Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Statistics and Probability Key Concepts
Uploaded by
titserscradle0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views4 pagesOriginal Title
MELCS Activity
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views4 pagesStatistics and Probability Key Concepts
Uploaded by
titserscradleCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
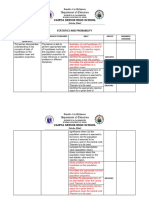
Statistics and Probability
Second Semester, 2020-2021
Quarter K-12 Learning MELCs
Competencies
Q3 Merged illustrates a random variable (discrete and
continuous).
distinguishes between a discrete and a
continuous random variable.
finds the possible values of a random variable.
illustrates a probability distribution for a
discrete random variable and its properties.
computes probabilities corresponding to a given
random variable.
illustrates the mean and variance of a discrete
random variable.
calculates the mean and the variance of a
discrete random variable.
interprets the mean and the variance of a
discrete random variable.
solves problems involving mean and variance of
probability distributions.
Retained illustrates a normal random variable and its
characteristics.
identifies regions under the normal curve
corresponding to different standard normal
values.
converts a normal random variable to a
standard normal variable and vice versa.
computes probabilities and percentiles using the
standard normal table.
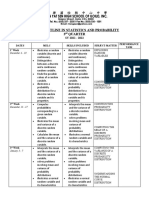
key concepts of apply suitable sampling illustrates random sampling.
Statistics and Probability
Second Semester, 2020-2021
sampling and and sampling distinguishes between parameter and statistic.
sampling distributions of the
distributions of sample mean to solve identifies sampling distributions of statistics
the sample real-life problems in (sample mean).
mean. different disciplines. finds the mean and variance of the sampling
distribution of the sample mean.
defines the sampling distribution of the sample
mean for normal population when the variance
is: (a) known; (b) unknown
illustrates the Central Limit Theorem.
defines the sampling distribution of the sample
mean using the Central Limit Theorem.
solves problems involving sampling distributions
of the sample mean.
key concepts of estimate the population illustrates the t-distribution.
estimation of mean and population
population mean proportion to make identifies percentiles using the t-table.
and population sound inferences in real- identifies the length of a confidence interval.
proportion. life problems in different
disciplines. computes for the length of the confidence
interval.
computes for an appropriate sample size using
the length of the interval.
solves problems involving sample size
determination.
key concepts of perform appropriate illustrates: (a) null hypothesis; (b) alternative
tests of tests of hypotheses hypothesis; (c) level of significance; (d) rejection
hypotheses on involving the population region; and (e) types of errors in hypothesis
the population mean and population testing.
mean and proportion to make identifies the parameter to be tested given a real-
population inferences in real-life life problem.
proportion. problems in different formulates the appropriate null and alternative
disciplines. hypotheses on a population mean.
identifies the appropriate form of the test-statistic
Statistics and Probability
Second Semester, 2020-2021
when: (a) the population variance is assumed to
be known; (b) the population variance is
assumed to be unknown; and (c) the Central
Limit Theorem is to be used.
identifies the appropriate rejection region for a
given level of significance when: (a) the
population variance is assumed to be known; (b)
the population variance is assumed to be
unknown; and (c) the Central Limit Theorem is
to be used.
computes for the test-statistic value (population
mean).
draws conclusion about the population mean
based on the test-statistic value and the rejection
region.
solves problems involving test of hypothesis on
the population mean.
identifies the appropriate form of the test-statistic
when the Central Limit Theorem is to be used.
identifies the appropriate rejection region for a
given level of significance when the Central
Limit Theorem is to be used.
computes for the test-statistic value (population
proportion).
draws conclusion about the population
proportion based on the test-statistic value and
the rejection region.
solves problems involving test of hypothesis on
the population proportion.
key concepts of perform correlation illustrates the nature of bivariate data.
correlation and and regression analyses
constructs a scatter plot.
regression on real-life problems in
analyses. different disciplines. describes shape (form), trend (direction), and
variation (strength) based on a scatter plot.
calculates the Pearson’s sample correlation
coefficient.
Statistics and Probability
Second Semester, 2020-2021
solves problems involving correlation analysis.
identifies the independent and dependent
variables.
Quarter Content Performance Standards MELCs
Standards
The learner The learner is able to … The learner …
demonstrates
understanding of
…
calculates the slope and y-intercept of the
regression line.
interprets the calculated slope and y-intercept of
the regression line.
predicts the value of the dependent variable
given the value of the independent variable.
solves problems involving regression analysis.
You might also like
- q4 Topic OutlineDocument4 pagesq4 Topic Outlinegmanalo638No ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Learning Module 3rd QuarterDocument65 pagesStatistics and Probability Learning Module 3rd QuarterLANY T. CATAMINNo ratings yet
- Tecniphi SHS Reviewer for Statistics TopicsDocument3 pagesTecniphi SHS Reviewer for Statistics TopicsEZEKIEL MARK ADDURUNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Learning Module 3rd QuarterDocument69 pagesStatistics and Probability Learning Module 3rd QuarterLANY T. CATAMIN100% (1)
- DLL Stat and Probab 1st Quarter RevDocument8 pagesDLL Stat and Probab 1st Quarter RevJoselito UbaldoNo ratings yet
- CSBS - AD3491 - FDSA - IA 2 - Answer KeyDocument14 pagesCSBS - AD3491 - FDSA - IA 2 - Answer KeyR.Mohan Kumar100% (1)
- Distance-Learning-Course-Plan Math1-StatisticsDocument13 pagesDistance-Learning-Course-Plan Math1-StatisticsHarvey RatunilNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Grade 11 ObjectivesDocument11 pagesStatistics and Probability Grade 11 ObjectivesJoecel De Guzman TorrefrancaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Methods Sample Questions STDocument1 pageQuantitative Methods Sample Questions STLukundo SichalweNo ratings yet
- Psych Assessment Chap 2Document4 pagesPsych Assessment Chap 2Elijah DiazNo ratings yet
- Distinguishing Between Random and Fixed: Variables, Effects, and CoefficientsDocument3 pagesDistinguishing Between Random and Fixed: Variables, Effects, and CoefficientsPradyuman SharmaNo ratings yet
- Third Least Mastered SkillsDocument1 pageThird Least Mastered Skillsflorabel hilarioNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - Statistics 2Document2 pagesMathematics - Statistics 2Zaman Ali RajaNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Module 6: Week 6: Third QuarterDocument7 pagesStatistics and Probability Module 6: Week 6: Third QuarterALLYSSA MAE PELONIANo ratings yet
- CH 7 Statistical Data Treatment and EvaluationDocument30 pagesCH 7 Statistical Data Treatment and Evaluationjhzlbarrera09No ratings yet
- Course Outline in Statistics and Probability 3 Quarter: Dates Melc Skills Included Subject-Matter Performance Task 1 WeekDocument2 pagesCourse Outline in Statistics and Probability 3 Quarter: Dates Melc Skills Included Subject-Matter Performance Task 1 WeekTiffany Joy Lencioco GambalanNo ratings yet
- Survey Adjustment NotesDocument7 pagesSurvey Adjustment NotesF1031 Hariz HilmiNo ratings yet
- Distribution Test: Nadira Wulan Ramadhini 190403093 Kelompok VII Gelombang I CDocument10 pagesDistribution Test: Nadira Wulan Ramadhini 190403093 Kelompok VII Gelombang I CDira WRNo ratings yet
- Stat W2Document4 pagesStat W2Melody De VeraNo ratings yet
- G11 2ND Sem Quarter1 Tos StatisticsDocument2 pagesG11 2ND Sem Quarter1 Tos StatisticsRuby Ann Almazan MatutinoNo ratings yet
- tarea-3-distribuciones-de-probabilidadDocument14 pagestarea-3-distribuciones-de-probabilidadFernando SisaNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument15 pagesMeasures of Central TendencyAbhinav MohantyNo ratings yet
- Normal CurveDocument80 pagesNormal CurvePrecious EspejoNo ratings yet
- It Involves The Analysis of The Frequency of Past Events It Refers To Data Continuos, Fraction Not Countable Discrete CountableDocument3 pagesIt Involves The Analysis of The Frequency of Past Events It Refers To Data Continuos, Fraction Not Countable Discrete CountablecolNo ratings yet
- Avance Tarea 3 PDFDocument5 pagesAvance Tarea 3 PDFjennifer florez tovarNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Feb 02, 2023Document13 pagesAdobe Scan Feb 02, 2023sirigames1No ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Learning Module (3rd Quarter)Document95 pagesStatistics and Probability Learning Module (3rd Quarter)Moises John SangalangNo ratings yet
- AP Statistics Vocabulary ListDocument3 pagesAP Statistics Vocabulary ListVodounnouNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary ListDocument3 pagesVocabulary ListErick SanchezNo ratings yet
- Quarterly Exam Specification in Statistics and ProbabilityDocument2 pagesQuarterly Exam Specification in Statistics and ProbabilityCher Z 2No ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Guide for Home LearningDocument4 pagesStatistics and Probability Guide for Home LearningPrincess SanchezNo ratings yet
- (MATH 102) SUM OF THREE ReviewersDocument6 pages(MATH 102) SUM OF THREE ReviewersChelsea JacotNo ratings yet
- Probability DistributionDocument15 pagesProbability Distributionbutter is better than margarineNo ratings yet
- Basic StatisticsDocument4 pagesBasic StatisticsChandrani BasuNo ratings yet
- Business Modelling Confidence Intervals: Prof Baibing Li BE 1.26 E-Mail: Tel 228841Document11 pagesBusiness Modelling Confidence Intervals: Prof Baibing Li BE 1.26 E-Mail: Tel 228841Marina DragiyskaNo ratings yet
- Essential Math Competencies for Grades 11-12Document37 pagesEssential Math Competencies for Grades 11-12Alfred NaveaNo ratings yet
- Unidad 2 Tarea 3 - Martha MuñozDocument5 pagesUnidad 2 Tarea 3 - Martha MuñozMIGUEL ANGEL PADILLA DIAZNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Sampling Distribution (S) of Statistic (S) : StructureDocument24 pagesUnit 2 Sampling Distribution (S) of Statistic (S) : StructureBHARATH RAJA GAJULANo ratings yet
- And Estimation Sampling Distributions: Learning OutcomesDocument12 pagesAnd Estimation Sampling Distributions: Learning OutcomesTarek MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Gec410 Note ViDocument50 pagesGec410 Note ViechebimazNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probablity SHS 11-Module 1 - Week1Document23 pagesStatistics and Probablity SHS 11-Module 1 - Week1Mary Jane Ocampo93% (41)
- Aporte Alison OrtizDocument8 pagesAporte Alison OrtizCindy UrecheNo ratings yet
- Philippine High School Budget and CurriculumDocument4 pagesPhilippine High School Budget and Curriculumaljun badeNo ratings yet
- Subject CS1 - Actuarial Statistics 1 Core Principles For 2019 ExaminationsDocument10 pagesSubject CS1 - Actuarial Statistics 1 Core Principles For 2019 ExaminationsChirag GuptaNo ratings yet
- Alignment Classroom Instructon Delivery (Acid) PlanDocument7 pagesAlignment Classroom Instructon Delivery (Acid) PlanJonory Qaquilala BojosNo ratings yet
- Math 102 Midterms Reviewer (With Mock Tests)Document3 pagesMath 102 Midterms Reviewer (With Mock Tests)Jirish RiveraNo ratings yet
- Thesis Statistical TreatmentDocument8 pagesThesis Statistical TreatmentCarlville Jae EdañoNo ratings yet
- Random variables and distributions guideDocument7 pagesRandom variables and distributions guideRishiNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter StatDocument25 pages3rd Quarter Statzed coz100% (1)
- Interval EstimationDocument19 pagesInterval EstimationJim SteveNo ratings yet
- Name: Bienvenido D. Necesario, Iii Quarter Assigned: 1 Quarter Week Assigned: WEEK 1-6Document6 pagesName: Bienvenido D. Necesario, Iii Quarter Assigned: 1 Quarter Week Assigned: WEEK 1-6Benjr Junjun NecesarioNo ratings yet
- DLL-stat-and-prob - CentralLimit-confidence IntervalldocDocument4 pagesDLL-stat-and-prob - CentralLimit-confidence IntervalldocGladys Joy Santos MallariNo ratings yet
- x i s μ x N n: Easures OF AriabilityDocument2 pagesx i s μ x N n: Easures OF AriabilityErwin BulahaoNo ratings yet
- 40 2 Intvl Est Var PDFDocument10 pages40 2 Intvl Est Var PDFTarek MahmoudNo ratings yet
- SP ReviewerDocument4 pagesSP ReviewerMalayao, Philip Jude M.No ratings yet
- Week 5 - Result and Analysis 1 (UP)Document7 pagesWeek 5 - Result and Analysis 1 (UP)eddy siregarNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam in Statistics and Probability Grade 11Document2 pagesMidterm Exam in Statistics and Probability Grade 11Donna Angela Zafra Balbuena83% (6)
- Explaining Variational ApproximationsDocument14 pagesExplaining Variational ApproximationsMatesta MatestaNo ratings yet
- Rule of Inference ModuleDocument10 pagesRule of Inference ModuletitserscradleNo ratings yet
- Statistics Initial Release June 13Document82 pagesStatistics Initial Release June 13Joviner Yabres Lactam67% (3)
- Statistics and Probability (PIVOT)Document392 pagesStatistics and Probability (PIVOT)Cedrick Matibag83% (54)
- DocumentDocument1 pageDocumenttitserscradleNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability (PIVOT)Document392 pagesStatistics and Probability (PIVOT)Cedrick Matibag83% (54)
- Intuitive & Strategic Thinking for Global SuccessDocument1 pageIntuitive & Strategic Thinking for Global SuccesstitserscradleNo ratings yet
- Certi of EnrolmentDocument2 pagesCerti of EnrolmenttitserscradleNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability (PIVOT)Document392 pagesStatistics and Probability (PIVOT)Cedrick Matibag83% (54)
- Probability Lecture 1Document1 pageProbability Lecture 1titserscradleNo ratings yet
- The Little PlantDocument1 pageThe Little PlanttitserscradleNo ratings yet
- ZipGrade50QuestionV2 PDFDocument1 pageZipGrade50QuestionV2 PDFtitserscradleNo ratings yet
- Linear FX ActivityDocument1 pageLinear FX ActivitytitserscradleNo ratings yet
- 1 Short VowelsDocument1 page1 Short VowelsManikandan SudharsanNo ratings yet
- Rocket Graph For Grade 1Document1 pageRocket Graph For Grade 1titserscradleNo ratings yet
- Jagirdari SystemDocument10 pagesJagirdari Systemdevang guptaNo ratings yet
- Aditya Birla Grasim PaintsDocument19 pagesAditya Birla Grasim Paintsinternetsuks5631No ratings yet
- 2023 Congressional Baseball Sponsorship PackagesDocument2 pages2023 Congressional Baseball Sponsorship PackagesSpencer BrownNo ratings yet
- MKT202 - Group 6 - Marketing Research ProposalDocument9 pagesMKT202 - Group 6 - Marketing Research ProposalHaro PosaNo ratings yet
- Fitch BNG Bank N.V. 2019-08-13Document10 pagesFitch BNG Bank N.V. 2019-08-13Suranga FernandoNo ratings yet
- CV Raho 2020 PDFDocument5 pagesCV Raho 2020 PDFraholiveiraNo ratings yet
- The Effective Length of Columns in MultiDocument12 pagesThe Effective Length of Columns in MulticoolkaisyNo ratings yet
- Schoonebeek Kivi 09 AprilDocument25 pagesSchoonebeek Kivi 09 AprilmeloszNo ratings yet
- Onu - Escwa (Escwa) Report Workshop On International Migration and Development in The Arab Region: Integrating International Migration Into Development Strategies Beirut, 19-22 July 2010Document21 pagesOnu - Escwa (Escwa) Report Workshop On International Migration and Development in The Arab Region: Integrating International Migration Into Development Strategies Beirut, 19-22 July 2010ddufourtNo ratings yet
- Economics of The Environment - Theory and Policy (PDFDrive)Document328 pagesEconomics of The Environment - Theory and Policy (PDFDrive)danysubash100% (1)
- Utilization of Fluff From Reception To BurnerDocument28 pagesUtilization of Fluff From Reception To BurnerfylakyaNo ratings yet
- BatchGenerator UserReferenceDocument13 pagesBatchGenerator UserReferenceLuis OrtizNo ratings yet
- STD 2 ComputerDocument12 pagesSTD 2 ComputertayyabaNo ratings yet
- My Little Pony: Friendship Is Magic #14 PreviewDocument10 pagesMy Little Pony: Friendship Is Magic #14 PreviewGraphic Policy100% (3)
- Continuous Filters: - Proven Technology With The Latest InnovationsDocument12 pagesContinuous Filters: - Proven Technology With The Latest InnovationsabdelrhmanNo ratings yet
- Quality SND zones for big movesDocument4 pagesQuality SND zones for big movesAriel Gohoury100% (1)
- Design Model Are Included in One Part of The Graves (2000) ModelDocument8 pagesDesign Model Are Included in One Part of The Graves (2000) ModelPourya HellNo ratings yet
- HostsDocument4 pagesHostsakoe.hendryanaNo ratings yet
- HR Functions and ProceduresDocument7 pagesHR Functions and ProceduresSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Alfornon Joshua Madjos. Strategic Management Bsba 3FDocument7 pagesAlfornon Joshua Madjos. Strategic Management Bsba 3FJoshua AlfornonNo ratings yet
- SWOT Analysis of Standard Chartered BankDocument4 pagesSWOT Analysis of Standard Chartered BankparthNo ratings yet
- Improve Your Well-Being With The Wheel Of Life ExerciseDocument2 pagesImprove Your Well-Being With The Wheel Of Life ExerciseLINA PASSIONNo ratings yet
- How Historians Seek Historical TruthDocument30 pagesHow Historians Seek Historical Truthlezier Padilla SumagangNo ratings yet
- Setup NFS File Sharing Between Linux SystemsDocument6 pagesSetup NFS File Sharing Between Linux SystemsKurniawan Setyo NugrohoNo ratings yet
- The List, Stack, and Queue Adts Abstract Data Type (Adt)Document17 pagesThe List, Stack, and Queue Adts Abstract Data Type (Adt)Jennelyn SusonNo ratings yet
- Green Buildings and Rating Systems PDFDocument106 pagesGreen Buildings and Rating Systems PDFHarsheen kaurNo ratings yet
- Definition (Art. 1458)Document10 pagesDefinition (Art. 1458)Fatima SladjannaNo ratings yet
- Bibicoff Ic Resume 2022 09 For WebsiteDocument3 pagesBibicoff Ic Resume 2022 09 For Websiteapi-633250343No ratings yet
- Harmonization and Standardization of The ASEAN Medical IndustryDocument75 pagesHarmonization and Standardization of The ASEAN Medical IndustryGanch AguasNo ratings yet
- Cuprinol - Wood - Preserver - Clear - (BP) Safety Data SheetDocument13 pagesCuprinol - Wood - Preserver - Clear - (BP) Safety Data SheetEdgar ArdinazoNo ratings yet