Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tugas Mata Kuliah Bahasa Inggris Dalam Kebidanan: Dosen Pengampu: Esti Handayani, M.Mid
Uploaded by
Sovia pirnamaningsihOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tugas Mata Kuliah Bahasa Inggris Dalam Kebidanan: Dosen Pengampu: Esti Handayani, M.Mid
Uploaded by
Sovia pirnamaningsihCopyright:
Available Formats
TUGAS MATA KULIAH BAHASA INGGRIS DALAM
KEBIDANAN
Dosen Pengampu : Esti Handayani, M.Mid
Kelas : Rosella
Anggota Kelompok :
1. Fachrunnisa Nabilla P1337424219008
2. Siti Lailatul Latifah P1337424219010
3. Sovia Purnamaningsih P1337424219035
4. Imroatul Jannah P1337424219036
POLITEKNIK KESEHATAN KEMENTERIAN
KESEHATAN SEMARANG
TAHUN AKADEMIK 2020/2021
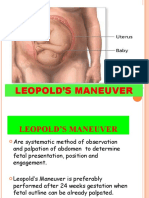
OPERATING PROCEDURE STANDART OF EXAMINATION
PALPATION LEOPOLD
LEOPOLD PALPATION
Definition A technique of examining pregnant women by means of touch,
which is to feel the parts in the belly of the pregnant woman using
the examiner's hand in a certain position, or move the parts in
certain ways using a certain level of pressure. This theory was
developed by Christian Gerhard Leopold
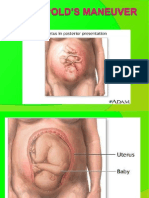
Destinationa a. Leopold I
ndPrinciple Aim to find outi TFU and part of the fetus presentin the
fundus.
b. Leopold II
Aims to find out what part of the fetus is on the right or left of
the mother.
c. Leopold III
Aims to find out what part of the fetus is under the uterus.
d. Leopold IV
Aims to find out which part of the fetus is at the bottom and to
find out whether the head has entered the pelvis or not.
PrincipleTo doAction
1. Toolmeasuring(metline)notmaymade ofelastic
2. MomentTo doActionbiologicalurinemotherinpositionempty
3. Placemotherwithgoodso
thatDuringActiondonenotdisturbcirculationbloodgoodmothern
orfetus.
Location 1. Feel the fundus
2. Right and left abdomen
3. The bottom of the fundus
Officer 1. Students who have completed the theory of the ASKEB
Pregnancy course, especially the leopold palpation.
2. Health care workers familiar with the theory of the Leopold
palpation examination.
Preparation 1. Prepare the patient.
of the 2. Describe the action to be taken.
patient
Preparation 1. Bed
of tools and 2. Loom and a pillow
materials
3. Fetoskop/pinard’s stethoscope
4. Metline / centimeter tape
5. MCH Handbook
6. SheetCohort
7. Toolwrite
Attitude 1. Friendly and careful
2. Be polite to patients
3. communicative
Implementat A. Pre-interaction stage:
ion 1. Get equipment near the patient.
procedure 2. Install sampiran.
3. Washing hands.
B. StepOrientation:
1. Giveregards
2. Describe the actions taken (objectives and procedures).
C. StepWork:
1. Position the patient as comfortable as possible.
2. Placeselfinnextrightpatient.
3. Do itexaminationLeopold I
How to check:
1. Examination facing the face of the pregnant woman.
2. Both hands feel the fundus and measure some fundal height.
3. Feel what part is in the fundus (head or fetal buttocks).
4. Get a Leopold II check
How to check:
1. The examiner's hands are on the right and left of the
mother's stomach.
2. When examining the right side, the right hand presses the
left abdomen to the right, and vice versa.
3. If you feel flat, there is resistance, then it is the baby's back,
if you feel a small protruding part, it is a small part of the
fetus.
5. Get a Leopold III checkup
How to check:
1. The left hand holds the fundus.
2. The right hand feels the part that is under the uters. If it
feels round, bouncy, hard, and can be shaken, then it is the
head. If the bottom two parts are not found then consider
the fetus in a transverse position.
3. At the location of the breech / cross-section of the
examiner's hand can feel a shake at the bottom, the left hand
feelsballottement(reflection from the head of the fetus,
especially found at 20-28 weeks gestation.
6. Get a Leopold IV exam
How to check:
1. The examiner faces the patient's feet.
2. Both hands feel the fetus underneath. If you feel the head,
place the two hands in opposite directions at the bottom.
3. If the two hands converge (can meet each other) it means
that the head has not entered the pelvis.
4. If the two hands are divergent (not meeting each other), it
means that the head has entered the pelvis.
7. Take the fundal height measurement
1. Place the tip of the measuring stick on the top of the
symphysis pubis.
2. Measure along the fundal diameter of the uterus to the
upper limit following the fundal curve (or without following
the fundus curve partiallyon).
3. Determine the fundal height
8. Calculate the estimated gestational age using the Mc Donald
formula.
9. Perform FHR calculations
1. Determine the location to listen to FHR by confirming fetal
back position or in the area of the fundus midline 2-3 cm
above the symphysis pubis continuing towards the left
quadrant.
2. Place the fetescope / pinard stethoscope in the designated
area to listen to FHR.
3. Calculate the FHR and determine the results of the
examination.
D. Termination stage
1. (Evaluate the client's feelings, simpose the results of
activities, lenter into contracts for further activities,
krestore equipment, cwash your hands).
2. Documentation (record the results of actions).
references 1. Health LawYear2009
2. PermenkesRI No. 1464 / Menkes / Per / X / 2010
3. PermenkesRI No. 17Year2013
4. RegulationsGovernorProvinceNTT No. 42Year2009about
RevolutionTHAT
5. StandardHandlingMedical
6. RegulationsRegentManggaraiEast NO. 7Year2011about
RevolutionTHAT
7. DecreeKadisHealthManggaraiEast No. Um.090 /Health
Office/ 04/1/2012aboutConcept7H2 Maternal
HealthdanAnakYear2012
https://www.academia.edu/31379567/STANDAR_OPERASION
AL_PROSEDUR_PEMERIKSAAN_PALPASI_LEOPOLD
You might also like
- Maternity and Infant Welfare: A Handbook for Health Visitors, Parents, & Others in IndiaFrom EverandMaternity and Infant Welfare: A Handbook for Health Visitors, Parents, & Others in IndiaNo ratings yet
- Leopods ManeuverDocument8 pagesLeopods ManeuverDaryl Adrian RecaidoNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Return DemonstrationDocument30 pagesProcedure For Return DemonstrationMaria Angelika BughaoNo ratings yet
- The Labor Progress Handbook: Early Interventions to Prevent and Treat DystociaFrom EverandThe Labor Progress Handbook: Early Interventions to Prevent and Treat DystociaNo ratings yet
- Rubric For Performing Fundal Height MeasurementDocument5 pagesRubric For Performing Fundal Height MeasurementPATRICIA JULIANNE CASTAÑETO RIVERANo ratings yet
- Dental Management of the Pregnant PatientFrom EverandDental Management of the Pregnant PatientChristos A. SkouterisNo ratings yet
- Leopold's Maneuvers: Determining Fetal PositionDocument7 pagesLeopold's Maneuvers: Determining Fetal PositionCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- Leopolds Maneuvers Fundic Height Measurement and FHT Determination ChecklistDocument6 pagesLeopolds Maneuvers Fundic Height Measurement and FHT Determination ChecklistChristine Joy MolinaNo ratings yet
- DR Manual 2022Document17 pagesDR Manual 2022Vaniegrace Angel BalagonNo ratings yet
- Leopold's ManeuversDocument5 pagesLeopold's ManeuversUri Perez MontedeRamos100% (2)
- 10 Leopold's ManeuverDocument5 pages10 Leopold's ManeuverKrizia R. Pingke83% (6)
- ' Leopold S ManaeuverDocument30 pages' Leopold S ManaeuverjamilliumNo ratings yet
- Leopolds ManueverDocument6 pagesLeopolds ManueverSupnet QueeneeNo ratings yet
- Focus:: Canossa CollegeDocument23 pagesFocus:: Canossa CollegeZyrene RiveraNo ratings yet
- Leopold S ManeuverDocument5 pagesLeopold S Maneuverastak ghisingNo ratings yet
- Leopolds-Maneuver ChecklistDocument4 pagesLeopolds-Maneuver ChecklistZabelle BungarNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing (NCM 104) Ivy L. Villalobos BSN 2DDocument4 pagesCommunity Health Nursing (NCM 104) Ivy L. Villalobos BSN 2DIvy VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Leopolds LectureDocument2 pagesLeopolds Lecturejacynda linsanganNo ratings yet
- Leopold's Maneuvers: Assessing Fetal PositionDocument6 pagesLeopold's Maneuvers: Assessing Fetal PositionJoeyca Shien PiolNo ratings yet
- Routine Newborn Care LectureDocument78 pagesRoutine Newborn Care LectureSheene Ainasthazia Diego AngNo ratings yet
- OB Return DemoDocument7 pagesOB Return DemoSophia RubiaNo ratings yet
- Reproduksi Check ListDocument16 pagesReproduksi Check ListPutri Rara BalernaPratiwiNo ratings yet
- Leopolds-Maneuver 2Document31 pagesLeopolds-Maneuver 2maidymae lopezNo ratings yet
- Leoplods Care of MotherDocument2 pagesLeoplods Care of MotherAqoh C MayNo ratings yet
- AntenatalcareDocument33 pagesAntenatalcareDinny Novia WNo ratings yet
- Labor RoomDocument3 pagesLabor RoomDakayu Amin LugitNo ratings yet
- Obs - GynaecDocument18 pagesObs - GynaecNathalie DeebNo ratings yet
- Essential Intrapartum and Newborn Care 1Document5 pagesEssential Intrapartum and Newborn Care 1Genierose YantoNo ratings yet
- Notes On LaborDocument4 pagesNotes On Laboraijiel talisikNo ratings yet
- Checklist LeopoldsDocument5 pagesChecklist LeopoldsSiak Ni PaulNo ratings yet
- RetdemDocument3 pagesRetdemShanelle Clariz RayaNo ratings yet
- Leopolds Manuever Performance ChecklistDocument6 pagesLeopolds Manuever Performance ChecklistPrincess ZantuaNo ratings yet
- 2-Leopolds Maneuver and FHT FHDocument4 pages2-Leopolds Maneuver and FHT FHJirah DawalNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Checklist OnlyDocument6 pagesPrenatal Checklist OnlyReniella HidalgoNo ratings yet
- MAN223 Clinical Practice: Julius Rayos Dela CruzDocument36 pagesMAN223 Clinical Practice: Julius Rayos Dela CruzolacactusNo ratings yet
- Obgyn Osce - LeopoldDocument2 pagesObgyn Osce - LeopoldErika Leah ManaloNo ratings yet
- Are Four Specific Steps in Palpating The Uterus Through The Abdomen in Order To Determine The Lie and Presentation of The FetusDocument2 pagesAre Four Specific Steps in Palpating The Uterus Through The Abdomen in Order To Determine The Lie and Presentation of The FetusMoiraMaeBeridoBalite100% (3)
- Done LEOPOLDS MANEUVER MONICITDocument2 pagesDone LEOPOLDS MANEUVER MONICITMoiraMaeBeridoBaliteNo ratings yet
- Leopold's Maneuver GuideDocument2 pagesLeopold's Maneuver GuideMoiraMaeBeridoBaliteNo ratings yet
- Station 5 Leopolds Fundic HeightDocument1 pageStation 5 Leopolds Fundic Heightflorante AbiogNo ratings yet
- Osce Abdominal Exam and Leopolds ManeuversDocument11 pagesOsce Abdominal Exam and Leopolds ManeuversAbegail IbañezNo ratings yet
- Leopold ManeuverDocument4 pagesLeopold ManeuverFaye MoralesNo ratings yet
- Leopold'S Maneuver: Richard Hermes Tantiado, RM RNDocument17 pagesLeopold'S Maneuver: Richard Hermes Tantiado, RM RNRichard TantiadoNo ratings yet
- 7,2.1 Sop Antenatal CareDocument5 pages7,2.1 Sop Antenatal CarekalsumNo ratings yet
- SCHOOL RLE ChecklistDocument3 pagesSCHOOL RLE ChecklistRafaela Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Catheterization ProcedureTITLE Leopold's Maneuver for Fetal PositioningDocument5 pagesCatheterization ProcedureTITLE Leopold's Maneuver for Fetal PositioningGrasyang FernandezNo ratings yet
- Modul Normal Delivery 2016Document8 pagesModul Normal Delivery 2016Alvin FarhanNo ratings yet
- LEOPOLD's MANEUVER RATIONALEDocument3 pagesLEOPOLD's MANEUVER RATIONALEAngela AquisapNo ratings yet
- Leopold's ManeuverDocument22 pagesLeopold's ManeuverArlene Cerdeña Salceda100% (1)
- Leopolds and FetalDocument7 pagesLeopolds and Fetaltyche100% (1)
- Chest PhysiotherapyDocument18 pagesChest PhysiotherapyZubaydatul UlumNo ratings yet
- Labor and DeliveryDocument74 pagesLabor and DeliveryRussel Kate SulangNo ratings yet
- Leopolds Manuever Final 21aDocument27 pagesLeopolds Manuever Final 21aArun Roa DanielNo ratings yet
- Leopold's Maneuver.2Document23 pagesLeopold's Maneuver.2Ces Aria100% (1)
- Leopold's Maneuver ResearchDocument4 pagesLeopold's Maneuver ResearchCarl Andre ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ceklis APN 1920Document12 pagesCeklis APN 1920wahyu kijang ramadhanNo ratings yet
- TH Leopold Maneuver LectureDocument9 pagesTH Leopold Maneuver LectureAngelo P. VeluzNo ratings yet
- Cowper's gland seminal fluid function reproductive anatomy menstrual cycle stagesDocument12 pagesCowper's gland seminal fluid function reproductive anatomy menstrual cycle stagescresia hidalgoNo ratings yet
- Skills Checklist and Study Handout - MeasurementDocument2 pagesSkills Checklist and Study Handout - Measurementmaxi noveloNo ratings yet
- JC - Group C Obstetrics and Gynaecology MCQsDocument5 pagesJC - Group C Obstetrics and Gynaecology MCQsCedric KyekyeNo ratings yet
- Презентация На Английском Языке «Human Tissues and Muscles» (Мышцы и Ткани Человека) Для Студентов Медицинских Специальностей.Document28 pagesПрезентация На Английском Языке «Human Tissues and Muscles» (Мышцы и Ткани Человека) Для Студентов Медицинских Специальностей.Гулбахор ИсаковаNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument46 pagesHow Do Organisms Reproduceharshita0% (1)
- 1c ReproductiveOrgansDocument4 pages1c ReproductiveOrgansKenjie Palaganas CentenoNo ratings yet
- Robbins Pathology - Chapter 4 TransDocument9 pagesRobbins Pathology - Chapter 4 Transnath nathNo ratings yet
- BSc. MEDICAL IMAGING TECHNOLOGY - 2019 PDFDocument91 pagesBSc. MEDICAL IMAGING TECHNOLOGY - 2019 PDFMujahid Pasha0% (1)
- General Anatomy Connective TissueDocument48 pagesGeneral Anatomy Connective TissueJuned LabbaiNo ratings yet
- Laparoscopic Anterior Resection For Cancer: A Step-By-Step TechniqueDocument4 pagesLaparoscopic Anterior Resection For Cancer: A Step-By-Step TechniqueDaham ThuljayaNo ratings yet
- Workbook3 ExcretionDocument12 pagesWorkbook3 ExcretionDarambazar GantulgaNo ratings yet
- Composition and Functions of BloodDocument17 pagesComposition and Functions of Blood19ucha023 19ucha023No ratings yet
- Immunogen, Antigen, Epitope, HaptenDocument28 pagesImmunogen, Antigen, Epitope, HaptenReni MulianiNo ratings yet
- 2-Transfusion of Blood and Blood ProductsDocument47 pages2-Transfusion of Blood and Blood ProductsAiden JosephatNo ratings yet
- Class Ix Subject Enrichment ActivitiesDocument2 pagesClass Ix Subject Enrichment ActivitiesShalini Hotwani Nathani100% (1)
- Blood Bank PracticalDocument24 pagesBlood Bank Practicalmoonfire2009No ratings yet
- Twin Anemia Polycythemia SyndromesDocument67 pagesTwin Anemia Polycythemia SyndromesBhupendra GuptaNo ratings yet
- Qimen Liv-14: Liver Channel 1Document2 pagesQimen Liv-14: Liver Channel 1ray72roNo ratings yet
- Full Offer File Order 10-15 (Membershop)Document4 pagesFull Offer File Order 10-15 (Membershop)Muhammad Ameer Hamza KayanNo ratings yet
- UTERINE RUPTURE Rupture of The Uterus During LaborDocument3 pagesUTERINE RUPTURE Rupture of The Uterus During LaborANNENo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion GuideDocument7 pagesBlood Transfusion GuideBELIGANIO JOHANNANo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Functions TableDocument2 pagesCell Parts and Functions TableStephen GutierrezNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 10 Biology Mock Paper 1 Questions and AnswersDocument37 pagesICSE Class 10 Biology Mock Paper 1 Questions and AnswersSiddhesh SrikantNo ratings yet
- Basics of Bio Mechanics NSRDocument30 pagesBasics of Bio Mechanics NSRAsina MilasNo ratings yet
- Biology PDFDocument120 pagesBiology PDFketakeeNo ratings yet
- 1.11 ANATOMY - The Nose and Paransal SinusesDocument4 pages1.11 ANATOMY - The Nose and Paransal SinusesPaolo NaguitNo ratings yet
- FlashcardsDocument18 pagesFlashcardsDaphne HernaezNo ratings yet
- Liver CancerDocument198 pagesLiver CancerCiocan AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Solutions AIATS Foundation-2018 Test-1B Class-09 (23!07!2017)Document7 pagesSolutions AIATS Foundation-2018 Test-1B Class-09 (23!07!2017)Chetanya aggarwalNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Department of PhysiologyDocument34 pagesAssignment: Department of PhysiologyMaria NeyveliNo ratings yet
- Oral Histology Lecture 1Document12 pagesOral Histology Lecture 1Mohamed Harun B. SanohNo ratings yet
- Hema LecDocument20 pagesHema LecJOWELA RUBY EUSEBIONo ratings yet