Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5.1.A 5.1.A Geometric Shapes PLTW PPT
Uploaded by
LOGAN HENSLEEOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
5.1.A 5.1.A Geometric Shapes PLTW PPT
Uploaded by
LOGAN HENSLEECopyright:
Available Formats
Presentation Name Course Name
Unit # – Lesson #.# – Lesson Name
Shape
Shape describes the two-dimensional
contour that characterizes an object or area,
in contrast to a three-dimensional solid.
Examples include:
Geometric Shapes and Area
Introduction to Engineering Design © 2012 Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Area Circles
Area is the extent or measurement of a A circle is a round
surface. All shapes represent enclosed two- plane figure whose
dimensional spaces and thus have area. boundary consists of
points equidistant
from the center.
Circles Area of a Circle
The circle is the simplest and strongest of all • In order to calculate the area of a circle,
the shapes. Circles are found within the the concept of (pi) must be understood.
geometry of countless engineered products, is a constant ratio that exists between
such as buttons, tubes, wires, cups, and the circumference of a circle and its
pins. A drilled hole is also based on the diameter.
simple circle.
• The ratio states that for every unit of
diameter distance, the circumference
(distance around the circle) will be
approximately 3.14 units.
Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Copyright 2010
1
Presentation Name Course Name
Unit # – Lesson #.# – Lesson Name
Area of a Circle Ellipses
To calculate the area of a circle, the radius An ellipse is generated
must be known. by a point moving in a
plane so that the sum
A=r2 of its distances from
two other points (the
foci) is constant and
≈ 3.14 equal to the major axis.
r = radius
A = area
Ellipses Polygons
A polygon is any plane figure bounded by
straight lines. Examples include the triangle,
rhombus, and trapezoid.
To calculate the area of an ellipse, the lengths
of the major and minor axis must be known.
A = ab
2a = major axis = 3.14
2b = minor axis A = area
Angles Triangles
An angle is the figure formed by the • A triangle is a three-sided polygon. The
intersection of two rays. Angles are sum of the interior angles will always equal
differentiated by their measure. 180º.
Acute Right Obtuse Straight
Less than Exactly 90º Between Exactly 180º
90º 90º and 180º
Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Copyright 2010
2
Presentation Name Course Name
Unit # – Lesson #.# – Lesson Name
Triangles Triangles
• All triangles can be classified as: • The triangle is the
• Right Triangle simplest and most
• One interior right angle structurally stable of
all polygons.
• Acute Triangle
• This is why triangles
• All interior angles are acute
are found in all types
• Obtuse Triangles of structural designs.
• One interior obtuse angle
Trusses are one such
Sign support
example. truss based on
a right triangle
Triangles Triangles
• Sometimes the terms
inscribed and
circumscribed are
associated with the
creation of triangles
and other polygons, as
well as area
Light weight space frame roof calculations.
system based on the equilateral
triangle
Area of Triangle Quadrilaterals
The area of a triangle can be calculated by A quadrilateral is a four-sided polygon.
Examples include the square, rhombus,
1 trapezoid, and trapezium:
A = 2(bh)
h
b = base
h = height
b
A = area
Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Copyright 2010
3
Presentation Name Course Name
Unit # – Lesson #.# – Lesson Name
Parallelograms Parallelograms
A parallelogram is a four- The area of a
sided polygon with both parallelogram can be
pairs of opposite sides calculated by
parallel. Examples
include the square, A = bh h
rectangle, rhombus, and
rhomboid. b = base
h = height
A = area
Multisided Regular Polygons Multisided Regular Polygons
A regular polygon is a A regular polygon can
polygon with all sides be inscribed in a circle
equal and all interior
angles equal. • An inscribed polygon is a
polygon placed inside a circle
so that all the vertices of the
polygon lie on the
circumference of the circle
Multisided Regular Polygons Regular Multisided Polygon
A regular polygon can Examples of regular multisided polygons
also circumscribe include the pentagon, hexagon, heptagon,
around a circle. and octagon.
• A circumscribed polygon is a
polygon placed outside a
circle so that all of sides of
the polygon are tangent to
the circle
Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Copyright 2010
4
Presentation Name Course Name
Unit # – Lesson #.# – Lesson Name
Multisided Polygons Multisided Polygons
The area of a multisided Area calculation of a
regular polygon can be multisided regular
calculated if a side polygon:
length and the number
of sides is known. A = area
s = side length
n = number of sides
Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Copyright 2010
5
You might also like
- Healthy Life Style 3Document10 pagesHealthy Life Style 3Chelsea AikoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Essential of GeometryDocument14 pagesChapter 1 Essential of GeometryNina HNo ratings yet
- Gr8 Math Notes (ch25)Document5 pagesGr8 Math Notes (ch25)Akshara ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- CircumferenceDocument10 pagesCircumferenceyetriNo ratings yet
- Geometry Team 10 - Bip-2Document23 pagesGeometry Team 10 - Bip-2Rosiana RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Math 7Document7 pagesWeek 7 Math 7Girlie Mae FloresNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Circle PresentationDocument14 pagesParts of A Circle Presentationromar.allen73No ratings yet
- Area Wiki PDFDocument6 pagesArea Wiki PDFgooglepleckNo ratings yet
- Topik-2 Bulatan CircleDocument36 pagesTopik-2 Bulatan Circle许如楠No ratings yet
- CircleDocument11 pagesCircleKathleen Bermejo CatainNo ratings yet
- Circle (Parts, Circumference, and Area)Document12 pagesCircle (Parts, Circumference, and Area)Jerry Mae RanesNo ratings yet
- Solid Mensuration REVIEWERDocument5 pagesSolid Mensuration REVIEWER21-07543No ratings yet
- Basic Geometry - Summer of 2023 H.WDocument11 pagesBasic Geometry - Summer of 2023 H.WFizah MNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Quarter 2 Module 3Document14 pagesMath 10 Quarter 2 Module 3Meizen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Circles and Circumference: Lesson 9-5Document10 pagesCircles and Circumference: Lesson 9-5Irene LebrillaNo ratings yet
- Shape Descriptors SurveyDocument25 pagesShape Descriptors SurveyVikrant ViksNo ratings yet
- Circles IntroductionDocument1 pageCircles IntroductionNelda OabelNo ratings yet
- Parts of Circles (Read) Geometry CK-12 FoundationDocument1 pageParts of Circles (Read) Geometry CK-12 FoundationJohn Thiery FedericoNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Session 4 CircleDocument57 pagesGrade 10 Session 4 CirclemarlonNo ratings yet
- Q2 LAS4 Secants Tangent and SecantsDocument3 pagesQ2 LAS4 Secants Tangent and SecantsJayvee MagnayeNo ratings yet
- S1-2 Key Points: Part II: Measures, Shape and Space StrandDocument44 pagesS1-2 Key Points: Part II: Measures, Shape and Space StrandCharlotteNo ratings yet
- Viva Questions PDFDocument5 pagesViva Questions PDFADARSH RAJNo ratings yet
- Glossary (Extended)Document23 pagesGlossary (Extended)bugsbunny82No ratings yet
- Plane and Solid MensurationDocument48 pagesPlane and Solid Mensuration1900248No ratings yet
- MELVINDocument16 pagesMELVINRosito BaragoNo ratings yet
- COLLEGE PREP Section 10.1/10.2: Distance & Midpoint Formulas, and Circ LesDocument3 pagesCOLLEGE PREP Section 10.1/10.2: Distance & Midpoint Formulas, and Circ LesAml AmlNo ratings yet
- Surveying NotesDocument39 pagesSurveying NotesInhen Yero75% (4)
- Circles Pythagoras and Trigonometry The Secondary VersionDocument91 pagesCircles Pythagoras and Trigonometry The Secondary VersionTonluck Kaimak100% (1)
- Math 1Document3 pagesMath 1Yuki YoshidaNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan Exemplar For Jhu FinalDocument27 pagesUnit Plan Exemplar For Jhu Finalapi-466205055No ratings yet
- Las Mathematics 10 Week 2 Quarter 2 Jonathan D NunagDocument9 pagesLas Mathematics 10 Week 2 Quarter 2 Jonathan D NunagJONATHAN NUNAGNo ratings yet
- Circle TheoremDocument5 pagesCircle TheoremJadesola AwosikaNo ratings yet
- 2 Marks Previous Board Exam Questions & AnswersDocument7 pages2 Marks Previous Board Exam Questions & AnswersAkhil .sNo ratings yet
- Points, Lines, Angles, and Parallel LinesDocument14 pagesPoints, Lines, Angles, and Parallel LinesShafika Aida100% (2)
- Hand-Out No. 1Document2 pagesHand-Out No. 1Mark Joefill SalgadoNo ratings yet
- Geometric Design of Highways 2 - Horizontal AlignmentDocument35 pagesGeometric Design of Highways 2 - Horizontal Alignmentrodge macaraegNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. CircleDocument18 pagesChapter 7. CirclealkristiyantoNo ratings yet
- PRE CALCULUS Q2 Angle Measures in A Unit Circle Standard Position of Angles and Its Coterminal AnglesDocument16 pagesPRE CALCULUS Q2 Angle Measures in A Unit Circle Standard Position of Angles and Its Coterminal AnglesekloymontecalvoNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Perimeters Areas and Geometric FiguresDocument7 pagesTopic 2 Perimeters Areas and Geometric FiguresMatias ArevaloNo ratings yet
- CO1 CircleDocument57 pagesCO1 CircleReinabelle Marfil MarquezNo ratings yet
- Plane and Solid GeomDocument251 pagesPlane and Solid Geomalagonmiles06No ratings yet
- Worksheet Q3 Week 6Document2 pagesWorksheet Q3 Week 6Jaybie Tejada100% (1)
- Mensuration Tricks and TipsDocument40 pagesMensuration Tricks and TipsShobha AkulaNo ratings yet
- Eg BitsDocument15 pagesEg Bitsashishgandi2005No ratings yet
- Solid Geometry: Clarita R. GuevaraDocument157 pagesSolid Geometry: Clarita R. GuevaraJoshua Saldaña100% (1)
- CO1 CircleDocument50 pagesCO1 CircleReinabelle Marfil Marquez100% (1)
- Properties of A ParallelogramDocument7 pagesProperties of A ParallelogramKristel Mae CaveroNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of A Circles and Its Related TermsDocument22 pagesBasic Concepts of A Circles and Its Related TermsAngelica MontezonNo ratings yet
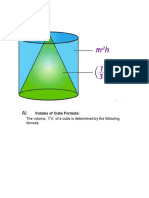
- The Volume,, of A Cube Is Determined by The Following FormulaDocument12 pagesThe Volume,, of A Cube Is Determined by The Following FormulaMolla DerbewNo ratings yet
- Relationships Among Chords, Arcs, Central Angles, and Inscribed AnglesDocument12 pagesRelationships Among Chords, Arcs, Central Angles, and Inscribed AnglesMobile legends gamer100% (2)
- 7.1 Circle Vocab and Radians Notes-BlankDocument2 pages7.1 Circle Vocab and Radians Notes-BlankDNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS (Part 3) - Raditya NuartaDocument4 pagesMATHEMATICS (Part 3) - Raditya NuartaDepok PutraCVNo ratings yet
- 4.properties of Shapes PDFDocument17 pages4.properties of Shapes PDFDanish AimanNo ratings yet
- Determining Density: Matter: Mass vs. Weight Matter: Mass vs. WeightDocument3 pagesDetermining Density: Matter: Mass vs. Weight Matter: Mass vs. WeightLOGAN HENSLEENo ratings yet
- 5.4.A Properties Geometric Solids.Document5 pages5.4.A Properties Geometric Solids.LOGAN HENSLEENo ratings yet
- 6.1.A Elements Principles of DesignDocument7 pages6.1.A Elements Principles of DesignLOGAN HENSLEENo ratings yet
- Celldivisionexplorelearningwendy Aiss Science 9 CompressDocument7 pagesCelldivisionexplorelearningwendy Aiss Science 9 CompressLOGAN HENSLEENo ratings yet
- Celldivisionexplorelearningwendy Aiss Science 9 CompressDocument7 pagesCelldivisionexplorelearningwendy Aiss Science 9 CompressLOGAN HENSLEENo ratings yet
- MCQ MicrosDocument5 pagesMCQ Microsamitrameshwardayal50% (2)
- Fluid Mechanics Is The Branch of Physics and Engineering That Studies The Behavior of FluidsDocument2 pagesFluid Mechanics Is The Branch of Physics and Engineering That Studies The Behavior of FluidsIkechukwu OkekeNo ratings yet
- Serway - Quiz RapidosDocument19 pagesSerway - Quiz RapidosJuan Sebastian Quimbayo GomezNo ratings yet
- Manual Deron 1Document15 pagesManual Deron 1Cristian OrtuzarNo ratings yet
- Paper 2-Y6Document13 pagesPaper 2-Y6shinyNo ratings yet
- Venturimeter: Aim:-Apparatus RequiredDocument4 pagesVenturimeter: Aim:-Apparatus RequiredChibuike CharlesNo ratings yet
- PPT07 Electric Potential and CapacitorDocument35 pagesPPT07 Electric Potential and CapacitorNovita Sari GultomNo ratings yet
- Fisa Diesis Evo 24v 1010251Document1 pageFisa Diesis Evo 24v 1010251taurusland6996No ratings yet
- Ieee Paper 1Document5 pagesIeee Paper 1Chandan LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Wa0000.Document52 pagesWa0000.akashrathor19115No ratings yet
- Yearly Lesson Plan 2014 Physics Form 4 Alamanda & 4 Blossom: Tingkatan 4Document8 pagesYearly Lesson Plan 2014 Physics Form 4 Alamanda & 4 Blossom: Tingkatan 4GeraldJoelBillihNo ratings yet
- Shs Grade 11 - TVL SmawDocument34 pagesShs Grade 11 - TVL SmawLara Jeane Losbañes100% (3)
- Special Topics Lecturers Physics 10 THX - EsguerraDocument3 pagesSpecial Topics Lecturers Physics 10 THX - EsguerraHarold CoNo ratings yet
- Alarmes - Soluções FONTE LASER IPGDocument21 pagesAlarmes - Soluções FONTE LASER IPGRoger Flores100% (1)
- Radar Report by HBPDocument61 pagesRadar Report by HBPKumar MaheshNo ratings yet
- Automatic Labeling Machine and MethodDocument14 pagesAutomatic Labeling Machine and MethodHùng ThanhNo ratings yet
- Catalogue - Proflex Disc DiffuserDocument2 pagesCatalogue - Proflex Disc DiffuserAzhar MandhraNo ratings yet
- Engineering Practice Lab Manual (Electrical and Electronics)Document55 pagesEngineering Practice Lab Manual (Electrical and Electronics)Maheswaran Umaiyorupagan70% (10)
- Allison Taylor Dissertation Heinrich SchliemannDocument6 pagesAllison Taylor Dissertation Heinrich SchliemannPaperWritingServiceSuperiorpapersSpringfield100% (1)
- RF24FSEDBSR AA Samsung Refrigerator Service Manual PDFDocument130 pagesRF24FSEDBSR AA Samsung Refrigerator Service Manual PDFLynn Boyd78% (9)
- Reliability Problems Synthesis Compressor-Drive TurbineDocument10 pagesReliability Problems Synthesis Compressor-Drive TurbineSoumitra GuptaNo ratings yet
- Karma ChameleonDocument36 pagesKarma ChameleonAngelica CamilonNo ratings yet
- High Volteage EngineeringDocument5 pagesHigh Volteage EngineeringSenthil NathanNo ratings yet
- Air - Prandtl NumberDocument12 pagesAir - Prandtl NumberHew LetNo ratings yet
- Design, Construction and Testing of A Dry Sand Sieving Machine Oladeji Akanni OgunwoleDocument3 pagesDesign, Construction and Testing of A Dry Sand Sieving Machine Oladeji Akanni OgunwoleRex Sotelo BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Society of Young Engineers Towards Achieving ExcellenceDocument4 pagesSociety of Young Engineers Towards Achieving ExcellenceAslagNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01 Introduction To Sinusoidal WaveformsDocument6 pagesLecture 01 Introduction To Sinusoidal WaveformsOnofre Algara Jr.No ratings yet
- ESR-3037 Simpson Strong-BoltDocument17 pagesESR-3037 Simpson Strong-BoltKen SuNo ratings yet
- DS - 20211207 - MVS8960-LV Datasheet - Preliminary - V12 - ENDocument2 pagesDS - 20211207 - MVS8960-LV Datasheet - Preliminary - V12 - ENNguyễn Công ThànhNo ratings yet
- Seismic Resistance of Type 2 Exterior Beam-ColumnDocument10 pagesSeismic Resistance of Type 2 Exterior Beam-ColumnMarimuthu Kaliyamoorthy100% (1)