Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Numerical Overcurrent Relay
Numerical Overcurrent Relay
Uploaded by
Tariq Mohammed OmarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Numerical Overcurrent Relay
Numerical Overcurrent Relay
Uploaded by
Tariq Mohammed OmarCopyright:
Available Formats
Numerical overcurrent relay
An overcurrent relay is the simplest form of protective relay which operates when the current
in any circuit exceeds a certain predetermined values, i.e. the pick-up value. It is extensively
used for the protection of distribution lines, industrial motors and equipment Using a
multiplexer, the microprocessor can sense the fault currents of a number of circuits.
If the fault current in any circuit exceeds the pick-up value, the microprocessor sends a
tripping signal to the circuit breaker of the faulty circuit.
As the microprocessor accepts signals in voltage form, the current signal derived from the
current transformer is converted into a proportional voltage signal using a current to voltage
converter. The ac voltage proportional to the load current is converted into dc. using a
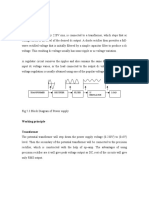
precision rectifier. Thus, the microprocessor accepts dc voltage The block schematic diagram
of the relay is shown in Fig.
Current is taken from C.T. and given to I to V converter because many electronics
circuit require voltage signal for operation.
The A.C. voltage is converted into D.C. voltage by using rectifier.
This D.C. voltage is proportional to load current only.
The output of rectifier is given to Multiplexer.
The Multiplexer gives output to A/D Converter where Analog DC voltage is
converted to Digital form (in form of O and 1 i.e. binary form).
Microprocessor understands only codes in 0 and 1 form.
HP (Microprocessor) gives S/C (start of conversion) signal to A/D converter (I.e.
analogue to digital conversion is started and HP gives permission to A/D convertor
for this by sending S/C)
You might also like
- Digital VoltmeterDocument17 pagesDigital VoltmeterVincent KorieNo ratings yet
- 5.LDR Based Highways Road Light Failed Intimation Using GSMDocument44 pages5.LDR Based Highways Road Light Failed Intimation Using GSMfotronichs velloreNo ratings yet
- Bxe Unit 4Document12 pagesBxe Unit 4aryaagharkar7100% (1)
- 2010 Me 105Document11 pages2010 Me 105Omer NadeemNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - MicroprocessorDocument16 pagesUnit 2 - MicroprocessorsenthilNo ratings yet
- Een 11 Finals Lec1Document46 pagesEen 11 Finals Lec1lavadiajhonNo ratings yet
- EEN11, Finals CombinedDocument105 pagesEEN11, Finals CombinedlavadiajhonNo ratings yet
- C T I/O P: Hapter Hree RocessingDocument22 pagesC T I/O P: Hapter Hree RocessingMohamed OmarNo ratings yet
- Data Conversion DevicesDocument6 pagesData Conversion Devicesriya vermaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document13 pagesUnit 4yamunaoli87No ratings yet
- Frequency To Voltage Converter Circuit DiagramDocument8 pagesFrequency To Voltage Converter Circuit DiagramNabendu GhoshNo ratings yet
- Micro Controller ProjectDocument12 pagesMicro Controller Projecthedo7No ratings yet
- Diode Rectifier Then Provides A Full-WaveDocument4 pagesDiode Rectifier Then Provides A Full-Waveprem035No ratings yet
- Resonant DC-DC Converting Controller Santhosh112Document21 pagesResonant DC-DC Converting Controller Santhosh112SanthoshNo ratings yet
- Single Transistor 12v To 230v InverterDocument7 pagesSingle Transistor 12v To 230v Inverteryr48No ratings yet
- HVAC Control Boards 01Document11 pagesHVAC Control Boards 01Osama AhmedNo ratings yet
- Speed Checkers For HighwaysDocument35 pagesSpeed Checkers For HighwaysKarthik Mvs100% (1)
- Chapter 4Document23 pagesChapter 4Tejan Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Based Impedance RelayDocument11 pagesMicroprocessor Based Impedance RelaySuresh100% (1)
- LSC Presentation: Topic:-Dual Slope A/D ConvertorDocument8 pagesLSC Presentation: Topic:-Dual Slope A/D ConvertorSatyakam JhaNo ratings yet
- ColocviuDocument6 pagesColocviuAndra BordeaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 Eng NaderDocument8 pagesExperiment 2 Eng Naderياسر العويطيNo ratings yet
- High Sensitive LPG Sensor With Gas Leakage Alert BuzzerDocument27 pagesHigh Sensitive LPG Sensor With Gas Leakage Alert Buzzerkprk414No ratings yet
- ECE 027 - RectifiersDocument39 pagesECE 027 - RectifiersMiyuki NakiriNo ratings yet
- Ec1355 Esd EceDocument31 pagesEc1355 Esd EceSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- 2.control of Heavy Electrical Loads Using DTMF SignalsDocument42 pages2.control of Heavy Electrical Loads Using DTMF Signalsfotronichs velloreNo ratings yet
- Ch.7 Data AcquisitionDocument9 pagesCh.7 Data AcquisitionaattishNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1-DC Power SupplyDocument30 pagesUNIT 1-DC Power SupplyMuizz ZainolNo ratings yet
- Simple AC To DC Converter Using Bridge RectifierDocument2 pagesSimple AC To DC Converter Using Bridge RectifierMahum JamilNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv Data Converters: Types of Analog To Digital ConvertersDocument3 pagesUnit Iv Data Converters: Types of Analog To Digital ConvertersAshrith LadiNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Converters PDFDocument7 pagesDC-DC Converters PDFRidaNo ratings yet
- Signal ProcessingDocument47 pagesSignal ProcessingAthira rcNo ratings yet
- Digital-to-Analog (D/A) Converters Lec8 1 Introduction To D/A ConvertersDocument4 pagesDigital-to-Analog (D/A) Converters Lec8 1 Introduction To D/A ConvertersKhalifa EltayebNo ratings yet
- TWO Power Conversion Systems 2.1 Power Electronic ConvertersDocument17 pagesTWO Power Conversion Systems 2.1 Power Electronic ConvertersAlhussain EmbarkNo ratings yet
- Z Source ConverterDocument12 pagesZ Source Converterravirnjn88No ratings yet
- 5V Power SupplyDocument20 pages5V Power SupplyAnujNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4.1 Signal ConditioningDocument34 pagesChapter 4.1 Signal ConditioningmathewosNo ratings yet
- Improved Power Quality AC-DC Converters With High Frequency Transformer IsolationDocument69 pagesImproved Power Quality AC-DC Converters With High Frequency Transformer IsolationZlatian RaduNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Based Impedance Relay: TechnicalsymposiumDocument14 pagesMicroprocessor Based Impedance Relay: TechnicalsymposiumGaurav JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 ADCDocument8 pagesUnit-5 ADCDr. M Kiran KumarNo ratings yet
- 12V DC To 220V AC ConverterDocument7 pages12V DC To 220V AC ConverterAedrian M LopezNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument105 pagesChapter Oneadugna abdissaNo ratings yet
- Final ReviewDocument19 pagesFinal ReviewSanyam JainNo ratings yet
- AC To DC Project ReportDocument2 pagesAC To DC Project ReportAryaan Revs0% (1)
- مناقشة اولية1Document17 pagesمناقشة اولية1ahmedNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 (2 Mark)Document2 pagesUnit-5 (2 Mark)sharmilakumari sNo ratings yet
- Inverter and Its TopologiesDocument14 pagesInverter and Its TopologiesAvnesh SuryavanshiNo ratings yet
- 12V DC To 220V AC Converter DesignDocument7 pages12V DC To 220V AC Converter DesigntintuvrNo ratings yet
- Digital Assignment 2Document6 pagesDigital Assignment 2rkNo ratings yet
- EDC Lab 4Document10 pagesEDC Lab 4Z S PlaysNo ratings yet
- Oraye - ELX20 - Lab 4 Halfwave Rectifier PDFDocument8 pagesOraye - ELX20 - Lab 4 Halfwave Rectifier PDFXheluj Sheluj ZhelujNo ratings yet
- Fire Detection and ControlDocument16 pagesFire Detection and ControlvaisnanyNo ratings yet
- EI5007W2Document17 pagesEI5007W2PyiAungNo ratings yet
- IE Mod 01 PowerSupplyDocument25 pagesIE Mod 01 PowerSupplyRy AnNo ratings yet
- Maths OperationDocument27 pagesMaths OperationTurkish GatxyNo ratings yet
- Power Supplies: Types of Power SupplyDocument18 pagesPower Supplies: Types of Power SupplyArasu LoganathanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three2Document12 pagesChapter Three2Fuh ValleryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document40 pagesChapter 8UMMU MARDHIAH ABDUL HALIMNo ratings yet
- DC - AC ConvertorsDocument3 pagesDC - AC Convertorskarthick LNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Analogue Signals From CT and PTDocument2 pagesAnalogue Signals From CT and PTTariq Mohammed OmarNo ratings yet
- 3.3.5 TCSC Controller Model For Stability: Fig.3.6. Modes of TCSC OperationDocument1 page3.3.5 TCSC Controller Model For Stability: Fig.3.6. Modes of TCSC OperationTariq Mohammed OmarNo ratings yet
- Numerical Transformer Differential RelayDocument2 pagesNumerical Transformer Differential RelayTariq Mohammed OmarNo ratings yet
- 3.3.2 Operation of The TCSC 3.3.2.1 Basic Principle: Figure 3.4 A Variable Inductor Connected in Shunt With An FCDocument1 page3.3.2 Operation of The TCSC 3.3.2.1 Basic Principle: Figure 3.4 A Variable Inductor Connected in Shunt With An FCTariq Mohammed OmarNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Variable Impedance Type Series Compensator: Figure 3.3 Basic Thyristor-Controlled Series Capacitor SchemeDocument2 pages3.3 Variable Impedance Type Series Compensator: Figure 3.3 Basic Thyristor-Controlled Series Capacitor SchemeTariq Mohammed OmarNo ratings yet
- Numerical Relays: Please Submit The Report in DOC and PTT FormatDocument2 pagesNumerical Relays: Please Submit The Report in DOC and PTT FormatTariq Mohammed OmarNo ratings yet