Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geometry Measurement
Uploaded by
api-5566011150 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
67 views2 pagesOriginal Title
geometry measurement
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
67 views2 pagesGeometry Measurement
Uploaded by
api-556601115Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
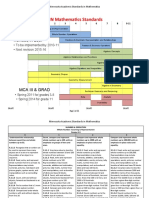
Minnesota Academic Standards in Mathematics
GEOMETRY & MEASUREMENT
Geometry: Measurement
Grades K-11
K 1 2 3 4 5
Compare and Use basic Understand length as a Understand perimeter as a Understand angle and area as Determine the area of triangles
order objects concepts of measurable attribute; use measurable attribute of measurable attributes of and quadrilaterals; determine
according to measurement in tools to measure length. real-world and mathematical real-world and mathematical the surface area and volume of
location and real-world and objects. Use various tools to objects. Use various tools to rectangular prisms in various
measurable mathematical 2.3.2.1 Understand the measure distances. measure angles and areas. contexts.
attributes. situations relationship between the size
involving length, of the unit of measurement 3.3.2.1 Use half units when 4.3.2.1 Measure angles in 5.3.2.1 Develop and use formulas
K.3.2.1 Use time and money. and the number of units measuring distances. geometric figures and real-world to determine the area of triangles,
words to needed to measure the 3.3.2.2 Find the perimeter of a objects with a protractor or parallelograms and figures that
compare 1.3.2.1 Measure length of an object. polygon by adding the lengths of angle ruler. can be decomposed into triangles.
objects the length of an 2.3.2.2 Demonstrate an the sides. 4.3.2.2 Compare angles 5.3.2.2 Use various tools and
according to object in terms understanding of the 3.3.2.3 Measure distances according to size. Classify angles strategies to measure the volume
length, size, of multiple relationship between length around objects. as acute, right and obtuse. and surface area of objects that
are shaped like rectangular
weight and copies of and the numbers on a ruler 4.3.2.3 Understand that the
prisms.
position. another object. by using a ruler to measure Use time, money and area of a two-dimensional figure
5.3.2.3 Understand that the
K.3.2.2 Order 1.3.2.2 Tell time lengths to the nearest temperature to solve real-world can be found by counting the
volume of a three-dimensional
2 or 3 objects to the hour and centimeter or inch. and mathematical problems. total number of same size
figure can be found by counting
using half-hour. square units that cover a shape the total number of same-sized
measurable 1.3.2.3 Identify Use time and money in 3.3.3.1 Tell time to the minute, without gaps or overlaps. Justify cubic units that fill a shape
attributes, pennies, nickels real-world and using digital and analog clocks. why length and width are without gaps or overlaps. Use
such as length and dimes; find mathematical situations. Determine elapsed time to the multiplied to find the area of a cubic units to label volume
and weight. the value of a minute. rectangle by breaking the measurements.
group of these 2.3.3.1 Tell time to the 3.3.3.2 Know relationships rectangle into one unit by one 5.3.2.4 Develop and use the
coins, up to one quarter-hour and distinguish among units of time. unit squares and viewing these formulas V = ℓwh and V = Bh to
dollar. between a.m. and p.m. 3.3.3.3 Make change up to one as grouped into rows and determine the volume of
2.3.3.2 Identify pennies, dollar in several different ways, columns. rectangular prisms. Justify why
nickels, dimes and quarters. including with as few coins as 4.3.2.4 Find the areas of base area B and height h are
Find the value of a group of possible. geometric figures and real-world multiplied to find the volume of a
coins and determine 3.3.3.4 Use an analog objects that can be divided into rectangular prism by breaking the
combinations of coins that prism into layers of unit cubes.
thermometer to determine rectangular shapes. Use square
equal a given amount.
temperature to the nearest units to label area
degree in Fahrenheit and measurements.
Celsius.
DRAFT DRAFT DRAFT DRAFT
Page 1 of 2
Minnesota Academic Standards in Mathematics
GEOMETRY & MEASUREMENT
Geometry: Measurement
Grades K-11
Grade 6 Grade 7 Grade 8 Grades 9-11
Calculate perimeter, area, surface area and Use reasoning with proportions Solve problems involving right Calculate measurements of plane
volume of two- and three-dimensional and ratios to determine triangles using the Pythagorean and solid geometric figures; know
figures to solve real-world and mathematical measurements, justify formulas Theorem and its converse. that physical measurements depend
problems. and solve real-world and on the choice of a unit and that they
mathematical problems 8.3.1.1 Use the Pythagorean are approximations.
6.3.1.1 Calculate the surface area and involving circles and related Theorem to solve problems
volume of prisms and use appropriate units, geometric figures. involving right triangles. 9.3.1.1 Determine the surface area
such as cm2 and cm3. Justify the formulas 8.3.1.2 Determine the distance and volume of pyramids, cones and
used. Justification may involve 7.3.1.1 Demonstrate an between two points on a spheres. Use measuring devices or
decomposition, nets or other models. understanding of the horizontal or vertical line in a formulas as appropriate.
6.3.1.2 Calculate the area of quadrilaterals. proportional relationship coordinate system. Use the 9.3.1.2 Compose and decompose
Quadrilaterals include squares, rectangles, between the diameter and Pythagorean Theorem to find two- and three-dimensional figures;
rhombuses, parallelograms, trapezoids and circumference of a circle and that the distance between any two use decomposition to determine the
kites. When formulas are used, be able to the unit rate (constant of points in a coordinate system. perimeter, area, surface area and
explain why they are valid. proportionality) is . Calculate volume of various figures.
6.3.1.3 Estimate the perimeter and area of the circumference and area of 9.3.1.3 Understand that quantities
irregular figures on a grid when they cannot circles and sectors of circles to associated with physical
be decomposed into common figures and use solve problems in various measurements must be assigned
correct units, such as cm and cm2. contexts. units; apply such units correctly in
7.3.1.2 Calculate the volume and expressions, equations and problem
surface area of cylinders and solutions that involve measurements;
justify the formulas used. and convert between measurement
systems.
9.3.1.4 Understand and apply the
fact that the effect of a scale factor k
on length, area and volume is to
multiply each by k, k2 and k3,
respectively.
9.3.1.5 Make reasonable estimates
and judgments about the accuracy of
values resulting from calculations
involving measurements.
DRAFT DRAFT DRAFT DRAFT
Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- Expanded Unit OverviewDocument3 pagesExpanded Unit Overviewapi-300394682No ratings yet
- Myp Math Standard Unit 11Document4 pagesMyp Math Standard Unit 11Suran LeeNo ratings yet
- FKB 6thgrademath Utahmiddleschoolmathproject ch5 Parent Edition WorkbookDocument110 pagesFKB 6thgrademath Utahmiddleschoolmathproject ch5 Parent Edition WorkbookSelvi RamasamyNo ratings yet
- Mathematics RevisedCurriculum 2021-2022Document9 pagesMathematics RevisedCurriculum 2021-2022iqra darNo ratings yet
- Haisham ICPDocument6 pagesHaisham ICPJijo JosephNo ratings yet
- Perimeter and AreaDocument3 pagesPerimeter and AreaEstherTangUQ恩祈No ratings yet
- Class 4 WorksheetDocument2 pagesClass 4 WorksheetYuvraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- GR 8-NumberDocument96 pagesGR 8-NumberZabrinaNo ratings yet
- Las 4 Carpentry 7 8 q3Document5 pagesLas 4 Carpentry 7 8 q3cristy olivaNo ratings yet
- M6u5 Student Friendly StandardsDocument1 pageM6u5 Student Friendly Standardsapi-366304862No ratings yet
- CAT 4 Level 8Document10 pagesCAT 4 Level 8Felix LeNo ratings yet
- Ued400 Watkins Math Final Unit PlanDocument10 pagesUed400 Watkins Math Final Unit Planapi-656628418No ratings yet
- Tp2 m 2678928 y6 Measurement Planit Maths Steps to Progression Overview English Ver 1Document10 pagesTp2 m 2678928 y6 Measurement Planit Maths Steps to Progression Overview English Ver 1Ritah NantezaNo ratings yet
- 7 MathDocument6 pages7 Mathksmxosnsod jenxisnsNo ratings yet
- Ued 400 Peltonen Kimberly Final Design Curriculum Unit MathDocument8 pagesUed 400 Peltonen Kimberly Final Design Curriculum Unit Mathapi-434364529No ratings yet
- 5 Class Area and Its BoundaryDocument2 pages5 Class Area and Its BoundaryAtifNo ratings yet
- Mathoverview 1Document3 pagesMathoverview 1api-346485577No ratings yet
- 5 Mathematics Measurement & Geometry Levels 7-10ADocument1 page5 Mathematics Measurement & Geometry Levels 7-10ADamon KeyNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Text 2015Document186 pagesTrigonometry Text 2015raduNo ratings yet
- Measure Density with UncertaintyDocument8 pagesMeasure Density with UncertaintySmilindNo ratings yet
- DLL-8th-week 41-51Document12 pagesDLL-8th-week 41-51Jerson YhuwelNo ratings yet
- Special Right Triangles: Lesson SummaryDocument4 pagesSpecial Right Triangles: Lesson SummaryEdilbert Bonifacio GayoNo ratings yet
- Class 8Document130 pagesClass 8Ajmal NayabNo ratings yet
- (DLP) RPT Modular MT KSSR SemakanDocument13 pages(DLP) RPT Modular MT KSSR SemakanScNo ratings yet
- 2023.workbook - Maths Literacy Grade 12Document12 pages2023.workbook - Maths Literacy Grade 12tinashe chirukaNo ratings yet
- Activity Sheet No. 1: Instructional Materials Usage Competencies/SkillsDocument2 pagesActivity Sheet No. 1: Instructional Materials Usage Competencies/SkillsISAGANINo ratings yet
- Day 1Document5 pagesDay 1Emelyn AbucayNo ratings yet
- (DLP) RPT MODULAR MT KSSR SEMAKAN Year 3Document14 pages(DLP) RPT MODULAR MT KSSR SEMAKAN Year 3Tamilarrasi RajamoneyNo ratings yet
- Formal of Geometry III TrimestreDocument10 pagesFormal of Geometry III TrimestreJoanis TorreglosaNo ratings yet
- 10 Maths Term 4 Unit Plan 2021Document3 pages10 Maths Term 4 Unit Plan 2021Jeremy JaquesNo ratings yet
- Presents: The Common Core State Standards Checklist Grades 3-5Document19 pagesPresents: The Common Core State Standards Checklist Grades 3-5Katt DuangmalaiNo ratings yet
- MensurationDocument1 pageMensurationrajindergoyal15No ratings yet
- Ic 1Document5 pagesIc 1api-384929754No ratings yet
- Fundamental Math Geometry GuideDocument120 pagesFundamental Math Geometry Guidefrans NgobeniNo ratings yet
- A. Geometry of Shape and Size: Geometry (3Rd Year High School)Document4 pagesA. Geometry of Shape and Size: Geometry (3Rd Year High School)Raymond Gorda100% (1)
- 10 Maths Term 4 Unit PlanDocument3 pages10 Maths Term 4 Unit PlanJeremy JaquesNo ratings yet
- 2 Grade (US) or Year 3 (UK) : A Full Month of Real Life Problem Solving!Document32 pages2 Grade (US) or Year 3 (UK) : A Full Month of Real Life Problem Solving!Jwan DelawiNo ratings yet
- Dimension PDFDocument10 pagesDimension PDFAndreGuilhermeNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Math CurriculumDocument15 pagesGrade 7 Math CurriculumBabNo ratings yet
- Maths Curriculum Year 6Document3 pagesMaths Curriculum Year 6soe myatmonNo ratings yet
- GED102 Week 5 WGN - JINGONADocument4 pagesGED102 Week 5 WGN - JINGONAFatimah Rahima JingonaNo ratings yet
- Math g2 m8 Full ModuleDocument244 pagesMath g2 m8 Full ModuleRivka ShareNo ratings yet
- School: Grade Level: Teacher: Learning Area: Teaching Dates and Time: Quarter: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument3 pagesSchool: Grade Level: Teacher: Learning Area: Teaching Dates and Time: Quarter: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayVirginia BautistaNo ratings yet
- Term 3 Maths Unit PlanDocument7 pagesTerm 3 Maths Unit Planapi-558132010No ratings yet
- SK CONVENT JALAN PEEL YEARLY LESSON PLAN FOR MATHEMATICSDocument21 pagesSK CONVENT JALAN PEEL YEARLY LESSON PLAN FOR MATHEMATICSVijayan KasturiNo ratings yet
- Geometric Measurement: Understand Concepts of Area and Relate Area To Multiplication and To AdditionDocument2 pagesGeometric Measurement: Understand Concepts of Area and Relate Area To Multiplication and To Additionapi-284190382No ratings yet
- JISMO MATH P5Document33 pagesJISMO MATH P5Astri Mustika dewiNo ratings yet
- Math 4 Week 7Document7 pagesMath 4 Week 7Marites MandiaNo ratings yet
- SD – SMP – SMA – National+/International – O Lvl Program – A Lvl ProgramDocument2 pagesSD – SMP – SMA – National+/International – O Lvl Program – A Lvl ProgramSulphiteNo ratings yet
- Math g3 m4 Topic A OverviewDocument2 pagesMath g3 m4 Topic A OverviewLama SadeddinNo ratings yet
- Algebra II m2 Topic A Lesson 4 TeacherDocument15 pagesAlgebra II m2 Topic A Lesson 4 TeacherJames SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Math 4 - 3RDQDocument23 pagesMath 4 - 3RDQMark Anthony EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Multiply & Divide Fractions: Concept SkillsDocument2 pagesUnit 5 - Multiply & Divide Fractions: Concept SkillsMegan EarlyNo ratings yet
- Yeomans CM Educ350 4 17 2022Document3 pagesYeomans CM Educ350 4 17 2022api-609846266No ratings yet
- Todhunter Trigonometry For BeginnersDocument241 pagesTodhunter Trigonometry For Beginnersnewtonfogg123No ratings yet
- Math News: 2nd Grade Math Focus Area - Topic ADocument7 pagesMath News: 2nd Grade Math Focus Area - Topic Aapi-257305841No ratings yet
- Geometry & Shapes UnderstandingDocument2 pagesGeometry & Shapes UnderstandingPiyush AgrahariNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Unit Plan: Title of Unit Grade Level Subject Time Frame Developed byDocument11 pagesTrigonometry Unit Plan: Title of Unit Grade Level Subject Time Frame Developed byapi-547915807No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document52 pagesChapter 1hem.mukhopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Geometry ShapesDocument1 pageGeometry Shapesapi-556601115No ratings yet
- 2007 Mathematics Standards by Progression 2Document21 pages2007 Mathematics Standards by Progression 2api-556601115No ratings yet
- Euclidean Geometry and ReasoningDocument2 pagesEuclidean Geometry and Reasoningapi-556601115No ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument2 pagesProbabilityapi-556601115No ratings yet
- Data AnalysisDocument2 pagesData Analysisapi-556601115No ratings yet
- Algebra in GeometryDocument1 pageAlgebra in Geometryapi-556601115No ratings yet
- Algebra Equations and InequalitiesDocument3 pagesAlgebra Equations and Inequalitiesapi-556601115No ratings yet
- Algebra Relationships and FunctionsDocument2 pagesAlgebra Relationships and Functionsapi-556601115No ratings yet
- Fraction Decimals OperationsDocument1 pageFraction Decimals Operationsapi-556601115No ratings yet
- Algebra Concepts Ratios To Proportions To FunctionsDocument1 pageAlgebra Concepts Ratios To Proportions To Functionsapi-556601115No ratings yet
- Algebra ExpressionsDocument1 pageAlgebra Expressionsapi-556601115No ratings yet
- Numbers Operation Counting RepresentationDocument1 pageNumbers Operation Counting Representationapi-556601115No ratings yet
- Fractions Decimals Representations RelationshipsDocument3 pagesFractions Decimals Representations Relationshipsapi-556601115No ratings yet
- Whole Number OperationsDocument2 pagesWhole Number Operationsapi-556601115No ratings yet
- Algebraic ExpressionsDocument2 pagesAlgebraic Expressions7A06 AZARIAH SAMUEL JNo ratings yet
- 12 11 2023 SR Super60 NUCLEUS & STERLING BT Jee Adv2022 P2 CTA 08Document21 pages12 11 2023 SR Super60 NUCLEUS & STERLING BT Jee Adv2022 P2 CTA 08dhruv1007bansalNo ratings yet
- Parametric-Curves (Examples)Document29 pagesParametric-Curves (Examples)Carolo DemoNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Mechanisms: Motion Study and AnalysisDocument82 pagesKinematics of Mechanisms: Motion Study and AnalysisDharmesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Kinds of QuadrilateralsDocument7 pagesKinds of QuadrilateralsJonard G. TrajanoNo ratings yet
- LOG TRI QB SolDocument34 pagesLOG TRI QB SolRahul JainNo ratings yet
- Inter 2nd Year Maths IIB (English Medium) 2024 Guess PaperDocument3 pagesInter 2nd Year Maths IIB (English Medium) 2024 Guess Papershaikalthaf900000No ratings yet
- Draftsman Civil - 0Document22 pagesDraftsman Civil - 0khanabdulha789No ratings yet
- Sacred Soul'S School Maths Class-Iv Attempt All The Questions Time: - 1 Hr. Max. Marks - 40Document4 pagesSacred Soul'S School Maths Class-Iv Attempt All The Questions Time: - 1 Hr. Max. Marks - 40rajurana25No ratings yet
- Www.mathkamgaroo.comDocument5 pagesWww.mathkamgaroo.comjjang203us100% (2)
- 60 Geometry Problems - Amir Hossein ParvardiDocument9 pages60 Geometry Problems - Amir Hossein ParvardiRoberto MariñosNo ratings yet
- BR Math 11Document3 pagesBR Math 11Phoenix RockiNo ratings yet
- Module 1 2nd Quarter d12Document5 pagesModule 1 2nd Quarter d12Abbie RañosaNo ratings yet
- A14 VectorsDocument8 pagesA14 Vectorsapple liew ler xinNo ratings yet
- MHT Cet Question Bank MathsDocument31 pagesMHT Cet Question Bank Maths86bqmhkypwNo ratings yet
- Congruent Triangle Proofs & CPCTCDocument14 pagesCongruent Triangle Proofs & CPCTCKimverly Ledda GanadenNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in Modern WorldDocument2 pagesMathematics in Modern WorldYzza BiblaniasNo ratings yet
- PythagoreanTheoremWorksheet PDFDocument2 pagesPythagoreanTheoremWorksheet PDFjyepezcas33% (3)
- Hanoi Open Mathematical Competition 2016: Junior SectionDocument8 pagesHanoi Open Mathematical Competition 2016: Junior Sectionscribd.thctNo ratings yet
- PythagorasDocument16 pagesPythagorasSamuel GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Parallel and Perpendicular Lines GCSE WorksheetDocument15 pagesThird Space Learning Parallel and Perpendicular Lines GCSE WorksheetAyana KhudaiberganovaNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1 MAT133 MarchAugust2023Document10 pagesAssessment 1 MAT133 MarchAugust2023さmuiNo ratings yet
- 4-Congruence and TrianglesDocument4 pages4-Congruence and TrianglesUganda Williams Jr.No ratings yet
- Homework Reviw 5Document3 pagesHomework Reviw 5Minecraft SweatNo ratings yet
- Math9 Q3 Module6Document17 pagesMath9 Q3 Module6Althea RejaeNo ratings yet
- 12th Maths Book-Chapter-7Document23 pages12th Maths Book-Chapter-7No OneNo ratings yet
- Solutions of Triangles Past SPM QuestionsDocument6 pagesSolutions of Triangles Past SPM QuestionsHo Yen SzeNo ratings yet
- Ramon Teves Pastor Memorial - Dumaguete Science High School: Prepared By: Miss Kassandra VenzueloDocument10 pagesRamon Teves Pastor Memorial - Dumaguete Science High School: Prepared By: Miss Kassandra Venzuelomarjun catanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Test BankDocument22 pagesChapter 10 Test BankNguyễn Mai HươngNo ratings yet