Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ilovepdf Merged
Uploaded by
Benjie Ortiz BatoonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ilovepdf Merged
Uploaded by
Benjie Ortiz BatoonCopyright:
Available Formats
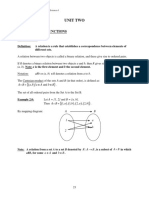
A B
A function is a relation that map each
element x of a set A with only one element 5 2
y of set B 6 3
FUNCTIONS 7 4
Function f: A B is given as 8 5
y= f(x) 9 6
7
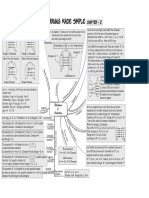
Types Of Functions
(1) One to one function/ Injective (2) Many to one function
f: A B is one to one if every element f: A B is many to one if two or more
of A has distinct image in B. elements of A have same image in B
A B A B
a c a d
b d b e
e c f
g
(3) Onto function/ Surjective (4) One-one and onto function
f: A B is onto if every element of B is / Bijective
related to at least one element of A f: A B is one-one and onto if it satisfies
A B both the condition for one-one and onto
a e A B
b f a e
c g b f
d c g
d h
Invertible functions Composite functions
f: A B and g: B C can be composed
If
f to form a function which maps from
A B A to C.
A composite function is denoted by
Then (gof)(x): g(f(x))
f -1 A f B g C
B A
x f(x) g(f(x))
For a function to be invertible it needs
to be both one-one and onto function gof
Relation R from set A to set B is a subset of the cartesian product
RELATIONS A X B and is derived by describing a relationship between first and
second element of the ordered pair A X B
Representation Of Relation
For A={ 9, 16, 25} B= { 5, 4, 3 , -3, -4,-5}
A B
Here, relation is that elements of A are
square of elements of B 3
-3
9
(1) Set buider form 4
16
R= { (x,y), x is square of y, x Є A and y Є B } -4
25
5
(2) In roster form -5
R= { (9, 3), (9, -3), (16, 4) , (16, -4), (25, 5), (25, -5) }
Number Of Relations Types Of Relation
If A has h elements and B has k (1) Universal Relation
elements then number of relations
Each element of A is related
from A to B are 2hk. to every element of A
i.e, R= A X A
(2) Identity Relations/Reflexive
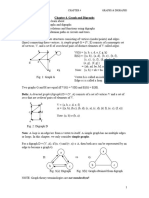
Terminologies related to Each element of A is related to
Relations itself
i.e, R= { (a,a) a Є A}
A B (3) Inverse Relation
7 R is a relation from A to B then
5 R-1 is inverse relation from B to A
8
6
9 (4) Symmetric Relation
7
10
8 For a relation R, if (a,b) Є R then
11 (b, a) Є R; V a, b Є A
9
12
(5) Transitive Relation
Domain = Collection of elements of A For a relation R, if (a,b) Є R ,
= {5, 6, 7, 8 , 9} (b, c) Є R then (a, c) Є R; V a, b, c Є R
Co-domain = Collection of elements of B
= {7, 8 , 9, 10, 11,12} (6) Equivalence Relation
Range = Collection of elements of B
related to A A transitive, symmetric and reflexive
= {7, 8 , 9, 10, 11} relation is an equivalence relation.
You might also like
- Representation of Relation: RelationsDocument2 pagesRepresentation of Relation: RelationsDhruv BhandariNo ratings yet
- Xii Maths Ch1 Relations Functions HssliveDocument4 pagesXii Maths Ch1 Relations Functions HssliveMuhammad SaleemNo ratings yet
- Relations & Functions Chapter SummaryDocument4 pagesRelations & Functions Chapter Summarykps evilNo ratings yet
- Functions and Mappings ExplainedDocument11 pagesFunctions and Mappings ExplainedANTONY MUUONo ratings yet
- Chapter2 - Part2 - FunctionsDocument40 pagesChapter2 - Part2 - FunctionsliasakinahNo ratings yet
- Ch4 FunctionsDocument27 pagesCh4 Functionsloay abukhalafNo ratings yet
- MathDocument12 pagesMathPunya Prasun DasNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Maths KV RaipurDocument130 pagesClass Xii Maths KV RaipurAnsia MeenazNo ratings yet
- Maths Xii Chapter 1 Relations and FunctionsDocument27 pagesMaths Xii Chapter 1 Relations and FunctionsSsNo ratings yet
- RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONSDocument26 pagesRELATIONS AND FUNCTIONSDara PascualNo ratings yet
- Xii - 2022-23 - Maths - RaipurDocument124 pagesXii - 2022-23 - Maths - RaipurGAME NATION100% (2)
- Unit 3 FunctionsDocument27 pagesUnit 3 Functionsmustafa enamNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chapter 1 Maths Important FormulasDocument3 pagesClass 12 Chapter 1 Maths Important FormulasSoham patilNo ratings yet
- Discrete Structure 3Document17 pagesDiscrete Structure 3malikabdullah0120No ratings yet
- Maths Xii Important Formulae Chapterwise For Final RevisionDocument78 pagesMaths Xii Important Formulae Chapterwise For Final Revisionarise study guidelinesNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - e Vidyarthi 2024Document45 pagesFormula Sheet - e Vidyarthi 2024stormbreaker7200No ratings yet
- Relations and Functions Formula ListDocument35 pagesRelations and Functions Formula ListGajendra Sagar100% (1)
- w06 Cits2211lectures FunctionsDocument16 pagesw06 Cits2211lectures FunctionsFredNo ratings yet
- Functions Handout PDFDocument16 pagesFunctions Handout PDFMariam Christine CañanesNo ratings yet
- With Question/Answer AnimationsDocument27 pagesWith Question/Answer AnimationsGamesome GoshawkNo ratings yet
- csc447 ln010Document26 pagescsc447 ln010Jordan RamseyNo ratings yet
- Relation and FunctionDocument6 pagesRelation and FunctionJitesh RatawaNo ratings yet
- Introductory CalculusDocument46 pagesIntroductory CalculusNana Kofi JuniorNo ratings yet
- Assignment Number 1Document3 pagesAssignment Number 1markjan felicianoNo ratings yet
- Maths Xii Important Formulae Chapterwise 2017 18Document43 pagesMaths Xii Important Formulae Chapterwise 2017 18Preeti AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Xii - Math - ch1 - Relationsfunctions (JPEG) BWDocument4 pagesXii - Math - ch1 - Relationsfunctions (JPEG) BWsuraj_14No ratings yet
- STD 11 Maths CH 2 Full MaterialDocument27 pagesSTD 11 Maths CH 2 Full MaterialHimanshu PatelNo ratings yet
- F4 AM Chapter 1 - FunctionsDocument16 pagesF4 AM Chapter 1 - Functions李冠霖No ratings yet
- Relation & FunctionDocument3 pagesRelation & Functionjohhnysins1978No ratings yet
- Dr. Abdul Azeez N.P. Aligarh Muslim UniversityDocument49 pagesDr. Abdul Azeez N.P. Aligarh Muslim UniversityMD Shadan KausarNo ratings yet
- Discrete Mathematics (CSC 1204) : 2.3 FunctionsDocument43 pagesDiscrete Mathematics (CSC 1204) : 2.3 FunctionsHoroscoe ENo ratings yet
- Relations and FunctionsDocument4 pagesRelations and Functionsscholars learningNo ratings yet
- Relations and FunctionsDocument4 pagesRelations and FunctionspraveenNo ratings yet
- Functions GuideDocument3 pagesFunctions Guidegoosey ganderNo ratings yet
- Subsets Docx WebDocument30 pagesSubsets Docx Webapi-357336035No ratings yet
- Functions and Inverses: CS 2800: Discrete Structures, Spring 2015 Sid ChaudhuriDocument28 pagesFunctions and Inverses: CS 2800: Discrete Structures, Spring 2015 Sid ChaudhuriDupla PaltaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Maths Notes 2024-245Chapter - 1 Relations and FunctionsDocument45 pagesClass 12 Maths Notes 2024-245Chapter - 1 Relations and Functionsa.dasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Directed GraphsDocument15 pagesChapter 4 Directed GraphsMOHAMAD HAZRIL ASH'ARINo ratings yet
- Math 196, Section 59 (Vipul Naik)Document18 pagesMath 196, Section 59 (Vipul Naik)Brian HaraNo ratings yet
- Functions (Basics)Document2 pagesFunctions (Basics)Aadi SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Functions MA PDFDocument10 pagesFunctions MA PDFKarthik BingiNo ratings yet
- Munna 108Document10 pagesMunna 108sapal16176No ratings yet
- Maths Project 2Document16 pagesMaths Project 2Shivam kumar Verma91% (11)
- CBSE Class XII Math RevisionDocument19 pagesCBSE Class XII Math RevisionRadz100% (1)
- Functions Note and Exercise and WorksheetDocument8 pagesFunctions Note and Exercise and WorksheetEmily ZhengNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16Document25 pagesLecture 16Haseeb AliNo ratings yet
- X STD K.exp MATHS FORMULA EMDocument21 pagesX STD K.exp MATHS FORMULA EMBaskar ElNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Sets and FunctionsDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Sets and FunctionsKaushil KundaliaNo ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument22 pagesFunctionsМишээл ЯдамсүрэнNo ratings yet
- Relations and FunctionsDocument22 pagesRelations and FunctionsJ Anne LatozaNo ratings yet
- Maths 12Document305 pagesMaths 12Lalita PatelNo ratings yet
- RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS OVERVIEWDocument17 pagesRELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS OVERVIEWManjeet Singh RATHORENo ratings yet
- Relations and FunctionsDocument2 pagesRelations and FunctionsLets Learn MathsNo ratings yet
- JEE MAINS - VOL - I Functions SummaryDocument58 pagesJEE MAINS - VOL - I Functions SummaryAmol ChavanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document17 pagesLecture 4Варис ВарисовNo ratings yet
- Sets, Relations and Functions AssignmentDocument2 pagesSets, Relations and Functions AssignmentRohitNo ratings yet
- FunctionDocument19 pagesFunctionPranav DessaiNo ratings yet
- JEE Math Book with Theories, Exercises and SolutionsDocument102 pagesJEE Math Book with Theories, Exercises and SolutionsAntonioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 (I) CSC510 FunctionsDocument25 pagesLecture 7 (I) CSC510 Functions2023400072No ratings yet
- PTDP Bylaws - Membership Organization Article 1 - Name, PurposeDocument6 pagesPTDP Bylaws - Membership Organization Article 1 - Name, PurposeBenjie Ortiz BatoonNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Sets: Module in Mathematics 7 First QuarterDocument30 pagesIntroduction of Sets: Module in Mathematics 7 First QuarterBenjie Ortiz BatoonNo ratings yet
- Know Your Rights: A Citizen's Primer On Law EnforcementDocument50 pagesKnow Your Rights: A Citizen's Primer On Law EnforcementJoan AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet For Financial MathematicsDocument4 pagesFormula Sheet For Financial MathematicsMilon SultanNo ratings yet
- Electron ConfigurationsDocument2 pagesElectron ConfigurationsLaura lau100% (1)
- Introduction of Sets: Module in Mathematics 7 First QuarterDocument30 pagesIntroduction of Sets: Module in Mathematics 7 First QuarterBenjie Ortiz BatoonNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Sets: Module in Mathematics 7 First QuarterDocument30 pagesIntroduction of Sets: Module in Mathematics 7 First QuarterBenjie Ortiz BatoonNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Sets: Module in Mathematics 7 First QuarterDocument30 pagesIntroduction of Sets: Module in Mathematics 7 First QuarterBenjie Ortiz BatoonNo ratings yet
- Science7 - q1 - Mod2 - Elements Are Like Spices, When Mixed Together, They Become Better - FINAL08032020 PDFDocument35 pagesScience7 - q1 - Mod2 - Elements Are Like Spices, When Mixed Together, They Become Better - FINAL08032020 PDFVickie Santos100% (2)
- Formula Sheet For Financial MathematicsDocument4 pagesFormula Sheet For Financial MathematicsMilon SultanNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet For Financial MathematicsDocument4 pagesFormula Sheet For Financial MathematicsMilon SultanNo ratings yet
- L300 Mitsubishi Delica 4D56 Engine PDFDocument76 pagesL300 Mitsubishi Delica 4D56 Engine PDFerilNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 Planar Motion 2022Document29 pagesChapter3 Planar Motion 2022crazytrabzonlu28No ratings yet
- Smta 1101Document1 pageSmta 1101VISVAA.JNo ratings yet
- Weld Design BS 5950-1 (Ok)Document16 pagesWeld Design BS 5950-1 (Ok)Zaido Al HalabiNo ratings yet
- Math8 q1 Mod6 Go Illustrating Rectangular Coordinate System 08092020Document20 pagesMath8 q1 Mod6 Go Illustrating Rectangular Coordinate System 08092020Cassandra Nicole FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Tamil Nadu IX MathematicsDocument3 pagesTamil Nadu IX MathematicsVasu DevanNo ratings yet
- PreAssessment Quadratic Unit Multiple ChoiceDocument13 pagesPreAssessment Quadratic Unit Multiple ChoiceJoby ChenNo ratings yet
- (Maximum Marks: 15)Document2 pages(Maximum Marks: 15)ZEEL PATELNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Surveying I Course: Practical Content GuideDocument21 pagesCivil Engineering Surveying I Course: Practical Content GuideArinze samuel100% (1)
- Algebra and Calculus PDFDocument135 pagesAlgebra and Calculus PDFjardmonNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 5 and 6Document9 pagesWorksheet 5 and 6husan hashNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3 - HydraulicsDocument11 pagesMODULE 3 - HydraulicsNicole Ann ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Sample Worksheet FromDocument42 pagesSample Worksheet FromRaajaiswar Agnihatri KaulNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Mathematics Important Questions on Pair of Linear Equations in Two VariablesDocument118 pagesCBSE Class 10 Mathematics Important Questions on Pair of Linear Equations in Two VariablesMADAN MOHAN PANIGRAHINo ratings yet
- EE263 Homework SolutionsDocument4 pagesEE263 Homework SolutionsJoel M ChNo ratings yet
- MCR3U Unit #6 NotesDocument11 pagesMCR3U Unit #6 NotesShoalehNo ratings yet
- Olimpiade Matematika SMP Soal LatihanDocument3 pagesOlimpiade Matematika SMP Soal LatihanLuthfi Setiawan ArifNo ratings yet
- Geometry Regents Review: QuadrilateralsDocument9 pagesGeometry Regents Review: QuadrilateralsDwi Ika YuliantiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Vector - Matrix (Updated 2020)Document3 pagesTutorial 1 Vector - Matrix (Updated 2020)Jeevan KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Quiz No. 1 - 3rd Quarter-G10Document2 pagesQuiz No. 1 - 3rd Quarter-G10Farra ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Maths-II Sem PDFDocument28 pagesMaths-II Sem PDFHema RamaswamyNo ratings yet
- Math BattleshipDocument3 pagesMath Battleshipapi-332233770No ratings yet
- Crane Hook Stress Concentration FactorDocument3 pagesCrane Hook Stress Concentration FactortvaprasadNo ratings yet
- (Proceedings of Symposia in Pure Mathematics 98) Amir-Kian Kashani-Poor, Ruben Minasian, Nikita Nekrasov, Boris Pioline, Editors-String-Math 2016-American Mathematical Society (2018) PDFDocument314 pages(Proceedings of Symposia in Pure Mathematics 98) Amir-Kian Kashani-Poor, Ruben Minasian, Nikita Nekrasov, Boris Pioline, Editors-String-Math 2016-American Mathematical Society (2018) PDFLav100% (1)
- Cogalois TheoryDocument182 pagesCogalois TheoryDenken AsomircalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12-Full (1) 5757Document59 pagesChapter 12-Full (1) 5757Zoker_45No ratings yet
- Mathematical Economics W 04Document18 pagesMathematical Economics W 04AsiiyahNo ratings yet
- Exam J2, I2 (Algebra and Geometry) : Australian Mathematical Olympiad Committee 2021 Selection SchoolDocument2 pagesExam J2, I2 (Algebra and Geometry) : Australian Mathematical Olympiad Committee 2021 Selection SchoolBobNo ratings yet
- JMathPhys 31 725 (Lee and Wald)Document19 pagesJMathPhys 31 725 (Lee and Wald)Juan PerezNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Mathematics Q2 Week 7Document2 pagesLesson Plan in Mathematics Q2 Week 7Nimfa MalizaNo ratings yet
- SP Maths Basic 1 Unsolved-MergedDocument248 pagesSP Maths Basic 1 Unsolved-MergedMANARSHNo ratings yet