Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Leopolds Manuever Performance Checklist
Uploaded by
Princess ZantuaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Leopolds Manuever Performance Checklist
Uploaded by
Princess ZantuaCopyright:
Available Formats
VISION
“MABINI COLLEGES shall
cultivate a CULTURE of
EXCELLENCE in Education.”
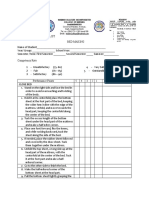
PERFORMANCE
CHECKLIST
Leopold’s Maneuver and Taking Fetal Heart Tone
Name of
Student______________________________________________________________________
Year/ Group: _______________ School Year : ___________________________________
Semester /Term: First Semester ______ Second Semester _______ Summer ____________
Competency Rate
1 - Unsatisfactory (75- 80) 4 - Very Satisfactory ( 91 – 95)
2 - Fair (81 – 85) 5 - Outstanding (96 – 100)
3 - Satisfactory (86 – 90)
Performance Points 5 4 3 2 1 CI’s Remarks
I – KNOWLEDGE (40%)
1. Defines Leopold’s Maneuver and Taking FHT
2. State the purposes
3. Enumerate special considerations.
4. Identify materials/equipment needed.
5. State preparation of the patient.
6. State the principles/rationale behind specific
action.
II – SKILLS / ABILITY (40%)
1. Assess the physical condition of the mother
and baby.
2. Determine the nursing needs of mother and
baby.
3. Wash hands.
4. Prepare the client for the procedure.
5. Identify the client.
6. Explain the procedure.
7. Instruct patient/client to void or empty the
bladder.
8. Assist client and position in dorsal
recumbent.
9. Drape client to provide privacy.
10. Expose the abdomen from the level of
xyphoid process down to symphysis pubis.
11. Warm two hands by rubbing against the
other before placing them on the abdomen.
12. Perform the four maneuvers. During the
three maneuvers, the examiner stands at the
side of the (client) bed and faces the client.
First Maneuver
A. With both hands, palpate upper
abdomen and fundus for:
Consistency – head is round, hard,
breech is well defined.
Mobility – head moves independently,
breech lees mobile.
Second Maneuver
A. With both hands moving down; palpate
the sides of the uterus from the top to
bottom.
1. One side – smooth, hard, resistant
surface (back)
Other side – angular modulation
(knees and elbows).
Third Maneuver
A. With the right hand over the symphysis
pubis, identify the presenting part by
grasping the lower abdomen with
thumb and fingers.
Assess whether the presenting part is
engaged in the pelvis (if head is
engaged, it will nt move. If it is soft, it is
the back.
Fourth Maneuver
The nurse alters position by turning toward
the patient’s feet, with both hands; assess the
descent of the presenting part by locating the
cephalic prominence of brow.
A. Place your fingers on both sides of the
uterus, about two inches above the
inguinal ligament. Press downwards and
inward.
B. If the fetal back is palpated, it meets no
obstruction.
C. The other hand will meet obstruction,
the fetal brow is palpated.
14. If the uterus is not contracting, place the
bell of the stethoscope over the quadrant of
the mother’s abdomen where the fetal back is
located.
15. Listen for and count the fetal heart tone in
one full minute. Take note of the rate,
regularity, strengths and any deviation of the
fetal heart tone.
16. Make the client comfortable.
17. Record/chart any abnormal observation and
findings on the mother and baby. Chart the
characteristics of the fetal heart tone along the
position on the abdomen where fetal heart
tone was obtained.
III – ATTITUDE (20%)
1. Demonstrate preparedness, readiness and
confidence in the performance of the
procedure.
2. Accepts corrections/suggestions and shows
willingness to improve performance.
3. Answers questions politely and tactfully.
4. Shows respect and consideration of the
recipient of care.
5. Observe proper decorum and behave as a
mature student nurse.
Evaluated by: Conforme:
_____________________________ ______________________________
Signature over Printed Name / Date Signature over
Printed Name/Date
Clinical Instructor Student
Leopold’s Maneuver and Taking Fetal Heart Tone
Definition:
The Leopold maneuvers are used to palpate the gravid uterus systematically. This
method of abdominal palpation is of low cost, easy to perform, and non-invasive. It is
used to determine the position, presentation, and engagement of the fetus in utero.
Leopold’s Maneuver is the abdominal palpation of pregnant women performed after 24
weeks gestation when fetal outline can be palpated
Purpose:
To locate the fetal heart sound
To determine FHR
To determine single vs. multiple gestation
To detect deviation from normal
Materials:
Draw sheet
Pinard Stethoscope
Measuring tape
Sanitizing gel
You might also like
- 10 Leopold's ManeuverDocument5 pages10 Leopold's ManeuverUri Perez MontedeRamos100% (2)
- Are Four Specific Steps in Palpating The Uterus Through The Abdomen in Order To Determine The Lie and Presentation of The FetusDocument2 pagesAre Four Specific Steps in Palpating The Uterus Through The Abdomen in Order To Determine The Lie and Presentation of The FetusMoiraMaeBeridoBalite100% (3)
- The Labor Progress Handbook: Early Interventions to Prevent and Treat DystociaFrom EverandThe Labor Progress Handbook: Early Interventions to Prevent and Treat DystociaNo ratings yet
- Paternity Leave LawDocument15 pagesPaternity Leave LawJohnny Castillo SerapionNo ratings yet
- Body Mechanics ChecklistDocument7 pagesBody Mechanics ChecklistPrincess ZantuaNo ratings yet
- Leopolds Maneuvers Fundic Height Measurement and FHT Determination ChecklistDocument6 pagesLeopolds Maneuvers Fundic Height Measurement and FHT Determination ChecklistChristine Joy MolinaNo ratings yet
- RLE Checklist Evaluation (Leopold's Maneuver)Document4 pagesRLE Checklist Evaluation (Leopold's Maneuver)Cameron De Guzman100% (1)
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD) Part I: Molar PregnancyDocument88 pagesGestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD) Part I: Molar Pregnancyhafidzz1100% (1)
- Bed Making Performance ChecklistDocument6 pagesBed Making Performance ChecklistPrincess ZantuaNo ratings yet
- Luteinizing and Follicle Stimulating Hormone (Powerpoint)Document23 pagesLuteinizing and Follicle Stimulating Hormone (Powerpoint)Phoebe Guevarra100% (6)
- Final Checklist On Leopolds Fundic and FHTDocument3 pagesFinal Checklist On Leopolds Fundic and FHTCharlmagne LinnamNo ratings yet
- 10 Leopold's ManeuverDocument5 pages10 Leopold's ManeuverKrizia R. Pingke83% (6)
- Population Dynamics NewDocument169 pagesPopulation Dynamics Newhiral mistryNo ratings yet
- Objective Structured Clinical ExaminationDocument6 pagesObjective Structured Clinical ExaminationRajaNo ratings yet
- Breast Examination Prenatal PostpartumDocument2 pagesBreast Examination Prenatal PostpartumMaria Rose Ann YeeNo ratings yet
- Rubric For Performing Fundal Height MeasurementDocument5 pagesRubric For Performing Fundal Height MeasurementPATRICIA JULIANNE CASTAÑETO RIVERANo ratings yet
- Prolonged Lactation 101Document4 pagesProlonged Lactation 101James Louis B. AntonioNo ratings yet
- MCN Lec QuizzesDocument22 pagesMCN Lec QuizzesRaquel Monsalve67% (3)
- Rating Scale For The Gynecologic ExamDocument3 pagesRating Scale For The Gynecologic ExamAnonymous qJM3kLDtNo ratings yet
- Essential Intrapartum and Newborn Care Practice Session ChecklistDocument28 pagesEssential Intrapartum and Newborn Care Practice Session ChecklistMonica Melchor DoriaNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument32 pagesResearch Proposalku daarayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of The Postpartum ClientDocument13 pagesNursing Care of The Postpartum ClientLyca Mae AurelioNo ratings yet
- Leopold's Maneuver RetdemDocument2 pagesLeopold's Maneuver RetdemHASMAIRA P. ABDUL0% (1)
- Leopolds ManueverDocument6 pagesLeopolds ManueverSupnet QueeneeNo ratings yet
- Leopolds ManeuversDocument3 pagesLeopolds ManeuversAira RoxanneNo ratings yet
- LEOPOLD'S MANEUVER RATIONALE&CHECKLISTDocument3 pagesLEOPOLD'S MANEUVER RATIONALE&CHECKLISTNhadzmae Asmadul IsnainNo ratings yet
- RD1 Leopolds ManeuverDocument2 pagesRD1 Leopolds ManeuverMargarette AfanNo ratings yet
- School of Health and Naturalsciences Nursing Department Bayombong, Nueva VizcayaDocument3 pagesSchool of Health and Naturalsciences Nursing Department Bayombong, Nueva VizcayaCharlmagne LinnamNo ratings yet
- The Shape, Size, Mobility, and Consistence of What He or She FeelsDocument3 pagesThe Shape, Size, Mobility, and Consistence of What He or She FeelsPrincess Pilove Gawongna100% (1)
- Leopolds ManueverDocument2 pagesLeopolds ManueverlampayanantonethNo ratings yet
- Leopold's ManueverDocument3 pagesLeopold's Manueverpart-time pl3asureNo ratings yet
- Leopolds Maneuver ChecklistDocument5 pagesLeopolds Maneuver ChecklistSheen CatayongNo ratings yet
- Leopolds-Maneuver ChecklistDocument3 pagesLeopolds-Maneuver ChecklistMira AurumtinNo ratings yet
- Done LEOPOLDS MANEUVER MONICITDocument2 pagesDone LEOPOLDS MANEUVER MONICITMoiraMaeBeridoBaliteNo ratings yet
- Done LEOPOLDS MANEUVER MONICITDocument2 pagesDone LEOPOLDS MANEUVER MONICITMoiraMaeBeridoBaliteNo ratings yet
- Leopold's Maneuver ResearchDocument4 pagesLeopold's Maneuver ResearchCarl Andre ReyesNo ratings yet
- Leopolds Manuever CHECKLISTDocument1 pageLeopolds Manuever CHECKLISTElmer DaquilañeaNo ratings yet
- Focus:: Canossa CollegeDocument23 pagesFocus:: Canossa CollegeZyrene RiveraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Management - 107: de La Salle Lipa College of NursingDocument3 pagesNursing Care Management - 107: de La Salle Lipa College of NursingThe Blue and Gold RvdNo ratings yet
- Leopolds ManeuDocument2 pagesLeopolds ManeuAbby Trisha MadularaNo ratings yet
- NCM 220 Procedural ChecklistDocument41 pagesNCM 220 Procedural ChecklistJeralyn GabagatNo ratings yet
- 2-Leopolds Maneuver and FHT FHDocument4 pages2-Leopolds Maneuver and FHT FHJirah DawalNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Leopolds Maneuver 2Document2 pagesChecklist For Leopolds Maneuver 2krischaniNo ratings yet
- SCHOOL RLE ChecklistDocument3 pagesSCHOOL RLE ChecklistRafaela Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Leopolds ManeuverDocument1 pageLeopolds ManeuverALIZA BAKILNo ratings yet
- CHECKLIST Leopolds Maneuver Fundal HeightDocument4 pagesCHECKLIST Leopolds Maneuver Fundal Heightmiguela juguetaNo ratings yet
- Leopods ManeuverDocument8 pagesLeopods ManeuverDaryl Adrian RecaidoNo ratings yet
- Leopold'S Manuever: Procedure Rationale Rating RemarksDocument2 pagesLeopold'S Manuever: Procedure Rationale Rating RemarkskarmaNo ratings yet
- MAN223 Clinical Practice: Julius Rayos Dela CruzDocument36 pagesMAN223 Clinical Practice: Julius Rayos Dela CruzolacactusNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care During LaborDocument12 pagesNursing Care During LaborJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Assignment Abdominal ExaminationDocument2 pagesAssignment Abdominal ExaminationAnnie TomasNo ratings yet
- Checklist Ritgens DianeDocument4 pagesChecklist Ritgens DianekristiannedenNo ratings yet
- Antenatal PalpationDocument2 pagesAntenatal PalpationNandhiniNo ratings yet
- Antenatal PalpationDocument2 pagesAntenatal PalpationNandhiniNo ratings yet
- Leopold Maneuvers How To Correctly Perform Leopold Maneuvers Clinical Nursing SkillsDocument1 pageLeopold Maneuvers How To Correctly Perform Leopold Maneuvers Clinical Nursing SkillsCamille GalasNo ratings yet
- Fbao ChecklistDocument2 pagesFbao ChecklistPrincess Ronnie BascuñaNo ratings yet
- Checklist Leopolds Manuever FINALDocument3 pagesChecklist Leopolds Manuever FINALdodongtacordajrNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Checklist OnlyDocument6 pagesPrenatal Checklist OnlyReniella HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing (NCM 104) Ivy L. Villalobos BSN 2DDocument4 pagesCommunity Health Nursing (NCM 104) Ivy L. Villalobos BSN 2DIvy VillalobosNo ratings yet
- FHT ChecklistDocument3 pagesFHT ChecklistNhadzmae Asmadul IsnainNo ratings yet
- DR Manual 2022Document17 pagesDR Manual 2022Vaniegrace Angel BalagonNo ratings yet
- How To Correctly Perform Leopold's ManeuverDocument4 pagesHow To Correctly Perform Leopold's ManeuverLorenn AdarnaNo ratings yet
- Leopold's Manuever ChecklistDocument3 pagesLeopold's Manuever ChecklistMelchizeder Solis LumanogNo ratings yet
- OB Skills DemoDocument5 pagesOB Skills DemoNikko OngNo ratings yet
- Moving A Patient in Bed Moving Up Logrolling and Turning To SidesDocument4 pagesMoving A Patient in Bed Moving Up Logrolling and Turning To SidesJohn Paul BelenNo ratings yet
- BreastDocument3 pagesBreastUriel NateNo ratings yet
- Skills Input - Leopold's ManeuverDocument13 pagesSkills Input - Leopold's ManeuverJerald FernandezNo ratings yet
- Abdominal AssessmentDocument2 pagesAbdominal AssessmentZarida ArabainNo ratings yet
- Emergency Nursing ChecklistDocument6 pagesEmergency Nursing ChecklistMark DomingoNo ratings yet
- Performance Checklist Bag Technique: VisionDocument3 pagesPerformance Checklist Bag Technique: VisionPrincess ZantuaNo ratings yet
- Drug Administration: Color Coding and FrequencyDocument2 pagesDrug Administration: Color Coding and FrequencyPrincess ZantuaNo ratings yet
- Heavy Menstrual Bleeding Assessment and Management PDF 1837701412549Document33 pagesHeavy Menstrual Bleeding Assessment and Management PDF 1837701412549Meera Al AliNo ratings yet
- Hard Spelling Bee WordsDocument8 pagesHard Spelling Bee WordsLee LedesmaNo ratings yet
- Reasoning Speed Test-14 (Answer)Document3 pagesReasoning Speed Test-14 (Answer)souparna duttaNo ratings yet
- Discussion TextDocument6 pagesDiscussion TextIndri FitrialstiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy For Beginners - Reproduction WorksheetDocument4 pagesAnatomy For Beginners - Reproduction WorksheetJames Dauray100% (1)
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bengaluru, KarnatakaDocument25 pagesRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bengaluru, Karnatakaannu panchalNo ratings yet
- The High Risk New BornDocument23 pagesThe High Risk New Bornchhaiden100% (4)
- Sambia: Papua New GuineaDocument11 pagesSambia: Papua New GuineasandyNo ratings yet
- Uso de Miso en Obstetricia Ipas Mexico PDFDocument39 pagesUso de Miso en Obstetricia Ipas Mexico PDFthedNo ratings yet
- 1425 25 2628 1 10 20200518 DikonversiDocument7 pages1425 25 2628 1 10 20200518 DikonversiErna YulianaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - KinshipDocument2 pagesLesson 1 - KinshipGlester SevillaNo ratings yet
- Gynae SNI Final Print VersionDocument34 pagesGynae SNI Final Print VersionMr Soman Nadim IqbalNo ratings yet
- MCN 2 Practice QuestionsDocument17 pagesMCN 2 Practice QuestionsMae RealesNo ratings yet
- 1) Uterine Fibroids د.حنان خامسةDocument20 pages1) Uterine Fibroids د.حنان خامسةAsem Al-domainiNo ratings yet
- Investigating The Causes and Consequences of Marital Rape PDFDocument22 pagesInvestigating The Causes and Consequences of Marital Rape PDFLet's Go SpaceNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 Intro 1Document34 pagesNCM 107 Intro 1Riegne Chiara Fay AcuzarNo ratings yet
- 3rd Stage of LabourDocument26 pages3rd Stage of Labournixon odoyoNo ratings yet
- Dysfunctional Uterine BleedingDocument6 pagesDysfunctional Uterine Bleedingboorai^_^No ratings yet
- Ginecologie An.v EngDocument67 pagesGinecologie An.v EngAhmad Abu KushNo ratings yet
- 2 - PPT DR Liong Boy Kurniawan - Recent Update of Semen Analysis, LBK, KONAS 2022Document34 pages2 - PPT DR Liong Boy Kurniawan - Recent Update of Semen Analysis, LBK, KONAS 2022NANANo ratings yet
- Etiologi Dan Gejala Klinis Pneumonia RevisiDocument15 pagesEtiologi Dan Gejala Klinis Pneumonia Revisiazis purwantoNo ratings yet
- Ovarian - and - Fallopian - Tube - Torsion UpToDateDocument18 pagesOvarian - and - Fallopian - Tube - Torsion UpToDateFELIPE MEDINANo ratings yet