Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Determining Density: Matter: Mass vs. Weight Matter: Mass vs. Weight
Uploaded by
LOGAN HENSLEEOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Determining Density: Matter: Mass vs. Weight Matter: Mass vs. Weight
Uploaded by
LOGAN HENSLEECopyright:
Available Formats
Presentation Name Course Name
Unit # – Lesson #.# – Lesson Name
Density
• Density is a measure of the amount of matter
per unit of volume
High Density Low Density
Determining Density
– Objects more dense than water sink
– Objects less dense than water float
Introduction to Engineering Design © 2012 Project Lead The Way, Inc.
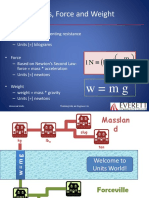
Matter: Mass vs. Weight Matter: Mass vs. Weight
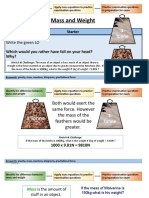
Mass and Weight are often confused.
• Mass is the amount of matter in an object or the
• An example using SI units
quantity of the inertia of the object.
– A man has a mass of 100 kg
• Weight is the force of gravity on mass.
W = mg
W = mg W = (100 kg)(9.8 m/sec2)
W = weight = 980 Newton
m = mass
g = acceleration of gravity – He weighs 980 N
• Many materials are purchased by weight
Matter: Mass vs. Weight Mass vs. Weight
Mass and Weight are often confused. • Pound-mass (lbm) is a unit of mass
• US Customary units example 1 lbm = 0.45359237 kg (by definition)
– A woman weighs 100 pounds 1 kg = 2.205 lbm (formula sheet)
W = mg 1 slug = 32.2 lbm (formula sheet)
W Formula Sheet
m =
g
100 lb
= = 3.1 slugs
ft
32.2
s 2
– Her mass is 3.1 slugs
Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Copyright 2010
1
Presentation Name Course Name
Unit # – Lesson #.# – Lesson Name
Mass vs. Weight Mass vs. Weight
• Pound-force (lb) is a unit of force • How are pound-mass and pound-force
The gravitational force exerted on a mass of related?
one lbm on the surface of the Earth – On Earth (g = 32.174 ft/s2)
1 lb = 4.44822162 N • 1 pound-mass object weighs1 pound-force
1 N = 0.225 lb – In outer space (no gravity)
• 1 pound-mass object has no weight
Formula Sheet – On the moon (g = 5.32 ft/s2)
• 1 pound-mass object weighs 0.166 pound-force
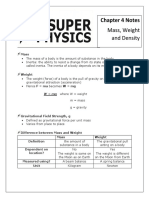
Density Mass/Weight Density
• Density can be indicated in multiple ways • Mass Density commonly used for SI units
– Mass Density = mass per unit volume – g/cm3 or kg/m3
– Weight Density = weight per unit volume • Weight Density commonly used for U.S.
Formula Sheet Customary units
m = VDm – lb/in.3 or lb/ft3
Material Mass Density Weight Density
m (g/cm3) (lb/in.3)
Dm =
V Apples 0.64 0.023
Water (Pure) 1.00 0.036
Water (Sea) 1.03 0.037
Ice 0.92 0.034
W = VDw Concrete 2.40 0.087
W Aluminum 2.71 0.098
Dw =
V Steel (1018) 7.8 0.282
Gold 19.32 0.698
Mass and Weight: Measurement Volume: Measurement
• Balance—measures mass • Volume is the amount of three
– Uses objects of known mass to find the dimensional space enclosed by
unknown mass of an object
an object.
– Measurement is unaffected by difference in
gravity – Two methods to determine volume
• Calculate using geometry of object
• Scale—measures weight
– Measures force caused by gravity
– Measurement is affected by difference in the • Measure indirectly using water
acceleration of gravity displacement (or 3D scanner)
– May display a “mass” measurement reading
by using an assumed acceleration of gravity
to convert from weight to mass
Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Copyright 2010
2
Presentation Name Course Name
Unit # – Lesson #.# – Lesson Name
Volume: Calculation Volume: Indirect Measure
• Some object volumes can be calculated. • Volume of an irregular object can be
• What is the volume formula for each object? determined indirectly with fluid
displacement. Level
Elevates
Volume: Indirect Measure Example
• What is the density of a 2.24 in. diameter
• Record water level with only water.
sphere of titanium that weighs 0.82 lb?
• Add samples. 4
V= π r3
• Record new level. 3 W = VDw
3
4 2.24 in.
• Difference is sample volume. V= π
3 2 W 0.82 lb
Dw = =
V 5.88 in. 3
4
V= π 1.12 in. 3 Dw = 0.14 lb/in.3
3
Volume
Read
Change
V = 5.88 in3
level
here • What volume of water (mL) would it displace?
1 ft3 1L
5.88 in. 3 = 0.096 L or 96 mL
Meniscus shape is 1728 in. 3 0.0353 ft3
exaggerated for clarity
Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Copyright 2010
3
You might also like
- Acceleration of A 50G Weight Affected by Gravity (Year 10 Report)Document4 pagesAcceleration of A 50G Weight Affected by Gravity (Year 10 Report)Weber Liu0% (1)
- Physics ProblemsDocument19 pagesPhysics ProblemsArthur1966100% (1)
- Learning Objectives: Core SupplementDocument19 pagesLearning Objectives: Core SupplementNilar LwinNo ratings yet
- 4.mass, Weight & DensityDocument14 pages4.mass, Weight & DensityFaNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document4 pagesModule 3delunaluisa19No ratings yet
- Mass and Weight: 1 TonneDocument12 pagesMass and Weight: 1 TonneRula KaradshehNo ratings yet
- W01 Yr08 Matter Volume MassDocument30 pagesW01 Yr08 Matter Volume MassrschaaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Lesson 1 Introduction To MatterDocument11 pagesUnit 1: Lesson 1 Introduction To MatterAbeer Alnajjar عبير النجارNo ratings yet
- (PHY) Chapter 4 - Mass, Weight, DensityDocument6 pages(PHY) Chapter 4 - Mass, Weight, Densitymicole.kohNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics Chapter 4 NotesDocument6 pagesO Level Physics Chapter 4 NoteshelloNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Thermodynamic Properties, Systems and ProcessesDocument10 pagesLecture 1 Thermodynamic Properties, Systems and ProcessesDyann LandinginNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Mass and WeightDocument25 pages1.3 Mass and WeightLaw PeterNo ratings yet
- Mass Weight N DensityDocument23 pagesMass Weight N DensitySiya ParmaniNo ratings yet
- Forces Within LiquidsDocument4 pagesForces Within LiquidsJayr LiuNo ratings yet
- 54 FluidsDocument2 pages54 FluidsnikobelookNo ratings yet
- Young's ModulusDocument2 pagesYoung's Modulus530 B Y ManojNo ratings yet
- Mass vs Weight - Key Differences Between Two Important ConceptsDocument5 pagesMass vs Weight - Key Differences Between Two Important ConceptsHibaNo ratings yet
- Mass & MomentumDocument6 pagesMass & MomentumJannatul Ferdoush SadiaNo ratings yet
- Mass and WeightDocument13 pagesMass and WeightcutekookieoppaNo ratings yet
- (PHY) Chapter 4 - Mass, Weight, DensityDocument7 pages(PHY) Chapter 4 - Mass, Weight, DensityHibaa NafeesNo ratings yet
- DENSITYDocument2 pagesDENSITYm1kuuuNo ratings yet
- Mass and WeightDocument19 pagesMass and WeightAly KhaledNo ratings yet
- Mass vs Weight - Understanding the DifferenceDocument1 pageMass vs Weight - Understanding the DifferenceSyed Wajahat AliNo ratings yet
- 3.1 DensityDocument27 pages3.1 Densityamnaasif829No ratings yet
- Physics IGCSE RevisionDocument29 pagesPhysics IGCSE RevisionPJNo ratings yet
- Gravity, Mass and Weight WorksheetDocument5 pagesGravity, Mass and Weight WorksheetJadeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Mass Weight DensityDocument2 pagesChapter 15 Mass Weight DensityAlexisNo ratings yet
- Grade-12 General-Physics-1 Q2 Wk6 GLAKbookletDocument16 pagesGrade-12 General-Physics-1 Q2 Wk6 GLAKbookletItsme LuisNo ratings yet
- PS.10 Study Guide - KeyDocument8 pagesPS.10 Study Guide - KeyR MathewNo ratings yet
- PM TB Solutions C04Document5 pagesPM TB Solutions C04Vishwajeet Ujhoodha75% (4)
- LESSON 2 - Matter and DensityDocument28 pagesLESSON 2 - Matter and DensityKate OchaveNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2 - Matter and DensityDocument28 pagesLESSON 2 - Matter and DensityKate OchaveNo ratings yet
- Mass, Weight and DensityDocument6 pagesMass, Weight and DensityheheheNo ratings yet
- Mass & Energy Balance - Introduction To Process VariablesDocument75 pagesMass & Energy Balance - Introduction To Process VariablesMhmd RobertoNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes BinderDocument166 pagesPhysics Notes BinderHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Gse 1Document3 pagesGse 1Nayan PaulNo ratings yet
- MVWLessonNotes PDFDocument1 pageMVWLessonNotes PDFHarrisonNo ratings yet
- Matter Mass Weight DensityDocument10 pagesMatter Mass Weight DensityA3 EntertainmentsNo ratings yet
- mass weight densityDocument5 pagesmass weight densityShiva Sankar BeharaNo ratings yet
- Mass Significance Physics Weight ForceDocument10 pagesMass Significance Physics Weight ForceSir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.1 Introduction To Matter and Calculations GR 8Document28 pagesLesson 2.1 Introduction To Matter and Calculations GR 8rBdNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - PROPERTIES OF MATTERDocument11 pagesModule 4 - PROPERTIES OF MATTERJBM 0531No ratings yet
- Phsyics IA Term 1 - DENSITYDocument5 pagesPhsyics IA Term 1 - DENSITYD12No ratings yet
- Mechanical Variables Measurement, Instruments and Sensor PART 1Document53 pagesMechanical Variables Measurement, Instruments and Sensor PART 1Eugene YuNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument3 pagesThermodynamicsjudith matienzoNo ratings yet
- April 20 Grade 8 Density Answers ENGDocument1 pageApril 20 Grade 8 Density Answers ENGElmaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics CIE: 1.3 Mass, Weight & DensityDocument25 pagesIGCSE Physics CIE: 1.3 Mass, Weight & Densityshiya.aayanNo ratings yet
- Static and Dynamic Chapter 1: Introduction: Norhafizah Binti Salleh 017-7722715 MANO11Document29 pagesStatic and Dynamic Chapter 1: Introduction: Norhafizah Binti Salleh 017-7722715 MANO11HawaiiChongNo ratings yet
- 8-Force, Mass, Density, AmountDocument27 pages8-Force, Mass, Density, Amountsteph curryNo ratings yet
- VMRDocument117 pagesVMRM Sandesh ShenoyNo ratings yet
- Thermo DyDocument18 pagesThermo Dykeeno manzanoNo ratings yet
- Solid and Fluids: (Physics For Engineer)Document42 pagesSolid and Fluids: (Physics For Engineer)Lee TalierNo ratings yet
- C4 Mass Weight and Density NotesDocument2 pagesC4 Mass Weight and Density NotesBlue - Devil OPNo ratings yet
- Lesson 28: Gravitational Forces: Weight Vs MassDocument3 pagesLesson 28: Gravitational Forces: Weight Vs MassGajendraNo ratings yet
- 2.8 Weight 2023Document13 pages2.8 Weight 2023Xinpei ShimNo ratings yet
- MeasurementDocument6 pagesMeasurementHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- The Perfect Answer Physics Revision Guide Edexcel IGCSE 9 1 1st EditionDocument37 pagesThe Perfect Answer Physics Revision Guide Edexcel IGCSE 9 1 1st EditionGiovi 88No ratings yet
- Properties of MatterDocument12 pagesProperties of MatterKriz ZiaNo ratings yet
- Properties of FluidDocument55 pagesProperties of Fluidmj4893968No ratings yet
- An Introduction to Mass and Weight 3rd Grade : Physics for Kids | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandAn Introduction to Mass and Weight 3rd Grade : Physics for Kids | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Potential Energy vs. Kinetic Energy - Physics Made Simple - 4th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPotential Energy vs. Kinetic Energy - Physics Made Simple - 4th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- 5.4.A Properties Geometric Solids.Document5 pages5.4.A Properties Geometric Solids.LOGAN HENSLEENo ratings yet
- 6.1.A Elements Principles of DesignDocument7 pages6.1.A Elements Principles of DesignLOGAN HENSLEENo ratings yet
- Celldivisionexplorelearningwendy Aiss Science 9 CompressDocument7 pagesCelldivisionexplorelearningwendy Aiss Science 9 CompressLOGAN HENSLEENo ratings yet
- Celldivisionexplorelearningwendy Aiss Science 9 CompressDocument7 pagesCelldivisionexplorelearningwendy Aiss Science 9 CompressLOGAN HENSLEENo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics Revision Notes For Chapter 5 - Law of MotionDocument1 pageClass 11 Physics Revision Notes For Chapter 5 - Law of MotionUday SinghNo ratings yet
- Open-Channel Flow WikiDocument3 pagesOpen-Channel Flow WikiNel Tong0% (1)
- Rectangular Beam 1VB16-300x800mm - Sagging: InputDocument4 pagesRectangular Beam 1VB16-300x800mm - Sagging: InputSiti Fatimah MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Secondary FlowDocument7 pagesSecondary Flowkallurkar23No ratings yet
- TOEFL ReadingDocument7 pagesTOEFL ReadingFredy ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Practical Use of EntropyDocument10 pagesPractical Use of EntropySantiago SeveinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Transport Eqn, EosDocument15 pagesTutorial - Transport Eqn, Eossiti azilaNo ratings yet
- Design Recommendations for Plate Girders from Lehigh UniversityDocument14 pagesDesign Recommendations for Plate Girders from Lehigh UniversityTAIYONG GUONo ratings yet
- Bossanyi 2003Document16 pagesBossanyi 2003Hamdan HamdanNo ratings yet
- Theoretical and Experimental Contactless Eddy Current Braking SystemDocument3 pagesTheoretical and Experimental Contactless Eddy Current Braking SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws Practice Ideal Gas Law Worksheet PV NRT: R 0.0821 (L Atm) / (K Mol) or R 8.31 L Kpa / (K Mole)Document5 pagesGas Laws Practice Ideal Gas Law Worksheet PV NRT: R 0.0821 (L Atm) / (K Mol) or R 8.31 L Kpa / (K Mole)Alyssa ColeNo ratings yet
- Index of Key Seismic Design ConceptsDocument11 pagesIndex of Key Seismic Design ConceptsMarie Isabella De LeonNo ratings yet
- TOM IES GATE IAS 20 Years Question and Answers by S K Mondal PDFDocument137 pagesTOM IES GATE IAS 20 Years Question and Answers by S K Mondal PDFSudhir JainNo ratings yet
- Water-Propanol-Salt Phase DiagramDocument8 pagesWater-Propanol-Salt Phase DiagramYENTHIL ALEXANDRA VALENCIA REINANo ratings yet
- Bolted Connections FundamentalsDocument75 pagesBolted Connections Fundamentalsnupur0% (1)
- En 1993-1-8Document69 pagesEn 1993-1-8atiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Finite Element MethodsDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Finite Element Methodsaap1No ratings yet
- 16700Document9 pages16700harshNo ratings yet
- RELATIVE MOTION ANALYSIS: ACCELERATION COMPONENTSDocument25 pagesRELATIVE MOTION ANALYSIS: ACCELERATION COMPONENTSJoshua D'CruzNo ratings yet
- Column Interaction CurvesDocument58 pagesColumn Interaction Curvesdbircs1981No ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Bangalore - East Physics Force and Pressure (Answer Key) Class: Viii Sec: DateDocument6 pagesDelhi Public School Bangalore - East Physics Force and Pressure (Answer Key) Class: Viii Sec: DateSaket TNo ratings yet
- Design of Hydraulic Road BlockerDocument52 pagesDesign of Hydraulic Road BlockerAbdalhady Joharji100% (1)
- Equilibrium of A ParticleDocument39 pagesEquilibrium of A ParticleTayabaNo ratings yet
- Fan Blade Design & TestingDocument6 pagesFan Blade Design & TestinggregkilatonNo ratings yet
- Similitude and Hydraulic ModelsDocument6 pagesSimilitude and Hydraulic Modelskasandra01No ratings yet
- Chemistry Presentation Report - MT2Document7 pagesChemistry Presentation Report - MT2Nisarg BediyaNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science: Compression, Tension and Shearing of RockDocument15 pagesEarth & Life Science: Compression, Tension and Shearing of Rockben beniolaNo ratings yet