Time Anupana
1 Gandharvhastadi kwatha 40ml twice a day Before food Luke warm water
2 Kaishore guggulu 2 tab thrice a day After food Luke worm water
3 Ashwagandhadi leham 1 tsf twice a day Morning & evening in empty stomach Milk
4 Giloy choorna 3 gm After food Luke worm water
Yashti choorna 3 gm
Vacha choorna 500 mg twice a day
5 Balarishta 15 ml twice a day After food Luke worm water
6 Kamdudha rasa 1 tab thrice a day After food Luke worm water
7 Gandharvhastadi taila 1 tsf Bed time Luke worm water
Table 10: Medication prescribed on discharge
S.N. Name of medicine Dose Time Anupana
1 Ashwagandha choorna 2gm BD After food Luke worm water
Giloy choorna 2gm BD
Yashti choorna 2gm BD
2 Brahma rasayan 1TSF BD Before food Milk
3 Balarishta 15ml BD After food Luke worm water
4 Shilajatvadi lauh 1tab BD After food Luke worm water
5 Balashwagandha taila Abhyanga - -
RESULT swelling in forearm, insomnia and slurred
Patient did not take any speech was reduced after 8 days of
contemporary medicine and he got treatment and also improved swallowing
symptomatic relief after 16 days of and loss of sensation in left upper limb after
Ayurveda treatment. After 3rd day of the 11 days of treatment. But after completion
treatment, improvement was seen in of 16th day of matra basti along with
incontinence of urine and stool. Ptosis, sarvanga abhyanga, vashpa swedana,
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research (www.ijhsr.org) 113
Vol.10; Issue: 1; January 2020
Santosh Kumar Bhatted et.al. Treatment protocol of stroke (pakshaghata) through ayurveda medicine - a case
study
shirodhara and internal medicine patient himself with support. After that he was
was able to do daily routine (eating, discharged and was advised to continue
drinking, bathing), standing and walking by internal medicine for 15 days.
Observation
Table 11: National Institute of Health Stroke Scale (NIH-SS)
Score NIH scale Range of score BT AT
1-a Level of consciousness 0 to 3 0 0
1-b LoC Question 0 to 2 1 0
1-c LoC 0 to 2 1 0
2 Best gaze 0 to 2 0 0
3 Visual 0 to 3 2 0
4 Facial palsy 0 to 3 1 0
5 Motor arm Right 0 to 4 0 0
Left 0 to 4 4 2
6 Motor leg Right 0 to 4 0 0
Left 0 to 4 3 1
7 Limb ataxia 0 to 2 1 0
8 Sensory 0 to 2 2 0
9 Best language 0 to 3 0 0
10 Dysarthria 0 to 2 1 1
11 Extinction and inattention (formerly neglect) 0 to 2 0 0
Total 42 16 04
0 = no stroke, 1-4 = minor stroke, 5-15 = moderate stroke, 15-20 = moderate/severe stroke, 21-42 = severe stroke.
Table 12: Barthel index
Domain name Range of score BT AT
1 Feeding 0 = unable 5 10
5 = needs help in cutting, spreading butter, etc. or requires modified dait
10 = independent
2 Bathing 0 = dependent 5 = independent (or in shower) 0 5
3 Grooming 0 = needs to help with personal care 0 0
5 = independent face /hair/teeth/shaving (implements provided)
4 Dressing 0 = dependent 0 5
5 = needs help but can do about half unaided
10 = independent (including buttons, zips, laces etc.)
5 Bowel 0 = incontinent (or needs to be given enemas) 0 10
5 = occasional accident
10 = continent
6 Bladder 0 = incontinent or catheterized and unable to manage alone 0 10
5 = occasional accident
10 = continent
7 Toilet use 0 = dependent 0 5
5 = needs some help, but can do something alone
10 = independent (on and off, dressing, wiping)
8 Transfers (bed to chair and back) 0 = unable, no sitting balance 5 10
5 = major help (of one or two people, physical) can sit
10 = minor help (verbal or physical)
15 = independent
9 Mobility (on level surface) 0 = immobile or <50 yards 5 10
5 = wheelchair independent, including corners, >50 yards
10 = walks with help of one person (verbal or physical) >50 yards
15 = independent (but may use any aid;for example,stick) > 50 yards
10 Stairs 0 = unable 0 5
5 = needs help (verbal, physical, carrying aid)
Total 15 70
BT = Before treatment, AT = After treatment
Table 13: Visual analog scale for pain DISCUSSION
S.N. SYMPTOMS OF PAKSHAGHAT BT AT AF
1 Vama sandhibandhan vimokshyana 8 4 3 Acharya Charak has described
2 Dakshida sandhibandhan vimokshyana 0 0 0 Pakshaghata in vata nanatmaj vyadhi [6] and
3 Cheshta nivritti 8 3 2
4 Ruja 6 2 0 Acharya Sushrut has mention in
[7]
5 Vakastambha 8 2 1 mahavatvyadhi and also Acharya Charak
6 Akarmandyam 6 2 1
7 Achetnam 0 0 0
& Sushrut has given treatment protocol of
0 = No pain, 1-3 = mild pain, 4-5 = moderate pain, 6-7 = severe Pakshaghata [8] which is snehana, swedana,
pain, 8-9 = very severe pain, 10 = excruciating pain. mridu virechana, basti karma, murdhani
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research (www.ijhsr.org) 114
Vol.10; Issue: 1; January 2020
Santosh Kumar Bhatted et.al. Treatment protocol of stroke (pakshaghata) through ayurveda medicine - a case
study
taila Accordingly treatment was in this patient was followed up for two months and
patient. there was no any deterioration. As this is a
Patient was admitted on 18/3/19 in single case study, there is a need for large
IPD AIIA. Treatment was started number of patients randomized clinical trial
gandharvhastadi kwatha, [9] kaishore to establish the effectiveness of the above
guggulu, [10] ashwagandhadi avleha, [11] treatment protocol in the management of
giloy choorna, [12] yashti choorna, [13] vacha Pakshaghata. This case report serves as a
choorna, [14] balarishta, [15] kamdudha rasa, lead for further researches in the
[16]
gandharvhastadi taila [17] after two days management of Stroke (Pakshaghata).
Panchakarma treatment started. Sarvanga
Abhyanga [18] was done with ksheerbala REFERENCES
taila [19] because it is snehana vata- 1. Walter Johnson, Oyere Onuma, Mayowa
pittashamak & balya and Vashpa swedana Owolabi & Sonal Sachdev. Bulletin of the
[20]
with dashmoola kwatha [21] together World Health Organization 2016.
2. Hatano S. Experience from a multicentre
snehana & swedana liquefies the dosha and stroke register: a preliminary
brings them to koshtha. [22] Anuvasan basti report. Bulletin of the World Health
[23]
as a Matra Basti [24] was given with Organisation. 1976;54(5):541–553.
ksheerbala taila because it is vata- 3. Nicki R. Colledge, Brian. R. Walker, Stuart
pittashamak. After 6th day of procedure H. Ralston Ian D. Penman, editors.
patient was complaining fever and itching in Davidsonʼs principles & practice of
whole body due to severe aggravating of medicine. 22nd edition. Churchil livingstone
pitta sanshrishta vata dosha. So that elsvier. p-1237.
internal medicine was revised Avipattikar 4. Agnivesha. CharakaSamhita. Panday
choorna [25] 5gm BD as a was given of and kashinnath & Chaturvedi Gorakhnath,
eladi kerum [26] for local application added editor. ChikitsaSthana, Vatavyadhichikitsa
28/53. Varanasi: CukhambhaSanhaskrit
with previous medicine & Panchakarma SeriesOffice; 2013. p-787.
procedure was stopped for two days till the 5. Susruta. SusrutaSamhita. Shri
Jwara coming down. After that started Dalhanacharya, editor. ChikitsaSthana,
Shirodhara [27] with coconut oil because of 5/19, Varanasi: ChaukhambhaSurbharti
pitta-vata shamak. And of sarvanga publisher; 2018. p-43.
abhyanga was given with Madhuyashti taila 6. Agnivesha. CharakaSamhita. Panday
[28]
it’s also vata-pitta shamak property & kashinnath & Chaturvedi Gorakhnath,
mridu vashpa swedana with dashmoola editor. SutraSthana, 20/11. Varanasi:
kwatha and matra basti with ksheerbala Cukhambha Sanhaskrit SeriesOffice;
taila. 2013.p-399.
7. Susruta. SusrutaSamhita. Shri
Dalhanacharya, editor. ChikitsaSthana,
CONCLUSION 5/19, Varanasi: ChaukhambhaSurbharti
Several reports suggest that in about publisher; 2018. p-43.
20% of non-cardio-embolic strokes in 8. Agnivesha. CharakaSamhita. Panday
young (<45 years), the commonly believed kashinnath & Chaturvedi Gorakhnath,
risk-factors (e.g. hypertension diabetes editor. ChikitsaSthana, Vatavyadhichikitsa
mellitus, tobacco use, etc.) are absent. [29] 28/100. Varanasi: CukhambhaSanhaskrit
On the basis of results observed in this case; SeriesOffice; 2013. p-795.
it can be said that, Ayurvedic management 9. Dr. D.B.Panditrao & Dr. Sharda Nayar,
with Panchakarma procedure like editor. Sahasrayoga. Purvardha, Pratham
Abhyanga, Vashpa swedana, Anulomana, & Prakranam. published from central council
Shirodhara along with oral Ayurveda for research in Ayurvedic science, ministry
of ayush; 2011.p-22.
medication are effective in the management 10. Sarngadhara. Sarngadharasamhita.
of Pakshaghata. These approaches are safe, Commentary by Acharya Adhamalla &
cost effective and easy to follow. The Kasirama, editor. Pratham khanda,
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research (www.ijhsr.org) 115
Vol.10; Issue: 1; January 2020
Santosh Kumar Bhatted et.al. Treatment protocol of stroke (pakshaghata) through ayurveda medicine - a case
study
Gugguluvidhanam 7/70-81. Varanasi: 21. Susruta. SusrutaSamhita. Shri
Chaukhamba surbharti prakashan ; 2013. p- Dalhanacharya, editor. SutraSthana, 38/71,
203. Varanasi: ChaukhambhaSurbharti publisher;
11. Dr. D.B.Panditrao & Dr. Sharda Nayar, 2018. p-189.
editor. Sahasrayoga. Purvardha, pratham 22. Agnivesha. CharakaSamhita. Panday
prakranam. published from central council kashinnath & Chaturvedi Gorakhnath,
for research in Ayurvedic science, ministry editor. VimanSthana, 11/48. Varanasi:
of ayush; 2011.p-22. CukhambhaSanhaskrit SeriesOffice; 2013.
12. Mishra Brahmasankara & Vaisya p-235.
Rupalalajia, ediyor. Bhavmishra, 23. Susruta. SusrutaSamhita. Shri
Bhavprakash, purvakhanda, Dalhanacharya, editor. ChikitsaSthana,
guduchyadivarga. Varanasi: Chaukhambha 37/4, Varanasi: ChaukhambhaSurbharti
Sanskrit Bhavan publisher; 2016. p-269. publisher; 2018. p-531.
13. Ayurveda Sarsangrah. choorna chepter. 24. Agnivesha. CharakaSamhita. Panday
Allahabad: Shri Baidyanath Ayurveda kashinnath & Chaturvedi Gorakhnath,
bhavan limited; 2015. p-683. editor. SiddhiSthana, 4/52-54. Varanasi:
14. Mishra Brahmasankara & Vaisya CukhambhaSanhaskrit SeriesOffice;
Rupalalajia, ediyor. Bhavmishra, 2013.p-1013.
Bhavprakash, purvakhanda, 25. Dr. D.B.Panditrao & Dr. Sharda Nayar,
Haritkyadivarga. Varanasi: Chaukhambha editor. Sahasrayoga, purvardha, 3rd
Sanskrit Bhavan publisher; 2016. p-43. prakranam. published from central council
15. Kaviraj Govind Das Sen, Bhaishajya for research in Ayurvedic science, ministry
ratnawali, Mishra Sidhhi Nandan, editor. of ayush; 2011. p-173.
Vatavyadhirogadhikar 26/572-575. 26. Dr. D.B.Panditrao & Dr. Sharda Nayar,
Varanasi: Chaukhamba surbharti prakashan editor. Sahasrayoga. Taila prakranam.
; 2014. p-518. published from central council for research
16. Vaidya Sharma, Pandit Hariprapanna, in Ayurvedic science, ministry of AYUSH;
Rasayogasagara, editor. Yoga-156/707-710 2014. p-124.
Varanasi: Chaukhamba Krishnadas 27. Susruta. SusrutaSamhita. Shri
Academy; 2010. p-260. Dalhanacharya, editor. Uttartantra, 18/46.
17. Acharya Vagbhatta. Astangahridaya. Shri Varanasi: ChaukhambhaSurbharti publisher;
Arunadatta & Hemadri, editor. 2018. p-636.
ChikitsaSthana, 15/21. Varanasi: 28. Dr. D.B.Panditrao & Dr. Sharda Nayar,
Chaukhambha surbharti prakashan ; 2017. editor. Sahasrayoga, purvardha, 3rd
p-648. prakranam. published from central council
18. Acharya Vagbhatta. Astangahridaya. Shri for research in Ayurvedic science, ministry
Arunadatta & Hemadri, editor. of ayush; 2011. p-173.
SutraSthana, 2/8. Varanasi: Chaukhambha 29. Hatano S. Experience from a multicentre
surbharti prakashan ; 2017. p-26. stroke register: a preliminary
19. Dr. D.B.Panditrao & Dr. Sharda Nayar, report. Bulletin of the World Health
editor. Sahasrayoga. purvardha, 5th Organisation. 1976;54(5):541–553.
prakranam. published from central council
for research in Ayurvedic science, ministry How to cite this article: Bhatted SK, Yadav U.
of ayush; 2011.p-292. Treatment protocol of stroke (pakshaghata)
20. Susruta. SusrutaSamhita. Shri through ayurveda medicine - a case study. Int J
Dalhanacharya, editor. ChikitsaSthana, Health Sci Res. 2020; 10(1):111-116.
37/4, Varanasi: ChaukhambhaSurbharti
publisher; 2018. p-531.
******
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research (www.ijhsr.org) 116
Vol.10; Issue: 1; January 2020
You might also like
- A Case Study On Hypothyroidism Treated With Ayurvedic DrugsDocument5 pagesA Case Study On Hypothyroidism Treated With Ayurvedic DrugsIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- CVA-notesDocument21 pagesCVA-notesVaibhav BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Pakshaghatha A Case StudyDocument4 pagesPakshaghatha A Case StudyDipin NarayananNo ratings yet
- LT 22 Maret 2019Document17 pagesLT 22 Maret 2019Anthony WijayaNo ratings yet
- A Critical Review of Kushmandaghritain The Management of Generalized Tonic-Clonic SeizuresDocument5 pagesA Critical Review of Kushmandaghritain The Management of Generalized Tonic-Clonic SeizuresIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- 16.daftar Pustaka PenatalaksanaanDocument22 pages16.daftar Pustaka PenatalaksanaanKenny FathurNo ratings yet
- Cerebral PalsyDocument9 pagesCerebral PalsysanjayNo ratings yet
- Assessment & Reasoning Cardiac System: Suggested Cardiac Nursing Assessment Skills To Be DemonstratedDocument8 pagesAssessment & Reasoning Cardiac System: Suggested Cardiac Nursing Assessment Skills To Be DemonstratedSharon Tanveer100% (1)
- Ayurvedic Management of Pakshaghata (Cerebrovascular Accident) : A Case StudyDocument5 pagesAyurvedic Management of Pakshaghata (Cerebrovascular Accident) : A Case Study65. Surbhi PandeyNo ratings yet
- Fneur 13 1053642Document16 pagesFneur 13 1053642Văn Dũng nguyenNo ratings yet
- Ayurvedic Management of Brachial Plexopathy: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesAyurvedic Management of Brachial Plexopathy: A Case ReportIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On The Ayurvedic Management of Ankylosing SpondylitisDocument8 pagesA Case Study On The Ayurvedic Management of Ankylosing SpondylitisPrasad PrasadNo ratings yet
- Case 1 Block NBSSDocument13 pagesCase 1 Block NBSSRuswinata ApitoNo ratings yet
- James Carter US Olympic Team Track & Field: Amitabh Bachchan Indian ActorDocument22 pagesJames Carter US Olympic Team Track & Field: Amitabh Bachchan Indian ActorSri KombongNo ratings yet
- A Stroke of Luck: Abolition of Parkinson's Tremor With StrokeDocument3 pagesA Stroke of Luck: Abolition of Parkinson's Tremor With StrokePutri Tamara DasantosNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Benign Hand TremorsDocument7 pagesCase Study of Benign Hand TremorsLupa Ingatan100% (1)
- Pulse: Good Width at Medium Level, Regular, 78 BPM, Wiry On Right, Thin On LeftDocument11 pagesPulse: Good Width at Medium Level, Regular, 78 BPM, Wiry On Right, Thin On LeftHui YingNo ratings yet
- Ijccm 23 129Document8 pagesIjccm 23 129Jean Brando Torres GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Research Article: Yu Zheng, Jiping Zhang, Yanjie Wang, Yuying Wang, Yujun Lan, Shanshan Qu, Chunzhi Tang, and Yong HuangDocument10 pagesResearch Article: Yu Zheng, Jiping Zhang, Yanjie Wang, Yuying Wang, Yujun Lan, Shanshan Qu, Chunzhi Tang, and Yong Huangmazh21No ratings yet
- Article 14859273241Document8 pagesArticle 14859273241pokeman693No ratings yet
- James Carter US Olympic Team Track & Field: Amitabh Bachchan Indian ActorDocument22 pagesJames Carter US Olympic Team Track & Field: Amitabh Bachchan Indian ActorDummy AccountNo ratings yet
- Insomnia in Older AdultsDocument2 pagesInsomnia in Older AdultssavitageraNo ratings yet
- Akut Abdomen PresentasiDocument7 pagesAkut Abdomen PresentasiAina CempakaNo ratings yet
- Efficacy of Physiotherapy Rehabilitation For Hemiparesis Following Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis, A Rare Case ReportDocument5 pagesEfficacy of Physiotherapy Rehabilitation For Hemiparesis Following Cerebral Venous Sinus Thrombosis, A Rare Case ReportRhevensa SantosoNo ratings yet
- STUDENT-Eating - Disorder-F&E-UNFOLDING ReasoningDocument14 pagesSTUDENT-Eating - Disorder-F&E-UNFOLDING ReasoningPeggy100% (12)
- An Open Clinical Trial To Evaluate The Efficacy of Nyagrodhadi Asthapana Basti in The Management of Prameha Upadrava With Special Reference To Diabetic NeuropathyDocument7 pagesAn Open Clinical Trial To Evaluate The Efficacy of Nyagrodhadi Asthapana Basti in The Management of Prameha Upadrava With Special Reference To Diabetic NeuropathyEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis A.: Excellent History But Was This Copy-Pasted?Document8 pagesAmyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis A.: Excellent History But Was This Copy-Pasted?Allan CastroNo ratings yet
- 4 5 16 123Document4 pages4 5 16 123Asaad AlnhayerNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On MigraineDocument35 pagesA Case Study On MigraineRitu ShewaniNo ratings yet
- Efficacy of Laksha Sheerapana and Manjistadi Lepa in Prakostasthibhagna Colles Frature A Case StudyDocument5 pagesEfficacy of Laksha Sheerapana and Manjistadi Lepa in Prakostasthibhagna Colles Frature A Case StudyEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Laboratory: Supporting ExaminationDocument4 pagesLaboratory: Supporting ExaminationkeluargacendanaNo ratings yet
- (KULIAH 7) Acupuncture For Treatment Stroke and Bell PalsyDocument62 pages(KULIAH 7) Acupuncture For Treatment Stroke and Bell PalsycallNo ratings yet
- Physical Therapy For Neurological Disorders: Muskan AhujaDocument15 pagesPhysical Therapy For Neurological Disorders: Muskan AhujaMuskan AhujaNo ratings yet
- (Toni) TX MS W Chinese Scalp AcupDocument16 pages(Toni) TX MS W Chinese Scalp AcupAngelaNo ratings yet
- Stroke Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pagesStroke Nursing Care PlanNikko Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- (NS) Week 11 SBL Fractures QuestionsDocument16 pages(NS) Week 11 SBL Fractures QuestionsJoei “Jojo” GohNo ratings yet
- Effect of Ayurvedic and Panchakarma Treatment in Asthi Majja Gata Vata (Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis) : A Case StudyDocument6 pagesEffect of Ayurvedic and Panchakarma Treatment in Asthi Majja Gata Vata (Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis) : A Case StudyDevinder PrasadNo ratings yet
- Laporan Kasus (NHS Stroke)Document8 pagesLaporan Kasus (NHS Stroke)keluargacendanaNo ratings yet
- A Cup ArkinsonDocument6 pagesA Cup Arkinsontito zambranoNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Acupuncture WorksDocument31 pagesPowerpoint Acupuncture WorksrdmhlNo ratings yet
- Laporan Kasus (Stroke NHS)Document4 pagesLaporan Kasus (Stroke NHS)keluargacendanaNo ratings yet
- PAPER1Document3 pagesPAPER1GianeNo ratings yet
- Scalp Acupuncture2Document64 pagesScalp Acupuncture2Ganga Singh100% (1)
- TG 3 Stroke - LADocument43 pagesTG 3 Stroke - LANovi AdriNo ratings yet
- 18-Article Word Document-46-2-10-20171111Document5 pages18-Article Word Document-46-2-10-20171111Vaibhav ManeNo ratings yet
- 4513 10918 1 PB PDFDocument13 pages4513 10918 1 PB PDFRama BayuNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Study of Migraine in Ayurveda (Ardhavbhedaka)Document5 pagesConceptual Study of Migraine in Ayurveda (Ardhavbhedaka)Editor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Asne 03 0233Document9 pagesAsne 03 0233Ganesh GaitondeNo ratings yet
- (1-3) Hypoglycemia Induced Hemichorea (HpogC) (IJGN) - Shashi PrakashDocument3 pages(1-3) Hypoglycemia Induced Hemichorea (HpogC) (IJGN) - Shashi Prakashneeraj2811No ratings yet
- Physiotherapy Assessment in NeurologyDocument55 pagesPhysiotherapy Assessment in Neurologywml3648100% (2)
- II-E Altered PerceptionDocument16 pagesII-E Altered PerceptionDharylle CariñoNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Stroke: Interprofessional Learning Maldives National University 26th October 2022Document43 pagesCase Study of Stroke: Interprofessional Learning Maldives National University 26th October 2022Riphu RashydNo ratings yet
- Ayurveda Management of GBSDocument5 pagesAyurveda Management of GBSLinbdsellNo ratings yet
- E.T.D.'s Medical History and ExamDocument8 pagesE.T.D.'s Medical History and ExamZadkiel VelasquezNo ratings yet
- PTC 62 308Document8 pagesPTC 62 308naufal12345No ratings yet
- Chlampah, Journal Edit CR ParkinsonDocument8 pagesChlampah, Journal Edit CR ParkinsonIhsanul Ma'arifNo ratings yet
- Discussion: Summary & ConclusionDocument29 pagesDiscussion: Summary & ConclusionVENU B ANo ratings yet
- 2 - Review of AyurvedaDocument65 pages2 - Review of AyurvedaVENU B ANo ratings yet
- 14 BibliographyDocument3 pages14 BibliographyVENU B ANo ratings yet
- 9 - Clinical StudyDocument61 pages9 - Clinical StudyVENU B ANo ratings yet
- Modern Review: Gross Anatomy of BrainDocument32 pagesModern Review: Gross Anatomy of BrainVENU B ANo ratings yet
- P.G. Department of Panchkarma National Institute of Ayurveda, Jaipur-302002Document11 pagesP.G. Department of Panchkarma National Institute of Ayurveda, Jaipur-302002VENU B ANo ratings yet
- A Current Trend in the Treatment of Major Joint Disorder in Ayurveda: Pakshaghata (HemiplegiaDocument4 pagesA Current Trend in the Treatment of Major Joint Disorder in Ayurveda: Pakshaghata (HemiplegiaVENU B ANo ratings yet
- 18 PhotoDocument8 pages18 PhotoVENU B ANo ratings yet
- Observations & Results: Table No. 1 Status of 76 Patients of Pakshaghata No. of Patients Total Group A Group B Group CDocument15 pagesObservations & Results: Table No. 1 Status of 76 Patients of Pakshaghata No. of Patients Total Group A Group B Group CVENU B ANo ratings yet
- 80 RecommendationDocument31 pages80 RecommendationVENU B ANo ratings yet
- 19 SummaryDocument31 pages19 SummaryVENU B ANo ratings yet
- 17 GraphDocument14 pages17 GraphVENU B ANo ratings yet
- Sheelawati Monlai (EVS)Document358 pagesSheelawati Monlai (EVS)VENU B ANo ratings yet
- General Consideration of Pakshaghata and Its Management Using Natural Medicine and Ayurveda PrinciplesDocument4 pagesGeneral Consideration of Pakshaghata and Its Management Using Natural Medicine and Ayurveda PrinciplesVENU B ANo ratings yet
- Management of Pakshaghata (Hemiplegia Due To Basal Ganglia Bleed) Through Panchakarma: A Case StudyDocument6 pagesManagement of Pakshaghata (Hemiplegia Due To Basal Ganglia Bleed) Through Panchakarma: A Case StudyVENU B ANo ratings yet
- Observations & Results: Table No. 1 Status of 76 Patients of Pakshaghata No. of Patients Total Group A Group B Group CDocument15 pagesObservations & Results: Table No. 1 Status of 76 Patients of Pakshaghata No. of Patients Total Group A Group B Group CVENU B ANo ratings yet
- Ayurvedic Treatment of StrokeDocument6 pagesAyurvedic Treatment of StrokeVENU B ANo ratings yet
- Plants Used in Mexican Traditional Medicine July 04Document180 pagesPlants Used in Mexican Traditional Medicine July 04Luis NagueraNo ratings yet
- Sheelawati Monlai (EVS)Document358 pagesSheelawati Monlai (EVS)VENU B ANo ratings yet
- Nature's Gift to Mankind: The Multifarious Uses of Nirgundi (Vitex negundoDocument28 pagesNature's Gift to Mankind: The Multifarious Uses of Nirgundi (Vitex negundoVENU B ANo ratings yet
- Efficacy of in Preterm Infants-A Comparative Pilot Study SuvarnaprashanDocument8 pagesEfficacy of in Preterm Infants-A Comparative Pilot Study SuvarnaprashanVENU B ANo ratings yet
- Electroencephalography: EEG ElectrodesDocument3 pagesElectroencephalography: EEG ElectrodesVENU B ANo ratings yet
- Super Astrology PDFDocument43 pagesSuper Astrology PDFseevalee Bandara100% (4)
- EEG CorticalArousalDocument24 pagesEEG CorticalArousalTaufikHidayatNo ratings yet
- Phytoantidotes of Tumkur District Karnataka IndiaDocument9 pagesPhytoantidotes of Tumkur District Karnataka IndiaVENU B ANo ratings yet
- Medical Management of Asthma and Folk Medicine inDocument9 pagesMedical Management of Asthma and Folk Medicine inVENU B ANo ratings yet
- Kidney Book in KannadaDocument96 pagesKidney Book in KannadaVENU B ANo ratings yet
- EEG IntroductionDocument29 pagesEEG IntroductionNita HandayaniNo ratings yet
- Me Project MHRDMDocument36 pagesMe Project MHRDMYatinMhapankarNo ratings yet
- Russell Vs Vestil 304 SCRA 738Document2 pagesRussell Vs Vestil 304 SCRA 738Joshua L. De JesusNo ratings yet
- Zanussi ZBF 569 Oven ManualDocument24 pagesZanussi ZBF 569 Oven ManualJoohlsNo ratings yet
- EthicsDocument10 pagesEthicsEssi Chan100% (4)
- Likes and Dislikes 1Document2 pagesLikes and Dislikes 1LAURA MELISSA SANCHEZ SUAREZ50% (2)
- Ish300 Chapter 3Document20 pagesIsh300 Chapter 3Amanina AyuniNo ratings yet
- BRI Divisions and Branches Level ReportDocument177 pagesBRI Divisions and Branches Level ReportCalvin Watulingas100% (1)
- Swift Group Technical HandbookDocument8 pagesSwift Group Technical HandbookLukasz WilkNo ratings yet
- Wireless Local LoopDocument8 pagesWireless Local Loopapi-3827000100% (1)
- Magh Bihu or Maghar DomahiDocument8 pagesMagh Bihu or Maghar Domahihackdarenot4No ratings yet
- Activity Sheets in Science VIDocument24 pagesActivity Sheets in Science VIFrauddiggerNo ratings yet
- Flamme Rouge - Grand Tour Rules - English-print-V2Document3 pagesFlamme Rouge - Grand Tour Rules - English-print-V2dATCHNo ratings yet
- Techniques To Prevent Food SpoilageDocument30 pagesTechniques To Prevent Food SpoilageCourtney GrahamNo ratings yet
- Cagayan Electric vs. CIRDocument4 pagesCagayan Electric vs. CIRGladys BantilanNo ratings yet
- Sensory Evaluation of FoodDocument38 pagesSensory Evaluation of FoodKHOZA SBUSISIWENo ratings yet
- The Kano Model: How To Delight Your CustomersDocument16 pagesThe Kano Model: How To Delight Your CustomersRoen RamonalNo ratings yet
- Case - History WPC 3790-2013Document2 pagesCase - History WPC 3790-2013Sachin solomonNo ratings yet
- RD276-QP (S) Attendance Record Mr. Muthu Senthil KumarDocument2 pagesRD276-QP (S) Attendance Record Mr. Muthu Senthil Kumaralfie100% (1)
- Decision Criteria For Ethical ReasoningDocument14 pagesDecision Criteria For Ethical ReasoningZara ImranNo ratings yet
- The Irish Light 10Document28 pagesThe Irish Light 10Twinomugisha Ndinyenka RobertNo ratings yet
- Teas Cookbook 6.8Document13 pagesTeas Cookbook 6.8Natalia CruzNo ratings yet
- Azure Blockchain Workbench guideDocument183 pagesAzure Blockchain Workbench guideAhmed AyadNo ratings yet
- T e 2552731 Describe The Creature Writing Worksheet - Ver - 2Document3 pagesT e 2552731 Describe The Creature Writing Worksheet - Ver - 2Minah ZamanNo ratings yet
- Exercise For FitnessDocument44 pagesExercise For FitnessSheena Mae Sube PoNo ratings yet
- Covid19-Drug StudyDocument7 pagesCovid19-Drug StudynicoleNo ratings yet
- Milking MachineDocument10 pagesMilking Machineuniversaldairy100% (2)
- Quality Management and Control in ConstructionDocument22 pagesQuality Management and Control in ConstructionjennyNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Types of Hydrogen Fuel CellDocument57 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Different Types of Hydrogen Fuel CellSayem BhuiyanNo ratings yet
- 2013 Typhoon YolandaDocument7 pages2013 Typhoon YolandaDieanne MaeNo ratings yet
- Micro To MACRO Mathematical Modelling in Soil Mechanics (Trends in Mathematics)Document407 pagesMicro To MACRO Mathematical Modelling in Soil Mechanics (Trends in Mathematics)Renova HnNo ratings yet