Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5.4.A Properties Geometric Solids.
Uploaded by
LOGAN HENSLEEOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
5.4.A Properties Geometric Solids.
Uploaded by
LOGAN HENSLEECopyright:
Available Formats
Presentation Name Course Name
Unit # – Lesson #.# – Lesson Name
Geometric Solids
Solids are three-
dimensional objects.
• In sketching, two-
dimensional shapes are
used to create the
illusion of three-
Properties of Geometric Solids dimensional solids.
Introduction to Engineering Design © 2012 Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Properties of Solids Volume
Volume, mass, weight, density, and surface Volume (V) refers to the amount of three-
area are properties that all solids possess. dimensional space occupied by an object or
These properties are used by engineers and enclosed within a container.
manufacturers to determine material type,
cost, and other factors associated with the
design of objects.
Metric English System
cubic cubic inch
centimeter (in.3)
(cc)
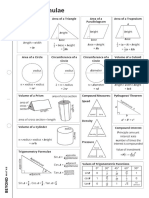
Volume of a Cube Volume of a Rectangular Prism
A cube has sides (s) of equal length. A rectangular prism has at least one side
that is different in length from the other
The formula for calculating the volume (V) of two.
a cube is:
The sides are identified as width (w), depth
(d), and height (h).
V = s3
V= s3
V= 4.0 in. x 4.0 in. x 4.0 in.
V = 64 in.3
Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Copyright 2010
1
Presentation Name Course Name
Unit # – Lesson #.# – Lesson Name
Volume of Rectangular Prism Volume of a Cylinder
The formula for calculating the volume (V) of To calculate the volume of a cylinder, its
a rectangular prism is: radius (r) and height (h) must be known.
• The formula for calculating the volume (V)
of a cylinder is:
V = wdh
V = r2h
V= wdh
V= r2h
V= 4.00 in. x 5.25 in. x 2.50 in.
V= 3.14 x (1.50 in.)2 x 6.00 in.
V = 52.5 in.3
V = 42.4 in.3
Volume of a Cone Formula Sheet
• The formula for calculating the volume (V)
of a cone is:
πr2 h 1.50
V=
3
π(0.75 in.)2 (2.00 in.)
V=
3
V = 1.18 in.3
Mass Weight
Mass (M) refers to the quantity of matter in Weight (W) is the force of gravity acting on
an object. It is often confused with the an object. It is often confused with the
concept of weight in the SI system. concept of mass in the U.S. Customary
System.
SI U.S. Customary SI U.S. Customary
System System
gram slug Newton pound
(g)
(N) (lb)
Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Copyright 2010
2
Presentation Name Course Name
Unit # – Lesson #.# – Lesson Name
Mass vs. Weight Mass vs. Weight
Contrary to popular practice, the terms mass • An object, whether on the surface of the
and weight are not interchangeable and do earth, in orbit, or on the surface of the
not represent the same concept. moon, still has the same mass.
• However, the weight of the same object
will be different in all three instances
W = mg because the magnitude of gravity is
weight = mass x acceleration due to gravity different.
(lb) (slugs) (ft/sec2)
g = 32.16 ft/sec2
Mass vs. Weight Density
• Each measurement system has fallen prey Mass Density (Dm) is an object’s mass per
to erroneous cultural practices. unit volume.
SI System
• In the SI system, a person’s weight is grams per cubic centimeter
typically recorded in kilograms when it (g/cm3)
should be recorded in Newtons.
Weight density (Dw) is an object’s weight per
• In the U.S. Customary System, an object’s
unit volume.
mass is typically recorded in pounds when
it should be recorded in slugs. U.S. Customary System
pounds per cubic inch
(lb/in.3)
Examples of Density Calculating Mass
Material Mass Density Weight Density To calculate the mass (m) of any solid, its
(g/cm3) (lb/in.3)
volume (V) and mass density (Dm) must be
Apples 0.64 0.023
known.
Water (Pure) 1.00 0.036
Water (Sea) 1.03 0.037
Ice 0.92 0.034 m = VDm
Concrete 2.40 0.087 Dm (aluminum) = 2.71 g/cm3
Aluminum 2.71 0.098
Steel (1018) 7.8 0.282 m = VDm
Gold 19.32 0.698 m = (3.81cm)(8.89 cm)(17.28 cm)(2.71 g/cm 3)
m = 1586 g = 1.59 kg
Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Copyright 2010
3
Presentation Name Course Name
Unit # – Lesson #.# – Lesson Name
Calculating Weight Area vs. Surface Area
To calculate the weight (W) of any solid, its There is a distinction between area (A) and
volume (V) and weight density (Dw) must surface area (SA).
be known.
• Area describes the measure of the two-
W = VDw dimensional space enclosed by a shape.
Dw (aluminum) = 0.098 lb/in.3 • Surface area is the sum of all the areas of
the faces of a three-dimensional solid.
W = VDw
W = 36.75 in.3 x .098 lb/in.3
W = 3.60 lb
Calculating Surface Area Calculating Surface Area
In order to calculate the surface area (SA) of Another way to represent the formula for
a rectangular prism, the area (A) of each surface area of a rectangular prism is given
faces must be known and added together. on the formula sheet.
Area A = 3.0 in. x 4.0 in. = 12 in.2
B
Area B = 4.0 in. x 8.0 in. = 32 in.2
C
Area C = 3.0 in. x 8.0 in. = 24 in.2
A D F Area D = 4.0 in. x 8.0 in. = 32 in.2
E Area E = 3.0 in. x 8.0 in. = 24 in.2
Area F = 3.0 in. x 4.0 in. = 12 in.2
Surface Area = 136 in.2
Calculating Surface Area Surface Area Calculations
What is the surface area of this rectangular
prism?
Surface Area = 2 [(8.0 in.)(4.0 in.)
+ (8.0 in.)(3.0 in.) SA = 2(wd + wh + dh)
SA = 2[(4.00 in.)(5.25 in.) + (4.00 in.)(2.50 in.) + (5.25 in.)(2.50 in.)]
+ (4.0 in.)(3.0 in.)]
= 136 in.2 SA = 2 [44.125 in.2]
SA = 88.3 in.2
Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Copyright 2010
4
Presentation Name Course Name
Unit # – Lesson #.# – Lesson Name
Calculating Surface Area Surface Area Calculations
In order to calculate the surface area (SA) of In order to calculate the surface area (SA) of
a cube, the area (A = s2) of any one of its a cylinder, the area of the curved face and
faces must be known. the combined area of the circular faces must
The formula for calculating the surface area be known.
(SA) of a cube is: SA = (2r)h + 2(r2)
SA = 6s2 SA = 2()(1.50 in.)(6.00 in.) + 2()(1.50 in.)2
SA = 56.55 in.2 + 14.14 in.2
SA = 6 (4.00 in.)2
SA = 96.0 in.2 SA = 70.7 in.2
Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Copyright 2010
5
You might also like
- G5 Q4W2 DLL MATH (MELCs)Document14 pagesG5 Q4W2 DLL MATH (MELCs)Rina MagaboNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan TemplateDocument15 pagesUnit Plan Templateapi-354426240No ratings yet
- Physics Expt 0 - Vernier and Screw GaugeDocument7 pagesPhysics Expt 0 - Vernier and Screw GaugeDebayan MaitiNo ratings yet
- GEARS SolidWorks Samples PDFDocument32 pagesGEARS SolidWorks Samples PDFHussein MohamedNo ratings yet
- Overview of An Engineering DrawingDocument23 pagesOverview of An Engineering DrawingEslam Mohammed AhmedNo ratings yet
- HW 9303 6751 G9HW2Dshapesand3DsolidsDocument58 pagesHW 9303 6751 G9HW2Dshapesand3Dsolidskhanfamily.07.02No ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document27 pagesLecture 6Green JeskNo ratings yet
- Matth DLL Q3 W5Document6 pagesMatth DLL Q3 W5Jimson Querol RiñonNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan Exemplar For Jhu FinalDocument27 pagesUnit Plan Exemplar For Jhu Finalapi-466205055No ratings yet
- T M 1649755090 Year 3 Measure Perimeter Maths Differentiated Activity Sheets - Ver - 1Document6 pagesT M 1649755090 Year 3 Measure Perimeter Maths Differentiated Activity Sheets - Ver - 1pamNo ratings yet
- Dimensions of Length: This Chapter Will Show YouDocument10 pagesDimensions of Length: This Chapter Will Show YouqarreeNo ratings yet
- Mass PropertiesDocument17 pagesMass Propertiespalaniappan_pandianNo ratings yet
- Myp Math Standard Unit 11Document4 pagesMyp Math Standard Unit 11Suran LeeNo ratings yet
- IX Final Assessment Portion 2021-2022Document22 pagesIX Final Assessment Portion 2021-2022Shreyash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Forging New Generations of EngineersDocument21 pagesForging New Generations of Engineerszmadhatter1No ratings yet
- Mathematics Intermediate Phase Term 2 Teaching Pace Setter 2020Document3 pagesMathematics Intermediate Phase Term 2 Teaching Pace Setter 2020cindyNo ratings yet
- Chinese-Maths - ShapesDocument10 pagesChinese-Maths - ShapesGloria YongNo ratings yet
- A Prism Is A 3D Shape That Has A Constant: Cross-Section Along Its LengthDocument14 pagesA Prism Is A 3D Shape That Has A Constant: Cross-Section Along Its Lengthzhu qingNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocument16 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationjxhroyNo ratings yet
- Geometric Figures & Their Formula Counterparts: Lecture by Ms. Lexi 12 Grade GeometryDocument22 pagesGeometric Figures & Their Formula Counterparts: Lecture by Ms. Lexi 12 Grade Geometryapi-544940455No ratings yet
- PerimeterDocument4 pagesPerimeterpayal jainNo ratings yet
- Linear Relations IntroDocument2 pagesLinear Relations Introapi-310503032No ratings yet
- 5.1.A 5.1.A Geometric Shapes PLTW PPTDocument5 pages5.1.A 5.1.A Geometric Shapes PLTW PPTLOGAN HENSLEENo ratings yet
- Class07 Maths NSTSE SampleDocument15 pagesClass07 Maths NSTSE SampleJ SoujanyaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 6 LAS Q4.PDF RemovedDocument10 pagesMathematics 6 LAS Q4.PDF RemovedShefa CapurasNo ratings yet
- Unit V Assembly of Parts and Product Data ExchangeDocument104 pagesUnit V Assembly of Parts and Product Data Exchangepalaniappan_pandian100% (1)
- Engineering Drawing Lecture Note PDFDocument212 pagesEngineering Drawing Lecture Note PDFrangavaliNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Lecture Note PDFDocument212 pagesEngineering Drawing Lecture Note PDFrangavaliNo ratings yet
- CAT 4 Level 8Document10 pagesCAT 4 Level 8Felix LeNo ratings yet
- Did You Do Your Homework??? 666392037Document20 pagesDid You Do Your Homework??? 666392037RaeNo ratings yet
- Maths Formulae - FoundationDocument1 pageMaths Formulae - FoundationKateNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Mensuration Perimeter Area Volume inDocument12 pagesGrade 7 Mensuration Perimeter Area Volume innitinNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Class 10 Syllabus Break Up AY 2022-23Document4 pagesMathematics Class 10 Syllabus Break Up AY 2022-23alfredo pastaNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 DLL MATH 5 Q4 Week 3Document8 pagesGrade 5 DLL MATH 5 Q4 Week 3shiela pandacNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade 10 Chrismas SchemeDocument4 pagesMathematics Grade 10 Chrismas SchemeJapheus DaSilvaNo ratings yet
- Tolarance AnalysisDocument20 pagesTolarance AnalysisMEET BHANUSHALI 19BMA0061No ratings yet
- Differential Geometry M Usman HamidDocument126 pagesDifferential Geometry M Usman HamidLuqman ArshadNo ratings yet
- Math 4 Week 7Document7 pagesMath 4 Week 7Marites MandiaNo ratings yet
- Materials: Aggregate Roundness Classification Using A Wire Mesh MethodDocument9 pagesMaterials: Aggregate Roundness Classification Using A Wire Mesh Methodragunas tatyaNo ratings yet
- Volume Elo Booster UbdDocument10 pagesVolume Elo Booster Ubdapi-317044756No ratings yet
- Finding Area and PerimeterDocument4 pagesFinding Area and PerimeterMaya NguyenNo ratings yet
- Math 4 Week 7Document7 pagesMath 4 Week 7Neriza JeanNo ratings yet
- Formal Methods: Lecture 5:set TheoryDocument19 pagesFormal Methods: Lecture 5:set TheoryStatus LifeNo ratings yet
- Length Area VolumeDocument62 pagesLength Area VolumeFatima AnwarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Basics of Geometry PDFDocument62 pagesChapter 1 - Basics of Geometry PDFArvinder Pal SinghNo ratings yet
- Q3 Week-2 Math7 DLLDocument7 pagesQ3 Week-2 Math7 DLLJo Ann Chrysol IringanNo ratings yet
- Differential Geometry.Document132 pagesDifferential Geometry.Hammad AhmadNo ratings yet
- 7.3 Finding Volume Using Cross Sections: Warm Up: Find The Area of The Following FiguresDocument11 pages7.3 Finding Volume Using Cross Sections: Warm Up: Find The Area of The Following FigurestanjanuuuuNo ratings yet
- Geometry MeasurementDocument2 pagesGeometry Measurementapi-556601115No ratings yet
- Chap 4Document12 pagesChap 4Barnabas DuferaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Exemplar: Learning Area Mathematics Learning Delivery Modality Modular Distance Modality (Learners-Led Modality)Document10 pagesLesson Exemplar: Learning Area Mathematics Learning Delivery Modality Modular Distance Modality (Learners-Led Modality)JEFFREY SORIANONo ratings yet
- 2 Marks Previous Board Exam Questions & AnswersDocument7 pages2 Marks Previous Board Exam Questions & AnswersAkhil .sNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document13 pagesChapter 15Erwin ManansalaNo ratings yet
- Exercise Short Questions F.sc. Part 1Document33 pagesExercise Short Questions F.sc. Part 1Kamran Khursheed100% (2)
- ED Engineering Drawing Lecture - 1Document25 pagesED Engineering Drawing Lecture - 1Ijaz Ahmed Khan 856-FET/BSME/F19No ratings yet
- Vernier Calipers: ObjectiveDocument7 pagesVernier Calipers: ObjectiveSURESH SURAGANINo ratings yet
- Nets - Volume - Surface Area of Prisms PDFDocument9 pagesNets - Volume - Surface Area of Prisms PDFTaseen TanvirNo ratings yet
- Q4 Wk3 Le Math5 Quines KenetteDocument4 pagesQ4 Wk3 Le Math5 Quines KenetteKenette QuinesNo ratings yet
- A Manual of Elementary Geometrical Drawing Involving Three Dimensions: In Five Divisions, Div. I. Elementary Projections Div. II. Details of Constructions in Masonry Wood, and Metal Div. III. Rudimentary Exercises in Shades and Shadows Div. IV. Isometrical Drawing Div. V. Elementary Structural DrawingFrom EverandA Manual of Elementary Geometrical Drawing Involving Three Dimensions: In Five Divisions, Div. I. Elementary Projections Div. II. Details of Constructions in Masonry Wood, and Metal Div. III. Rudimentary Exercises in Shades and Shadows Div. IV. Isometrical Drawing Div. V. Elementary Structural DrawingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Two Dimensional Geometric Model: Understanding and Applications in Computer VisionFrom EverandTwo Dimensional Geometric Model: Understanding and Applications in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Section-1: Material-Independent Property Relations: AnswersDocument20 pagesSection-1: Material-Independent Property Relations: Answersnkosana2No ratings yet
- 6 NSEP-TEST-6 Fluidsoundwave PCDocument11 pages6 NSEP-TEST-6 Fluidsoundwave PCShohom DeNo ratings yet
- JournalDocument6 pagesJournalamirpouyanNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Porosity and Fluid Constituents From Neutron and Density Logs Using An Interactive Matrix ScaleDocument12 pagesEstimation of Porosity and Fluid Constituents From Neutron and Density Logs Using An Interactive Matrix Scalereservoir_ffNo ratings yet
- Elasticity - Thermal Expansion - Calorimetry - Heat - CC - WADocument12 pagesElasticity - Thermal Expansion - Calorimetry - Heat - CC - WAHussain Ali PioneerNo ratings yet
- ASTM C-29 Bulk Density (Unit Weight) and Voids in Aggregate PDFDocument4 pagesASTM C-29 Bulk Density (Unit Weight) and Voids in Aggregate PDFNur Asriana -No ratings yet
- Reviewer in PhysicsDocument90 pagesReviewer in PhysicsLouise RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Design of High Efficiency Cyclone For Tiny Cement IndustryDocument10 pagesDesign of High Efficiency Cyclone For Tiny Cement IndustryRaji SuriNo ratings yet
- SIM4ME ThermodynamicsDocument137 pagesSIM4ME ThermodynamicsFA AyNo ratings yet
- Process Control: Pcchp4Document25 pagesProcess Control: Pcchp4Can TekinalpNo ratings yet
- 4 - Weight Volume RelationshipDocument5 pages4 - Weight Volume RelationshipmanarajNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Laws of Nature: Weighing HelpsDocument53 pagesUnderstanding The Laws of Nature: Weighing HelpsleandroniedbalskiNo ratings yet
- Servo Material Safety Data SheetsDocument329 pagesServo Material Safety Data SheetsganeshsaligramaNo ratings yet
- A. Understanding The Relationship Between Brix and Density B. Effect of Concentration and TemperatureDocument3 pagesA. Understanding The Relationship Between Brix and Density B. Effect of Concentration and TemperatureAyesha MunawarNo ratings yet
- 1st QUIZ HydraulicsDocument2 pages1st QUIZ HydraulicsDonna Cece MelgarNo ratings yet
- Density Measurement in Dairy IndustryDocument4 pagesDensity Measurement in Dairy Industryibson045001256100% (1)
- Scalar Pneumatic ConveyingDocument11 pagesScalar Pneumatic ConveyingHeiderHuerta100% (1)
- Ceng 231 Tutor 1Document11 pagesCeng 231 Tutor 1lawekushNo ratings yet
- Tank Gauging Systems (2018)Document6 pagesTank Gauging Systems (2018)sure100% (1)
- Mixing Maching For Refractory ConcreteDocument9 pagesMixing Maching For Refractory Concreteorangel anayaNo ratings yet
- Iso 7345:1997Document10 pagesIso 7345:1997Blaise Roithridh100% (1)
- FVA TUBUX M30 Rotameter Flow Meter IcDocument15 pagesFVA TUBUX M30 Rotameter Flow Meter IcSarkodie KwameNo ratings yet
- SVM 3000 With XsampleDocument8 pagesSVM 3000 With XsampleZiauddeen NoorNo ratings yet
- Unit Operation Pharmaceutical Engineering Updated 24.8.2021Document54 pagesUnit Operation Pharmaceutical Engineering Updated 24.8.2021Nusrat ZahanNo ratings yet
- Soil Science FormulasDocument2 pagesSoil Science Formulasgljae479No ratings yet
- Irjet V6i5718 PDFDocument9 pagesIrjet V6i5718 PDFIrhami UsmanNo ratings yet
- IX - Science - Physics - Ch-9 Gravitation - Assignment-6Document1 pageIX - Science - Physics - Ch-9 Gravitation - Assignment-6Shweta DuhanNo ratings yet
- Sheet 2 - Solution - EE218Document10 pagesSheet 2 - Solution - EE218NouraNo ratings yet
- J2006 - Termodinamik 1 - UNIT1Document16 pagesJ2006 - Termodinamik 1 - UNIT1Amar ZalleeNo ratings yet
- Accurate Feeder Bvd2042gbDocument8 pagesAccurate Feeder Bvd2042gbAnthonyNo ratings yet