Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anemia DX TX
Uploaded by
Prosanjit MajumderOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anemia DX TX
Uploaded by
Prosanjit MajumderCopyright:
Available Formats
Yan Yu, 2012 (www.yanyu.
ca)
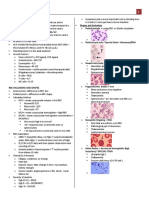
Anemia ([Hgb] < 120g/L)
(Average MCV, CBC, and reticulocyte count assists with diagnosis!)
Microcytic Normocytic Macrocytic
(MCV < 80fL) (MCV 80-100fL) (MCV > 100fL)
(↓ heme or globin synthesis) (RBCs lost, or less RBCs produced) (↓DNA synthesis, ↓ cell division)
Lead poisoning
(basophillic
stippling, Rule out Reticulocytosis
sideroblasts) Normal/high WBCs Low WBCs
(↑ #s of reticulocytes in blood, due to hemolysis or
acute bleeding, may ↑ MCV)
Iron deficiency
(Ferritin low, Reticulocytes: High
Fe low, TIBC high, Fe/TIBC Low/inappropriately reticulocytes High Low/normal Normal blood smear Abnormal blood
<18%, normal (Polychromatic reticulocytes reticulocytes Drugs (can often mimic smear Dysplasia (i.e.
Low retics -↑ w/ Tx, macrocytes) (marrow is fine) B12/folate deficiencies) Myelodysplasia –
(marrow is fine) bi-lobed
hypochromic RBCs, spoon Anemia of Chronic Look at blood neutrophils)
nails, pica, stomatitis, disease/inflammation smear!
glossy tongue) (Ferritin high, Marrow aplasia,
Splenomegaly/ Oval macrocytes, RBCs in Rouleaux
Assoc w/ celiac Fe low, TIBC low, Fe/TIBC Early Fe deficiency Hypersplenism (10
suppression, or
>18% (low-normal)) ↓ EPO (Hypothyroid (↓ infiltration Hyper-segmented formation (multiple
Thalassemia and 20) neutrophils, low retics myeloma) – false ↑ in MCV
TSH), renal failure) (pancytopenia)
MCV <73fL (very low!) Cancer (i.e. multiple B12/Folate deficiency (but ↑ after Tx), due to RBC agglutination
Ferritin/Fe/TIBC all normal, myeloma) pancytopenia,
Mediterranean/African/SE Asian megaloblastic anemia in Target cells, normal WBCs
Pregnancy (RBC dilution)
marrow Liver disease (more lipids in RBC
Abnormal Hb membrane)
↑HbA2, HbE (unstable
Normal HbA B-globin mut’n)
β-thal Low RBC folate, Low Serum B12
Normal RBCs: RBC spherocytes/ Abnormal RBCs High Hcy only
minor High Hcy, high MMA,
↑ ↑ HbH (β4), HbH Acute bleed schistocytes: infarct spleen (alcoholic?) (red tongue)
bodies, worse hemolysis Autoimmune or Sickle cells, target Folate deficiency, ↑ B12 deficiency,
anemia Hereditary spherocytosis cells, howell-jolly need, malabsorption
↑HbA2, ↑ HbF, malabsorption, ↑ need
HbH disease (3 α- Microangiopathic bodies Corrected w/ IF
NO HbA; hemolytic anemia Hemoglobinopathy (pernicious anemia:
globin gene
Hemolysis (MAHA): DIC, TTP, HUS (HbS, HbE, HbC) antibodies against
deletions) Not corrected w/ IF
triad, erythroid (HbE can be microcytic) IF/parietal cells)
bone expansion ↑ HbH (β4)
β-thal major α-thal trait (2 α- parasites
globin gene 4 α-globin gene
In >50yr old with normocytic/macrocytic No terminal ileum
deletions) deletions = hydrops
anemia, high calcium, bone pain, renal (Crohn's, celiac, deficiency, pancreatic disease Low stomach acid
fetalis; Hb Barts (γ4)!
issues/low albumin multiple myeloma resections) ↑ need, (no proteases) (esp in elderly)
Yan Yu, 2012 (www.yanyu.ca)
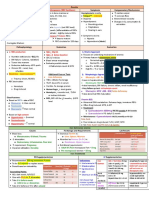
Anemia ([Hgb] < 120g/L)
Treatments
Microcytic Normocytic Macrocytic
(MCV < 80fL) (MCV 80-100fL) (MCV > 100fL)
Lead poisoning Rule out Reticulocytosis
(lead chelation)
Normal/high WBCs Low WBCs (pancytopenia)
Iron deficiency
oral iron (high dose, low Low/normal
compliance) retics High retics High retics Low/normal Normal blood smear Abnormal blood
IM/IV iron (for low oral (polychromasia) retics remove offending drug smear
tolerance, permanent iron Dysplastic (i.e.
malabsorption) Anemia of CD Myelodysplasia)
treat underlying disorder
Splenomegaly/
Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs): Folate Deficiency
Hypersplenism RBCs in Rouleaux
EPO, darbepoietin oral supplement
Thalassemia treat underlying Infiltrative (acute formation (stacked like
transfusion (rarely needed) rarely parenternal
Dx: Ethnicity, family Hx, blood spleen issue leukemia) chips – multiple myeloma)
smear (HbH bodies), HPLC, Hgb chemo/
electrophoresis hormonal cancer tx Aplastic anemia
stop causative agents & Target cells, normal WBCs
supplement B12/Folate. fix liver disease
HbE
Suppress T-Cells w/
Antithymocyte Globulin,
β-thalassemia
α-thal trait steroids, cyclosporin B12-deficiency
seen only after 6 mon Normal RBCs: RBC spherocytes/ Sickle-cell Anemia (HbSS):
No Tx Stem cell transplant
of life (after γ-globins Acute bleed, schistocytes: Sx: 1) vaso-occlusion of supportive care IF-treatment
stop being made) HbH disease AutoImmune or spleen, hands/feet, liver,
hemolysis (transfuse, antibiotics, etc)
High HbA2, HbF No Tx For pernicious
Hereditary brain, bones...; 2) hemolysis
anemia
spherocytosis – RBCs abnormal; 1+2 3) Not corrected w/ IF
Microangiopathic end-organ damage
β-thal major hemolytic anemia Dx: HPLC, Hgb
β-thal (MAHA) electrophoresis IM B12 injections Oral B12 (high dose,
smear: target cells, Minor Tx: prevent infection w/ (replenish stores) 1000ug)
nucleated RBCs B/B0 abx, hydration, pain control, (1% not absorbed
Tx: lifelong or B/B+ O2 (↓ sickling), transfusion, through IF pathway)
transfusion w/ iron no Tx
chelation (IV or oral) avoid hypoxia, immunization
re encapsulated bacteria.
You might also like
- 1001 Common Words in OET Exam Mini-DictionaryDocument38 pages1001 Common Words in OET Exam Mini-DictionaryProsanjit Majumder94% (18)
- Matchstick MenDocument9 pagesMatchstick Menmichael_arnesonNo ratings yet
- PoikilocytosisDocument3 pagesPoikilocytosisJasonNo ratings yet
- Rapini DermatopatologíaDocument474 pagesRapini DermatopatologíadrNo ratings yet
- Project NewDocument33 pagesProject Newceeyem83% (12)
- RBC DisordersDocument8 pagesRBC DisordersDavid JohnNo ratings yet
- Anemia Differential Diagnosis : Microcytic Normocytic MacrocyticDocument1 pageAnemia Differential Diagnosis : Microcytic Normocytic Macrocyticمحمد عقيلي100% (1)
- Systematic Approach in Anemia Evaluation and Review of Peripheral SmearsDocument72 pagesSystematic Approach in Anemia Evaluation and Review of Peripheral SmearsSukma Eka PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Anemia SDocument8 pagesAnemia SCarlo SantosNo ratings yet
- RED CELL MORPHOLOGY Tabulation SummaryDocument6 pagesRED CELL MORPHOLOGY Tabulation SummaryStephen YorNo ratings yet
- Basic HematologyDocument69 pagesBasic HematologyDimas Bayu FirdausNo ratings yet
- Overview of AnaemiaDocument2 pagesOverview of AnaemiaGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Reticulocyte Count: Esr: RBC Count: Reticulocyte Count: Low For Reticulocyte Count: Platelet Count: Packed Reticulocyte CountDocument3 pagesReticulocyte Count: Esr: RBC Count: Reticulocyte Count: Low For Reticulocyte Count: Platelet Count: Packed Reticulocyte CountVarshaa BharathiNo ratings yet
- Blood FilmDocument2 pagesBlood FilmGerardLum100% (1)
- RBC ANOMALIES AND INCLUSIONS With Their Associated DiseasesDocument2 pagesRBC ANOMALIES AND INCLUSIONS With Their Associated DiseasesCamella Beatrice Lujan ValleNo ratings yet
- Hematology 101: Interpreting Lab Results - Patterns and PitfallsDocument55 pagesHematology 101: Interpreting Lab Results - Patterns and PitfallsAmorrita Puspita Ratu100% (1)
- Anemia TutoringDocument28 pagesAnemia TutoringngNo ratings yet
- Poikilocytosis Review TableDocument5 pagesPoikilocytosis Review Tablekat100% (1)
- TrW-Guwv 0g VwhuPGl65PBCquGkt3j5Document65 pagesTrW-Guwv 0g VwhuPGl65PBCquGkt3j5Shikhar MishraNo ratings yet
- Approach To Anemia: - Reticulocyte Count Is Most Important TestDocument15 pagesApproach To Anemia: - Reticulocyte Count Is Most Important TestJanella SuerteNo ratings yet
- Degenevie - HematologyDocument71 pagesDegenevie - Hematologykkq7fhkwvkNo ratings yet
- Cara Mendiagnose AnemiaDocument1 pageCara Mendiagnose AnemiaMuchlissatus Lisa MedicalbookNo ratings yet
- Amboss Hemolytic AnemiaDocument16 pagesAmboss Hemolytic AnemiaAhmed Ali100% (2)
- Clinical Haematology-Lecture SlidesDocument55 pagesClinical Haematology-Lecture SlidesShiv Sookun100% (1)
- Red and White Blood Cell DisordersDocument11 pagesRed and White Blood Cell DisordersVittorio Di PaoloNo ratings yet
- Microcytic anaemia types and causesDocument7 pagesMicrocytic anaemia types and causesJason AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathology CBC GuideDocument38 pagesClinical Pathology CBC Guideyeshitla amsaluNo ratings yet
- Zako HematologyDocument35 pagesZako Hematologydoctormehmeteren8292No ratings yet
- An Approach To Anemia: Brad Lewis Director Hematology San Francisco General HospitalDocument47 pagesAn Approach To Anemia: Brad Lewis Director Hematology San Francisco General HospitalyapponNo ratings yet
- Anemia Workup - Approach Considerations, Investigation For Pathogenesis, Evaluation For Blood LossDocument14 pagesAnemia Workup - Approach Considerations, Investigation For Pathogenesis, Evaluation For Blood LossRahul SahadevanNo ratings yet
- 9 Hema Extrinsic RBC DefectsDocument2 pages9 Hema Extrinsic RBC DefectsGwen Kirsten AtayanNo ratings yet
- Anemia - AMBOSSDocument2 pagesAnemia - AMBOSStgayuNo ratings yet
- Anemia OutlineDocument3 pagesAnemia Outlinekaylakmills_10135868No ratings yet
- AnaemiaDocument7 pagesAnaemiaYousef El3alameyNo ratings yet
- Update On (Approach To) AnemiaDocument44 pagesUpdate On (Approach To) AnemiaIsaac MwangiNo ratings yet
- Anemia BloodDocument29 pagesAnemia BloodDalia EzzeddineNo ratings yet
- Hematology: Presented by Alyazeed Hussein, BSCDocument96 pagesHematology: Presented by Alyazeed Hussein, BSCMONFOLANo ratings yet
- Week 4 - HandoutDocument4 pagesWeek 4 - Handoutjess waldenNo ratings yet
- Patho HematologyDocument39 pagesPatho HematologyCastleKGNo ratings yet
- Anemia in Children: Causes, Types and TreatmentDocument61 pagesAnemia in Children: Causes, Types and TreatmentSamuel ManurungNo ratings yet
- Anemia - AmbossDocument10 pagesAnemia - AmbossGuga XachidzeNo ratings yet
- RBC anomalies-ANEMIADocument19 pagesRBC anomalies-ANEMIAJeremiahNo ratings yet
- Hema 2 Prelims MergedDocument26 pagesHema 2 Prelims MergedMYLENE POSTREMONo ratings yet
- Hematology 2 PrelimsDocument17 pagesHematology 2 PrelimsMYLENE POSTREMONo ratings yet
- Diagnosis Laboratorium ThalassemiaDocument36 pagesDiagnosis Laboratorium ThalassemiairanifianzaNo ratings yet
- RBC Morphology and InclusionsDocument3 pagesRBC Morphology and InclusionsDeomicah SolanoNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument2 pagesAnemiaRed DiggerNo ratings yet
- Physiology Lab V2Document14 pagesPhysiology Lab V2Mohammed EljackNo ratings yet
- Super Simplified Pathology Hematology - Dr. Priyanka SachdevDocument500 pagesSuper Simplified Pathology Hematology - Dr. Priyanka SachdevMohd SaquibNo ratings yet
- Anemia Testing Algorithm PDFDocument1 pageAnemia Testing Algorithm PDFBilly AuNo ratings yet
- Anemia Testing Algorithm PDFDocument1 pageAnemia Testing Algorithm PDFkatNo ratings yet
- Anemia Flow ChartDocument1 pageAnemia Flow ChartCynthiaNo ratings yet
- AnaemiaDocument83 pagesAnaemiadoc19019696No ratings yet
- 20.guidelines AnaemiaDocument5 pages20.guidelines AnaemiaRed DevilNo ratings yet
- Intravascular Extravascular: Fe Storage Tibc SerumDocument2 pagesIntravascular Extravascular: Fe Storage Tibc Serumazhar hussinNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approach: Anemia in ChildhoodDocument30 pagesClinical Approach: Anemia in ChildhoodYuffaa AinayyaaNo ratings yet
- Hematology: AnemiaDocument46 pagesHematology: AnemiaCyrus100% (1)
- Undergraduates—Medicine: Diagnosing Megaloblastic AnemiasDocument30 pagesUndergraduates—Medicine: Diagnosing Megaloblastic AnemiasAishwarya JeeNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Leucemia: Desde la mutación genética inicial hasta el apoyo para la supervivenciaFrom EverandFast Facts: Leucemia: Desde la mutación genética inicial hasta el apoyo para la supervivenciaNo ratings yet
- Basic Needs and Comfort MeasuresDocument73 pagesBasic Needs and Comfort MeasuresProsanjit MajumderNo ratings yet
- Pain ManagementDocument20 pagesPain ManagementProsanjit MajumderNo ratings yet
- Ielts & Toefl: Vocabulary Master ClassDocument18 pagesIelts & Toefl: Vocabulary Master ClassProsanjit MajumderNo ratings yet
- IELTS & TOEFL Vocabulary Master Class: 900+ Words to Boost Your ScoreDocument39 pagesIELTS & TOEFL Vocabulary Master Class: 900+ Words to Boost Your ScoreProsanjit Majumder0% (1)
- FWZ© Weáwß: Gv÷Vi Ae Cvewjk NJDocument3 pagesFWZ© Weáwß: Gv÷Vi Ae Cvewjk NJProsanjit MajumderNo ratings yet
- HR Specialist's ResumeDocument1 pageHR Specialist's ResumeProsanjit MajumderNo ratings yet
- FWZ© Weáwß: Gv÷Vi Ae Cvewjk NJDocument3 pagesFWZ© Weáwß: Gv÷Vi Ae Cvewjk NJProsanjit MajumderNo ratings yet
- Basic Science: Introduction To Science of BIOLOGYDocument5 pagesBasic Science: Introduction To Science of BIOLOGYProsanjit MajumderNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of Whole BodyDocument60 pagesBlood Supply of Whole BodyProsanjit Majumder100% (1)
- Candidate Guide To MRCS Examination July2018 PDFDocument51 pagesCandidate Guide To MRCS Examination July2018 PDFBakri MustafaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pediatric NursingDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Pediatric NursingProsanjit MajumderNo ratings yet
- Speaking Sub-Test Overview PDFDocument10 pagesSpeaking Sub-Test Overview PDFProsanjit MajumderNo ratings yet
- 100 Cases in General Practice 1st PDFDocument224 pages100 Cases in General Practice 1st PDFfunandlearningNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Lecture Notes ExplainedDocument108 pagesCell Biology Lecture Notes ExplainedpandaprasadNo ratings yet
- Roleplay Tasks PDFDocument5 pagesRoleplay Tasks PDFProsanjit MajumderNo ratings yet
- Roleplay Tasks PDFDocument5 pagesRoleplay Tasks PDFProsanjit MajumderNo ratings yet
- ABC of ICU by Mansdocs PDFDocument62 pagesABC of ICU by Mansdocs PDFProsanjit MajumderNo ratings yet
- Writing Assessment Criteria & FormatDocument15 pagesWriting Assessment Criteria & FormatProsanjit Majumder100% (1)
- Study Tips and Skill BuildingDocument6 pagesStudy Tips and Skill BuildingProsanjit MajumderNo ratings yet
- Writing Difficult Words-1Document11 pagesWriting Difficult Words-1Prosanjit Majumder100% (1)
- Medical Health Manager Job ApplicationDocument1 pageMedical Health Manager Job ApplicationProsanjit MajumderNo ratings yet
- English Grammar SecretsDocument66 pagesEnglish Grammar SecretsMbatutes94% (33)
- Pedi NotesDocument49 pagesPedi NotesProsanjit MajumderNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol Drug StudyDocument5 pagesParacetamol Drug StudyMatty Jolbitado50% (2)
- Problem TreeDocument1 pageProblem Treeyel5buscatoNo ratings yet
- ChlorphromazineDocument2 pagesChlorphromazineanreilegardeNo ratings yet
- 22 Phil 227 Bagtas Vs PaguioDocument4 pages22 Phil 227 Bagtas Vs PaguioGina Portuguese GawonNo ratings yet
- Sign Symptoms Ketoacidosis DiabeticDocument4 pagesSign Symptoms Ketoacidosis DiabeticMatthew NathanielNo ratings yet
- Geria ReviewerDocument2 pagesGeria ReviewerbillyktoubattsNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Assess Prep in AnesthesiaDocument26 pagesPreoperative Assess Prep in AnesthesiaShimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- ALBINISMDocument3 pagesALBINISMLawrence CezarNo ratings yet
- Rajinikanth: "Rajini" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeDocument15 pagesRajinikanth: "Rajini" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeArun SekarNo ratings yet
- Factors That Affect Physical DevelopmentDocument4 pagesFactors That Affect Physical DevelopmentmomuNo ratings yet
- Herbarium of IndiaDocument7 pagesHerbarium of IndiaStephanie MooreNo ratings yet
- Final Assessment Report Allium Sativum L Bulbus - enDocument90 pagesFinal Assessment Report Allium Sativum L Bulbus - enWidiyastuti DarwisNo ratings yet
- What Is Polio?: SymptomsDocument2 pagesWhat Is Polio?: SymptomsJP LandagoraNo ratings yet
- Acute Bronchitis Case StudyDocument6 pagesAcute Bronchitis Case Studyulka0750% (2)
- NBME Form 1 Step 2 ReviewDocument77 pagesNBME Form 1 Step 2 Reviewalex karevNo ratings yet
- Pneumokokus Dan Penyakit Pneumokokus - Ari PrayitnoDocument36 pagesPneumokokus Dan Penyakit Pneumokokus - Ari PrayitnoIndri MmrNo ratings yet
- High Prevalence of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Among People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in A Tertiary Care CenterDocument5 pagesHigh Prevalence of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Among People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in A Tertiary Care CenterPcrNo ratings yet
- Best ENT Surgeon in Hyderabad - ENT HospitalDocument14 pagesBest ENT Surgeon in Hyderabad - ENT HospitalMagnasVNo ratings yet
- Rare blistering skin condition linked to gluten intoleranceDocument2 pagesRare blistering skin condition linked to gluten intoleranceCharticha PatrisindryNo ratings yet
- Ginger ArticleDocument17 pagesGinger ArticleDr-Aftab Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Zuku Visual Flashnotes Distemper ExtendedDocument4 pagesZuku Visual Flashnotes Distemper ExtendedShubham HarishNo ratings yet
- SIP On Essential OilsDocument17 pagesSIP On Essential OilsJessa Marie SuarezNo ratings yet
- The Wonder of Herbs To Treat-AlopeciaDocument7 pagesThe Wonder of Herbs To Treat-AlopeciaLuca JohnNo ratings yet
- Practice Bulletin ACOG Antibiotic Prophylaxis For LabourDocument12 pagesPractice Bulletin ACOG Antibiotic Prophylaxis For LabourLorenzo TzuNo ratings yet
- Reversibledementias: Milta O. LittleDocument26 pagesReversibledementias: Milta O. LittleLUCAS IGNACIO SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- Pharm Quiz 1Document59 pagesPharm Quiz 1Anonymous vXOM1Wxt100% (1)
- Audit Worksheet PDFDocument1 pageAudit Worksheet PDFAgnelNo ratings yet